- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Generation of Mouse Lung Epithelial Cells
Published: Vol 3, Iss 15, Aug 5, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.837 Views: 14202
Reviewed by: Lin FangSalma HasanFanglian He

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Isolation of Murine Alveolar Type II Epithelial Cells
Fan Sun [...] Zhaoxia Qu
May 20, 2017 13116 Views

Soft Agar Colony Formation Assay as a Hallmark of Carcinogenesis
Feng Du [...] Daiming Fan
Jun 20, 2017 30592 Views

A Fast and Reliable Method to Generate Pure, Single Cell-derived Clones of Mammalian Cells
Zhe Han [...] Varun Kumar
Aug 20, 2022 4105 Views
Abstract
Although in vivo models are excellent for assessing various facets of whole organism physiology, pathology, and overall response to treatments, evaluating basic cellular functions, and molecular events in mammalian model systems is challenging. It is therefore advantageous to perform these studies in a refined and less costly setting. One approach involves utilizing cells derived from the model under evaluation. The approach to generate such cells varies based on the cell of origin and often the genetics of the cell. Here we describe the steps involved in generating epithelial cells from the lungs of KrasLSL-G12D/+;p53LSL-R172/+ mice (Kasinski and Slack, 2012). These mice develop aggressive lung adenocarcinoma following cre-recombinase dependent removal of a stop cassette in the transgenes and subsequent expression of Kra-G12D and p53R172. While this protocol may be useful for the generation of epithelial lines from other genetic backgrounds, it should be noted that the Kras; p53 cell line generated here is capable of proliferating in culture without any additional genetic manipulation that is often needed for less aggressive backgrounds.
Keywords: Mouse cellsMaterials and Reagents
- Collagenase/Dispase (F. Hoffmann-La Roche, catalog number: 10269638001 )
- PureCol Collagen I (Bovine-Fisher, catalog number: 50-360-230 )
- Fibronectin (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: PHE-0023 )
- Dulbecco's Phosphate-buffered saline (D-PBS)
- RPMI-1640 with L-Glutamine (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 11875-093 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (from multiple vendors)
- 0.25% Trypsin-EDTA (1x) (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 25200-056 )
- Collagen Coating Mix (see Recipes)
- Fibronectin Coating Mix (see Recipes)
- 1 mg/ml Collagenase (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 10 ml syringes
- 25 gauge needles
- 37 °C 5% CO2 cell culture incubator
- Refrigerated centrifuge
- Inverted microscope
- Tissue culture hood equipped with UV light source
- Vacuum aspirator
Procedure
- Coating tissue culture plates
Plates are coated with collagen and fibronectin to facilitate cell adhesion acting as a cellular matrix. Fibronectin specifically aids in anchoring the cells to the collagen.- Prepare collagen coating mix under sterile conditions.
- Add adequate volume of collagen coating mix to cover the bottom of the plate being coated (e.x. 5 ml/10 cm plate).
- Leave plates covered overnight in the tissue culture hood under the UV light to prevent contamination.
- The following day aspirate the coating mix.
- Air-dry the plates in the tissue culture hood.
- Rinse the plate 2x with D-PBS (2.5 ml/10 cm plate).
- Air-dry plates in the tissue culture hood.
- Cover the plates, seal with parafilm, and store at 4 °C until ready to coat with fibronectin (duration of storage has not been tested extensively; however, plates left at 4 °C for one week were successfully used).
- Prepare fibronectin coating mix.
- Add adequate volume of fibronectin mixture to cover the bottom of the plate being coated (e.x. 5 ml/10 cm plate).
- Incubate coated plates at 37 °C overnight in 5% CO2 cell culture incubator.
- The following day rinse the plates 2x with D-PBS (leave D-PBS in plates if not using immediately -do not allow plates to dry).
- Prepare collagen coating mix under sterile conditions.
- Extracting cells from Tumor tissue
Individual tumors, small areas of lung tissue, or entire lungs can be used to generate epithelial cells.- Sacrifice animals per the university/institute established animal care and use protocol.
- Open up the thoracic cavity immediately after sacrifice.
- Perfuse the lungs by slowly injecting 7-10 ml of D-PBS into the left ventricle of the heart using a 25 gauge needle and syringe. Successful perfusion will result in the lungs changing color from pink to white, representing displacing the RBCs.
- Carefully remove the lungs and place them into D-PBS.
- If large tumors are evident dissect them out and proceed; otherwise continue the procedure using the entire lung (see Figure 1 for lung tumors that can easily be harvested from the lung).
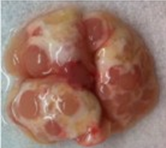
Figure 1. A KrasLSL-G12D/+; p53flx/flx mutant mouse was intratracheally infected with adenoviral particles expressing cre-recombinase to induce transgene recombination. Ten weeks following infection the mouse was sacrificed, lungs were perfused and harvested, and imaged. Multiple large tumor nodules are present on the surface. - Wash the tumors/lungs by rinsing the exterior 4x with D-PBS.
