- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Cytotoxicity Assay for Detection of Cereulide Produced by Emetic Bacillus cereus
Published: Vol 3, Iss 2, Jan 20, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.318 Views: 13061

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

β-lactamase (Bla) Reporter-based System to Study Flagellar Type 3 Secretion in Salmonella
Fabienne F. V. Chevance and Kelly T. Hughes
Jun 20, 2023 1774 Views

Determination of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Content in Cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803 Using Acid Hydrolysis Followed by High-performance Liquid Chromatography
Janine Kaewbai-ngam [...] Tanakarn Monshupanee
Aug 20, 2023 1824 Views

An HPLC-based Assay to Study the Activity of Cyclic Diadenosine Monophosphate (C-di-AMP) Synthase DisA from Mycobacterium smegmatis
Avisek Mahapa [...] Dipankar Chatterji
Dec 20, 2024 1789 Views
Abstract
The emetic subgroup of Bacillus cereus strains produces cereulide, a dodecadepsipeptide (1.2 kDa), which is the causative agent of food poisonings. Cereulide is synthesized by a nonribosomal peptide synthetase (NRPS), the Ces-NRPS (Ehling-Schulz et al., 2006). Cereulide is a cyclic and lipophilic potassium ionophor structurally related to the macrolide antibiotic valinomycin. Both substances act on mitochondria by depolarization and uncoupling of ATP synthesis, and this effect (mitochondrial swelling) is used to quantify cereulide in a HEp-2 cell based viability assay.
In this protocol, which was modified from an assay published by Finlay et al. (1999), valinomycin is used as a reference standard for ionophor–induced cytotoxicity, because purified cereulide is not commercially available yet. This assay has been used to quantify cereulide amounts from different B. cereus mutants (Lücking et al., 2009; Frenzel et al., 2012) and to estimate cereulide levels extracted from foods (artificially) contaminated with B. cereus (Frenzel et al., 2011).
Materials and Reagents
- Bacillus cereus F4810/72 (or other cereulide producing, emetic B. cereus strain)
- Tryptone
- Yeast extract
- NaCl
- HEp-2 cell line (Frenzel et al., 2011)
- MEM Earle′s medium (with 2.2 g/L NaHCO3, with stable glutamine) (Biochrom, catalog number: FG0325 )
- Penicillin-streptomycin solution (10,000 μg/ml; Biochrom, catalog number: A2212/3 )
- Sodium pyruvate solution (Biochrom, catalog number: L0473 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Biochrom, catalog number: S0113 )
- Phosphate Buffered Saline (PBS) (Biochrom, catalog number: L1825 )
- 99% Ethanol (highest purity grade available)
- WST-1 cell proliferation reagent (Roche, catalog number: 05015944001 )
- Valinomycin (reference standard) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 94675 )
- 10x Trypsin/EDTA solution (0.5 %/0.2 %) (Biochrom, catalog number: L2153 )
- LB-Miller (see Recipes)
- MEM-Earle HEp-2 medium (see Recipes)
- MEM-Earle HEp-2 medium with ethanol (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 30 °C incubator with aeration (for liquid bacterial cultures)
- 37 °C incubator with 5% CO2 (for HEp-2 cell cultures)
- Spectrophotometer
- Table top centrifuge
- Microplate shaker
- Microscope and counting chamber for cell culture
- Microscope and counting chamber for bacteria (e.g. Helber counting chamber; depth: 0.02 mm; small square area: 0.0025 mm2)
- Multichannel pipet (8 channels, manual or electronic; e.g. Transferpette®, BrandTech Scientific 10-200 μl; catalog number: 2705410 )
- Microplate reader (multiwell scanning spectrophotometer)
- 500 ml baffled flask
- Tissue culture flasks with filter caps, 75 cm2 (Biochrom catalog number: P90076 )
- Safe seal tubes (e.g. Eppendorf, catalog number: 0030120.094 ) 96-well cell culture plates, polystyrene (Biochrom, catalog number: P92696 )
Procedure
- Cereulide sample preparation (B. cereus culture and growth conditions)
- Inoculate 3 ml LB medium with B. cereus and incubate at 30 °C, 150 rpm for 16 h (pre-culture).
