- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Generation of Targeted Knockout Mutants in Arabidopsis thaliana Using CRISPR/Cas9
Published: Vol 7, Iss 13, Jul 5, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2384 Views: 25788
Reviewed by: Jihyun KimAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Identification of Insertion Site by RESDA-PCR in Chlamydomonas Mutants Generated by AphVIII Random Insertional Mutagenesis
Fantao Kong and Yonghua Li-Beisson
Feb 5, 2018 8591 Views

High Resolution Melting Temperature Analysis to Identify CRISPR/Cas9 Mutants from Arabidopsis
Cynthia Denbow [...] Sakiko Okumoto
Jul 20, 2018 8939 Views

Dual sgRNA-based Targeted Deletion of Large Genomic Regions and Isolation of Heritable Cas9-free Mutants in Arabidopsis
Yu Jin and Sebastian Marquardt
Oct 20, 2020 6772 Views
Abstract
The CRISPR/Cas9 system has emerged as a powerful tool for gene editing in plants and beyond. We have developed a plant vector system for targeted Cas9-dependent mutagenesis of genes in up to two different target sites in Arabidopsis thaliana. This protocol describes a simple 1-week cloning procedure for a single T-DNA vector containing the genes for Cas9 and sgRNAs, as well as the detection of induced mutations in planta. The procedure can likely be adapted for other transformable plant species.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9Background
The CRISPR/Cas9 system (Cas9) provides a simple and widely applicable approach to modify genomic regions of interest and has therefore become the tool of choice for genome editing in plants and other organisms (Schiml and Puchta, 2016). The system relies on the bacterial Cas9 nuclease from Streptococcus pyogenes (Cas9), which can be directed by a short artificial single guide RNA molecule (sgRNA) towards a genomic DNA sequence (Jinek et al., 2012), where it creates a double strand break (DSB). These DSBs are then repaired by the innate DNA repair mechanism of the plant cell. Here, two main pathways can be distinguished (Salomon and Puchta, 1998). (i) DNA molecules with high homology to the DSB site can be used as repair template. This homology directed repair (HDR) approach can be exploited to introduce specific sequences at the site of the DSB (Schiml et al., 2014; Baltes and Voytas, 2015). However, due to low integration rates of these sequences, HDR mediated gene editing in plants remains challenging. (ii) An easier and more efficient approach is the use of the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) repair pathway of the plant, which is the dominant repair pathway in most plants, such as Arabidopsis thaliana (Arabidopsis). Since NHEJ is error-prone, small insertions or deletions (indels) of a few base pairs (bp) occur often at the DSB site, leading to frameshift mutations and gene knockouts (Pacher and Puchta, 2016). Here, we provide a detailed protocol for targeted gene knockout in the model plant Arabidopsis including a simple 1-week cloning protocol for a plant vector system containing the Cas9 and sgRNA, and then Arabidopsis transformation and detection of mutations.
Materials and Reagents
- 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tubes (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 72.690.001 )
- 200 µl PCR tubes (Labomedic, catalog number: 2081644AA )
- Petri dishes (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 82.1472 )
- 2 ml microcentrifuge tubes (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 72.691 )
- 20 µl pipette tips (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 70.1116 )
- 200 µl pipette tips (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 70.760.012 )
- 1,000 µl pipette tips (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 70.762.010 )
- Agrobacterium tumefaciens (A. tumefaciens) strain GV3101::pMP90
- Arabidopsis thaliana seeds (Col-0)
- Vectors (see Figure 1)
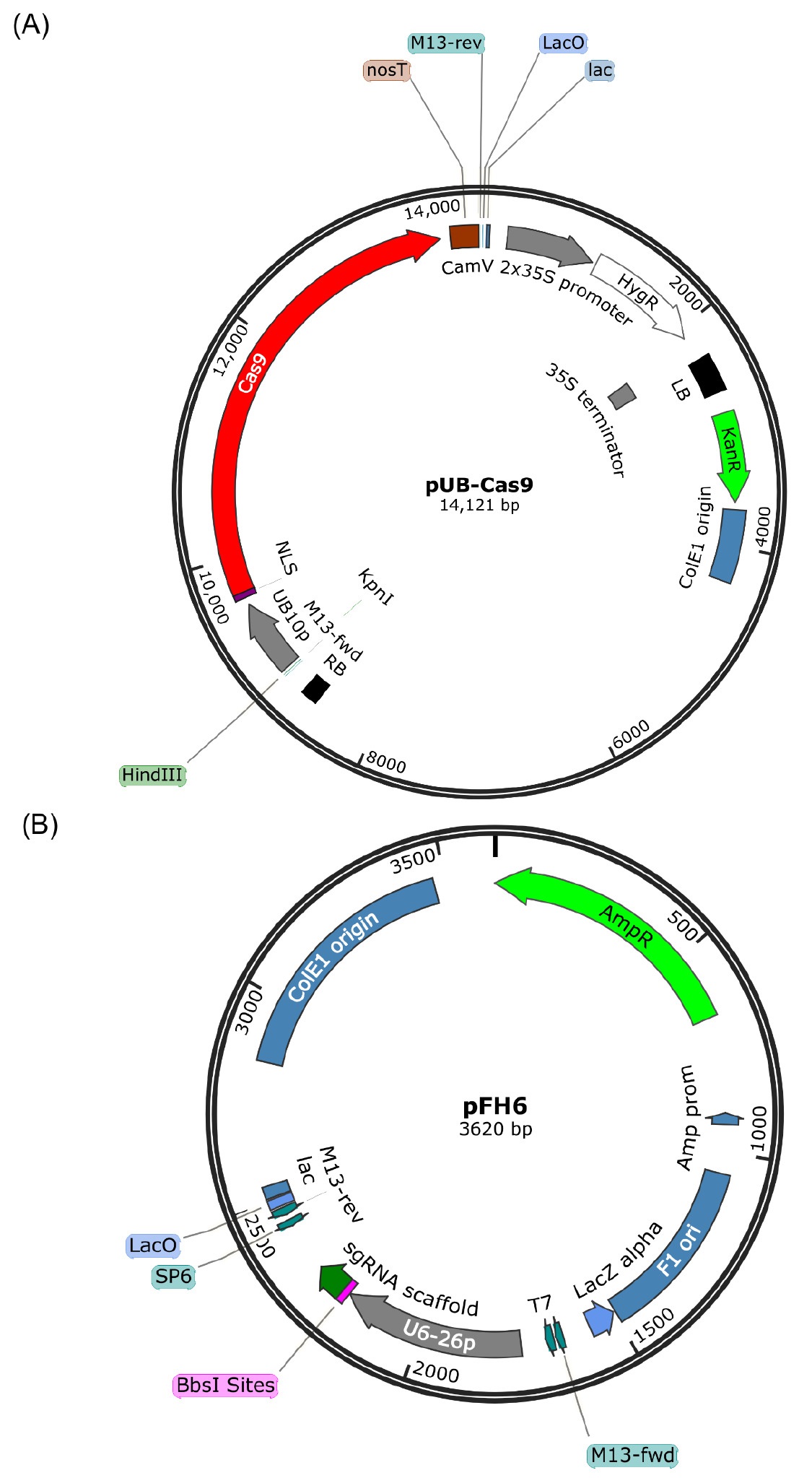
Figure 1. Vector maps of pUB-Cas9 (A) and pFH6 (B). pFH6 is used to integrate the 20 bp target sequence upstream of the sgRNA scaffold and under the control of the Arabidopsis U6-26 RNA polymerase III promoter. The whole sgRNA cassette is then transferred via Gibson cloning into the binary T-DNA vector pUB-Cas9 (contains the Cas9 gene under the control of the Ubiquitin10 promoter) for plant transformation. Maps were generated using SnapGene Viewer (http://www.snapgene.com/products/snapgene_viewer/).- Plant T-DNA Cas9 vector pUB-Cas9 (GenBank accession number KY080691), containing a Chlamydomonas reinhardtii codon-optimized ubiquitously (UBIQUITIN10 promoter) expressed Cas9 gene, a kanamycin resistance cassette for bacterial selection and a hygromycin resistance cassette as plant selection marker (Hahn et al., [2017]; available at Addgene, catalog number: 86556 )
- sgRNA subcloning vector pFH6 (GenBank accession number KY080689) containing the Arabidopsis U6-26 promoter, the integration site for the 20 bp protospacer sequence, the sgRNA scaffold and an ampicillin resistance cassette (Hahn et al. [2017]; available at Addgene, catalog number: 86555 )
