Advanced Search
Preparation of monobody mRNA libraries for selection against SARS-CoV-2 targets
Last updated date: Nov 9, 2020 Views: 1170 Forks: 0
T. Kondo1, Y. Iwatani2,3, K. Matsuoka2, T. Fujino1, S. Umemoto1, Y. Yokomaku2, K. Ishizaki1, S. Kito1, T. Sezaki1, G. Hayashi1,4, H. Murakami1,5*
1Department of Biomolecular Engineering, Graduate School of Engineering, Nagoya University
2Department of Infectious Diseases and Immunology, Clinical Research Center, National Hospital Organization Nagoya Medical Center
3Division of Basic Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Nagoya University
4 Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST), PRESTO
5Institute of Nano-Life-Systems, Institutes of Innovation for Future Society, Nagoya University
Correspondence to: murah@chembio.nagoya-u.ac.jp
See Figure 1 for the DNA and protein sequences of the monobody library.
See Figure 2 for the scheme of the mRNA preparation.
Materials
• Oligonucleotide sequences and suppliers were listed in Table 1.
• The T4 DNA ligase and BsaI were obtained from New England Biolabs (MA, USA).
• Preparation of the Pfu-S DNA polymerase [Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 1197-1207 (2004)] was described in Science Advances, 6(42), eabd3916 (2020).
• The T7 RNA polymerase was prepared using pT7-911Q [J. Biol. Chem. 272, 33009–33014 (1997)].
• 2 x Ligation solution : 100 mM Tris-HCl pH7.5, 12 mM MgCl2, 1 mM ATP,
16% PEG6000, 20 mM DTT, 4,000 units/ml T4 DNA ligase
• 1 x PCR solution : 10 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.4, 100 mM KCl, 0.1% (v/v) Triton X-100, 2% (v/v) DMSO, 2 mM MgSO4, 0.2 mM each dNTP, 0.375 µM each primer, and 2 nM of Pfu-S DNA polymerase
• 1 x RNA pol solution: 40 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0, 1 mM spermidine, 0.01% (v/v) Triton X-100, 10 mM DTT, 25 mM MgCl2, 5 mM each NTP, 1 µM T7 RNA polymerase.
Preparation of A-fragment DNA of the monobody library
Mixture of following solution (35 µL) was heated at 95˚C for 2 min and was placed at room temperature for 5 min.
FN3F0.F83 (2µM in final concentration)
FN3F1-2.F29(P) (2µM in final concentration)
FN3FF1coR8.F73 (1 µM in final concentration)
FN3FF1coR10.F79 (1 µM in final concentration)
Fn3an1.R20(3NH2) (4 µM in final concentration)
Fn3an2-1.R20(3NH2) (4 µM in final concentration)The 2 x Ligation solution (35 µL) was added to the solution, and incubated at 25˚C for 1 hour (Figure 3a).
- The entire mixture was added to 1 x PCR solution (15 mL). The DNA fragment was amplified using T7SD8M2.F44 and FN3BsaI.R40 by the following conditions: initial activation step at 94 °C for 1 min, 7 cycles of heat denaturation at 94 °C for 20 s, primer annealing at 55 °C for 20 s, and primer extension at 72 °C for 45 s.
The amplified A-fragment DNA was purified by phenol/chloroform extraction and isopropanol precipitation.
Preparation of B-fragment DNA of the monobody library
Mixture of following solution (35 µL) was heated at 95˚C for 2 min and was placed at room temperature for 5 min.
FN3FF2co.F72(p) (2 µM in final concentration)
FN3F3coR10.F70(p) (1 µM in final concentration)
FN3F3coR12.F76(p) (1 µM in final concentration)
Fn3an3.R20(3NH2) (4 µM in final concentration)The 2 x Ligation solution (35 µL) was added to the solution, and was incubated at 25˚C for 1 hour (Figure 3a).
- The entire mixture was added to 1 x PCR solution (15 mL). The DNA fragment was amplified using FN3BsaI.F33 and FN3Pri2.R44 by the following conditions: initial activation step at 94 °C for 1 min, 7 cycles of heat denaturation at 94 °C for 20 s, primer annealing at 55 °C for 20 s, and primer extension at 72 °C for 45 s
The amplified B-fragment DNA was purified by phenol/chloroform extraction and isopropanol precipitation.