- After 16 h, determine the cell count (CFU/ml) of the pre-culture with a counting chamber appropriate for bacteria (e.g. Helber counting chamber). Inoculate 100 ml LB in 500 ml baffled flask with 103 CFU/ml (approx. 1:10,000 dilution; i.e. add approx. 100 μl of 1:100 dilution of bacteria to 100 ml LB). Incubate at 30 °C, 150 rpm for 24 h.
- Cereulide accumulates to stable levels after 24 h of cultivation at 30 °C (Frenzel et al., 2011). Withdraw 1-2 ml samples of B. cereus cultures and autoclave in safe seal tubes (17 min at 121 °C). This step will denature heat-labile enterotoxins and proteases, whereas cereulide remains stable. Store samples at -20 °C.
- The remaining part of the B. cereus culture is autoclaved (17 min at 121 °C) and disposed.
- Inoculate 3 ml LB medium with B. cereus and incubate at 30 °C, 150 rpm for 16 h (pre-culture).
- HEp-2 cell based cereulide cytotoxicity assay
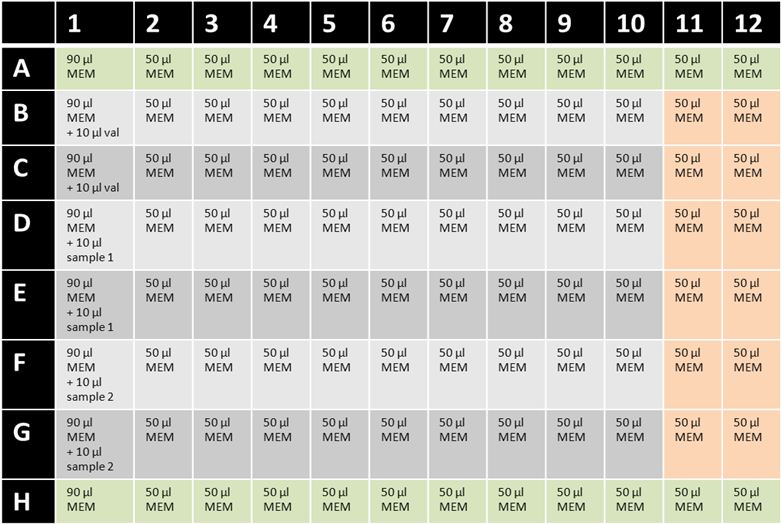
Figure 1: Example for setup of cereulide cytotoxicity 96-well assay plate. MEM = MEM-Earle HEp-2 medium with ethanol; val = valinomycin (5 μg/ml); green= background control wells; orange = 100% cell viability wells without test substance.- Maintain HEp-2 cells as monolayers in 75 cm2 tissue culture flasks at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. Routinely grow HEp-2 cells in 25 ml MEM-Earle HEp-2 medium and sub-culture cells 1:4 approximately every 2-3 days when they reach 70-80% confluence. To detach adherent cells for sub-culturing, add 5 ml of trypsin/EDTA solution and incubate for 5-10 min at 37 °C. Add 5 ml of MEM-Earle HEp-2 medium and resuspend detached HEp-2 cells. Centrifuge cells (5 min, 150 x g, room temperature) and resuspend pellet in 10 ml MEM-Earle HEp-2 medium. Split cells 1:4 in new tissue culture flask containing 25 ml MEM-Earle HEp-2 medium.
- If cells from point 2a) reach 70-80% confluence, cytotoxicity assay can be performed. Add 90 μl of MEM-Earle HEp-2 medium with ethanol to wells A1 to H1 of a 96-well cell culture plate (see Figure 1). Fill the remaining wells with 50 μl MEM-Earle HEp-2 medium with ethanol.