Note: pFH6 contains an additional 9 bp fragment (GTCCCTTCG) between the 3’ end of the U6-26 promoter and the protospacer integration site. In several experiments, we could show that this does not affect gene editing activity. However, we have also cloned a new version of the subcloning vector without the additional fragment (pFH6_new), which shows high cleavage activity in preliminary experiments and can be obtained from us. This version only contains an additional guanine (G) between the 3’ end of the U6-26 promoter and the protospacer integration site, which allows the integration of any 20 bp protospacer without restriction of G as first bp (compare e.g., Fauser et al. [2014]). The cloning strategy for pFH6_new is analogous to the one described in this protocol, the only difference is that the forward primer for cloning your 20 bp protospacer sequence contains a different overlap and lacks the need for an initial G at the beginning (ATTG-N20, compare procedure section).
- Plant T-DNA Cas9 vector pUB-Cas9 (GenBank accession number KY080691), containing a Chlamydomonas reinhardtii codon-optimized ubiquitously (UBIQUITIN10 promoter) expressed Cas9 gene, a kanamycin resistance cassette for bacterial selection and a hygromycin resistance cassette as plant selection marker (Hahn et al., [2017]; available at Addgene, catalog number: 86556 )
- Competent Escherichia coli (E. coli) cells (e.g., Mach1TM competent cells, Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: C862003 )
- BbsI-HF + CutSmart buffer (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R3539S )
- Distilled H2O
- Plasmid mini prep kit and agarose gel extraction kit (e.g., GeneMATRIX 3 in 1–Basic DNA Purification Kit, Roboklon, catalog number: E3545 )
- T4 DNA ligase with 10x ligation buffer (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0202S )
- Ampicillin (Amp) (Carl Roth, catalog number: K029.2 )
- Primers (see Table 1)
Table 1. List of oligonucleotides
- 5x Green GoTaq Reaction buffer (Promega, catalog number: M791A )
- dNTPs (10 mM each) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: R0192 )
- GoTaq G2 polymerase (Promega, catalog number: M7841 ) or other standard PCR polymerase
- HindIII-HF + CutSmart buffer (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R3104S )
- KpnI-HF + CutSmart buffer (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R3142S )
- Phusion High-Fidelity polymerase (New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0530S ) or other proofreading polymerases
- Gibson Assembly Cloning Kit (New England Biolabs, catalog number: E5510S )
- Kanamycin sulfate (Kan) (Carl Roth, catalog number: T832.4 )
- Rifampicin (Rif) (Molekula, catalog number: 32609202 )
- Gentamycin sulfate (Gent) (Carl Roth, catalog number: 0233.3 )
- Hygromycin B (Hyg) (Carl Roth, catalog number: CP12.2 )
- T7 Endonuclease I (optional; New England Biolabs, catalog number: M0302S )
- LB medium (agar plates and liquid), supplemented with 200 μg/ml ampicillin (see Recipes)
- LB medium (agar plates and liquid), supplemented with 30 μg/ml kanamycin sulfate (see Recipes)
- YEP medium (agar plates and liquid), supplemented with 150 μg/ml rifampicin, 50 μg/ml gentamycin sulfate, 50 μg/ml kanamycin (see Recipes)
- ½ MS medium agar plates, supplemented with 33.3 μg/ml hygromycin B (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Agarose gel electrophoresis equipment (e.g., VWR, Peqlab, model: PerfectBlueTM Gel System Mini M, catalog number: 700-0434 )
- Bacteria plate incubators (28 °C, 37 °C, e.g., Memmert, model: IN55 ) and shaker (28 °C, 37 °C; e.g., Eppendorf, New BrunswickTM, model: Innova® 44 , catalog number: M1282-0002)
- Heating blocks (e.g., Eppendorf, model: Thermomixer Compact , catalog number: T1317-1EA)
- PCR cycler (e.g., Thermo Fisher Scientific, Applied BiosytemsTM, model: VeritiTM 96-well Thermal Cycler, catalog number: 4375786 )
- 10 µl pipette (e.g., Pipetman Neo P10N, Gilson, catalog number: F144562 )
- 20 µl pipette (e.g., P20N, Gilson, catalog number: F144563 )
- 200 µl pipette (e.g., P200N, Gilson, catalog number: F144565 )
- 1,000 µl pipette (e.g., P1000N, Gilson, catalog number: F144566 )
- Plant growth chamber (e.g., CLF Plant Climatics, Percival Scientifici, model: AR-66L )
Software
- SerialCloner
- Cas-OFFinder
- 4Peaks software
- MUSCLE (Optional)
Procedure
- Design of sgRNA sequence for gene knockout
The design of the sgRNA is possibly the most critical step of Cas9-mediated gene editing. Thus, the Cas9 target site should be carefully selected. Several online tools (Heigwer et al., 2014; Lei et al., 2014; Xie et al., 2014) assist with finding suitable target sites, however, we still choose most target sites manually in standard molecular biology software (e.g., SerialCloner, http://serialbasics.free.fr/Serial_Cloner.html). When choosing the target site, the following aspects should be taken into account:- Search your gene of interest (GOI) for a GN19NGG sequence on both strands to find putative target sites. The NGG is the Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9 protospacer adjacent motive (PAM), which has to be present in the target locus for efficient binding of the Cas9 protein (Jinek et al., 2012). The GN19 represents the 20 bp long protospacer motif, defining the target site where you want to create mutations. This 20 bp sequence, which marks the 5’ end of your sgRNA molecule, should start with a G, since this is a prerequisite for transcription of the sgRNA under the control of the U6-26 promoter of Arabidopsis.
