- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Isolation of Infiltrating Leukocytes from the Spinal Cord of Mice
Published: Vol 3, Iss 10, May 20, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.775 Views: 12669
Reviewed by: Xuecai Ge
Abstract
The infiltration of leukocytes into the central nervous system (CNS) is a common feature of many neuroinflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis, and also occurs during certain microbial infections such as by West Nile Virus. Here, we describe a method to isolate leukocytes from the spinal cords of mice. This method can be used for the characterization of leukocyte populations that infiltrate the spinal cord, and to perform functional studies with the isolated cells. The CNS of naive mice is infiltrated by very low numbers of leukocytes, however, upon inflammation increased numbers of mononuclear cells traffic to the CNS. The number of leukocytes that can be isolated roughly correlates with the degree of inflammation.
Keywords: Experimental Autoimmune EncepahlomyelitisMaterials and Reagents
- 1x PBS and 10x PBS
- Surgical instruments: scissors, forceps, scalpel
- Percoll (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P4937 )
Note: prepare isotonic Percoll solution stock (one part 10x PBS and 9 parts Percoll).
Equipment
- Centrifuge with swing-out bucket rotor (e.g. Eppendorf, model: 5810 R )
- 75 mm petri dish
- 18 G and 27 G needle (BD Biosciences)
- 10 ml syringe (BD Biosciences)
- 15 and 50 ml conical centrifuge tubes
- Plastic Pasteur pipette
- 70 μm cell strainer (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 352350 )
Procedure
- Preparation of the animal
- Euthanize the mouse using CO2 gas (cervical dislocation might damage the spinal cord therefore it should be avoided).
- Spray the mouse with 70% ethanol to maintain aseptic conditions and cut open the chest wall to expose the heart.
- Perfusion of the animal
- Attach a 27G needle to a 10 ml syringe pre-filled with ice-cold PBS.
- Cut the right atrium of the heart with scissors (Figure 1).
- Perfuse the animal with the entire 10 ml of PBS through the left ventricle (Figure 1), repeat this procedure for 3-5 times (final volume of ~50 ml). Alternatively, a perfusion pump can be used in this step. By the end of the perfusion, the effluent from the atrium should be clear and the liver should have lost its red color. If this does not occur, continue to perfuse.
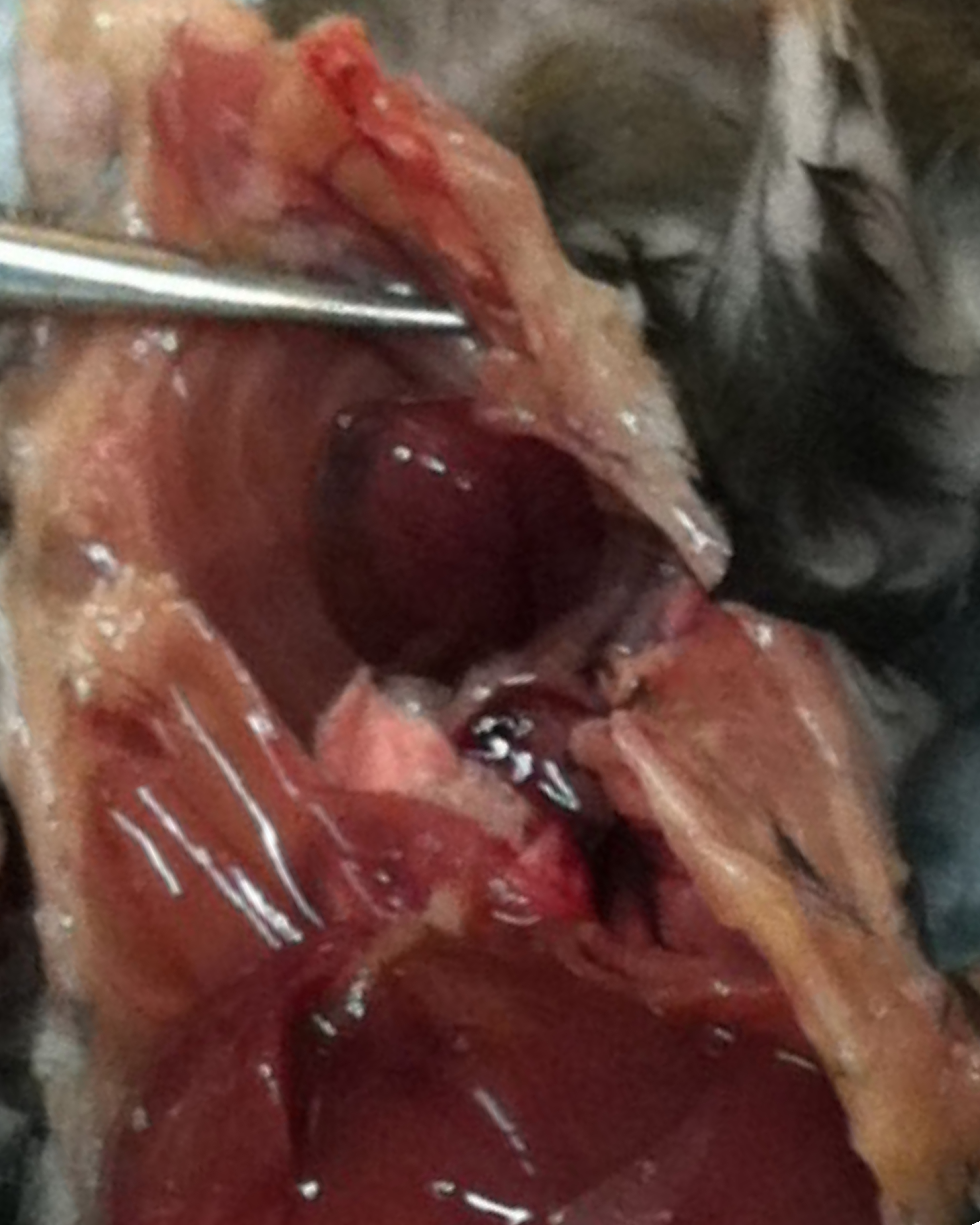
Figure 1. Photograph of the heart with the incision site (right atrium) and injection site (left ventricle) indicted.
