- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Polysome Analysis
Published: Vol 7, Iss 6, Mar 20, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2192 Views: 22160
Reviewed by: HongLok LungAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Revised iCLIP-seq Protocol for Profiling RNA–protein Interaction Sites at Individual Nucleotide Resolution in Living Cells
Syed Nabeel-Shah and Jack F. Greenblatt
Jun 5, 2023 5218 Views

Determination of Ligand-Target Interaction in vitro by Cellular Thermal Shift Assay and Isothermal Dose-response Fingerprint Assay
Danyu Du [...] Jing Xiong
Aug 5, 2024 4917 Views

Purification of Native Acetyl CoA Carboxylase From Mammalian Cells
Yaxue Sun [...] Hongtao Zhu
Feb 20, 2025 2192 Views
Abstract
Polysome analysis is a method to separate mRNAs from a cell into actively translating and non-translating fractions depending on their association with polysomes. By this protocol, cell lysates are fractionated by sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation. Free mRNA fraction and various ribosomal fractions, such as 40S, 60S, monosomes and polysomes are collected by fractionation. Association of particular mRNAs with these fractions is detected by reverse transcription – PCR to investigate the translational state of the mRNA.
Keywords: TranslationBackground
The cellular mRNAs are distributed into an actively translating and a non-translating pool at any point of time and can dynamically redistribute between these pools in response to various stimuli. The actively translating mRNAs have a higher number of ribosomes associated with them and the number of ribosome associated with an mRNA is a measure of the translation state of the mRNA. Therefore on fractionating the ribosomes from a cell, actively translating mRNAs will be found in the polysomal fraction whereas non-translating/poorly-translating mRNAs will be either found in the free mRNA fraction or associated with 40S ribosomal subunits. Polysome analysis is therefore a method to separate mRNAs from a cell into actively translating and non-translating fractions depending on their association with polysomes (Ray et al., 2009; Poria et al., 2016). Association of individual mRNAs with translating/non-translating fractions can be detected by RT-PCR, whereas the entire translation or non-translating pool of mRNAs can be identified by RNA sequencing or microarray analysis.
Materials and Reagents
- Ultracentrifuge tube for SW41Ti (Seton Scientific, catalog number: 7030 )
- Permanent ink marker
- 10 ml syringe with wide gauge luer lock cannula (Vita Needles, gauge 14)
- 10 cm dish (Eppendorf, catalog number: 0030702115 )
- 1.5 ml tube (RNase and DNase free) (Corning, Axygen®, catalog number: MCT-150-C or equivalent)
- MCF7 human breast carcinoma cell line (ATCC, catalog number: HTB22 )
- Cycloheximide (CHX) (AMRESCO, catalog number: 94271 )
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 10010023 )
- DEPC treated water (AMRESCO, catalog number: E174 )
- Citrate saturated phenol (pH 4.5) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P4682 )
- Chloroform (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C2432 )
- 75% ethanol
- Nuclease free water
- Oligo dT primer
- dNTP mix
- 5x RT buffer
- Dithiothreitol (DTT) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: R0861 )
- RNase inhibitor (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: EO0381 )
- cDNA synthesis reagents (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 28025013 )
- 10x PCR buffer (with 15 mM MgCl2)
- 10 µM forward primer for gene of interest/control gene
- 10 µM reverse primer for gene of interest/control gene
- PCR reagents (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0273L )
- Sucrose (RNase and DNase free) (AMRESCO, catalog number: 0335 )
- Potassium chloride (KCl) (AMRESCO, catalog number: 0395 )
- Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) (AMRESCO, catalog number: 0288 )
- HEPES (pH 7.4) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Affymetrix, catalog number: 16926 )
- IGEPAL CA-360 detergent (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: I3021 )
- Protease inhibitor cocktail (AMRESCO, catalog number: M250 )
- 10% sucrose solution (for 8 ml) (see Recipes)
- 50% sucrose solution (for 8 ml) (see Recipes)
- Polysome lysis buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Gradient Station or any equivalent gradient fractionators (Biocomp, catalog number: 153-002 )
- Tube holder
- Ultra-centrifuge (Beckman Coulter, model: Optima L-70 or equivalent)
- Rotor SW41Ti (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 331362 )
- 200 µl pipette
- Spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: NanoDropTM 2000 )
- Fraction collector (Gilson, model: FC203B )
- UV monitor (Bio-Rad Laboratories, model: EM1-EconoTM )
- Balance
- Vortex
Software
- Gradient Master software (included with the Gradient Station)
Procedure
- Gradient preparation
- Prepare 8 ml of 10% and 50% sucrose solution each in 1x sucrose gradient buffer for a single gradient (see Recipes, Table 1).
- Degas the solution under vacuum for 5 min.