Digestion of the A-fragment and B-fragment DNA with BsaI
The reaction mixture (1 x CutSmart® buffer, 2 µM the fragment, 200 units/mL BsaI-HF®; in total 400 µL) was incubated at 37˚C for 4 days.
The digested A-fragment and B-fragment DNA were purified by phenol/chloroform extraction and isopropanol precipitation (optional: polyacrylamide gel purification if the digested small fragments were remained).
Ligation of the digested A-fragment and B-fragment DNA
The solution containing 2 µM each A-fragment and B-fragment DNA products (100 µL) was mixed with the 2 x Ligation solution (100 µL), and the resulting mixture was incubated at 25˚C for 1 hour (Figure 3b).
PCR amplification of the DNA fragment
- The entire mixture was added to 1 x PCR solution (60 mL). The DNA fragment was amplified using T7SD8M2.F44, G5S-4Gan21-3.R42 by the following conditions: initial activation step at 94 °C for 1 min, 4 cycles of heat denaturation at 94 °C for 20 s, primer annealing at 55 °C for 20 s, and primer extension at 72 °C for 45 s.
The amplified DNA was purified by phenol/chloroform extraction and isopropanol precipitation.
mRNA transcription
The mixture ( 1xRNA pol solution, 50 nM amplified DNA; in total 11 mL) was incubated at 37˚C for 6 hours.
The mRNA was purified by isopropanol precipitation followed by PAGE purification. The eluted DNA was purified by phenol/chloroform extraction and isopropanol precipitation. After air dry, the pellet was dissolved in ultra-pure water. The mRNA concentration was determined by OD at 260 nm.
mRNA/HEX-PuL preparation
The solution (25 mM HEPES-K pH 7.8, 200 mM potassium acetate, 4 µM RNA, and 4 µM HEX-PuL; in total 80 µL) was heated at 95 ˚C for 2 min and then was cooled down to 25˚C. The resulting complex was directly used for 1st round selection.
(a)
ATACTAATACGACTCACTATAGGATTAAGGAGGTGATATTTATGCAAGCCAATTCTGGTTCTCTGGAAGTTGTGGAAGCCAGCCCGACGAGCATTCAGATTTCTTGGGACGCT
-(NNK) 8,10-GTTCGCTACTATCGCATTACCTATGGCGAAACCGGCGGTAACAGTCCGGTCCAGGAATTTACGGTGCCGGGTTCAAAATCGACCGCGACGATTTCCGGCCTGAAACCGGGTGTTGATTATACCATCACGGTGTACGCAGTTACC
-(NNK) 10,12-CCGATTTCTATCAACTACCGCACGGGTGGAGGAGGAGGTAGCTAGGGACGGCGGGCGCGAGGCGGG
(b)
MQANSGSLEVVEASPTSIQISWDA
-(X)8,10-
VRYYRITYGETGGNSPVQEFTVPGSKSTATISGLKPGVDYTITVYAVT
-(X)10,12-
PISINYRTGGGGGS-GRGAGGG
Figure 1. The monobody library sequences. (a) The DNA sequence of the monobody library [T7 promoter, green; NKK codon mix (20% Tyr, 10% Ser, 15% Gly, 10% Trp, and 3% each of all the other amino acids except for Cys), yellow; an21 sequence, cyan]. (b) The protein sequence of the monobody library (the randomized residues X, yellow).
