- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Preparation of a Single-cell Suspension from Drosophila Wing Imaginal Discs
Published: Vol 12, Iss 16, Aug 20, 2022 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4494 Views: 2587
Reviewed by: Pilar Villacampa AlcubierreJer-Yen YangLijuan DuSandhya Ganesan

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Isolation and Infection of Drosophila Primary Hemocytes
Charles Tracy and Helmut Krämer
Jun 5, 2017 11139 Views

Probe-Seq: Method for RNA Sequencing of Specific Cell Types from Animal Tissue
Ryoji Amamoto [...] Constance L. Cepko
Sep 20, 2020 7221 Views
Preparation of Drosophila Larval Blood Cells for Single-cell RNA Sequencing
Sudhir Gopal Tattikota and Norbert Perrimon
Aug 20, 2021 3726 Views
Abstract
The wing imaginal discs in Drosophila larvae are a pair of sac-like structures that later form the wings of the adult fly. During the past decades, wing discs have been used as a simple and accessible model system, for identifying genes and deciphering signaling cascades that play crucial roles in many aspects of development. In this protocol, we describe a simple method for preparing a cell suspension from wing discs (see Graphical abstract). This method can also be applied to the preparation of single-cell suspensions from other types of Drosophila tissues. When combined with genetic labeling, the dissociated cells are suitable for downstream analysis, such as flow cytometry. This method was recently used to isolate different populations of cells from Drosophila imaginal discs (Yang et al., 2022).
Graphical abstract:

Procedures to prepare a single-cell suspension from Drosophila imaginal discs. Illustration of the main steps to dissect, temporarily store, and dissociate imaginal discs from Drosophila larvae. Refer to the Procedure section for detailed description of each step.
Background
The wing imaginal discs (wing discs) are located within the body cavity of the larvae and give rise to the wing, wing hinge, and the dorsal half of the body wall in the second thoracic segment (Tripathi and Irvine, 2022). The wing discs first form from a cluster of approximately 30 cells, which is located in the second thoracic segment during embryogenesis. These cells undergo extensive proliferation during larval stages, to form a mature larval wing disc of approximately 35,000 to 50,000 cells (Milan et al., 1996; Tripathi and Irvine, 2022). The majority of the wing disc is comprised of epithelial cells, with associated myoblasts, tracheal cells, neurons, and glia. Given the simplicity and accessibility of these structures, wing discs have been widely used as a model system for studying many aspects of biology, including tissue patterning, growth control, morphogenesis, and signal transduction.
In Drosophila, the Gal4/upstream activating sequence (UAS) transgenic system (Brand and Perrimon, 1993) can be used to label specific populations of cells via the expression of a fluorescent reporter gene, such as green fluorescent protein (GFP). The labeled GFP-positive cells can then be isolated from GFP-negative cells via fluorescence-activated cell sorting (FACS). In this protocol, we describe a simple method for the preparation of an epithelial cell suspension. This method was recently used to isolate different populations of cells from Drosophila imaginal discs following Gal4/UAS-based genetic labeling (Yang et al., 2022). This method can also be applied to the preparation of single-cell suspensions from other types of Drosophila tissues.
Materials and Reagents
9 depression spot plate (Pyrex, catalog number: 89090-482)
60 mm Petri dish (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: AS4051)
1.5 mL low retention microcentrifuge tubes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 21-402-903)
200 µL ultra-low retention micropipette tip (USA Scientific, catalog number: 1161-1700)
1,250 µL ultra-low retention micropipette tip (USA Scientific, catalog number: 1161-1720)
BD needles, 21 gauge (BD, catalog number: 305165)
BD needles, 25 gauge (BD, catalog number: 305125)
5 mL FACS tubes with a 35 µm strainer cap (Olympus PlasticsTM, catalog number: 28-154)
Schneider's Drosophila medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 21720)
Fetal bovine serum, qualified, heat-inactivated, USDA-approved regions (Omega Scientific, catalog number: FB-02)
Penicillin-streptomycin (P/S) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 10378016)
Non-enzymatic cell dissociation solution (Sigma, catalog number: C1544)
Elastase (Sigma, catalog number: E0258)
Propidium iodide (InvitrogenTM, catalog number: P3566)
10× PBS (for 1 L) (see Recipes)
1× PBS (see Recipes)
Elastase cell dissociation solution (see Recipes)
S2 medium (for 500 mL) (see Recipes)
Equipment
Nikon TS100 dissecting microscope
#3 forceps for transferring larvae (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 11231-30)
#5 forceps for dissecting imaginal discs (Fine Science Tools, catalog number: 11295-51)
Single Channel Pipette, 2–20 µL
Single Channel Pipette, 100–1000 µL
3 mL syringe (BD, catalog number: 309577)
Magnetic micro stir bar (StirBars, catalog number: SBM-0603-MIC)
Magnetic stirrer
Procedure
Dissection
Prepare 1,000 µL of S2 medium for each 1.5 mL low retention microcentrifuge tube. Keep the tubes on ice.