- Mark ultracentrifuge tubes at 50% of tube height with permanent ink marker using the marker block provided with the Gradient Station.
- Carefully add 10% sucrose solution upto the 50% mark of the tube with a wide gauge cannula.
- Aspirate the 50% sucrose solution into a syringe and insert the cannula directly to the bottom of the tube through the 10% sucrose solution then slowly layer the heavier solution to the bottom of the tube without disturbing the 10% sucrose solution. The heavier sucrose solution will slowly push the 10% solution up, and the 50% sucrose solution should reach up to the 50% marking of the ultracentrifuge tube.
- Cover the tube with rubber cap and place the tube in the tube holder on the rotor of the gradient station.
- Run the following pre-set program in the Gradient Master software
Program name: Short Sucrose 10-50% (w/v) Fast
Program specification: 10-50%; Step: S1/1; Time: 1 min 45 sec; Angle: 81.5; rpm: 25 (Video 1). - Carefully take out the tubes and store vertically at 4 °C for 2 h without disturbance.Video 1. Gradient preparation
- Prepare 8 ml of 10% and 50% sucrose solution each in 1x sucrose gradient buffer for a single gradient (see Recipes, Table 1).
- Cell lysate preparation for polysome profiling
- Treat 70-80% confluent cells in a 10 cm dish with 100 µg/ml cycloheximide (CHX) by directly adding it to the culture media at 15 to 30 min prior to harvesting.
- Wash the cells twice with PBS containing 100 µg/ml CHX, and harvest them by scraping into 10 ml ice cold PBS containing 100 µg/ml CHX. Centrifuge at 600 x g for 5 min at 4 °C and discard the supernatant carefully.
- Lyse the cell pellet by adding 200 µl of polysome lysis buffer (see Recipes). Mix gently with 200 µl pipette for a number of times and incubate on ice for 15 min.
- Centrifuge at 10,000 x g for 20 min at 4 °C.
- Transfer the supernatant to a pre-chilled 1.5 ml tube.
- Measure OD at 254 nm using a spectrophotometer.
- Overlay 25-50 OD equivalent of lysate gently on top of the gradient in the ultracentrifuge tube without disturbing the gradient. Leave around 2 mm of space in the gradient tube on top of the lysate layer (Figure 1).
- Weigh each gradient tube in a balance and adjust the weight of each tube containing the gradient to be exactly equal by adding polysome lysis buffer to the overlaid layer without disturbing the gradient.
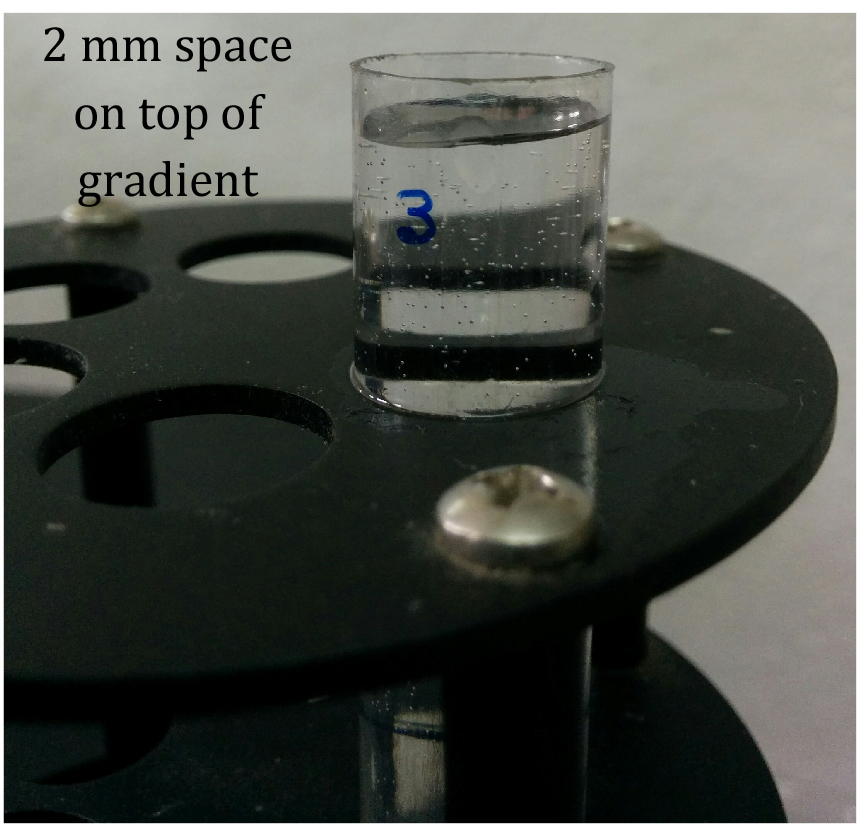
Figure 1. 10%-50% sucrose gradient showing 2 mm space on top of gradient
- Treat 70-80% confluent cells in a 10 cm dish with 100 µg/ml cycloheximide (CHX) by directly adding it to the culture media at 15 to 30 min prior to harvesting.