Note: If there is no suitable target sequence, you might just add the G as 21st bp, even if it does not have a complementary base in the target locus. These sgRNAs might still lead to cleavage at the target site (e.g., Hahn et al., 2017). However, we recommend using the canonical 20 bp protospacer sequences if possible. - Choose a target site in an exon of your GOI, which is preferably close to the 5’ end of the coding sequence, since mutations in this region are more likely to disrupt the protein’s function. If you know highly important domains of the protein, such as nucleic acid binding sites, you might want to create mutations in these regions.
- Consider choosing several different target sites, since not all sgRNAs work equally well (Liang et al., 2016). Additionally, you might want to use two sgRNAs at once (see cloning strategy) to create large deletions, which might cause more drastic effects.
- Search for putative off-target sites to avoid knocking out genes that share the 20 bp target site or highly similar sites. For this purpose, we use the Cas-OFFinder program (Bae et al., 2014), which is available at http://www.rgenome.net/cas-offinder/. Here, we use the following settings:
PAM-Type: SpCas9 from Streptococcus pyogenes: 5’-NRG-3’ (R = A or G)
Target genome: Arabidopsis thaliana (TAIR 10)
Mismatch number: 3
After searching for your 20 bp target site in the reference genome, the program displays all similar sites with up to 3 mismatches. If you have more than one hit with zero mismatches (one is always your GOI), you should choose a different target site. If you have 1-3 mismatches, you should take into account that Cas9 might also mutagenize these sites, especially if these mismatches are at the 5’ end of the 20 bp sequence (Semenova et al., 2011). Even though the affinity for Cas9 will be lower than to your GOI and plants seem to be in general less affected by off targeting (Feng et al., 2014), we recommend careful sequencing of these off target site in the knockout plants to ensure the absence of mutations in these genes. - Consider using a 20 bp target site that also contains a recognition site of a commercially available restriction enzyme. The target site of the restriction enzyme should span the site of Cas9 cleavage (3 bp in front of the PAM). This will allow you to use the restriction enzyme length polymorphism assay to detect mutations in your GOI.
- Search your gene of interest (GOI) for a GN19NGG sequence on both strands to find putative target sites. The NGG is the Streptococcus pyogenes Cas9 protospacer adjacent motive (PAM), which has to be present in the target locus for efficient binding of the Cas9 protein (Jinek et al., 2012). The GN19 represents the 20 bp long protospacer motif, defining the target site where you want to create mutations. This 20 bp sequence, which marks the 5’ end of your sgRNA molecule, should start with a G, since this is a prerequisite for transcription of the sgRNA under the control of the U6-26 promoter of Arabidopsis.
- Subcloning of 20 bp protospacer sequence into pFH6
- An overview how to perform the subcloning of the protospacer sequence into pFH6 is given in Figure 2.
- Order forward and reverse primers for your candidate target sequence N20 with overlaps for cloning and dilute them to a final concentration (f.c.) of 10 μM.
Forward primer: TTCG-GN19
Reverse primer: AAAC-N19 (reverse complement) C (see Figure 2)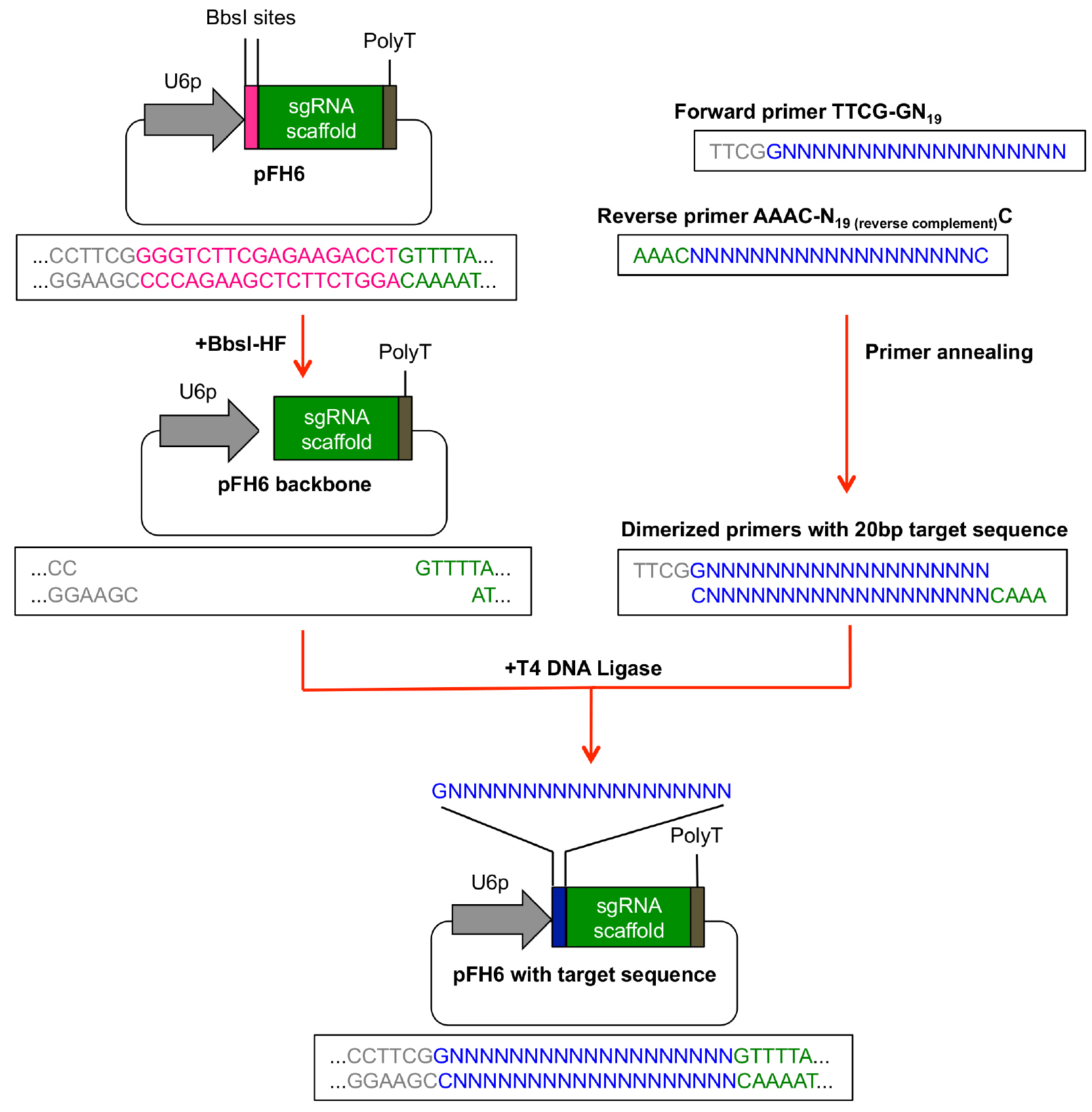
Figure 2. Subcloning of protospacer sequence in pFH6. The 20 bp protospacer sequence can be integrated between the sgRNA scaffold and the U6-26 promoter (U6p) by ligation of dimerized primers into BbsI-digested pFH6 vector. - Pipette 10 μl of each primer dilution into a 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube and mix.
