- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Measurement of Extracellular Ca2+ Influx and Intracellular H+ Efflux in Response to Glycerol and PEG6000 Treatments
Published: Vol 3, Iss 18, Sep 20, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.911 Views: 10217
Reviewed by: Tie Liu

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Bacterial Intracellular Sodium Ion Measurement using CoroNa Green
Yusuke V. Morimoto [...] Tohru Minamino
Jan 5, 2017 10420 Views
Live Cell Measurement of the Intracellular pH of Yeast by Flow Cytometry Using a Genetically-Encoded Fluorescent Reporter
Catherine G. Triandafillou and D. Allan Drummond
Jun 20, 2020 4812 Views
Single Cell Analysis and Sorting of Aspergillus fumigatus by Flow Cytometry
Gareth Howell and Robert-Jan Bleichrodt
Apr 20, 2021 5269 Views
Abstract
The characteristics of Ca2+ and H+ fluxes may reflect the activities of aquaporins, as the up-regulation of aquaporin activities is directly associated with the decrease in cytoplasmic H+ concentration and increase in cytoplasmic Ca2+ concentration. The higher aquaporin activities can protect cells against osmotic stresses by altering water flow into and out of the cells. In order to confirm the contribution of aquaporins to the cell tolerance to different osmotic stresses, net Ca2+ and H+ fluxes are measured using the noninvasive micro-test technique (NMT). NMT provides the real-time in situ detection of net ion transport across membranes. Here, we describe the protocol of in situ detection of net Ca2+ and H+ fluxes across transformed Pichia pastoris cells in response to glycerol and polyethylene glycol 6000 (PEG6000) treatments. The transformed yeast cells are loaded onto a coverslide pre-processed in the poly-L-lysine solution (0.1% w/v aqueous solution). After cell immobilization, microelectrodes are positioned above a monolayer of attached cell population. Micro-volts differences are measured at two excursion points manipulated by a computer. Micro-volts differences could be converted into ion fluxes using the ASET 2.0 and iFluxes 1.0 Software. The method is expected to promote the application of NMT in microbiology. We are very grateful to Younger USA (Xuyue Beijing) NMT Service Center for their critical reading of the manuscript.
Keywords: Ion fluxMaterials and Reagents
- Transformed Pichia pastoris cells (Invitrogen, catalog number: V200-20 )
- Poly-L-lysine solution (0.1% w/v aqueous solution) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P4707 )
- Polyethylene glycol 6000 (PEG6000) (Merck KGaA, catalog number: 807491 )
- Glycerol (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent, catalog number: 10010692 )
- Yeast extract (Oxoid, catalog number: LP0021 )
- Peptone (Oxoid, catalog number: LP0037 )
- D-glucose (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent, catalog number: 10010592 )
- MES
- Standard medium buffer (pH 6.0) (see Recipes)
- Yeast extract peptone dextrose (YPD) medium (see Recipes)
- Calibration medium buffer (pH 7.0) (see Recipes)
- Calibration medium buffer (pH 5.0) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Non-invasive Micro-test System (YoungerUSA, model: NMT100 series )
- Shaking incubator (Shanghai Anting Scientific Instrument Factory, model: HZQ-F160 )
- Centrifuge (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: Fresco 21 )
- Microplate Reader Spectra (Molecular Devices, model: SpectraMax 190 )
- Glass coverslide (20 mm x 20 mm)
- Petri dish (35 mm in diameter)
- Micropipettor (Eppendorf, 100-1,000 μl and 10-100 μl)
Software
- JCal V3.2.1 (a free MS Excel spreadsheet, available at http://www.youngerusa.com or http://www.ifluxes.com)
- ASET 2.0 software (available at http://www.youngerusa.com)
- iFluxes 1.0 software (available at http://www.youngerusa.com)
Procedure
- The transformed cells are incubated in 10 ml YPD at 30 °C in a shaking incubator (200 rpm) for 12 h.
- Overnight cultures of different transformed cells are adjusted to an OD600nm of 0.2. OD600nm is monitored using microplate reader spectra.
- Fifty microliters of each are taken and added to 10 ml YPD containing a final concentration of 25% PEG6000 or 1 M glycerol or no exogenous osmolytes. The transformed yeast cells are grown to an OD600nm of 1.0 in YPD containing different exogenous osmolytes at 30 °C in a shaking incubator (200 rpm). OD600nm is monitored using microplate reader spectra.
- One milliliter of each is taken and pelleted at 2,000 rpm for 5 min at room temperature.
- Nine hundred microliters of supernatant are removed, and the cells are resuspended in the rest of YPD media.
- The coverslips are immersed in the poly-L-lysine solution (0.1% w/v aqueous solution) for 24 h.
- Prior to each flux measurement, the microelectrodes must be calibrated in calibration medium (pH 7.0 and pH 5.0), respectively, following to the same procedure and standards. Only Ca2+ electrodes with Nernstian slope > 26 mV/decade and H+ electrodes with Nernstian slope > 53 mV/decade are used in the protocol. Data are discarded if the post-test calibrations fail.