- Ultracentrifugation and fraction collection
- Pre-cool the rotor assembly and the tube buckets at 4 °C.
- Load the tubes carefully into the buckets without disturbing the gradients. Load the buckets on the rotor assembly ensuring equal weights in opposing positions. Perform the ultracentrifugation at 111,000 x g (Avg RCF) for 4 h at 4 °C at maximum vacuum.
- During the last hour of the ultracentrifugation switch on the gradient profiler, UV detector, gradient profiling software and wash the fractionator tubing with running DEPC treated water for several times and dry by running air.
- Carefully take out the tubes, one at a time, from the buckets and load into the tube holder of the gradient fractionator, and place at the proper position under the collector piston.
- Run water through the tubing and press auto zero on the UV monitor.
- Set up the tube length, gradient length (75 cm for SETON open top polyclear tube), fraction number (12 to 16) in the set up window.
- Run the fractionation and collect fractions (Figure 2) in 1.5 ml tubes and transfer to ice immediately.
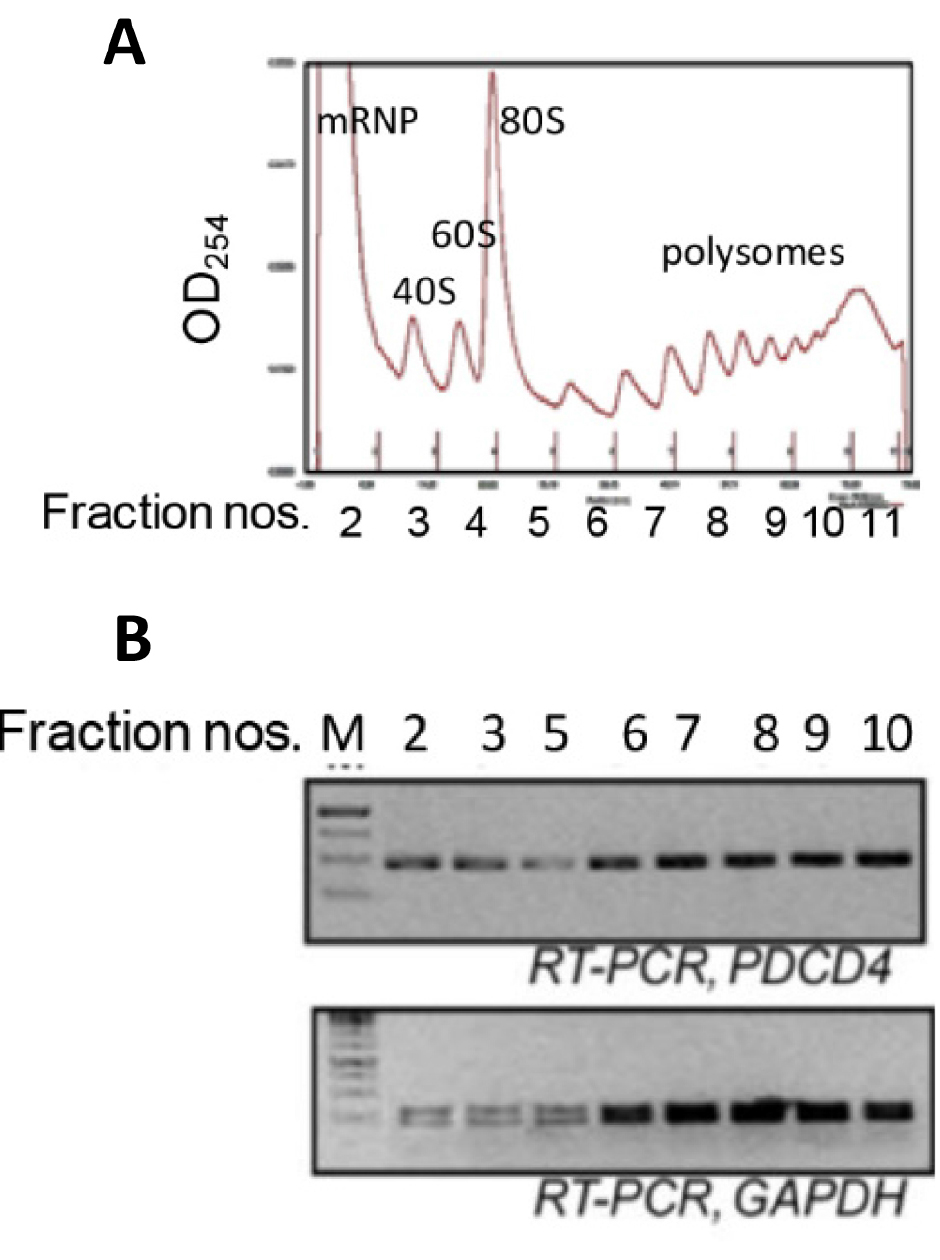
Figure 2. Ribosomal fractions from MCF7 cells were analysed by 10-50% sucrose density gradient fractionation. A. Ribosomal RNA content, measured at 254 nm, is plotted against fraction numbers (top panel). B. RNA isolated from selected fractions was analyzed by semiquantitative RT-PCR using PDCD4 and GAPDH primers (bottom panel).
