- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Extraction and Reglucosylation of Barbarea vulgaris Sapogenins
Published: Vol 3, Iss 14, Jul 20, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.826 Views: 10466
Reviewed by: Tie Liu

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
A Quick Method to Quantify Iron in Arabidopsis Seedlings
Chandan Kumar Gautam [...] Wolfgang Schmidt
Mar 5, 2022 3890 Views
Isolation of Intact Vacuoles from Arabidopsis Root Protoplasts and Elemental Analysis
Chuanfeng Ju [...] Zhenqian Zhang
Mar 5, 2023 1994 Views
High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Quantification of Glyphosate, Aminomethylphosphonic Acid, and Ascorbate in Culture Medium and Microalgal Cells
Juan Manuel Ostera [...] Gabriela Malanga
Apr 5, 2025 1159 Views
Abstract
Plants produce a vast array of natural compounds. Many of them are not commercially available, and are thus lacking to be tested as substrates for enzymes. This protocol describes the extraction and acidic hydrolysis of metabolites from Barbarea vulgaris with special focus on saponins and their agylcones (sapogenins). It was developed to determine if some B. vulgaris UDP-glucosyltransferases (UGTs) that were shown to glucosylate commercially available sapogenins, would also accept additional sapogenins from this plant as substrate, which are yet chemically uncharacterized and/or commercially unavailable (Figure 1).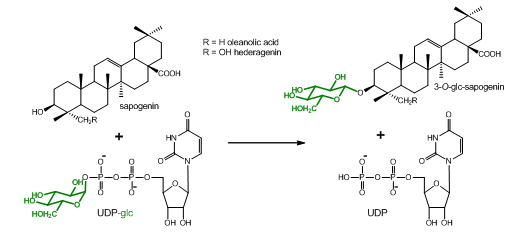
Figure 1. Glucosylation reaction catalyzed by UGT73C10-UGT73C13 from Barbarea vulgaris (Augustin et al., 2012). All four enzymes utilize uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-glc) as glucosyl-moiety donor and different sapogenins such as the oleanane sapogenins oleanolic acid and hederagenin as glucosyl-moiety acceptor. Oleanolic acid and hederagenin both naturally occur in G-type B. vulgaris, where they are predominantly found in their 3-O-cellobiosylated form. Additional saponins from G-type B. vulgaris have been identified by Nielsen et al., 2010. However, the majority of saponins and sapogenins that occur in B. vulgaris remain unidentified.
Materials and Reagents
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A7906 )
- Polyvinylpolypyrrolidone (PVPP) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 77627 )
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H1758 )
- Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (Tris base) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T1503 )
- Ethyl acetate (Sigmal-Aldrich, catalog number: 34972 )
- N-Tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl-3-aminopropanesulfonic acid (TAPS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T5130 )
- Dithiothreitol (DTT) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D0632 )
- Uridine-5’-diphosphoglucose (UDP-Glc) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S451649 )
- Silica gel 60 F254 TLC plates (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 1055540001 )
- Polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) filter plate (0.45 μm pore diameter) (EMD Millipore, catalog number: MAHVN4510 )
- FRETWorks S-tag assay kit (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 70724 )
Equipment
- Water bath
- Centrifuge for 50 ml and 15 ml conical centrifugation tubes (VWR international, catalog number: 89004-368 )
- Thermomixer (VWR international, catalog number: 21516-168 )
- pH indicator paper (Whatman, catalog number: 2600-100A )
- Vacuum centrifuge (Labogene, catalog number: 7.008.100.777 )
- Thin layer chromatography (TLC) developing chamber (VWR international, catalog number: 21432-739 )
- Aldrich flask-type sprayer (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z190373 )
- Heat block (VWR international, catalog number: 12621-120 )
- LC-MS analysis was carried out on an Agilent 1100 Series LC (Agilent Technologies), equipped with a Gemini NX column (Phenomenex), and coupled to a Bruker HCT-Ultra ion trap mass spectrometer (Bruker Daltonics)
Software
- DataAnalysis 4.0 (Bruker Daltonics)
Procedure
- Preparation of the crude metabolite extract
- Freshly harvested Barbarea vulgaris leaves were weighed and transferred to 15 ml centrifugation tubes.
- Following addition of 5 ml 55% ethanol per g fresh leaf material the leaves were boiled in a water bath for 10 min.
- To increase the extraction efficiency, the tubes were occasionally shaken while boiling.
- After heating the extracts were chilled on ice before they were centrifuged for 5 min (3,000 x g, room temperature) to precipitate insoluble leaf debris.
- The supernatant was transferred to fresh centrifugation tubes and stored at -20 °C until further usage. A minimum incubation time of 4 h at -20 °C is recommended to cause further unwanted compounds to precipitate from the solution.