- Mince the tissue in and equal volume ice-cold D-PBS with a sterile blade in tissue culture hood until the mass represents a slurry and few if any larger solid pieces are evident; however care should be taken to perform this step in a timely fashion to avoid cell death. The mincing step allows for easier retrieval of individual cells for propagating.
- Add the minced tissue to an equal volume of RPMI-1640 supplemented with 1 mg/ml collagenase and incubate for 1 h at 37 °C in 5% CO2 cell culture incubator.
- Remove cells intermittently from supernatant. Do not centrifuge. Let the larger pieces settle and remove the top-half of the supernatant containing individual cells every 10-15 min. Replenish RPMI/collagenase solution as needed and repeat 4-5 times.
- Pool and spin the collected supernatant at 1,000 x g at 4 °C for 5 min.
- Remove the supernatant and add 10 ml of RPMI-1640 supplemented with 10% FBS.
- Remove the D-PBS from the collagen/fibronectin coated plates.
- Immediately transfer the cell suspension to the coated plates being sure to supplement with additional RPMI-1640/10% FBS to cover the surface of the plate if necessary (10 ml/10 cm plate).
- Incubate cells at 37 °C in 5% CO2 cell culture incubator.
- Continue to passage on coated plates for three passages.
- Sacrifice animals per the university/institute established animal care and use protocol.
- Selecting epithelial cells
- Over the course of culturing select epithelial looking colonies. There are a few mechanisms to help in the selection process. Firstly, the fibroblasts are often more sensitive to trypsin and can therefore be removed from the plate while the epithelial cells will adhere for a longer time. This is done by treating the cells with trypsin and removing the first cells begin to slough off the plate as visualized under a microscope. This step helps to increase the epithelial cell population. Secondly, epithelial clones will become visible and are easily discernible from the fibroblast population.
- Once epithelial clones are evident, the clones are treated directly with a small amount of trypsin (50 μl dispensed directly on the clone) and visualized under a microscope until they begin to round up. The cells are then abducted using a sterile transfer pipette. The bulb of the pipette is squeezed in and held in that position while the tip of the pipette is placed over the individual clone. Once in place the pressure on the bulb is released slowly to encourage the cells to enter into the pipette. The entire contents are then transferred to individual wells in 12-well standard tissue-culture treated plates to further propagate (to enhance visualization of the clones, allow clones to be followed, and increase the abduction step, once identified, clones can be circled on the bottom of the plate with a sharpie).
- To confirm that cells are of epithelial origin stain with standard markers such as keratins. For the cells described here, keratin 14 was used.
- Thus far, cells generated by this procedure have been able to propagate beyond 50 passages.
Note: It is inherently difficult to generate cultures of normal cells. All the cells that formed clones and were isolated by this procedure (irrespective of being generated from tumors or the whole lung) were confirmed to be mutant for Kras and p53. This procedure will specifically allow one to "select" for epithelial cells that can propagate outside of the organ.
- Over the course of culturing select epithelial looking colonies. There are a few mechanisms to help in the selection process. Firstly, the fibroblasts are often more sensitive to trypsin and can therefore be removed from the plate while the epithelial cells will adhere for a longer time. This is done by treating the cells with trypsin and removing the first cells begin to slough off the plate as visualized under a microscope. This step helps to increase the epithelial cell population. Secondly, epithelial clones will become visible and are easily discernible from the fibroblast population.
Recipes
- Collagen coating mix (10 ml)
Item Final Stock Volume Collagen 0.4 mg/ml 3 mg/ml in water 1.33 ml D-PBS 8.67 ml - Fibronectin coating mix (10 ml)
Item Final Stock Volume Fibronectin 5 μg/ml 500 μg/ml in water 100 μl Ice-cold-D-PBS 9.9 ml - 1 mg/ml collagenase (2 ml)
Dilute collagenase stock in RPMI-1640
Add 20 μl of stock to 1980 μl of RPMI-1640.
Acknowledgments
The protocol presented herein was adapted from Kasinski and Slack (2012). This work was supported by an NIH grant to FJS and Joanne Weidhaas (NCI R01 CA131301). AK was supported by a US National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant (1F32CA153885-01) and an American Cancer Society Postdoctoral Fellowship (120,766-PF-11-244-01-TBG).
References
- Kasinski, A. L. and Slack, F. J. (2012). MiRNA-34 prevents cancer initiation and progression in a therapeutically resistant K-ras and p53-induced mouse model of lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 72(21): 5576-5587.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Kasinski, A. L. and Slack, F. J. (2013). Generation of Mouse Lung Epithelial Cells. Bio-protocol 3(15): e837. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.837.
Category
Cancer Biology > General technique > Cell biology assays > Cell isolation and culture
Cell Biology > Cell isolation and culture > Cell isolation
Cell Biology > Cell isolation and culture > Cell differentiation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