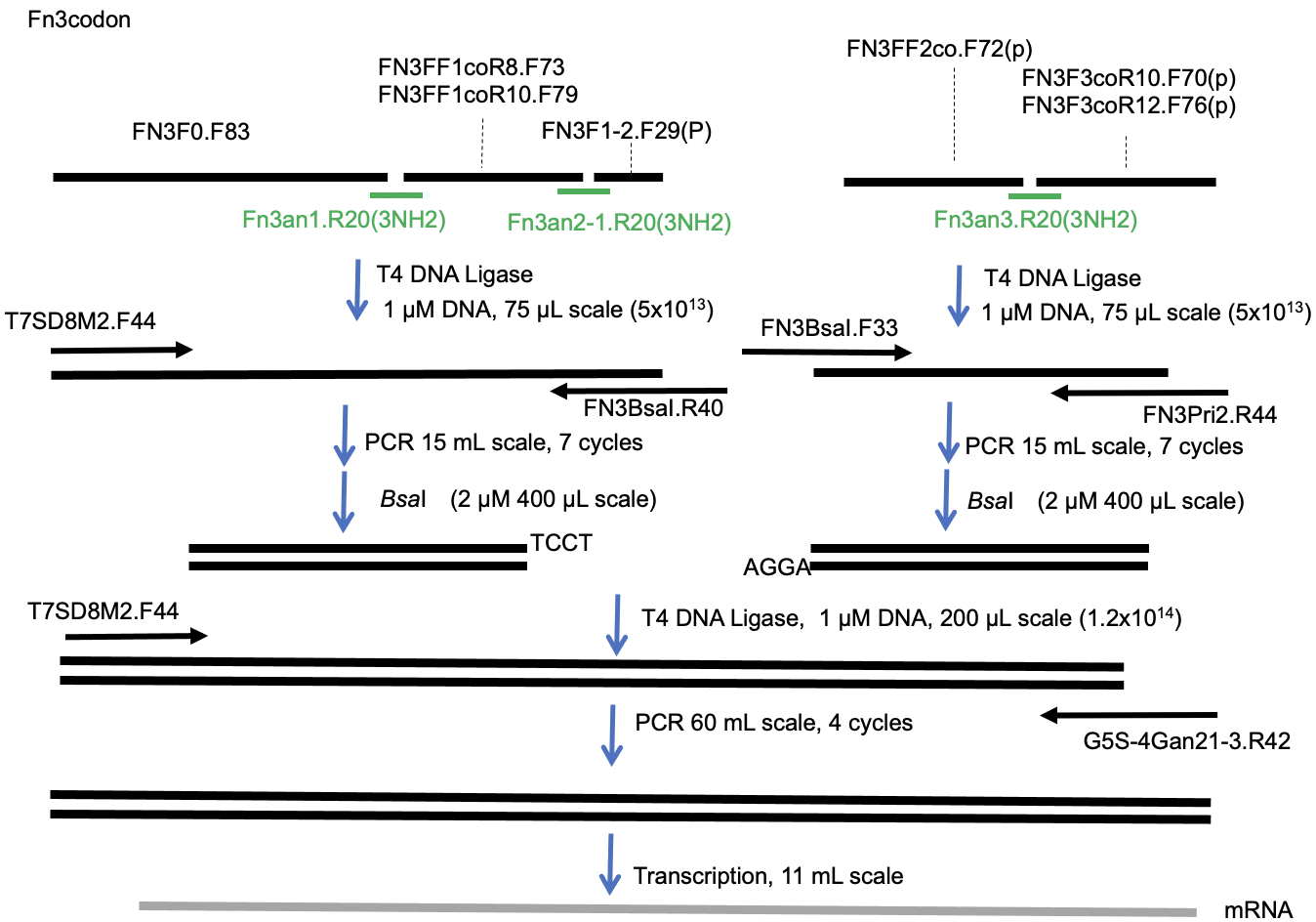
Figure 2. Scheme for preparation of monobody mRNA library.
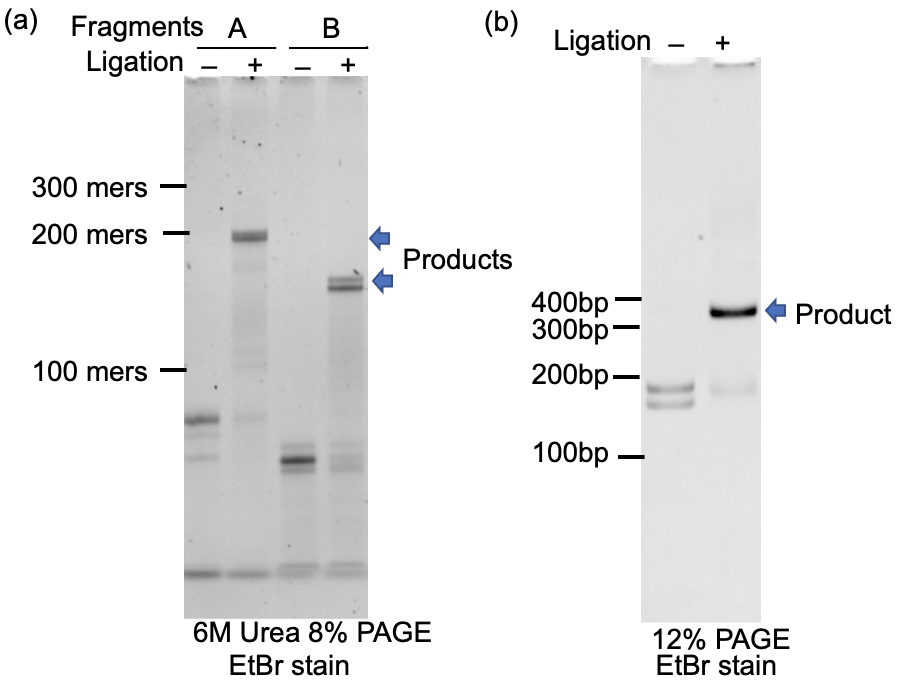
Figure 3. PAGE analysis of the ligation reactions. (a) Oligonucleotide ligation. (b) Ligation of the BsaI-treated fragment A and fragment B.
