- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Stable Transformation in Lotus japonicus
Published: Vol 3, Iss 12, Jun 20, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.796 Views: 16038

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Bi-directional Dual-flow-RootChip for Physiological Analysis of Plant Primary Roots Under Asymmetric Perfusion of Stress Treatments
Claudia Allan [...] Claudia-Nicole Meisrimler
Aug 5, 2023 1509 Views
A Novel Gene Stacking Method in Plant Transformation Utilizing Split Selectable Markers
Guoliang Yuan [...] Xiaohan Yang
Feb 20, 2025 1517 Views

Enzymatic Starch Quantification in Developing Flower Primordia of Sweet Cherry
Nestor Santolaria [...] Afif Hedhly
Apr 5, 2025 1384 Views
Abstract
This is a protocol to produce stable transgenic plants in Lotus japonicus, which is established based on methods previously reported (Handberg and Stougaard, 1992; Stiller et al., 1997; Thkjaer et al., 1998) with some modifications. In this protocol, hygromycin is used to select transgenic plants.
Materials and Reagents
- Germination plate (1% agar in sterilized water)
- B5 salt (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 399-00621 )
- Gamborg’s vitamin solution
- BAP (Wako Pure Chemical Industries, catalog number: 020-07621 )
- 1-Naphthaleneacetic acid (NAA)
- Acetosyringone
- MES
- (NH4)2SO4
- Phytagel (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P8169 )
- Meropen (Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma)
- Hygromycin B
- LB medium (nacalai tesque, catalog number: 20066-95 )
- Co-cultivation medium (see Recipes)
- YMB medium (see Recipes)
- Callus medium (see Recipes)
- Shoot elongation medium (see Recipes)
- Root induction medium (see Recipes)
- Root elongation medium (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Clean bench
- L. japonicus growth facility (we use several types of Biotrons such as LH-410S purchased from NIPPON MEDICAL & CHEMICAL INSTRUMENTS CO., LTD.)
- Surgical knife
- Sterilized dish ( 9 cm in diameter x 2 cm)
- Sterilized magenta box
- Sterilized filter paper (7 cm in diameter)
- Sterilized filter paper (6 x 6 cm)
- Vermiculite (Hakugen)
Procedure
A. Plant growth
- Sandpaper the surface of L. japonicus Gifu or MG-20 seeds, and then incubate them in 2% sodium hypochlorite solution for 5 min. Wash the seeds several times with sterilized water and incubate the seeds overnight in the sterilized water.
- Surface-sterilized L. japonicus Gifu or MG-20 seeds are germinated and grown in the germination plate.
- Place the plate vertically in a growth cabinet (Gifu; 23 °C 24 h dark for first 3 days, 23 °C 16 h light/8 h dark for next 2 days, MG-20; 23 °C 24 h dark for first 2 days, 23 °C 16 h light/8 h dark for next 2 days). Incubation time in the darkness is depends on ecotypes (hypocotyl growth speed of Gifu is slower than MG-20).
B. Culture of Agrobacterium
Streak A. tumefaciens harboring the desired construct on LB plate with appropriate antibodies for 2 days at 28 °C, then spread bacteria all around sterilized dish (9 cm in diameter) and incubate for 1 day. We use AGL1 as agrobacteria strain.
C. Infection of A. rhizogenes with L. japonicus
- Put about 5 mm piles of sterilized filter papers (6 x 6 cm) in a new dish and pour 20-25 ml co-cultivation medium (Figure 1A). Pouring the medium to the bottom of a dish and then it gradually permeates to the top of pilled filter papers. It enables us to recognize the saturation of filter papers with the medium.
- Collect the bacteria with bacteria spreader from LB plate and suspend 5 ml YMB medium.
- Put a sterilized filter paper (7-8 cm in diameter) in a new dish and saturate it with bacterial suspension by pipetting.
- Place the juvenile plants on the filter paper and cut their hypocotyls into about 3 mm length with surgical knife.
- Transfer the hypocotyl pieces onto the top of pilled filter papers saturated with co-cultivation medium and place the plate in a growth cabinet (23 °C 24 h dark) for 6 days (Figure 1B).
