Advanced Search
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene knockout and knock-in
Last updated date: Aug 6, 2021 Views: 957 Forks: 0
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene knockout
The Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR) Cas9 system contains two distinct components: (1) a guide RNA and (2) an endonuclease, CRISPR-Cas9. The sgRNA/Cas9 complex is recruited to the target sequence by base-pairing between the sgRNA sequence and the target sequence in the genomic DNA (contain the correct Protospacer Aduacent Motiff (PAM) sequence immediately following the target sequence). The wild-type Cas9 can cut both strands of DNA causing a Double Strand Break (DSB). Cas9 will cut 3-4 nucleotides upstream of PAM sequence. DSB will be repaired through (1) Non-Homologous End Joining (NHEJ) or (2) Homology Directed Repair (HDR) pathway. (Key references: PMID: 25430774, 24906146, addgene: http://www.addgene.org/CRISPR/guide/)
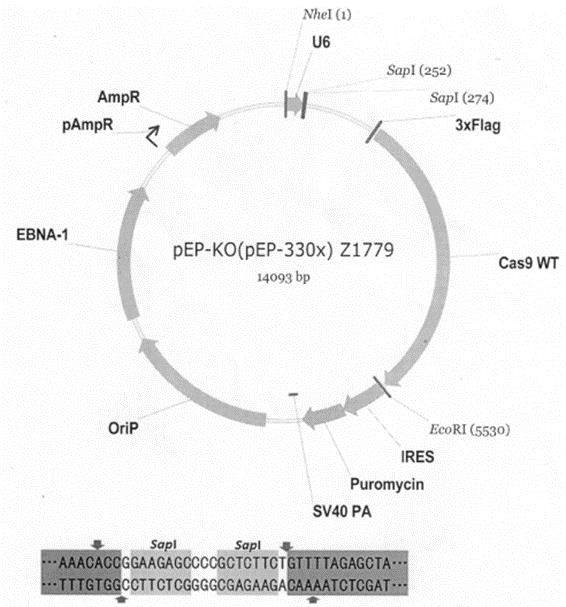
PEP-KO (Contain sgRNA and Cas9, Cloning site: SapI, Episomal, puromycin, from Xia Lab) was used in our previous work (PMID: 33988507) for gene knockout.
Step 1-1. Identify your target sequence
Find the transcript ID of your target gene from NCBI. If there are multiple transcripts, using the same sequences between each other as the candidate regions contain target sequences. For human genes, we recommend two ways to choose target sequence:
- Choose candidate unique sgRNA targets (5’-N20NGG-3’) in your target gene exons from the EXCEL file (http://arep.med.harvard.edu/human_crispr/) made by Church Lab (PMID: 23287722) (not filtered for potential off-target effects)
- Find in excel sheet of GeCKO v2 library made by Zhang Feng Lab (http://www.addgene.org/crispr/libraries/) (included 6 sgRNAs for each gene).
Do an alignment to double check position of target sequences on the gene by blast (http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi ) and off target (CRISPRdirect and RGEN Tools: Cas-OFFinder).
Step 1-2. Order primers to create the plasmid encoding your sgRNA
PEP-KO, the vector looks like this:
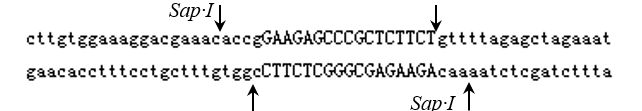
Oligos should look like:
Oligo1: 5’- ACCGNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN-3’
3’- CNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNCAA-5’ Oligo2
Step 1-3. Phosphorylate and anneal the two oligos
1. Make the reaction mix as follow:
Ingredient | Amount |
Oligo1 (100μM) | 1μl |
Oligo2 (100μM) | 1μl |
10× T4 Ligation Buffer (TaKaRa, #2011A) | 1μl |
T4 PNK (TaKaRa, #D2021) | 0.5μl |
ddH2O | 6.5μl |
Total | 10μl |
Phosphorylation of the primer largely increases efficiency (recommended), but is not absolutely required. If you decide to skip phosphorylation step, just omit T4 PNK (but not any other gradients in the mix) from the mix, and skip the first 37℃ for 30min step from the following incubation.