- Newly emerged precipitates were removed by centrifugation (3,000 x g, 5 min, 4 °C).
Notes:- Usage of the protocol has been limited so far to rosette leaves of 1-3 month old Barbarea vulgaris plants with a typical weight of 1.5-2 g fresh weight.
- Saponins can be extracted with this protocol from both fresh and ground plant material.
- 55% ethanol has been determined in pre-experiments to be hydrophobic enough to still extract B. vulgaris saponins, while being hydrophilic enough to lower the amount of some hydrophobic compounds that were previously seen to interfere with TLC analysis. However, it should be noted that these extracts still contains many more compounds than just saponins.
- Usage of the protocol has been limited so far to rosette leaves of 1-3 month old Barbarea vulgaris plants with a typical weight of 1.5-2 g fresh weight.
- Freshly harvested Barbarea vulgaris leaves were weighed and transferred to 15 ml centrifugation tubes.
- Acidic hydrolysis and purification:
- 2 x 1.25 ml of the crude saponin extract were transferred into 2 ml microcentrifuge tubes and mixed with 250 μl 6 M HCl to adjust the final HCl concentration to 1 M.
- The acidified extracts were incubated for 24 h in a thermomixer adjusted to a temperature of 99 °C and shaking at 1,400 rpm.
- After heating the extracts were chilled for approximately 1 h at -20 °C before they were combined in 50 ml centrifugation tubes.
- Remaining precipitates in both microcentrifuge tubes were recovered by washing each tube three times with 250 μl 96% ethanol. The resulting ethanol solutions of these three wash steps were added to the hydrolysate in the 50 ml centrifugation tubes.
- 1 M Tris base solution was added to the hydrolysate until the pH shifted from acidic to basic conditions (here: 4.5 ml).
- Subsequently, 13.55 ml water was added to lower the ethanol concentration to 14%. 1.125 g PVPP and 225 mg BSA were added to the solution to adjust their final concentrations to 5% (w/v) and 10 mg ml-1, respectively.
- The mixture was six times extracted ethyl acetate using 5 ml ethyl acetate per extraction step.
- Phase separation was achieved by centrifugation for 20 min at 5,200 x g. The ethyl acetate fraction will be the upper phase.
- The combined ethyl acetate fractions were evaporated to dryness in a vacuum centrifuge.
- Dried extracts were dissolved in 500 μl 96% ethanol and transferred to 15 ml centrifugation tubes. For a second round of purification 3,720 μl water, 480 μl 500 mM TAPS pH 9.1, 240 mg PVPP and 48 mg BSA were added in the given order and 5-fold ethyl acetate extraction performed with 2 ml ethyl acetate per extraction step.
- After evaporation of the solvent of the combined ethyl acetate fractions in a vacuum centrifuge, the dried extracts were dissolved in 1 ml 96% ethanol.
Notes:
- Brief spinning in a tabletop microcentrifuge was found sufficient during the washing steps to recover precipitates from the hydrolysate.
- Due to a lack of investigations if sapogenins will remain solubilized in the chosen hydrolysation conditions or are among the observed precipitates both fractions combined were subjected to subsequent purification steps.
- The pH of the hydrolysate was shifted to basic conditions by addition of Tris base prior extraction, since ethyl acetate extraction carries over low amounts of water/ions, which caused the initial hydrolysate extracts to be of slightly acidic pH. The UGTs investigated by us had a slightly basic pH optimum and a weakly basically buffered sapogenin extract was considered to have a lower effect on the pH of the final enzyme assay.
- pH changes were monitored by spotting 1 μl of the hydrolysate to pH indicator paper.
- The ethanol concentration of the hydrolysate had to be lowered prior ethyl acetate, extraction to enable formation of an organic phase upon addition of ethyl acetate.
- Early ethyl acetate extracts of hydrolysated crude Barbarea vulgaris leaf extracts generated without the PVPP/BSA purification step were seen to completely inhibit the activity of the investigated UGTs. PVPP was used to adsorb phenolic compounds. BSA was added in the purification step, since in enzyme assays using the early hydrolysation extracts proteins were seen to become brownish by binding to compounds from the extract. The addition of BSA was intended to remove such protein binding compounds.
- While drying down the ethyl acetate fractions in the vacuum centrifuge, new aqueous phases emerged, which were removed in the process.
- Brief spinning in a tabletop microcentrifuge was found sufficient during the washing steps to recover precipitates from the hydrolysate.
- 2 x 1.25 ml of the crude saponin extract were transferred into 2 ml microcentrifuge tubes and mixed with 250 μl 6 M HCl to adjust the final HCl concentration to 1 M.