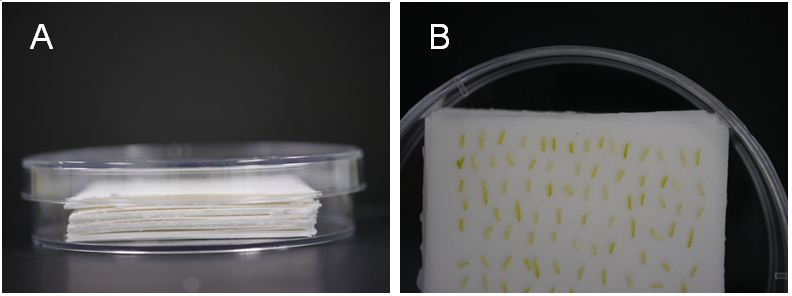
Figure 1. Infection of A. tumefaciens with L. japonicas
D. Callus induction
- Transfer the hypocotyl pieces from co-cultivation medium onto callus medium (about 1 cm thick) and place the plate in a growth cabinet (23 °C 16 h light/8 h dark) for 2-5 weeks (Figure 2A). Transfer the hypocotyl pieces onto new medium every 5 days.
- In 2-3 weeks, calluses should start to develop from the tips of hypocotyls. When they become more than 1 mm in size, cut off them from the hypocotyls and transfer them onto new medium (Figure 2B). You can trash white hypocotyls as it is unlikely that calluses develop from them.
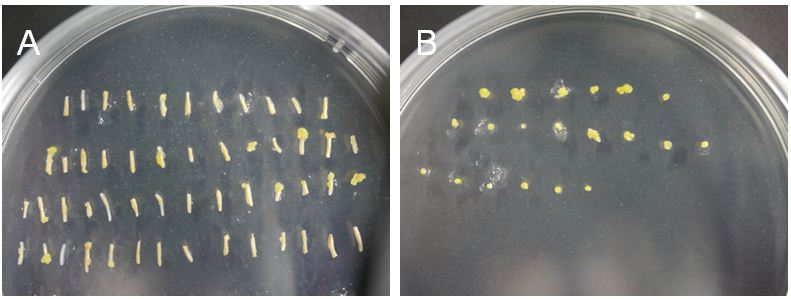
Figure 2. Callus induction
E. Shoot induction
Transfer the calluses onto callus medium without hygromycin B (about 1 cm thick) and place the plate in a growth cabinet (23 °C 16 h light/8 h dark) for no longer than 7 weeks. Transfer the calluses onto new medium every 5 days (Figure 3). Shoots start to appear in about 3 weeks.

Figure 3. Shoot induction
F.Shoot elongation
When shoots start to appear, transfer the calluses onto shoot elongation medium (about 1 cm thick) and place the plate in a growth cabinet (23 °C 16 h light/8 h dark) for no longer than 6 weeks. Transfer the calluses onto new medium every 5 days (Figure 4).
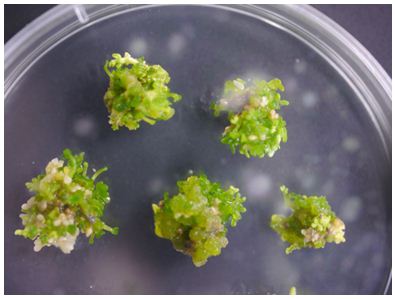
Figure 4. Shoot elongation
G.Root induction
1.When shoots become about 1 cm in length, cut off the shoots from the calluses and stick them shallowly into root induction medium (about 1 cm thick).
2.Place the plate in a growth cabinet (23 °C 16 h light/8 h dark) for 10 days (Figure 5).
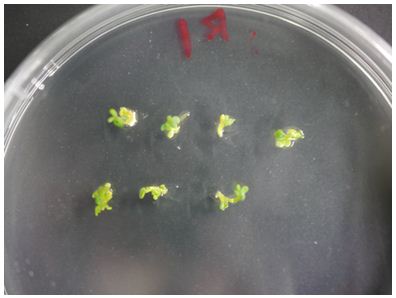
Figure 5. Root induction
H.Root elongation
Transfer and stick the shoots into root elongation medium (about 3 cm thick) and place the magenta box in a growth cabinet (23 °C 16 h light/8 h dark) until their root length become about 2-3 cm (Figure 6).