- Dilute valinomycin stock solution (50 μg/ml) 1:10 with MEM-Earle HEp-2 medium with ethanol. Add 10 μl in wells B1 and C1 (final concentration is 500 ng/ml).
- Two additional samples (prepared as described in point 1 and stored at -20 °C) can be tested on this plate: add 10 μl of sample 1 to wells D1 and E1; add 10 μl of sample 2 to wells F1 and G1. Rows A and H remain free of samples (background control wells).
- Mix samples and medium thoroughly by repeated pipetting using a multichannel pipet. Remove 50 μl of the wells and perform serial dilutions (1:1) of the samples to column A10-H10. Columns 11 and 12 remain free of sample (100% cell viability control wells).
- Remove growth medium from a HEp-2 culture flask containing a 70-80% confluent monolayer. Wash the cells with 5 ml PBS. Add 5 ml of trypsin/EDTA solution and incubate for 5-10 min at 37 °C.
- Add 5 ml of MEM-Earle HEp-2 medium and resuspend detached HEp-2 cells.
- Centrifuge cells (5 min, 150 x g, room temperature) and resuspend pellet in 10 ml MEM-Earle HEp-2 medium.
- Determine cell count with counting chamber. Adjust the cells count to 3.4 x105 cells/ml.
- Dispense 150 μl of cells per well (~5 x 104 cells/well). Incubate plate for 48 h at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere.
- To save WST-1 reagent, discard 100 μl of culture medium from each well and add 10 μl of WST-1 reagent to the remaining culture to detect mitochondrial activity of HEp-2 cells. Rows A and H remain free of WST-1 for calculation of the background value. Shake plate to distribute proliferation reagent uniformly and incubate plate for 20 min at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere.
- Shake plate thoroughly and measure absorbance in a microplate reader at 450 nm.
- Maintain HEp-2 cells as monolayers in 75 cm2 tissue culture flasks at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 atmosphere. Routinely grow HEp-2 cells in 25 ml MEM-Earle HEp-2 medium and sub-culture cells 1:4 approximately every 2-3 days when they reach 70-80% confluence. To detach adherent cells for sub-culturing, add 5 ml of trypsin/EDTA solution and incubate for 5-10 min at 37 °C. Add 5 ml of MEM-Earle HEp-2 medium and resuspend detached HEp-2 cells. Centrifuge cells (5 min, 150 x g, room temperature) and resuspend pellet in 10 ml MEM-Earle HEp-2 medium. Split cells 1:4 in new tissue culture flask containing 25 ml MEM-Earle HEp-2 medium.
- Calculation of cereulide amounts
- Import raw data from absorbance measurement to calculation/statistics program (e.g. Microsoft Excel).
- Perform background subtraction on all wells with the mean of the background control wells (Rows A and H; see Figure 2). Calculate dose-response curve for the internal standard valinomycin [Percent viability inhibition = (mean absorbance test wells /mean absorbance 100% cell viability control wells) x 100]. Determine the 50% inhibitory concentration for valinomycin by linear regression.
- Calculate dose-response curves for samples as given above. Determine the 50% inhibitory concentration for samples (presented by the reciprocal value of the sample dilution that resulted in 50% loss of mitochondrial activity). Calculate cereulide amounts as valinomycin equivalents (VE) by extrapolating the absorbance value at 50% cell viability inhibition to the dose response curve for valinomycin.
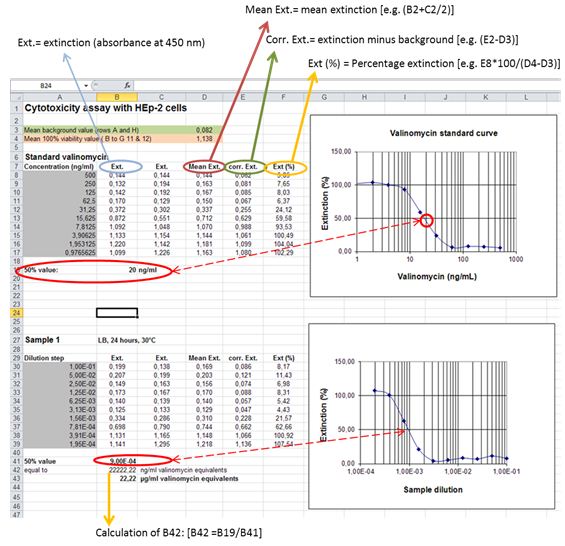
Figure 2. Example for calculation of cereulide concentrations (given in valinomycin equivalents) from dose-response-curves plotted in Microsoft Excel
- Import raw data from absorbance measurement to calculation/statistics program (e.g. Microsoft Excel).