- Isolation of the spinal cord
- Spray the back of the mouse with ethanol. Remove the head using scissors by doing a clean cut at the base of the head (start of the spinal column). Then expose the spinal column by cutting open the skin on the back from the base of the head to the tail of the animal. Identify where the base of the spinal column attaches to the pelvis.
- Using a pair of scissors, make a perpendicular cut through the spinal column at this location.
- Attach an 18G needle to a 10 ml syringe pre-filled with PBS. Hold the spinal column with forceps and identify the spinal canal at the caudal end of the spinal column. Carefully insert the 18G needle up to 10 mm at this point. Resistance will be encountered as the needle enters the spinal canal.
- Slowly push past the resistance in the canal until the point where the resistance is suddenly lost. Hold the spinal column over the 75 mm petri dish and flush the spinal cord out of the column.
- Dissociation of the spinal cord tissue
- Transfer the spinal cords to a 50 ml conical centrifuge tube containing 1x PBS and keep on ice (pool a maximum of 5 spinal cords per tube). In a petri dish and using scalpel or scissors and a pair of forceps, cut the spinal cords into very small pieces of about 10 mm.
- Transfer the spinal cord pieces into a 70 µm cell strainer placed on top of a 50 ml conical centrifuge tube and homogenize the tissue using the plunger of a 5 ml syringe. Add cold PBS to wash the cell strainer and top up to 50 ml.
- Centrifuge at 400 x g for 10 min, discard the supernatant and resuspend the cells in 5 ml of 30% isotonic Percoll (prepared using Percoll stock solution and 1x PBS). Add the 30% isotonic Percoll gently on top of 4 ml 70% isotonic Percoll (prepared using Percoll stock solution and 1x PBS) contained in a 15 ml conical centrifuge tube. Avoid mixing of the interface between the 70% and 30% solutions. Percoll should be used at room temperature, since cold cells tend to clump.
- Centrifuge for 20 min at 500 x g, at room temperature, without break or accelerator. The myelin will form a compact layer at the top, while the leukocytes will form an opaque ring between the two layers of Percoll, the so called interface.
- Remove the myelin and part of the supernatant above the interface by aspiration.
- Collect the cells in the interface into a clean 15 ml conical tube. Wash the cells 1-2x with 1x PBS by centrifuging at 400 x g for 5 min. Proceed with any further analysis of experimentation. If culturing of the cells is required, processing of the spinal cords (step IV) should be performed under sterile conditions, e.g. in a biological biosafety cabinet.
Acknowledgments
This protocol is was adapted from and utilized in a publication by Martinez Gomez et al. (2012).
References
- Martinez Gomez, J. M., Croxford, J. L., Yeo, K. P., Angeli, V., Schwarz, H. and Gasser, S. (2012). Development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis critically depends on CD137 ligand signaling. J Neurosci 32(50): 18246-18252.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Martinez Gomez, J. M., Gasser, S. and Schwarz, H. (2013). Isolation of Infiltrating Leukocytes from the Spinal Cord of Mice. Bio-protocol 3(10): e775. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.775.
- Martinez Gomez, J. M., Croxford, J. L., Yeo, K. P., Angeli, V., Schwarz, H. and Gasser, S. (2012). Development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis critically depends on CD137 ligand signaling. J Neurosci 32(50): 18246-18252.
Category
Immunology > Immune cell isolation
Neuroscience > Nervous system disorders
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link