- Pre-cool the rotor assembly and the tube buckets at 4 °C.
- RNA isolation and RT-PCR
- Add 300 µl phenol (citrate saturated, pH 4.5) and 300 µl chloroform to the tubes containing the gradient fractions.
- Vortex for 30-60 sec.
- Centrifuge at 16,000 x g for 15 min at 4 °C.
- Carefully transfer the supernatants to new tubes.
- Add 10 µg glycogen (RNase free) and equal volume of isopropanol and mix by inverting the tubes several times. Incubate at room temperature for 30 min.
- Centrifuge at 16,000 x g for 30 min at 4 °C.
- Wash the RNA pellet with 1 ml ice cold 75% ethanol.
- Air dry the RNA pellet and dissolve into 10-20 µl of nuclease free water.
- Measure the absorbance at 260 nm in a spectrophotometer to determine RNA concentration.
- cDNA synthesis: Setup the following reaction for cDNA synthesis for each RNA.
65 °C for 5 min. Keep on ice for 1 min.RNA 8 µl Oligo dT primer 1 µl 10 mM dNTP mix 1 µl
Add,
Incubate at 37 °C for 1 h. Then at 70 °C for 15 min.5x RT buffer 4 µl 100 mM DTT 2 µl RNase inhibitor 0.5 µl M-MLV RT (200 U/µl) 1 µl Nuclease free water 2.5 µl
Store at 4 °C. - PCR
Run thermal cycling for 30-35 cycles (Denaturation at 95 °C for 30 sec, annealing at 55 °C for 30 sec, elongation at 72 °C for 30 sec) and run the products on agarose gel (Figure 2).10x PCR buffer (with 15 mM MgCl2) 2 µl 10 µM forward primer for gene of interest/control gene 1 µl 10 µM reverse primer for gene of interest/control gene 1 µl Taq DNA polymerase (1 U/µl) 1 µl cDNA 2 µl Nuclease free water 13 µl
- Add 300 µl phenol (citrate saturated, pH 4.5) and 300 µl chloroform to the tubes containing the gradient fractions.
Recipes
- 10% sucrose and 50% sucrose solution (for 8 ml) (Table 1)
Table 1. Recipe for sucrose density gradient preparation10% sucrose solution (for 8 ml) 50% sucrose solution (for 8 ml) Sucrose 0.8 g 4.0 g 2 M KCl 400 µl 400 µl 1 M MgCl2 40 µl 40 µl 100 mM DTT 160 µl 160 µl 1 M HEPES pH 7.4 160 µl 160 µl 100 mg/ml Cycloheximide 8 µl 8 µl DEPC water Upto 8 ml Upto 8 ml - Polysome lysis buffer
100 mM KCl
5 mM MgCl2
20 mM HEPES (pH 7.4)
0.5% NP-40
100 μg/ml CHX
2 mM DTT
40 U/ml RNase inhibitor
1x protease inhibitor cocktail
Acknowledgments
We thank members of our laboratory for trying out and standardizing this protocol. Research which led to the development of these protocols was funded by a Wellcome Trust-DBT India Alliance Intermediate fellowship (WT500139/Z/09/Z) to PSR and a CSIR, India Senior Research Fellowship to DKP. This protocol is modified from the protocol described in Merrick and Hensold (2001).
References
- Merrick, W. C. and Hensold, J. O. (2001). Analysis of eukaryotic translation in purified and semipurified systems. Curr Protocols Cell Biolo 11-9.
- Poria, D. K., Guha, A., Nandi, I. and Ray, P. S. (2016). RNA-binding protein HuR sequesters microRNA-21 to prevent translation repression of proinflammatory tumor suppressor gene programmed cell death 4. Oncogene 35(13): 1703-1715.
- Ray, P. S., Jia, J., Yao, P., Majumder, M., Hatzoglou, M. and Fox, P. L. (2009). A stress-responsive RNA switch regulates VEGFA expression. Nature 457(7231): 915-919.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Poria, D. K. and Ray, P. S. (2017). Polysome Analysis. Bio-protocol 7(6): e2192. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2192.
Category
Cancer Biology > Cancer biochemistry > Protein
Biochemistry > RNA > RNA-protein interaction
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link