Recipes
- LB-Miller
10 g tryptone
5 g yeast extract
10 g NaCl
Add dH2O to 1 L
Adjust pH to 7.0 ± 0.2. Autoclave 121 °C, 15 min - MEM-Earle HEp-2 medium
488 ml MEM Earle′s medium (with 2.2 g/L NaHCO3, with stable glutamine)
2 ml penicillin-streptomycin solution (10,000 μg/ml)
5 ml sodium pyruvate solution
5 ml FBS - MEM-Earle HEp-2 medium with ethanol
478 ml MEM Earle′s medium (with 2.2 g/L NaHCO3, with stable glutamine)
2 ml penicillin-streptomycin solution (10,000 μg/ml)
5 ml sodium pyruvate solution
5 ml FBS
10 ml 99% ethanol (solvent for cereulide); highest purity grade available
Acknowledgments
This protocol was adapted from previously published papers: Finlay et al. (1999); Lücking et al. (2009); and Frenzel et al. (2011). This research project was supported by the German Ministry of Economics and Technology (via AiF) and the FEI (Forschungskreis der Ernährungsindustrie e.V., Bonn), projects AiF 15186 N and 16845 N. We thank Prof. Dr. Dr. E. Märtlbauer and Dr. R. Dietrich (Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich, Germany) for kindly providing the HEp-2 cell line.
References
- Ehling-Schulz M., Vukov, N., Schulz, A., Shaheen, R., Andersson, M., Martlbauer, E., and Scherer, S. (2005). Identification and partial characterization of the nonribosomal peptide synthetase gene responsible for cereulide production in emetic Bacillus cereus. Appl Environ Microbiol 71, 105-113.
- Finlay, W. J., Logan, N. A., Sutherland, A. D. (1999). Semiautomated metabolic staining assay for Bacillus cereus emetic toxin. Appl Environ Microbiol 65, 181-1812.
- Frenzel, E., Doll, V., Pauthner, M., Lücking, G., Scherer, S., Ehling-Schulz, M. (2012). CodY orchestrates the expression of virulence determinants in emetic Bacillus cereus by impacting key regulatory circuits. Mol Mic 85 (1), 67-88.
- Frenzel E., Letzel, T., Scherer, S., Ehling-Schulz, M. (2011). Inhibition of cereulide toxin synthesis by emetic Bacillus cereus via long-chain poly-phosphates. Appl Environ Microbiol 77, 1475-1482.
- Lücking, G., Dommel, M. K., Scherer, S., Fouet, A., Ehling-Schulz, M. (2009). Cereulide synthesis in emetic Bacillus cereus is controlled by the transition state regulator AbrB, but not by the virulence regulator PlcR. Microbiology 155, 922-931.
- The HEp-2 cell line is a permanent human larynx carcinoma cell line. The cells were kindly provided by Prof. E. Martlbauer and Dr. R. Dietrich (Ludwig Maximilians University Munich, Germany). See Nielsen, C., Casteel, M., Didier, A., Dietrich, R., Martlbauer, E. (2009). Trichothecene-induced cytotoxicity on human cell lines. Mycotox Res 25, 77-84.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Frenzel, E. and Ehling-Schulz, M. (2013). Cytotoxicity Assay for Detection of Cereulide Produced by Emetic Bacillus cereus. Bio-protocol 3(2): e318. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.318.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Other compound
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









