- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Staphylococcus aureus Killing Assay of Caenorhabditis elegans
Published: Vol 3, Iss 19, Oct 5, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.916 Views: 14006
Reviewed by: Fanglian HeLin Fang

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Amplex Red Assay for Measuring Hydrogen Peroxide Production from Caenorhabditis elegans
Ozgur Karakuzu [...] Danielle A. Garsin
Nov 5, 2019 12723 Views

Phytophthora infestans (Late blight) Infection Assay in a Detached Leaf of Potato
Hari S. Karki and Dennis A. Halterman
Feb 20, 2021 7191 Views

Brain-localized and Intravenous Microinjections in the Larval Zebrafish to Assess Innate Immune Response
Alison M. Rojas and Celia E. Shiau
Apr 5, 2021 6447 Views
Abstract
The Gram-positive bacterium Staphylococcus aureus is a human pathogen that displays virulence towards the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans. This property can be used to discover genes that are important for virulence in humans, because S. aureus possesses common virulence factors that are used in C. elegans and in humans to cause disease. S. aureus colonizes the C. elegans intestine, establishes an infection, and causes pathogenesis of the intestinal epithelium that ultimately kills the infected animal after 3 to 4 days (Sifri et al., 2003; Irazoqui et al., 2008; Irazoqui et al., 2010). The protocol described here is used to establish the rate of S. aureus-induced C. elegans death, which allows the comparison of wild type and mutant strains and thus ultimately aids in the identification of genes required either for S. aureus virulence or for C. elegans host defense. The assay can also be applied for antimicrobial drug discovery.
Materials and Reagents
- S. aureus wild type strain (e.g. the commonly-used NCTC8325 with natural Nal resistance, or its Kan-resistant derivative SH1000, Horsburgh et al., 2002) and/or any mutants of interest.
Note: S. aureus is a potential human pathogen that is classified as a Biosafety Level (BSL) 2 organism.
Please see the Center for Disease Control (CDC) resource http://www.cdc.gov/training/QuickLearns/biosafety/ for information on working under BSL2 conditions, including the use of appropriate personal protection equipment, the use of a biological safety cabinet to contain aerosols, and the autoclaving of all trash.
- E. coli strain HT115 expressing cdc-25.1 dsRNA (Ahringer Library, Kamath et al., 2000)
- E. coli strain OP50
- C. elegans wild type strain (most commonly Bristol N2) and/or any mutants of interest (available from the Caenorhabditis Genetics Center at http://www.cbs.umn.edu/cgc)
- Bacto Tryptic Soy Broth (TSB) (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 211825 )
- Difco Tryptic Soy Agar (TSA) (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 236950 )
- Luria Broth (LB) (MP Biomedicals, catalog number: 3002-021 )
- Luria Broth Agar (MP Biomedicals, catalog number: 3002-231 )
- Nalidixic acid sodium salt (Nal) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N4382 )
- Carbenicillin disodium salt (Carb) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C1389 )
- 5-fluorodeoxyuridine (FUDR) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F0503 )
- Nalidixic Acid (Nal) 1,000x stock solution (10 mg/ml) (see Recipes)
- Carbenicillin 1,000x stock solution (100 mg/ml) (see Recipes)
- TSB (see Recipes)
- LB (see Recipes)
- Large TSA + Nal (10 μg/ml) plates (see Recipes)
- Large LB + Carb (100 μg/ml) plates (see Recipes)
- Killing assay plates (see Recipes)
- Nematode growth media (NGM) plates (see Recipes)
- RNAi plates (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Dissection stereo microscope (e.g. Zeiss, model: Stemi 2000 )
- 15 °C and 25 °C C. elegans incubators (e.g. Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: 3940 )
- 37 °C bacterial incubator and shaker
- Platinum wire worm pick* and ethanol lamp (Cole-Parmer, catalog number: EW-48585-84 ) for sterile transfer of worms at dissection scope.
