- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
[3H]-Spiperone Saturation Binding to Dopamine D2, D3 and D4 Receptors
Published: Vol 3, Iss 20, Oct 20, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.945 Views: 10669
Reviewed by: Fanglian HeCheng ZhangAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Enrichment of Membrane Proteins for Downstream Analysis Using Styrene Maleic Acid Lipid Particles (SMALPs) Extraction
Benedict Dirnberger [...] Kathryn S. Lilley
Aug 5, 2023 2978 Views

A Computational Workflow for Membrane Protein–Ligand Interaction Studies: Focus on α5-Containing GABA (A) Receptors
Syarifah Maisarah Sayed Mohamad [...] Ahmad Tarmizi Che Has
Nov 20, 2025 2123 Views

Orthogonal Temperature-Related Intensity Change and Time-Resolved Förster Resonance Energy Transfer High-Throughput Screening Platform for the Discovery of SLIT2 Binders
Moustafa T. Gabr [...] Somaya A. Abdel-Rahman
Feb 20, 2026 99 Views
Abstract
This protocol is intended for use in 96 well plates (1,200 μl wells) but it can similarly be applied to standard test tubes (Levant, 2007). D2, D3, and D4 dopamine receptors are members of the D2-like class of dopamine receptors. They can be studied using the radioligand [3H]-spiperone, which is an antagonist binding to D2, D3, and D4 receptors with comparable affinity. A saturation assay can be used to determine the affinity of a radioligand to a receptor (Kd) and to determine the total number of receptors present in the assay (Bmax). If saturation binding experiments are performed in the absence and presence of a fixed concentration of another, not radiolabeled ligand, it can also be determined whether the other ligand acts in a competitive manner. If the specific radioactivity is low (tritiated) relative to the affinity of the radioligand (< 1 nM), a high assay volume (≥ 1 ml) is required to avoid ligand depletion; this is of particular importance if a receptor source with high expression density is used (e.g. expressed recombinant receptors). To obtain reliable estimates of these parameters at least 6 different concentrations of radioligand must be tested, but particularly when a receptor is first detected in a given tissue or cell type a greater number of concentrations are helpful. The incubation time and temperature are chosen to allow formation of equilibrium between association and dissociation with the receptor for both radioligand and competitor. Each experiment can be divided into different steps such as assay preparation, membrane preparation, incubation, filtration, counting of the samples and data analysis. To minimize experimental error all assays are performed at least in duplicate. Radioligand dilutions should be prepared to cover the desired concentration range. Optimally these concentrations should cover both the high range (corresponding to 5-10x Kd and hence saturation of the receptor) and the low range (around Kd), so that both Kd and Bmax can reliably be estimated without undue extrapolation. At each radioligand concentration total and non-specific binding should be determined; the agent used for the definition of non-specific binding (NSB) should be chemically (different family) and physically (avoid combination of two lipophilic compounds) distinct from the radioligand to avoid artifacts. For discussion of specific benefits of chosen assay conditions see van Wieringen et al. (2013) (copy can be obtained from the author).
Keywords: DopamineMaterials and Reagents
- Radioligand [3H]-spiperone (e.g. PerkinElmer, catalog number: NET565250UC )
- Butaclamol (e.g. Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 55528-07-9)
- Receptor-containing membrane suspension
- Whatman GF/C filters (e.g. PerkinElmer, catalog number: 6005174 )
- Poly(ethyleneimine) solution (PEI) (e.g. Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 9002-98-6 )
- Scintillation cocktail (e.g. PerkinElmer, catalog number: 6013641 )
- Tris-HCl
- KCl
- CaCl2
- MgCl2
- Destilled water
- Assay buffer (see Recipes)
- Wash buffer (see Recipes)
- NSB solution (see Recipes)
- Radioligand solutions (see Recipes)
- Radioligand Dilutions (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 96 well plates (polysterene)
- Cell harvester (e.g. PerkinElmer)
- Ultra-Turrax® (IKA, model: 0001602800 ) or similar disperser
- Water bath
- Scintillation counter
Software
- Prism (Graphpad Software, San Diego, CA, USA) or similar
Procedure
- Before the assay
- Prepare assay and wash buffer.
- With some receptor sources PEI-pretreated filterplates may improve the TB/SB ratio: Prepare 0.1% PEI solution and pipet 100 μl/filter on the filterplate, subsequently place in refrigerator (4 °C) for at least 2 hours.