- Heat primer mix to 98 °C, 10 min, then 55 °C, 10 min, afterwards slowly cool down to RT (e.g., by switching off the heating block). By doing so, a double stranded DNA including your protospacer sequence (= annealed primers) will be generated.
- Digest pFH6 with BbsI-HF for 3 h at 37 °C.

- Run the restriction digest on an agarose gel and extract the vector backbone (3,612 bp) from the gel using the GeneMATRIX 3 in 1–Basic DNA Purification Kit.
- Ligate annealed primers with digested pFH6 at 4 °C overnight.

- Transform competent MachI E. coli cells with the ligation reaction and spread the transformed cells on LB agar plates supplemented with Amp.
Note: Usually, plating 100 μl of the transformation mixture is sufficient. Protocols for transformation of E. coli cells are provided by the authors upon request. - Verify eight E. coli colonies by colony PCR using primer M13R and your protospacer primer TTCG-N20 with the following setup:

PCR program:
Note: We recommend using pFH6 as negative control. We have sometimes observed fragments at the expected band size (281 bp) in the negative control since the protospacer primer might partly bind to the BbsI-sites. However, positive colonies usually have a much stronger PCR product signal and can therefore be distinguished from negative clones. - Inoculate positive colony in LB medium supplemented with Amp and grow overnight.
- Purify the plasmid using the GeneMATRIX 3 in 1–Basic DNA Purification Kit.
- Sequence the plasmid and verify the sequence of the protospacer insertion using primer M13R (Table 1).
- An overview how to perform the subcloning of the protospacer sequence into pFH6 is given in Figure 2.
- Cloning of final plant T-DNA Cas9 vector using Gibson Assembly
- An overview how to clone the final plant T-DNA Cas9 vector is given in Figure 3.
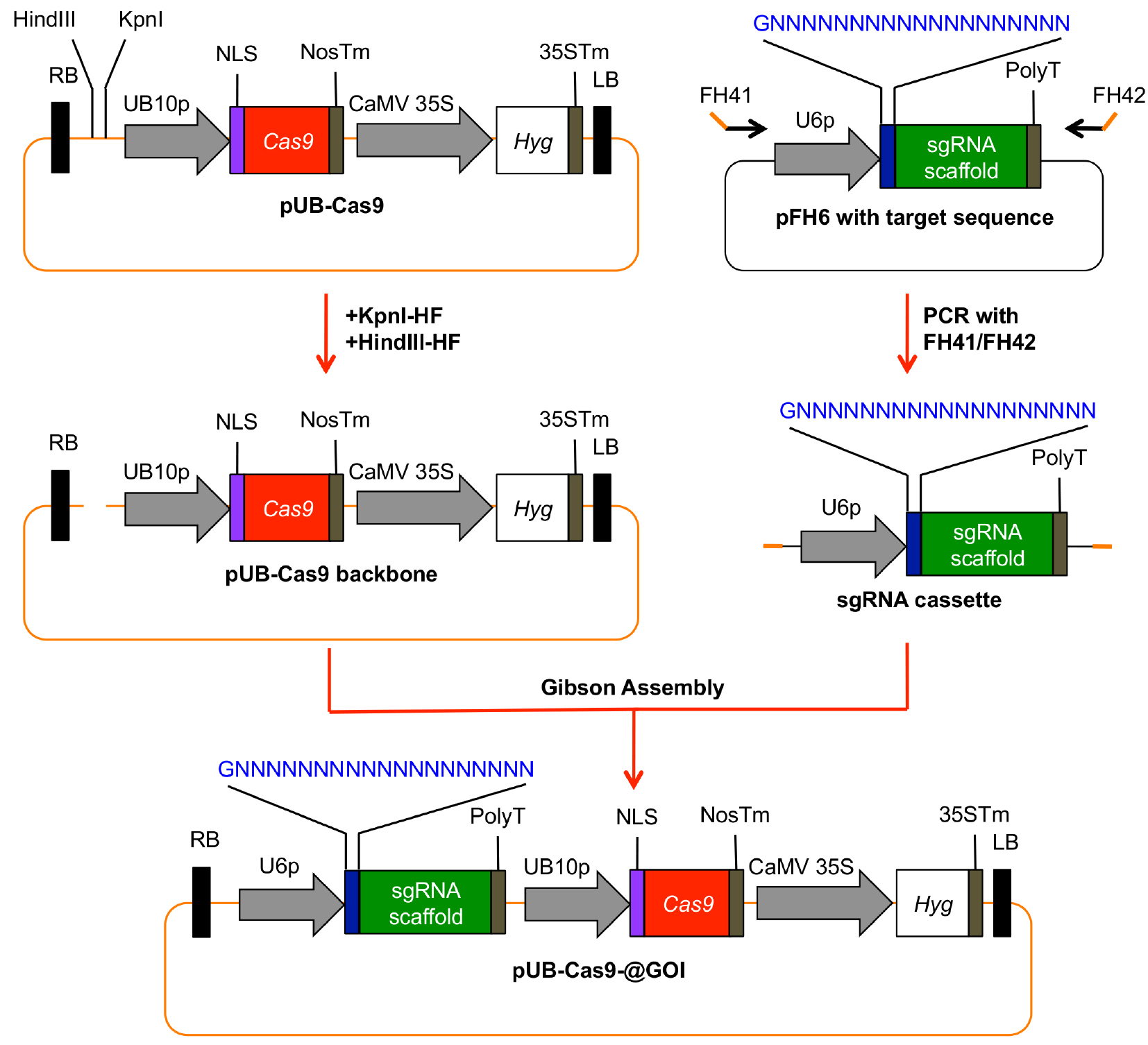
Figure 3. Generation of a plant T-DNA vector with all necessary components for Cas9 induced mutagenesis. The sgRNA cassette including the 20 bp target site is amplified from pFH6 and integrated into KpnI/HindIII-digested pUB-Cas9 via Gibson Assembly. The resulting vector contains the sgRNA cassette as well as the Cas9 gene under the control of the UBIQUITIN10 promoter (UB10p), and the hygromycin (Hyg) resistance gene as selection marker. RB, right T-DNA border; PolyT, polythymidine transcription terminator; NLS, nuclear localization signal; NosTm, nopaline synthase terminator; CaMV35S, Cauliflower Mosaic Virus 2x35S promoter; 35STm, 35S terminator; LB, left T-DNA border. - Digest vector pUB-Cas9 with HindIII-HF and KpnI-HF for 3 h at 37 °C.