*Worm picks can either be purchased (e.g. Genesse Scientific, catalog number: 59-AWP ) or made in the lab. To make a pick, insert a 5 cm segment of 90% platinum/10% iridium wire (Tritech Research, catalog number: PT-9010 ) into the narrow end of a glass Pasteur pipet, melt glass over Bunsen burner flame to fasten wire inside, and flatten the tip of the protruding wire (~5 mm) into a flat “spatula”-like structure using a pair of needle-nose pliers. The handle end of the glass pipet can be inserted into foam tubing (Maddak, catalog number: F766900183 ) for more comfortable manipulation (see Figure 1).
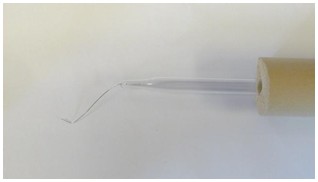
Figure 1. Example of a worm pick made in the lab. The pick consists of platinum wire inserted into a Pasteur pipet, held in foam tubing for easy handling. See text for details.
Software
- Microsoft Excel or any other spreadsheet software
- GraphPad Prism
Procedure
- Before starting
At least one month before “Day 1” (and ideally 2-3 months before):
Prepare killing assay plates (4 ml TSA per 35 x 10 mm plate, final Nal concentration 10 μg/ml) Store plates in a covered box at 4 °C (Nal is light-sensitive).
Note: “Aging” of the killing assay plates – i.e. storage of poured agar plates at 4 °C for at least 1 month prior to the spreading of bacteria – is done in order to slow the rate of S. aureus-induced death, so that differences in killing kinetics can be more readily observed. Spreading S. aureus on freshly-made (non-aged) agar plates and using them immediately for a killing assay will result in very rapid C. elegans death.
Between 1 and 7 days before “Day 2/step 3”:
Streak E. coli HT115 directly from 15% glycerol stock onto an LB + Carb (100 μg/ml) plate.
Grow plate at 37 °C overnight; can use the next day (step 6 below) or keep at 4 °C for at most one week.
Between 1 and 7 days before “Day 5/step 10”:
Streak S. aureus bacteria directly from 15% glycerol stock onto a TSA + Nal (10 μg/ml) plate.
Grow plate at 37 °C overnight; can use the next day (step 13 below) or keep at 4 °C for at most one week.
- After starting
Day 1- For each condition to be tested, pick 3-5 young adults onto three different NGM plates that have been seeded with OP50 (see Recipes).
- Incubate at 15 °C until Day 5. This ensures approximately 100 L4 animals for each condition at step 15 on Day 5 (i.e. the 3-5 adults will produce 30-40 L4’s per plate, x3 NGM-OP50 plates = approximately 100 L4 animals).
Day 2- Pick one colony from the HT115 cdc-25.1 plate into 5 ml of LB + Carb (100 μg/ml final concentration).
- Grow overnight at 37 °C with agitation.
Day 3- For each condition to be tested, spread 200 μl of the HT115 cdc-25.1 overnight culture to 3x RNAi plates (60 mm x 10 mm).
- Dry plates (open side up, lids aside) for 30 minutes in the flow hood.
- Incubate plates at 25 °C for 48 hours (until Day 5).
Note: Steps 3-7 can also be performed on Days 1/2 or Days 3/4, since HT115 cdc-25.1 needs to be grown on RNAi plates for 24 to 72 hours prior to the addition of C. elegans.
Day 5- For each condition to be tested, pick 35-50 L4 animals from the NGM + OP50 plates to each of the 3 RNAi plates prepared on Day 3 (step 5), for a total of 100-150 L4 animals per condition.
- Incubate 24 to 48 hours at 15 °C.
Note: cdc-25.1 is required for germ line mitotic proliferation, and thus targeting cdc-25.1 by RNAi renders the animals infertile (Ashcroft et al., 1999). This step serves to remove potential differences in death rate that are actually due to differences in fertility or egg-laying behavior among different C. elegans genotypes. Make sure the animals are late L4. If picked younger, the RNAi treatment will inhibit gonad development and skew results.