Transfer wandering third instar larvae from the inside wall of fly culturing bottles into a 60 mm Petri dish with #3 forceps, and wash them five times with 5 mL of 1× PBS, until all residual food is removed.
Using #3 forceps, transfer ~10–20 clean larvae into one depression plate spot filled with 1.5 mL of fresh cold 1× PBS.
Use a pair of #5 forceps to dissect out the imaginal discs (wing and haltere discs) from the larvae in cold 1× PBS.
Note: Video- or image-based descriptions of imaginal disc dissection procedures can be found elsewhere (Morimoto and Tamori, 2017; Purves and Brachmann, 2007; Witte et al., 2021).
Use #5 forceps to gently transfer the dissected discs into another well of the same depression plate filled with cold 1× PBS.
Each time, collect ~10 pairs of dissected imaginal discs in the depression plate before continuing to the next step.
Cut a P20 micropipette tip with scissors, and then coat it by pipetting the remaining carcasses several times up and down.
Wash the coated tip by pipetting fresh cold 1× PBS several times up and down before usage.
Use the coated P20 micropipette tip to transfer the dissected imaginal discs from the depression plate into the 1.5 mL low retention microcentrifuge tube with cold S2 medium. Discard the remaining carcasses.
Notes:
The coating procedure is critical to prevent sticking and loss of dissected tissue during transfer.
The use of a P20 micropipette minimizes the transfer of excess 1× PBS into S2 medium, limiting unwanted dilution.
Imaginal discs can be kept in ice-cold S2 medium for up to 4 h before tissue dissociation begins. In total, collect ~100–200 pairs of discs in each 1.5 mL low retention microcentrifuge tube before tissue dissociation.
Cell Dissociation
Allow the imaginal discs to settle to the bottom of the microcentrifuge tube by gravity, and then remove the S2 medium using a P1000 pipette.
Add 1,000 μL of non-enzymatic cell dissociation solution, and gently wash the imaginal discs by inverting the microcentrifuge tube.
Allow the imaginal discs to settle to the bottom of the microcentrifuge tube, and then remove the non-enzymatic cell dissociation solution using a P1000 pipette.
Repeat Steps B2 and B3, and wash the imaginal discs three times. In the final round of washing, remove as much solution as possible.
Add 1,000 μL of elastase cell dissociation solution into the microcentrifuge tube.
Add a clean magnetic micro stir bar into the microcentrifuge tube. Close the cap and invert the tube, to allow the stir bar to sink to the cap.
Place the inverted microcentrifuge tube in the center of a magnetic stirrer. Increase the stirring speed slowly to avoid spinout.
Incubate the imaginal discs with elastase cell dissociation solution in the magnetic stirrer at room temperature for 20–30 min.
While waiting, pre-wash P1250 micropipette tips and 3 mL syringes with 21G and 25G needles, by passing S2 medium through the tips or needles ten times.
Add 500 μL of S2 medium to the elastase cell dissociation solution and, using a pre-washed P1250 tip, gently pipette the solution up and down twenty times.
Gently pass the solution through the pre-washed 21G needle ten times, then through the 25G needle another ten times. Avoid creating bubbles when passing the solution through the needles.
Pre-wet a 35 µm cell strainer cap and its attached falcon tube with 500 µL of S2 medium. Discard the S2 medium flow-through.
Transfer the total 1,500 μL solution containing dissociated cells with a pre-washed P1250 tip and filter the solution through the wet cell strainer cap into the falcon tube. Continue tapping the tube until all of the solution goes through the strainer cap.
Wash the microcentrifuge tube with 500 μL of S2 medium and filter the solution through the cell strainer cap into the same falcon tube (total 2,000 μL).
Add the desired fluorescent dye (e.g., propidium iodide) and keep the tube on ice until FACS.
Note: ~100–200 pairs of imaginal discs (wing and haltere discs) can yield 5 × 106–10 × 106 dissociated cells at a concentration of 2 × 106–5 × 106 per mL, with a viability of ~90%. Figure 1 shows representative images of dissociated imaginal disc cells before and after cell sorting.