2. Incubate on thermo cycler using the following parameters
(37℃ for 30min, and 95℃ for 5min, then ramp down to 25℃ at 0.5℃/10s.):
Hold 37℃, 30min
Hold 95℃, 5min
Cycle 46
94.5℃, 10s
94℃, 10s
93.5℃, 10s
(More-Modify-AutoX-[-1.5, -1.5, -1.5])
Hold 25℃, 5min
Hold 4℃, forever
Dilute annealed oligos at a 1:200 dilution into water or Elution Buffer.
Step 1-4: Digest Vector for 30min at 37℃.
Ingredient | Amount |
PEP-KO | 1μg |
10× FastDigest Buffer | 2μl |
SapI/LguI: Fermentas, #FD1934 | 1μl |
ddH2O | Xμl |
Total | 20μl |
Gel purify digested Vector using AxyGen Gel extraction kit (AP-GX-50). Elute in 20-30μl, and measure concentration using NanoDrop (Normally about 10-30ng/μl).
Step 1-5. Ligation
Make the following mixture and incubate for 2h at RT or overnight at 16℃.
Ingredient | Amount |
Vector from step 1-4 | 30ng |
Oligo duplex from step 1-3 (1:200 dilution) | 1μl |
10×T4 Ligation Buffer (TaKaRa, #2011A) | 1μl |
T4 Ligase (TaKaRa, #2011A) | 1μl |
ddH2O | 6μl |
Total | 10μl |
Step 1-6: Transformation and clone identification
- Get DH5α competent cells from -80°C freezer, thaw on ice.
- Pipet 5ul ligation product from step 1-5 or 15ng vector from step 1-4 (as a negative control) gently into 40μl competent cells and tap the tube to mix.
- Incubate on ice for 15min.
- Heat shock in water bath at 42°C, 90s
- Immediately incubate on ice 2min.
- Add 600µl LB medium to transformation product, Shake in shaker at 37°C, 30min 250rpm for bacteria to recover.
- Pellet at RT 3min 3000rpm.
- Remove excess LB from the top so that 100µl LB with pellet is left.
- Resuspend pellet by pipetting up and down, plate all onto LB plates.
- Cap the plate and place up-side down in incubator to incubate at 37°C overnight.
- If the ligation product is much more than negative control, you only need to pick 2- 3 single colonies to 5ml of LB containing carbenicillin. Incubate overnight at 37°C with vigorous shaking. Plasmid extraction and sequence with U6 primer to get right clone.
Step 1-7. Transfection and colonies pick
- Use appropriate method to transfect cells with 500ng PEP-KO (based on 6-well plate). After transfection for 24h, select with puromycin (the concentration for each cell should be predetermined).
- After selection for about 2 days (control cells are all dead), trypsinize and re-plate cells at low density in 10cm dish in 3 different concentration to make single colonies pick convenient (for example, 100, 500, 2500 cells). One can also dilute cells and re-seed them into 96 well plate but should check under microscope to confirm only one cell in one well.
- Expand single colonies (picked from 10cm dish with 10μl tips after incomplete trypsinization or directly expanded from 96 well plate) and harvest a portion of cells for western blot, DNA extraction and analysis.
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated epitope tag knockin
To enhance specificity and efficiency, PEP-KI (derived from PEP-KO vector by replacing wild-type Cas9 with a D10A mutant) was used in our previous work (PMID: 33988507) for epitope tag knockin on C-terminal. Another vector, pSEPT (from Kaulich lab) containing left/right homogy arms(LHA/RHA), a 3x Flag or HA coding sequence, a T2A element, and a neomycin resistance gene was used as targeting vector.