- Re-glucosylation assay:
- In preparation of the re-glucosylation assays 500 μl of the hydrolysated and purified B. vulgaris leaf metabolite extracts were dried out in a vacuum centrifuge and subsequently dissolved in 78.13 μl dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
- Additionally, the recombinant expressed UGTs were directly quantified within E. coli lysates applying the FRETWorks S-tag assay kit.
- Following quantification, UGT concentrations were adjusted to 50 ng μl-1 by diluting the E. coli lysates with 10 mg ml-1 BSA in 10 mM TAPS pH 8.0.
- Enzymatic activity assays were performed in 1.5 ml microcentrifugation tubes in a final volume of 50 μl.
- Reaction conditions were adjusted to 25 mM TAPS pH 8.6 (UGT73C9-C11), pH 7.9 (UGT73C12/C13) or pH 8.2 (combination of UGT73C9, UGT73C10 or UGT73C11 with UGT73C12 or UGT73C13), 1 mM DTT and 1 mM UDP-Glc. The final UGT amount per reaction was 750 ng.
- Reactions were preincubated for 3 min at 30 °C and started by addition of 3.13 μl hydrolysated and purified B. vulgaris leaf metabolite extract in DMSO.
- The assays were incubated for 30 (LC-MS only) or 120 (TLC and LC-MS) min at 30 °C, and stopped by addition of 325 μl ice cold methanol (LC-MS) or 50 μl ice cold ethyl acetate (TLC).
Notes:
- The solvent of the hydrolysated extracts was exchanged from ethanol to DMSO prior to the re-glucosylation assays, as ethanol was found to act as substrate for the applied UGTs itself.
- Quantification with the FRETWorks S-tag assay kit is based on regeneration of RNase S activity due the interaction of the S protein (included in the kit) and the S-tag N-terminally fused to the recombinant expressed UGTs.
- The E. coli lysates were diluted with a BSA solution instead of pure buffer, since the recombinant UGTs were seen to lose specific activity upon reduction of the total protein concentration.
- Whenever combinations of different UGTs were tested, the individual enzymes were applied in equimolar amounts.
- The solvent of the hydrolysated extracts was exchanged from ethanol to DMSO prior to the re-glucosylation assays, as ethanol was found to act as substrate for the applied UGTs itself.
- In preparation of the re-glucosylation assays 500 μl of the hydrolysated and purified B. vulgaris leaf metabolite extracts were dried out in a vacuum centrifuge and subsequently dissolved in 78.13 μl dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO).
- Analysis by thin layer chromatography (TLC)
- Stopped enzymatic reactions were three times extracted with ethyl acetate (50 μl, 185 μl and 50 μl):
- Ethyl acetate was added to the enzymatic reaction and the sample thoroughly mixed for approximately 10-20 sec with a vortex shaker. (The ethyl acetate added to stop the reaction is at the same time also used for the first extraction step.)
- The samples were centrifuged for 5 min (16,100 x g, room temperature) to achieve phase separation. The ethyl acetate fraction will be the upper phase.
- Ethyl acetate was added to the enzymatic reaction and the sample thoroughly mixed for approximately 10-20 sec with a vortex shaker. (The ethyl acetate added to stop the reaction is at the same time also used for the first extraction step.)
- The combined ethyl acetate fractions were evaporated to dryness in a vacuum centrifuge and the dried extracts dissolved in 20 μl 96% ethanol.
- The re-dissolved extracts were stepwise, completely (3.5 μl per step) loaded to a silica gel TLC plate.
- TLC plates were pre-run in 100% methanol until the solvent front was approximately 1 cm above the loading line.
- The methanol was left to evaporate in a fume hood, and the TLC plates were subsequently developed using dichloromethane: methanol: water (80: 19: 1) as mobile phase.
- Sapogenins and sapogenin-glucosides were visualized by spraying TLC plates with 10% sulfuric acid in methanol using a flask-type sprayer (or similar) and subsequent heating to 100 °C on a heat block (Figure 2).