Note: Efficient digestion of the pUB-Cas9 plasmid is critical for further cloning steps. In case you have problems in the subsequent cloning steps, try to digest pUB-Cas9 with a fresh batch of enzymes and longer incubation times. - Run out the restriction digest reaction on an agarose gel and extract the vector backbone (14,097 bp) from the gel using the GeneMATRIX 3 in 1–Basic DNA Purification Kit.
- Amplify the sgRNA cassette (expected size: 771 bp) from pFH6 with target sequence using primer FH41 and FH42 (Table 1) and Phusion High-Fidelity polymerase and the following setup:

PCR program:
- Run out the PCR reaction on an agarose gel and extract the sgRNA cassette (771 bp) from the gel using the GeneMATRIX 3 in 1–Basic DNA Purification Kit.
- Assemble the pUB-Cas9 backbone and the sgRNA cassette to generate the final vector pUB-Cas9-@GOI using Gibson Assembly Master Mix according to the manufacturer’s instruction with an incubation time of 1 h.
Note: We propose a nomenclature for the final constructs, where the target gene is marked by the @-sign. A vector designed against the GL1 gene of Arabidopsis would therefore be called pUB-Cas9-@GL1 (Hahn et al., 2017). - Transform competent E. coli cells with the Gibson reaction mixture and spread the transformed cells on LB agar plates supplemented with Kan.
Note: New England Biolabs provides highly competent E. coli cells in the Gibson Assembly Cloning Kit. However, we also used competent E. coli cells produced in our lab. Since these are usually less competent, we recommend plating all transformed cells on the LB agar plate. A protocol for generation of competent MachI E. coli can be found in Sambrook and Russell (2006). - Verify eight positive colonies by colony PCR using primer M13F and FH179 (Table 1) with the following setup:

PCR program:
Note: Expected product size is 779 bp, pUB-Cas9 vector can be used as negative control. - Inoculate positive colony into LB medium supplemented with Kan and let grow overnight.
- Purify the plasmid using the GeneMATRIX 3 in 1–Basic DNA Purification Kit.
- Sequence the plasmid for verification of protospacer sequence insertion using primer FH179 and M13F (Table 1).
Note: The vector system also allows cloning of two different sgRNAs into the pUB-Cas9 vector backbone to induce large deletions in the target genome or to destroy two genes at once. Therefore, both protospacer sequences have to be cloned separately into pFH6 as described. Then, the first sgRNA cassette has to be amplified from its subcloning pFH6-construct using the primers FH41 and FH254 (Table 1). The second sgRNA cassette has to be amplified with FH42 and FH255 (Table 1), using the PCR conditions described above. Using the Gibson Assembly Master Mix, both cassettes can be integrated into KpnI-HF/HindIII-HF-digested pUB-Cas9 in a single step. As two fragments are integrated into the digested vector, the amount of colonies is usually lower compared to the integration of one fragment. However, the proportion of correctly assembled vectors is comparable. The colony PCR can be performed with the same primers but using a longer elongation time (1.5 min), since the PCR reaction amplifies both sgRNA cassettes (expected product size: 1,512 bp). Sequencing should be performed as described above.All cloning steps are summarized in Table 2:
Table 2. Timetable for cloning of plant T-DNA Cas9 vector for targeted gene knockout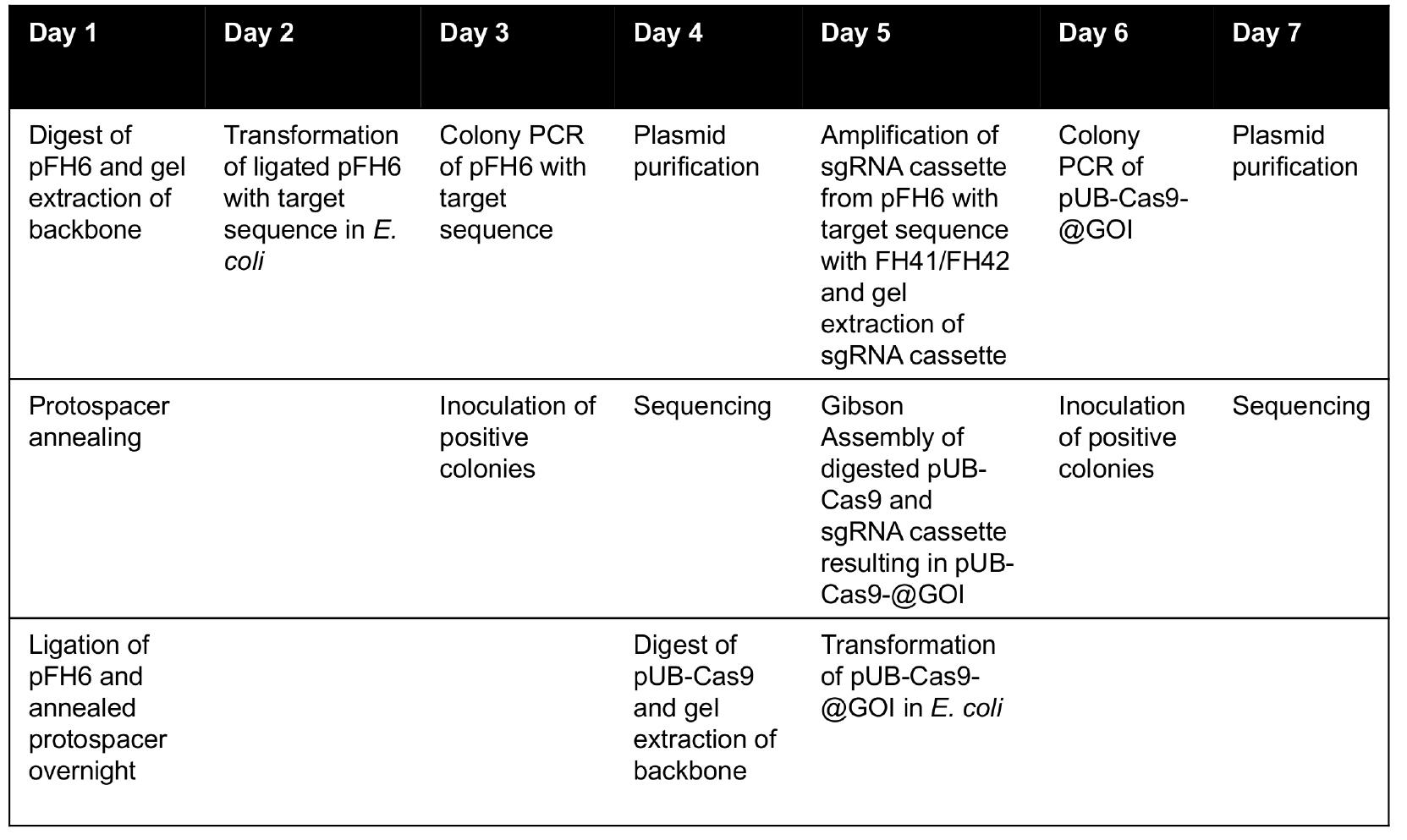
- An overview how to clone the final plant T-DNA Cas9 vector is given in Figure 3.