- The experiment is performed in 96 well plates (polysterene) with a total assay volume of 1,000 μl (450 μl assay buffer + 200 μl radioligand + 200 μl of assay buffer or 5 μM (+)-butaclamol + 150 μl membrane preparation).
- Prepare NSB solution.
- Prepare radioligand solutions.
- Membrane preparation.
Prepare receptor-containing membrane suspension according to preparation protocol. Re-homogenize suspension in small volume (< 2 ml) using short burst of Ultra-Turrax. Dilute to desired protein concentration and to yield a total volume of about 4 ml per 24 data point experiment. The protein concentration of the membrane suspension should be chosen so that a robust specific binding signal is obtained but at the same time total binding should be < 10% (even better < 5%) of free radioligand concentration. Protein content can be assayed by a variety of essays, e.g. Bradford (1976). Prepare the membrane suspension initially in ice.
- Pre warm all solutions for 15 min in 25 °C water bath.
- Final preparation (Table 1), add components to wells in following order:
- 450 μl assay buffer.
- 200 μl assay buffer (TB) or 200 μl 5 μM butaclamol (NSB).
- 150 μl membrane suspension.
- Start reaction by adding 200 μl radioligand.
Table 1. Pipetting scheme for sample on microtiter plateT1
T1
T2
T2
T3
T3
T4
T4
T5
T5
T6
T6
TB1
TB1
TB2
TB2
TB3
TB3
TB4
TB4
TB5
TB5
TB6
TB6
NSB1
NSB1
NSB2
NSB2
NSB3
NSB3
NSB4
NSB4
NSB5
NSB5
NSB6
NSB6
- 450 μl assay buffer.
- Prepare assay and wash buffer.
- During the assay
- Incubate for 120 min at 25 °C in water bath.
- Terminate reaction by rapid vacuum filtration over Whatman GF/C filters using a cell harvester. Wash filter 10 times with ice-cold wash buffer.
- Incubate for 120 min at 25 °C in water bath.
- After the experiment
- Add aliquots of 50 μl radioligand to wells of counting plate to determine total radioactivity.
- Dry, e.g. in oven for 2 h.
- Place sticker on bottom plate. Add scintillation cocktail (20 μl) to filters, place sticker on top of plate and count in a scintillation counter, allow adequate time (15 min) before counting samples.
- Add aliquots of 50 μl radioligand to wells of counting plate to determine total radioactivity.
- Data analysis
The following calculations are required to derive Kd and Bmax from the data.
- Carefully inspect raw data for consistency of replicates. Do not light-heartedly eliminate apparent ‘outliers’ from the data set.
- Subtract mean non-specific binding from each replicate of total binding to obtain specific binding.
- Transform totals to molar concentration of radioligand in the assay, and measured bound values (total binding, non-specific binding and specific binding) to molar amount of ligand based upon the specific radioactivity of the radioligand and the efficiency of the scintillation counter. A representative experiment with D2 receptors may look like this.
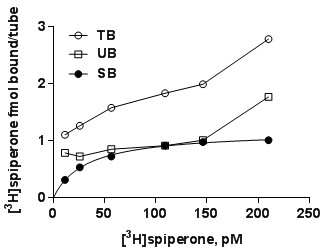
- Plot specific binding (y-axis) vs. concentration of radioligand (x-axis).
- Analyze data by non-linear iterative curve fitting using a rectangular hyperbolic function using one of many available iterative curve fitting programs, e.g. Prism.
- Molar amount of Bmax can be corrected for tissue content, mostly the amount of protein per well (mostly yielding fmol/mg protein); alternative normalization e.g. for tissue wet weight, number of cells or DNA content are possible.
- As internal quality check, determine the fraction of total binding from total radioactivity in the assay. This needs to be < 10% (better < 5%) as otherwise non-equilibrium conditions may exist. In the latter case, membrane concentration in the assay can be reduced if the measured signal remains robust. Alternatively, assay volume can be increased as this will increase total amount of radioligand (concentration constant) but not amount bound (membrane protein amount constant).
- In the past when no computer assisted data analysis was available Kd and Bmax were estimated with the Rosenthal plots, better known as Scatchard plots (Rosenthal invented them but Scatchard made them famous). In these plots the specifically bound radioligand is on the x-axis and is plotted against the ratio of bound/unbound radioligand on the y-axis. The x-intercept corresponds to Bmax and the negative reciprocal of the slope corresponds to Kd. Rosenthal/Scatchard plots can still be useful to visualize that data points indeed fall on a linear line but the estimates derived from this are less reliable than those from iterative curve fitting (the assumptions of linear regression used in these plots don’t meet because x and y are not independent of each other), making this an outdated analysis.