Notes: The amount of developing solution needed depends on the size of the used TLC plate. The plate should be consistently and homogeneously wetted. However, spraying of too much developing solution may cause the bands to diffuse.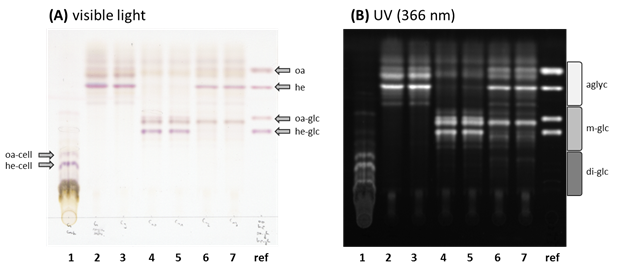
Figure 2. TLC plate with the (1) G-type B. vulgaris crude metabolite extract, the (2) corresponding acidic hydrolyzed metabolite extract and the (3)-(7) hydrolyzed metabolite extract treaded with different B. vulgaris UGTs. The TLC plate was evaluated under (A) visible (colored) as well as under (B) long wave UV (366 nm, black/white). The applied UGTs for the reglucosylation assays were (3) UGT73C9, (4) UGT73C10, (5) UGT73C11, (6) UGT73C12, (7) UGT73C13. For comparison purpose were authentic (oa) oleanolic acid, (he) hederagenin, (oa-glc) 3-O-glc oleanolic acid, (he-glc) 3-O-glc-hederagenin loaded to the (ref) reference lane (2 nmol each). Additionally are (oa-cell) oleanolic acid cellobioside and (he-cell) hederagenin cellobioside, the naturally in G-type B. vulgaris occurring di-glucosidic forms of these two sapogenins, marked in the crude metabolite extract. The accordingly estimated migration rate of (agly) aglycones, (m-glc) mono-glucosides and (di-glc) di-glucosides are shown on the right of Figure 2B.
- Stopped enzymatic reactions were three times extracted with ethyl acetate (50 μl, 185 μl and 50 μl):
- Analysis by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS)
- Stopped enzymatic reactions were centrifuged for 5 min (16,100 x g, room temperature) to precipitate proteins.
- Supernatants were transferred to fresh 1.5 ml microcentrifugation tubes and evaporated to dryness in a vacuum centrifuge.
- Dried extracts were dissolved in 30 μl methanol and the solvent subsequently diluted to a final concentration of 50% methanol by addition of 30 μl water.
- The methanol extracts were filtered (PVDF, 0.45 μm pore diameter) and transferred to 1.5 ml glass sample vials for LC-MS analysis.
- LC-MS analysis was carried out on an Agilent 1100 Series LC, equipped with a Gemini NX column (35 °C) (2.0 x 150 mm, 3.5 μm), and coupled to a Bruker HCT-Ultra ion trap mass spectrometer.
- Mobile phases in the LC were water with 0.1% (v/v) formic acid (eluent A) and acetonitrile with 0.1% (v/v) formic acid (eluent B). The gradient program was as follows: 0 to 1 min, isocratic 12% B; 1 to 33 min, linear gradient 12 to 80% B; 33 to 35 min, linear gradient 80 to 99% B; 35 to 38 min isocratic 99% B; 38 to 45 min isocratic 12% B at a constant flow rate of 0.2 ml min-1.
- The MS detector was operated in negative electrospray mode, and MS2 ( = MS/MS) and MS3 (=MS/MS of MS2 fragments) fragmentations were performed to obtain additional structural information of the detected ions.
- Run files were analyzed with DataAnalysis 4.0, a software to display the LC chromatograms and the corresponding MS spectrums. Please refer to Augustin et al., 2012 (and Online Supplemental Data) to see the LC chromatograms of crude metabolite extracts from G- and P-type B. vulgaris, the acidic hydrolyzed metabolite extracts from both plants as well as chromatograms of the corresponding reglucosylation assays with different B. vulgaris UGTs.
- Stopped enzymatic reactions were centrifuged for 5 min (16,100 x g, room temperature) to precipitate proteins.
References
- Augustin, J. M., Drok, S., Shinoda, T., Sanmiya, K., Nielsen, J. K., Khakimov, B., Olsen, C. E., Hansen, E. H., Kuzina, V., Ekstrom, C. T., Hauser, T. and Bak, S. (2012). UDP-glycosyltransferases from the UGT73C subfamily in Barbarea vulgaris catalyze sapogenin 3-O-glucosylation in saponin-mediated insect resistance. Plant Physiol 160(4): 1881-1895.
- Nielsen, N. J., Nielsen, J. and Staerk, D. (2010). New resistance-correlated saponins from the insect-resistant crucifer Barbarea vulgaris. J Agric Food Chem 58(9): 5509-5514.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Augustin, J. M., Olsen, C. E. and Bak, S. (2013). Extraction and Reglucosylation of Barbarea vulgaris Sapogenins. Bio-protocol 3(14): e826. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.826.
- Augustin, J. M., Drok, S., Shinoda, T., Sanmiya, K., Nielsen, J. K., Khakimov, B., Olsen, C. E., Hansen, E. H., Kuzina, V., Ekstrom, C. T., Hauser, T. and Bak, S. (2012). UDP-glycosyltransferases from the UGT73C subfamily in Barbarea vulgaris catalyze sapogenin 3-O-glucosylation in saponin-mediated insect resistance. Plant Physiol 160(4): 1881-1895.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Other compound
Biochemistry > Other compound > Saponin
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