Figure 6. Root elongation
I.Naturalization
Transplant the plants into 100% vermiculite and grow them with high humidity at least first 1 week (23 °C 16 h light/8 h dark), and keep growing them for further analysis. To keep high humidity, we cover the pots of plants with Saran wrap.
Recipes
- Co-cultivation medium (pH 5.5)
1/10x B5 salt
1/10x Gamborg’s vitamin solution
0.5 μg/ml BAP (Gifu)
0.2 μg/ml BAP (MG-20)
0.05 μg/ml NAA
5 mM MES (pH 5.2)
20 μg/ml acetosyringone
Prepare 1/10x B5 salt solution and adjust pH, and autoclave it. Add remaining components after autoclave. - YMB medium (100 ml)
0.2 g mannitol
0.04 g yeast extract
0.02 g MgSO4.7H2O
0.01 g NaCl
Mix all components and autoclave the mixture.
Add 1 ml 0.3 M potassium phosphate buffer (pH 6.8) before use.
- Callus medium (pH 5.5)
1x B5 salt
1x Gamborg’s vitamin solution
2% sucrose
0.5 μg/ml BAP (Gifu)
0.2 μg/ml BAP (MG-20)
0.05 μg/ml NAA
10 mM (NH4)2SO4
0.3% phytagel
12.5 μg/ml meropen
15-40 μg/ml HygromycinB (you need to find the optimal concentration of HygromycinB because its purity is different among materials)
Mix 1x B5 salt and 2% sucrose and adjust pH, and add 0.3% phytagel. Autoclave the mixture. Add remaining components after autoclave.
- Shoot elongation medium (pH 5.5)
1x B5 salt
1x Gamborg’s vitamin solution
2% sucrose
0.2 μg/ml BAP
0.3% phytagel
12.5 μg/ml meropen
Mix 1x B5 salt and 2% sucrose and adjust pH, and add 0.3% phytagel. Autoclave the mixture. Add remaining components after autoclave.
- Root induction medium (pH 5.5)
1/2x B5 salt
1/2x Gamborg’s vitamin solution
1% sucrose
0.5 μg/ml NAA
0.4% phytagel
12.5 μg/ml meropen
Mix 1/2x B5 salt and 1% sucrose and adjust pH, and add 0.4% phytagel. Autoclave the mixture. Add remaining components after autoclave.
- Root elongation medium (pH 5.5)
1/2x B5 salt
1/2x Gamborg’s vitamin solution
1% sucrose
0.4% phytagel
12.5 μg/ml meropen
Mix 1/2x B5 salt and 1% sucrose and adjust pH, and add 0.4% phytagel. Autoclave the mixture. Add remaining components after autoclave. Magenta boxes are used for this root elongation medium.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by MEXT/JSPS KAKENHI, Japan (22870035, 23012038, 25114519 to Takuya Suzaki).
References
- Handberg, K. and Stougaard, J. (1992). Lotus japonicus, an autogamous, diploid legume species for classical and molecular genetics. The Plant Journal 2(4): 487-496.
- Stiller, J., Martirani, L., Tuppale, S., Chian, R.-J., Chiurazzi, M. and Gresshoff, P. M. (1997). High frequency transformation and regeneration of transgenic plants in the model legume Lotus japonicus. J Exp Bot 48(7): 1357-1365.
- Suzaki, T., Yano, K., Ito, M., Umehara, Y., Suganuma, N. and Kawaguchi, M. (2012). Positive and negative regulation of cortical cell division during root nodule development in Lotus japonicus is accompanied by auxin response. Development 139(21): 3997-4006.
- Thykjaer T., Schauser L., Danielsen D., Finneman J., Stougaard J. (1998). Transgenic plants: Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of the diploid legume Lotus japonicus. In Cell Biology: A laboratory handbook. Second edition vol 3. Academic Press.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Sasaki, T., Suzaki, T. and Kawaguchi, M. (2013). Stable Transformation in Lotus japonicus. Bio-protocol 3(12): e796. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.796.
Category
Plant Science > Plant transformation > Agrobacterium
Molecular Biology > DNA > Transformation
Plant Science > Plant physiology > Plant growth
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Tips for asking effective questions
+ Description
Write a detailed description. Include all information that will help others answer your question including experimental processes, conditions, and relevant images.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link