- If saturation binding experiments are performed in the absence and presence of an inhibitor, the data can be used to test for a competitive nature of the inhibitor. This is the case if the presence of inhibitor changes the Kd but not the Bmax of the radioligand.
- Carefully inspect raw data for consistency of replicates. Do not light-heartedly eliminate apparent ‘outliers’ from the data set.
Recipes
- Assay buffer
50 mM TRIS: TRIS-HCl: 6.6 g and TRIS base 970 mg (or only 6.04 g TRIS base/L)
5 mM KCl: 373 mg/L
2 mM CaCl2: 220 mg/L
2 mM MgCl2(6 H2O): 410 mg/L
pH 7.4
- Wash buffer
50 mM TRIS: TRIS-HCl (33 g/5 L) and TRIS base (4.85 g/5 L) (or only 30.22 g/5 L TRIS base)
pH 7.4
- 0.1% PEI (only for D3 receptor assay)
Prepare 0.1% solution, PEI is delivered as a 50% solution, pipet 1 ml from this with a syringe and add to 9 ml aqua dest. To get 5%, pipet 400 μl PEI 5% + 19.6 ml destilled water to get PEI 0.1%
- NSB solution
3.98 mg butaclamol HCl/10 ml assay buffer yields 1.10-3 M (prepare aliquots of this)
Dilute this 1:200 to obtain 5 μM in solution, i.e. 1 μM final concentration in assay
- Radioligand solutions
The intended radioligand concentration range in the assay should be chosen to cover both the expected Kd and about 5-10x Kd (Kd spiperone in transfected cells according to literature ≈ 0.05 nM, 0.35 nM and 0.07 nM for D2, D3 and D4, respectively). The stock solution to be prepared needs to be 5x the assay concentration. Thus, the stock solution should be 25-50x Kd. The following is an example calculation based on a specific activity of 16.2 Ci/mmol radioactive of the radioactive stock solution for a D2 receptor assay. This needs to be adapted for the other subtypes based on their Kd values and for each batch of radioligand and its specific activity.
[3H]-spiperone concentration = 1 mCi/ml/(16.2 Ci/mmol x 1,000 mCi/Ci) = 61.7 μM
Highest concentration needed (10 x Kd x 5) = 10 x 0.05 x 5 = 2.5 nM
2.5 ml x 2.5 nM = 0.00625 nmol [3H]-spiperone needed
(0.00625 nmol)/61.7 x 103 nM = 0.1013 μl of [3H]-spiperone solution needed for 2.5 ml
Thus 1 μl [3H]-spiperone solution in 25.0 ml assay buffer to yield a concentration of 2.5 nM.
A free tool for such calculations can be found at www.graphpad.com/quickcalcs/chemMenu/.
- Radioligand Dilutions (Over a 100-fold Range) (Table 2).
Table 2. Dilution scheme to for radioligand working solutionsNumber
Relative concentration
Preparation
1
100
2.5 ml of radioligand at the highest concentration
2
66.67
Mix 800 μl from tube 1 + 400 μl assay buffer
3
50
Mix 1,000 μl from tube 1 + 1,000 μl assay buffer
4
25
Mix 1,000 μl from tube 3 + 1,000 μl assay buffer
5
12.5
Mix 1,000 μl from tube 4 + 1,000 μl assay buffer
6
6.25
Mix 1,000 μl from tube 5 + 1,000 μl assay buffer
Acknowledgments
This protocol is the adaptation of a protocol originally published by Levant (2007).
References
- Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248-254.
- Levant, B. (2007). Characterization of Dopamine Receptors. Curr Protoc Pharmacol 36:1.6.1–1.6.15.
- van Wieringen, J. P., Booij, J., Shalgunov, V., Elsinga, P. and Michel, M. C. (2013). Agonist high- and low-affinity states of dopamine D2 receptors: methods of detection and clinical implications. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 386(2): 135-154.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Wieringen, J. V. and Michel, M. C. (2013). [3H]-Spiperone Saturation Binding to Dopamine D2, D3 and D4 Receptors. Bio-protocol 3(20): e945. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.945.
Category
Neuroscience > Sensory and motor systems
Biochemistry > Protein > Interaction > Protein-ligand interaction
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