Table 1. Oligonucleotide sequences and suppliers.
| Names | Sequences (5' to 3') | Modification | Supplier |
| FN3FF1coR8.F73 | CGAGCATTCAGATTTCTTGGGACGCTNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKGTTCGCTACTATCGCATTACCTA | 5'-Phospholilation NNK(codon) | Nippon Bio Service (Japan) |
| FN3FF1coR10.F79 | CGAGCATTCAGATTTCTTGGGACGCTNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKGTTCGCTACTATCGCATTACCTA | 5'-Phospholilation NNK(codon) | Nippon Bio Service (Japan) |
| FN3FF2co.F72(P) | AGGAATTTACGGTGCCGGGTTCAAAATCGACCGCGACGATTTCCGGCCTGAAACCGGGTGTTGATTATACCA | 5'-Phospholilation NNK(codon) | Nippon Bio Service (Japan) |
| FN3F3coR10.F70(P) | TCACGGTGTACGCAGTTACCNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKCCGATTTCTATCAACTACCG | 5'-Phospholilation NNK(codon) | Nippon Bio Service (Japan) |
| FN3F3coR12.F76(P) | TCACGGTGTACGCAGTTACCNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKNNKCCGATTTCTATCAACTACCG | 5'-Phospholilation NNK(codon) | Nippon Bio Service (Japan) |
| FN3F1-2.F29(P) | TGGCGAAACCGGCGGTAACAGTCCGGTCC | Fasmac Co., Ltd. (Japan) | |
| FN3BsaI.F33 | ACGTTCGGTCTCAAGGAATTTACGGTGCCGGGT | Fasmac Co., Ltd. (Japan) | |
| FN3BsaI.R40 | GATCGTGGTCTCTTCCTGGACCGGACTGTTACCGCCGGTT | Fasmac Co., Ltd. (Japan) | |
| FN3Pri2.R44 | TAGCTACCTCCTCCTCCACCCGTGCGGTAGTTGATAGAAATCGG | Fasmac Co., Ltd. (Japan) | |
| Fn3an1.R20(3NH2) | TGAATGCTCGTCGGGCTGGC | 3'-Amino(C12) modification | Fasmac Co., Ltd. (Japan) |
| Fn3an2-1.R20(3NH2) | GGTTTCGCCATAGGTAATGC | 3'-Amino(C12) modification | Fasmac Co., Ltd. (Japan) |
| Fn3an3.R20(3NH2) | TACACCGTGATGGTATAATC | 3'-Amino(C12) modification | Fasmac Co., Ltd. (Japan) |
| T7SD8M2.F44 | ATACTAATACGACTCACTATAGGATTAAGGAGGTGATATTTATG | Fasmac Co., Ltd. (Japan) | |
| G5S-4Gan21-3.R42 | CCCGCCTCGCGCCCGCCGTCCCTAGCTACCTCCTCCTCCACC | Fasmac Co., Ltd. (Japan) | |
| FN3F0.F83 | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGATTAAGGAGGTGATATTTATGCAAGCCAATTCTGGTTCTCTGGAAGTTGTGGAAGCCAGCCCGA | Fasmac Co., Ltd. (Japan) |
- Kondo, T and Murakami, H(2020). Preparation of monobody mRNA libraries for selection against SARS-CoV-2 targets. Bio-protocol Preprint. bio-protocol.org/prep616.
- Kondo, T., Iwatani, Y., Matsuoka, K., Fujino, T., Umemoto, S., Yokomaku, Y., Ishizaki, K., Kito, S., Sezaki, T., Hayashi, G. and Murakami, H.(2020). Antibody-like proteins that capture and neutralize SARS-CoV-2. Science Advances 6(42). DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abd3916
Category
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link