- Ten microliters of transformed cells are loaded on the coverslip for 5 min, washed off with standard medium to ensure a monolayer of attached cells and incubated in the standard medium for 5 min at room temperature.
- Microelectrodes are positioned 10 μm above the attached cell population consisting of 15 cells with equal size. Micro-volts differences are measured at two excursion points, one 10 μm above the cell population and the other 20 μm away, at a frequency of 0.05 Hz manipulated by a computer. The kinetics of net Ca2+ and H+ fluxes near each cell population are monitored for 10 min.
- For each sample, four clones are incubated in 10 ml YPD, and the resulting four cell populations are measured (see steps 1-9).
- Micro-volts differences are exported as raw data before they are converted into net Ca2+ and H+ fluxes by using the JCal V3.2.1. The ion flux assay around each type of transformed cells is replicated independently three times.
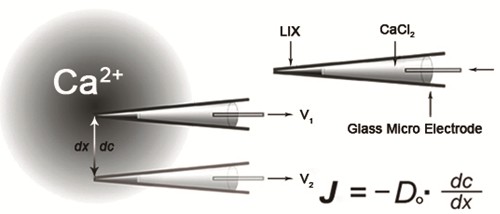
Figure 1. Schematic diagram of ion flux detection (www.xuyue.net). The microelectrode tip is filled with liquid ion exchanger (LIX). A voltage gradient (dV) is measured by the electrometer between two positions over the travel range dx. A concentration gradient (dc) is calculated based on dV. Do, ion diffusion constant; J, net ion flux.
Recipes
- Standard medium (aqueous solution) buffer (pH 6.0)
0.1 mM CaCl2
0.1 mM KCl
0.3 mM MES
10 mM glucose
pH is adjusted to 6.0 with HCl
Stored at 4 °C
- Yeast extract peptone dextrose (YPD) medium (1 L)
1% yeast extract
2% peptone
2% D-glucose (added to the medium after autoclave)
10 g yeast extract
20 g peptone are dissolved in 900 ml of water
The medium is autoclaved for 20 minutes on liquid cycle, cooled to ~55 °C
Mixed with 100 ml of 20% D-glucose
The liquid medium is stored at room temperature
- Calibration medium (aqueous solution) buffer (pH 7.0)
0.01 mM CaCl2
0.1 mM KCl
0.3 mM MES
10 mM glucose
pH is adjusted to 7.0 with HCl
The medium is stored at 4 °C
- Calibration medium (aqueous solution) buffer (pH 5.0)
0.1 mM CaCl2
0.1 mM KCl
0.3 mM MES
10 mM glucose
pH is adjusted to 5.0 with HCl
The medium is stored at 4 °C
Acknowledgments
The protocol was adapted from our previously published paper Li et al. (2013). We wish to thank Younger USA (Xuyue Beijing) NMT Service Center for the technical support. This research was financially supported by the Knowledge Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Project no. KZCX2-YW-BR-17) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (41371264, 41401281).
References
- Li, T., Hu, Y. J., Hao, Z. P., Li, H., Wang, Y. S. and Chen, B. D. (2013). First cloning and characterization of two functional aquaporin genes from an arbuscular mycorrhizal fungus Glomus intraradices. New Phytol 197(2): 617-630.
- McLamore, E. S. and Porterfield, D. M. (2011). Non-invasive tools for measuring metabolism and biophysical analyte transport: self-referencing physiological sensing. Chem Soc Rev 40(11): 5308-5320.
- Shabala, L., Ross, T., McMeekin, T. and Shabala, S. (2006). Non-invasive microelectrode ion flux measurements to study adaptive responses of microorganisms to the environment. FEMS Microbiol Rev 30(3): 472-486.
- Shabala, L., Ross, T., Newman, I., McMeekin, T. and Shabala, S. (2001). Measurements of net fluxes and extracellular changes of H+, Ca2+, K+, and NH4+ in Escherichia coli using ion-selective microelectrodes. J Microbiol Methods 46(2): 119-129.
- Wang, Q., Zhao, Y., Luo, W., Li, R., He, Q., Fang, X., Michele, R. D., Ast, C., von Wiren, N. and Lin, J. (2013). Single-particle analysis reveals shutoff control of the Arabidopsis ammonium transporter AMT1;3 by clustering and internalization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(32): 13204-13209.
- Xu, R. R., Qi, S. D., Lu, L. T., Chen, C. T., Wu, C. A. and Zheng, C. C. (2011). A DExD/H box RNA helicase is important for K+ deprivation responses and tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. FEBS J 278(13): 2296-2306.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Li, T. and 陈, �. (2013). Measurement of Extracellular Ca2+ Influx and Intracellular H+ Efflux in Response to Glycerol and PEG6000 Treatments. Bio-protocol 3(18): e911. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.911.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial cell biology > Cell-based analysis > Ion analysis
Cell Biology > Cell-based analysis > Ion analysis > Calcium
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link