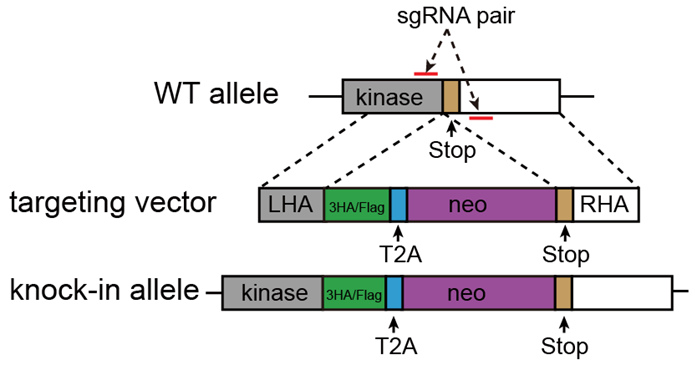
Step 2-1. Select a pair of sgRNAs for C-terminal tagging
Since Cas9 D10A nickase only cleaves DNA strand that complementary to sgRNA, a pair of sgRNAs respectively targeting sense and antisense DNA strands are necessary. Before start sgRNA design, find the genomic sequence around stop codon of your target gene (usually 200-300bp). Many online tools offer assistance for sgRNA pairs design, such as Benchling (https://www.benchling.com/crispr/) and E-CRISSP (http://www.e-crisp.org/E-CRISP/designcrispr.html). Follow the instruction and get your sgRNA sequences.
Step 2-2. Get a pair of PEP-KI vectors (PEP-KI#1, PEP-KI#2) expressing sgRNAs
The same with Step 1-2 to Step 1-6.
Step 2-3. Construct targeting vector with LHA and RHA
With pSEPT as targeting vector, LHA could be integrated using AgeI/NheI while RHA using EcorI/SalI. Homology arms could be gotten by PCR amplification with genomic DNA extracted from target cells as template. The recommended length of PCR products is 500-1000bp. To avoid targeting vector being cleaved, one guanine in the protospacer adjacent motif (NGG) could be mutated. If mutations is selected on the LHA, pay attention not to alter amino acid coding. Following the instruction of molecular cloning, get targeting vector constructed.
Step 2-4. Transfection and colonies pick
- Use appropriate method to transfect cells with 300ng targeting vector, 200ng PEP-KI#1 and 200ng PEP-KI#2 (based on 6-well plate). Control group is transfected under the same condition but replacing targeting vector with pSEPT vector not containing homology arms. After transfection for 24h, select with puromycin (the concentration for each cell should be predetermined).
- After selection for about 2 days, trypsinize and re-plate cells at low density in 10cm dish in 3 different concentration to make single colonies pick convenient (for example, 100, 500, 2500 cells). One can also dilute cells and re-seed them into 96 well plate but should check under microscope to confirm only one cell in one well. Culture medium containing G418 is refreshed every 2 days (concentration of G418 for each cell should be predetermined, the recommended time frame of selection is 10-14 days) till cells in control group die out.
- Expand single colonies (picked from 10cm dish with 10μl tips after incomplete trypsinization or directly expanded from 96 well plate) and harvest a portion of cells for western blot, DNA extraction and analysis.
- Zhang, H and Zhao, B(2021). CRISPR/Cas9-mediated gene knockout and knock-in. Bio-protocol Preprint. bio-protocol.org/prep1331.
- Zhang, H., Cao, X., Tang, M., Zhong, G., Si, Y., Li, H., Zhu, F., Liao, Q., Li, L., Zhao, J., Feng, J., Li, S., Wang, C., Kaulich, M., Wang, F., Chen, L., Li, L., Xia, Z., Liang, T., Lu, H., Feng, X. and Zhao, B.(2021). A subcellular map of the human kinome. eLife. DOI: 10.7554/eLife.64943
Category
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link