- Pick one colony from the S. aureus plate into 5 ml of TSB + NAL (10 μg/ml final concentration).
- Grow overnight at 37 °C with agitation.
- For each condition to be tested, spread 10 μl of the S. aureus overnight culture to 3 (aged) killing assay plates.
Note: S. aureus kills C. elegans best during exponential growth (i.e. the time interval when the bacterial lawn is progressively thickening), so strains with rapid growth should be diluted at this step to make sure they do not create a thick lawn too soon and cause an inhibition of virulence. For example, in our lab we plate 10 μl of undiluted NCTC8325, but we dilute the faster-growing SH1000 (1:1 in TSB media) before plating. It is also important in this step to spread S. aureus fully over the entire plate surface, so that animals cannot avoid the pathogen by crawling off the lawn.
- Incubate plates at 37 °C for 4-8 hours.
- Dry plates for 30 minutes in the flow hood.
- For each condition to be tested, pick 35-50 animals from the HT115 cdc-25.1 plates to each of the 3 killing assay plates prepared in steps 12-14 above.
Notes:
- Make sure to transfer as little E. coli as possible, as contaminating E. coli tends to inhibit killing. An alternative approach, that of rinsing animals from the HT115 plates and washing in M9 buffer before pipetting animals to killing assay plates, might eliminate even more E. coli; we do not use this approach because the experience of being placed in liquid, centrifuged, and vortexed triggers a stress response that could potentially confound the pathogen response.
- It is critically important that only animals that have gonads are used. Gonadless animals (generated by stronger RNAi) exhibit resistance to killing by pathogens, due to up-regulation of the stress transcription factor DAF-16 (Miyata et al., 2008).
- Make sure to transfer as little E. coli as possible, as contaminating E. coli tends to inhibit killing. An alternative approach, that of rinsing animals from the HT115 plates and washing in M9 buffer before pipetting animals to killing assay plates, might eliminate even more E. coli; we do not use this approach because the experience of being placed in liquid, centrifuged, and vortexed triggers a stress response that could potentially confound the pathogen response.
- Incubate at 25 °C, ~65-70% humidity.
Note: It is important that plates be neither too dry nor too wet. Low humidity, leading to dry plates, causes cracks in the agar, which distort results and make scoring death more challenging, and may cause the animals to desicate over the course of the experiment. High humidity, leading to condensation on the internal sides of the petri dish, allows animals to travel off the agar and eventually desiccate on the side of the plate (as the condensation fluctuates). In both cases, desiccated animals must be censored, and therefore do not give complete lifespan information (see below).
- Score dead animals twice a day. Data points are ideally collected every 10-12 hours during initial experiments, to determine the timeframe during which survival drops from 100% to 0%; in subsequent experiments, time points should be chosen to focus on this particular time window. Animals should be scored as dead or alive by gently prodding them with the worm pick under a dissecting microscope. Animals that died because of an extruded vulva or crawled off the agar should be counted in a separate category as “censored.” Remove both censored and dead animals from the plate when they are scored, to facilitate the next scoring period, by burning them off the pick.
- Enter data into GraphPad Prism or a similar software package to create survival graphs (based on the Kaplan-Meier method). Briefly, use one column for each condition, enter a “0” for a censored animal and a “1” for a dead animal, and enter a corresponding time point in the far-left column for each such event (note that a single time point will thus be entered for many different rows). An example of what the data entry will look like is shown in Figure 2.
Note: Survival data are reported using the full graph (survival over time), rather than using a comparison of survival at a single time point.