- Arabidopsis transformation with pUB-Cas9-@GOI
- Transform competent A. tumefaciens cells with 1 μg of pUB-Cas9-@GOI and spread the transformed cells on YEP agar plates supplemented with Rif/Gent/Kan.
Note: Protocols for generation of competent A. tumefaciens cells and transformation of A. tumefaciens cells are described elsewhere (Hofgen and Willmitzer, 1988). - After two days of growth at 30 °C, verify plasmid presence in at least three colonies by colony PCR using primer FH61 and FH201 (Table 1). In order to verify colony, pick half of a colony with a pipette tip and suspend cells in a 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube containing 100 μl ddH2O. Heat to 98 °C for 10 min and use 2 μl as DNA template for the PCR. Streak the other half of the colony on a fresh YEP agar plate supplemented with Rif/Gent/Kan. Grow cells at 30 °C for one day and then store at 4 °C. For the colony PCR, use the following setup:

PCR program:
Note: Expected product size is 1,003 bp. - Transform Arabidopsis plants using Agrobacterium-mediated T-DNA transfer with the floral dipping method (Clough and Bent, 1998).
Note: Per construct, we usually transform four pots with five Arabidopsis plants, each. We recommend removing of all present siliques before transformation to avoid excessive screening for transformation events afterwards. - Select the T1 generation plants for successful T-DNA insertion events on ½ strength MS agar plates supplemented with Hyg. Verify the integration of the T-DNA by isolating leaf genomic DNA (gDNA) and subsequent PCR using primers FH61/FH201with the parameters described before.
Note: A detailed protocol for plant gDNA extraction by isopropanol precipitation can be found elsewhere (Weigel and Glazebrook, 2009).
- Transform competent A. tumefaciens cells with 1 μg of pUB-Cas9-@GOI and spread the transformed cells on YEP agar plates supplemented with Rif/Gent/Kan.
- Detection of Cas9 induced mutations
The Cas9 protein in our vector system is transcribed under the control of the UBIQUITIN10 promoter of Arabidopsis, which allows Cas9 expression in nearly all tissues of the plant (Norris et al., 1993). Since the editing mechanisms of the Cas9 system work independently in each plant cell, T1 generation plants are usually chimeras with distinct genotypes in different cells. Only if mutations occur in germline cells, can progeny plants arise that have a uniform genotype. This is usually the prerequisite for further analyses. Therefore (and due to the limited amount of plants available in the T1 generation), screening approaches for detection of mutations should be applied to T2 or following generations. We recommend screening descendants of three to four independent transformed lines, since mutation efficiencies might vary between different lines due to the integration site of the T-DNA cassette. To choose promising T1 lines for further screening, we also searched for mutational events in the T1 generation. We suggest to screen the plants for mutation in this way:- Amplify the genomic region around the Cas9 cutting site in your GOI (± 300-500 bp upstream and downstream) with gene specific primers from leaf gDNA using Phusion polymerase.

PCR program:
- Run out the PCR products on an agarose gel and extract your GOI from the gel using the GeneMATRIX 3 in 1–Basic DNA Purification Kit.
- Sequence PCR product with Sanger sequencing. When Cas9 was active and mutations occurred at least in a part of the leaf cells, the sequencing histogram will show a mixture of WT sequence and mutated sequences (Figure 4).
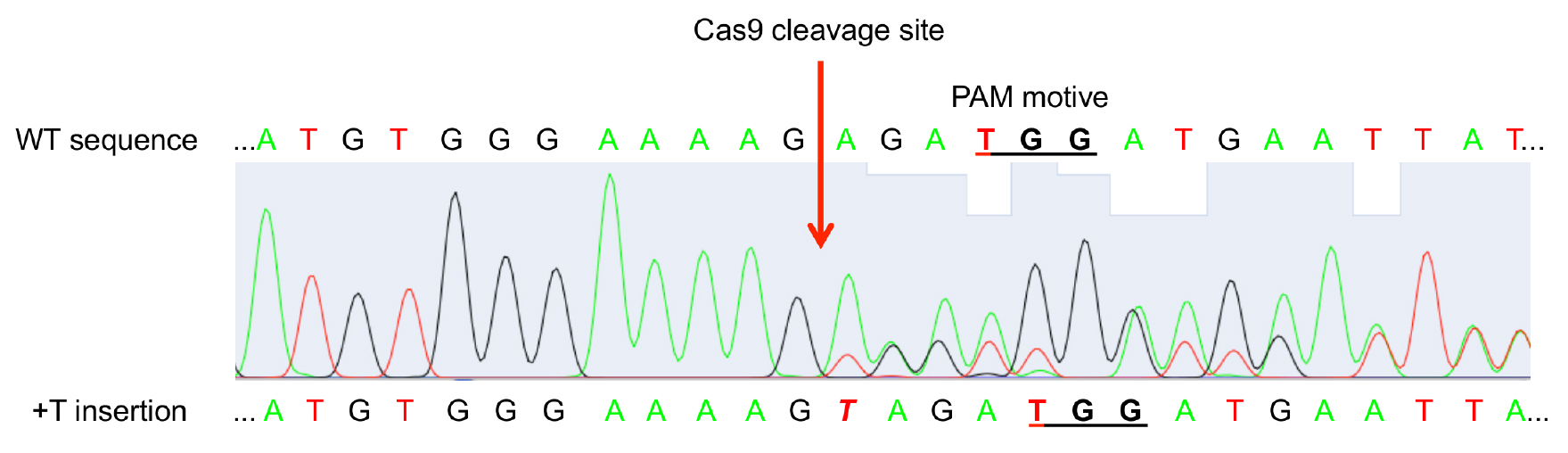
Figure 4. Exemplary sequencing result histogram of amplified target gene from chimeric leaf gDNA. Double peaks appear at the site of Cas9 cleavage (3 bp in front of the PAM motive NGG) pointing to mutation events in the GOI in a part of the leaf cells.