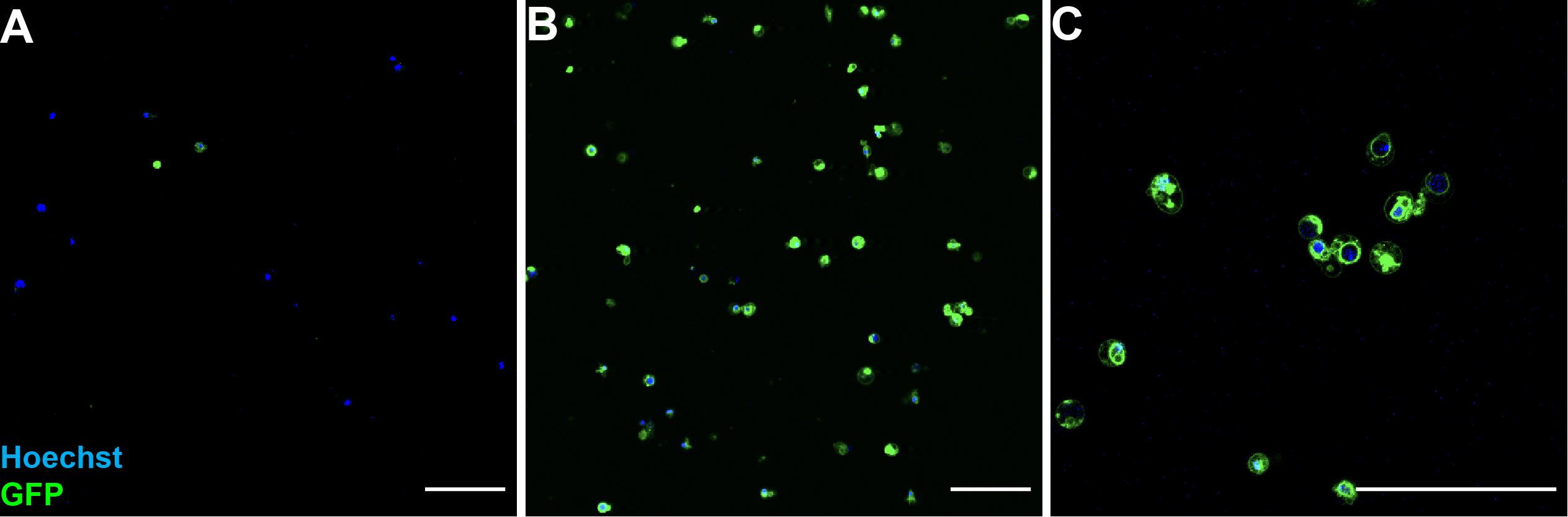
Figure 1. Images of dissociated imaginal disc cells before and after cell sorting.Dissociated wing disc cells from late third instar larvae carrying ptc-gal4 and UAS-mCD8GFP. (A) GFP positive and negative cells before FACS. (B) GFP-positive cells after FACS. (C) Zoomed view of post-FACS sorted GFP positive cells. Hoechst 33342 (blue) is used to visualize the entire cell population. Scale bars: 50 μm.
Recipes
10× PBS (for 1 L)
80 g NaCl
2 g KCl
14.4 g Na2HPO4 (anhydrous)
2.4 g KH2PO4
1 L dH2O
Mix well, and filter sterilize.
1× PBS (for 1 L)
100 mL 10× PBS
900 mL dH2O
Mix well, and filter sterilize.
Elastase cell dissociation solution
Elastase protein powder was reconstituted in ddH2O to 5 mg/mL.
Then, the solution was diluted to 0.4 mg/mL in the fresh cell dissociation solution.
S2 medium (for 500 mL)
500 mL Schneider's Drosophila medium
50 mL fetal bovine serum
5 mL penicillin-streptomycin (P/S)
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Institutes of Health grants R01GM117440 to X.Z. This protocol was used to isolate different populations of cells from Drosophila imaginal discs (Yang et al., 2022). The graphical abstract was generated with the help of Biorender (https://app.biorender.com/).
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
References
- Brand, A.H., and Perrimon, N. (1993). Targeted Gene-Expression as a Means of Altering Cell Fates and Generating Dominant Phenotypes. Development 118(2): 401-415.
- Milan, M., Campuzano, S. and Garcia-Bellido, A. (1996). Cell cycling and patterned cell proliferation in the wing primordium of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93(2): 640-645.
- Morimoto, K. and Tamori, Y. (2017). Induction and Diagnosis of Tumors in Drosophila Imaginal Disc Epithelia. J Vis Exp(125): 55901.
- Purves, D. C. and Brachmann, C. (2007). Dissection of imaginal discs from 3rd instar Drosophila larvae. J Vis Exp(2): 140.
- Tripathi, B. K. and Irvine, K. D. (2022). The wing imaginal disc. Genetics 220(4).
- Witte, L., Linnemannstons, K., Honemann-Capito, M. and Gross, J. C. (2021). Visualization and Quantitation of Wg trafficking in the Drosophila Wing Imaginal Epithelium. Bio-protocol 11(11): e4040.
- Yang, S., Wu, X., Daoutidou, E. I., Zhang, Y., Shimell, M., Chuang, K. H., Peterson, A. J., O'Connor, M. B., and Zheng, X. (2022). The NDNF-like factor Nord is a Hedgehog-induced extracellular BMP modulator that regulates Drosophila wing patterning and growth.Elife 11: e73357.
Article Information
Copyright
Yang et al. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0).
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Yang, S., Sears, B. and Zheng, X. (2022). Preparation of a Single-cell Suspension from Drosophila Wing Imaginal Discs. Bio-protocol 12(16): e4494. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.4494.
- Yang, S., Wu, X., Daoutidou, E. I., Zhang, Y., Shimell, M., Chuang, K. H., Peterson, A. J., O'Connor, M. B., and Zheng, X. (2022). The NDNF-like factor Nord is a Hedgehog-induced extracellular BMP modulator that regulates Drosophila wing patterning and growth.Elife 11: e73357.
Category
Cell Biology > Cell isolation and culture > Cell isolation
Developmental Biology > Cell signaling
Biological Sciences > Biological techniques
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link