Condition 1
Condition 2
Condition 3
Time:
# Censored
# Dead
# Censored
# Dead
# Censored
# Dead
10 h
2
(0)
(0)
(0)
(0)
1
20 h
1
4
(0)
1
2
5
35 h
0
13
1
(0)
1
3
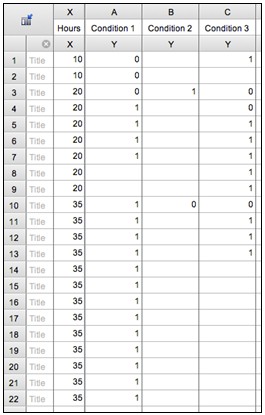
Figure 2. Demonstration of conversion of raw data into Prism survival data. In this example, data are entered for three time points (10, 20, 35 hours) and three conditions, according to the above raw results.
- Conduct statistical analyses (i.e. the log-rank test) to determine the significance of any differences in killing kinetics observed between test conditions and the wild type control.
- Report the following data along with the survival curve: (i) median survival (MS), as defined by Kaplan-Meier analysis, or Time to 50% Death (LT50), as defined by nonlinear regression, if MS values were skewed by having a small number of time points; (ii) N (total number of animals/censored), and (iii) p value.
Notes: If no C. elegans mutant strain is available, expression of the nematode gene of interest can be down-regulated using an RNAi approach. Use the above protocol with the following modifications:
Step 1: Instead of picking animals to NGM + OP50 plates, transfer them to RNAi plates spread with E. coli strain HT115 expressing dsRNA for the gene of interest (g.o.i). Follow the same steps to prepare the g.o.i. RNAi plates as those described above for cdc-25.1 plates. Note that this will mean carrying out steps 3-7 earlier, to have RNAi plates ready at step 1.
Step 8: Instead of transferring L4 animals to cdc-25.1 RNAi plates for sterilization, transfer them to a new set of g.o.i. RNAi plates containing FUDR (for chemical sterilization). FUDR-containing RNAi plates are made the same way as the other RNAi plates, with the simple addition of 200 μl of 5 mg/ml (50x) FUDR to the top of the lawn 1 hour before animals are transferred to it. Note that the RNAi plates for FUDR should be prepared according to the time frame described in the original protocol for cdc-25.1 plates, so that they are 24 to 72 hours old at step 7 instead of at step 1.
- For each condition to be tested, pick 3-5 young adults onto three different NGM plates that have been seeded with OP50 (see Recipes).
Recipes
- Nalidixic Acid (Nal) 1,000x stock solution (10 mg/ml)
200 mg of Nalidixic Acid Sodium Salt
20 ml of ddH2O
5 μl of 10 N NaOH
Vortex, filter, aliquot and store at -20 °C
- Carbenicillin 1,000x stock solution (100 mg/ml)
2 g of carbenicillin
20 ml of ddH2O
Vortex, filter, aliquot and store at -20 °C
- TSB
30 g of Bacto Tryptic Soy Broth
1 L of ddH2O
Autoclave 15 min at 121 °C
Store at room temperature
- LB
25 capsules of Luria Broth (or manufacturer’s instructions)
1 L of ddH2O
Autoclave 15 min at 121 °C
Store at room temperature
- Large TSA + Nal (10 μg/ml) plates
40 g of Bacto Tryptic Soy Agar
1 L of ddH2O
Autoclave 15 min at 121 °C
Cool down in a 55 °C water bath
Add 1 ml of NAL 1,000x stock solution
Pour 25 ml of TSA + Nal per 100 x 10 mm plate
Store at 4 °C
- Large LB + Carb (100 μg/ml) plates
40 capsules of Luria Broth Agar (or manufacturer’s instructions)
1 L of ddH2O
Autoclave 15 min at 121 °C
Cool down in a 55 °C water bath
Add 1 ml of Carb 1,000x stock solution
Pour 25 ml of LB Agar + Carb per 100 x 10 mm plate
Store at 4 °C
- Killing assay plates
40 g of Bacto Tryptic Soy Agar
1 L of ddH2O
Autoclave 45 min at 121 °C
Cool down in a 55 °C water bath
Add 1 ml of Nal 1,000x stock solution
Pour 4 ml of TSA + Nal per 35 x 10 mm tissue culture dish
Store at 4 °C, protected from light
Let the plate age for at least 1 month before use
- Nematode growth media (NGM) plates, seeded with OP50
Follow Recipes in Common Worm Media & Buffers (He, Bio-protocol, 2011) to make 60 mm x 10 mm NGM plates
Grow OP50 overnight culture in LB + Strep (190 μg/ml) at 37 °C without agitation
Spot desired amount of O.N. culture to center of plate (~200 μl is standard)
Notes:
a.A wide range of Streptomycin concentrations, i.e. 60-300 μg/ml, may be used.