The efficiency of the Cas9 system varies considerably as its mutagenic effect relies on various aspects, such as: the plant species, Cas9 and sgRNA expression levels, and the sequence of the target loci (Bortesi and Fischer, 2015; Paul and Qi, 2016). Therefore, it is difficult to predict how many plants have to be screened to identify a heritable mutation. We recommend starting screening 30 plants per line. Screening for mutations in the T2 generation can be performed by amplification and Sanger sequencing of your GOI as described before. As this can become costly, several methods enable detecting mutations on genomic level without sequencing. - If you expect a specific phenotype due to the knockout of your gene, the easiest way to screen for mutations is a visual screen in the first place. These phenotypes can be changes in anatomy or survival of plants on selection medium. Plants that show a phenotype are then analyzed on genomic level as described above.
- If you target two sites in your GOI at the same time, a simultaneous cleavage with two sgRNAs can result in large deletions, which can already be detected during the PCR amplification of your GOI (Figure 5A). Larger deletions can in theory also occur using one sgRNA, however, we usually discovered small indels in the range of a few bp, which usually cannot be detected by PCR product size difference using agarose gel electrophoresis.
Note: If you expect that only few cells contain the expected mutation (e.g., in chimeric plants), you can improve the PCR amplification efficiency of the mutant alleles by digesting unmutated gDNA with a restriction enzyme that cuts between the two sgRNA target sites before PCR amplification of your GOI.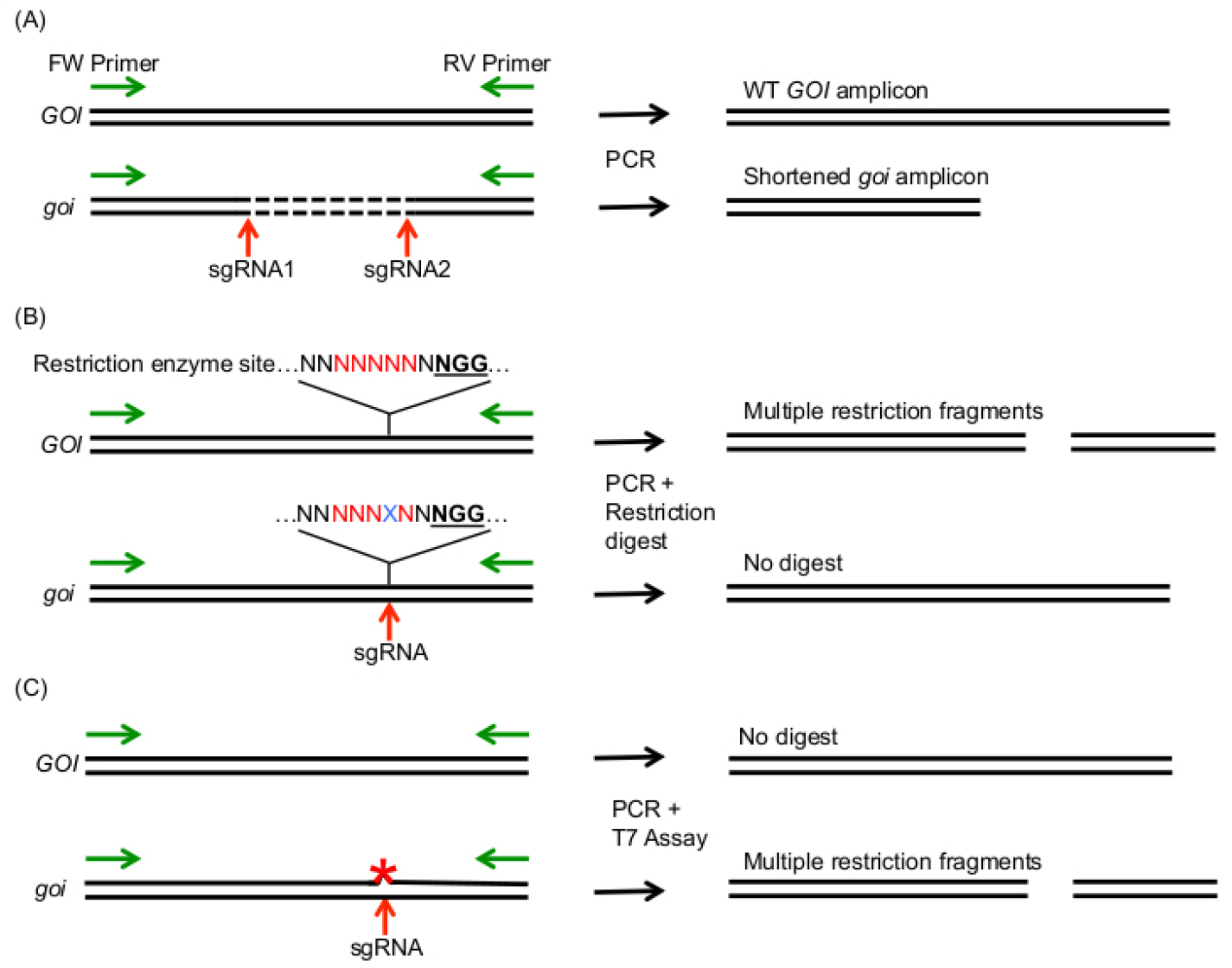
Figure 5. Summary of methods that allow the detection of induced mutations after amplification of the GOI with a forward (FW) and reverse (RV) primer (green arrows). A. Usage of two sgRNAs can induce larger deletions in the GOI, which can be detected by PCR amplicon size difference between WT and mutated GOI (goi). B. If a restriction site (red letters) is present in the mutagenic region 3 bp in front of the PAM site (bold, underlined), mutations (blue X) lead to cleavage resistant PCR amplicons. C. The T7 Endonuclease assay allows cleavage of heteroduplexes, which are produced by imperfect DNA pairing due to mutations on one strand of the DNA amplicon (red asterisk). - The restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) assay is an elegant method to detect bp exchanges or small indels in your GOI. The advantage of this method is that heterozygous, biallelic and homozygous mutations can be detected (Figure 5B). The RFLP assay relies on the disruption of a restriction enzyme target site by Cas9 induced mutations. Therefore, the restriction enzyme target site should span the region at 3 bp in front of the PAM motive. For detection of mutations, the GOI is amplified with gene specific primers as described above. The PCR amplicon is then digested with the restriction enzyme of choice according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The sizes of the restriction fragments are analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. For the RFLP assay, amplify your GOI as described before. Separate the PCR products on an agarose gel and extract the PCR product from the gel using the GeneMATRIX 3 in 1–Basic DNA Purification Kit. Digest the PCR product with the suitable restriction enzyme according to the manufacturer’s instruction.