b.If fungal contamination is a problem, add 1 ml of 1% Nystatin per 1 L of media.
- RNAi plates
Follow protocol for RNA Interference (RNAi) by Bacterial Feeding (He, Bio-protocol, 2011), with the following three modifications:
- Use more IPTG (5 mM instead of 1 mM).
- Use less antibiotic (25-50 μg/ml Carbenicillin instead of 100 μg/ml Ampicillin).
- Instead of “spotting” 50 μl of 20x concentrated culture to center of 35 mm plate, evenly spread 200 μl of overnight culture across 60 mm plate.
- Use more IPTG (5 mM instead of 1 mM).
Acknowledgments
This laboratory protocol is a free adaption of various published and unpublished protocols and has evolved over time (Irazoqui et al., 2010).
References
- Ashcroft, N. R., Srayko, M., Kosinski, M. E., Mains, P. E. and Golden, A. (1999). RNA-Mediated interference of a cdc25 homolog in Caenorhabditis elegans results in defects in the embryonic cortical membrane, meiosis, and mitosis. Dev Biol 206(1): 15-32.
- Horsburgh, M. J., Aish, J. L., White, I. J., Shaw, L., Lithgow, J. K., and Foster, S. J. (2002). σB modulates virulence determinant expression and stress resistance: characterization of a functional rsbU strain derived from Staphylococcus aureus 8325-4. J Bacteriol 184(19): 5457-5467.
- Irazoqui, J. E., Ng, A., Xavier, R. J. and Ausubel, F. M. (2008). Role for beta-catenin and HOX transcription factors in Caenorhabditis elegans and mammalian host epithelial-pathogen interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(45): 17469-17474.
- Irazoqui, J. E., Troemel, E. R., Feinbaum, R. L., Luhachack, L. G., Cezairliyan, B. O. and Ausubel, F. M. (2010). Distinct pathogenesis and host responses during infection of C. elegans by P. aeruginosa and S. aureus. PLoS Pathog 6: e1000982.
- Kamath, R. S., Martinez-Campos, M., Zipperlen, P., Fraser, A. G. and Ahringer, J. (2001). Effectiveness of specific RNA-mediated interference through ingested double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genome Biol 2(1): RESEARCH0002.
- Miyata, S., Begun, J., Troemel, E.R., and Ausubel, F.M. (2008). DAF-16-dependent suppression of immunity during reproduction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 178 (2): 903-918.
- Sifri, C. D., Begun, J., Ausubel, F. M. and Calderwood, S. B. (2003). Caenorhabditis elegans as a model host for Staphylococcus aureus pathogenesis. Infect Immun 71(4): 2208-2217.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Wollenberg, A. C., Visvikis, O., Alves, A. F. and Irazoqui, J. E. (2013). Staphylococcus aureus Killing Assay of Caenorhabditis elegans. Bio-protocol 3(19): e916. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.916.
- Irazoqui, J. E., Troemel, E. R., Feinbaum, R. L., Luhachack, L. G., Cezairliyan, B. O. and Ausubel, F. M. (2010). Distinct pathogenesis and host responses during infection of C. elegans by P. aeruginosa and S. aureus. PLoS Pathog 6: e1000982.
Category
Microbiology > Microbe-host interactions > In vivo model > Worm
Immunology > Host defense > General
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link