Notes:- WT gDNA should be used as negative control.
- In case you have a homozygous or a heterozygous mutation in your GOI, you either get only the undigested PCR amplicon or a mixture of undigested and digested PCR bands.
- It can be favorable if your PCR product contains more than one cleavage site of your restriction enzyme (which are not targeted by the Cas9) as it provides you with an internal control that the digest itself worked.
- If you have already detected mutations in your T1 plants by sequencing, you can use the sequenced PCR product as positive control for this assay.
- If you expect only small amounts of mutant alleles (e.g., in chimeric plants), you can enrich these amplicons by digesting the gDNA with the restriction enzyme before PCR amplification of your GOI. In this case, no other cut sites besides the one in the sgRNA target site should be present between your primer annealing sites.
- WT gDNA should be used as negative control.
- The T7 endonuclease assay and the Surveyor assay allow detection of small indels and bp exchanges in your target site (Figure 5C). First, the GOI is PCR amplified using a proofreading DNA polymerase. The PCR amplicon is then denatured and reannealed. In this step, ssDNA strands containing a mutation will anneal to DNA strands that do not contain a mutation, leading to non-perfectly matching dsDNA strands. These heteroduplexes are then recognized and cleaved by the T7 Endonuclease I or the Surveyor Nuclease. The restriction fragment pattern is analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. The advantage of these methods is that they do not require a restriction site within your gRNA target site. For details on this method, we refer to detailed protocols of the Endonuclease suppliers (e.g., https://www.neb.com/protocols/2014/08/11/determining-genome-targeting-efficiency-using-t7-endonuclease-i) and the experimental procedures of other research groups (Mao et al., 2013; Xie and Yang, 2013; Qiu et al., 2004).
Note: These assays are not able to detect homozygous mutations as no heteroduplexes occur.
- Amplify the genomic region around the Cas9 cutting site in your GOI (± 300-500 bp upstream and downstream) with gene specific primers from leaf gDNA using Phusion polymerase.
Data analysis
- There is no specific requirement for large-scale data analysis to generate Cas9-mediated knockout mutants. The mutagenic effect of the Cas9 system varies considerably depending on the plant species, Cas9 and sgRNA expression levels, and the sequence of the target loci (Bortesi and Fischer, 2015; Paul and Qi, 2016). Additionally, the Cas9 system produces chimeric plants due to the possibility of independent mutation events in each cell. Therefore, statistical analyses of mutation efficiencies are complicated and the results of one experiment might not be transferable to another one, especially if a different sgRNA is used.
- Sequencing data obtained from transformed plants can be compared to sequences from WT plants using alignment tools like MUSCLE with default settings (Edgar, 2004). Sequencing histograms can be analyzed using 4Peaks software.
Notes
- All analyses on gDNA level (sequencing, RFLP-assay, T7 assay) rely on the gDNA of a single leaf. If your knockout mutant does not display a visible phenotype and the Cas9 cassette is still integrated into the plant genome, it is difficult to tell whether you are analyzing a chimeric mutation only present in the leaf that you used for gDNA isolation or if your whole plant is already mutagenized. You should therefore consider the following aspects.
- Isolation of gDNA from several different leaves followed by GOI-amplification should result in similar sequencing histograms.
- The mutation should show a Mendelian inheritance pattern in the progeny generation.
- Loss of the Cas9 T-DNA cassette by backcrossing and/or segregation should not affect the mutation. The presence of the Cas9 T-DNA can be detected by PCR using primers FH61/FH201 and plant gDNA as template.
Recipes
- LB-medium
10 g/L Bacto-tryptone (BD)
5 g/L yeast extract (BD)
5 g/L NaCl (Fisher Scientific)
Optional: 15 g/L Bacto agar for plates (BD) - YEP-medium
10 g/L yeast extract (BD)
10 g/L Bacto-peptone (BD)
5 g/L NaCl
Optional: 15 g/L Bacto agar for plates (BD) - ½ MS-medium
2.2 g/L Murashige & Skoog medium (Duchefa Biochemie)
0.5 g/L MES (Carl Roth)
Adjust pH to 5.7 with KOH (Carl Roth)
Optional: 8 g/L plant agar for plates (Duchefa Biochemie)
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Cluster of Excellence on Plant Science (CEPLAS, EXC 1028) and the HHU Center for Synthetic Life Sciences (CSL). We thank Peter Hegemann and André Greiner (Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin) for providing us with Cas9 and sgRNA genes. We thank Holger Puchta, Felix Wolter and Dr. Nadine Rademacher for helpful discussions. We thank Franziska Kuhnert for critical reading of the manuscript. The protocol is adapted from Hahn et al. (2017).
References
- Bae, S., Park, J., and Kim, J. S. (2014). Cas-OFFinder: a fast and versatile algorithm that searches for potential off-target sites of Cas9 RNA-guided endonucleases. Bioinformatics 30(10): 1473-1475.
- Baltes, N. J. and Voytas, D. F. (2015). Enabling plant synthetic biology through genome engineering. Trends Biotechnol 33(2): 120-131.
- Bortesi, L. and Fischer, R. (2015). The CRISPR/Cas9 system for plant genome editing and beyond. Biotechnol Adv 33(1): 41-52.
- Clough, S. J. and Bent, A. F. (1998). Floral dip: a simplified method for Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 16(6): 735-743.
- Edgar, R. C. (2004). MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32(5), 1792-1797.
- Fauser, F., Schiml, S., and Puchta, H. (2014). Both CRISPR/Cas-based nucleases and nickases can be used efficiently for genome engineering in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 79(2): 348-359.
- Feng, Z., Mao, Y., Xu, N., Zhang, B., Wei, P., Yang, D. L., Wang, Z., Zhang, Z., Zheng, R., Yang, L., Zeng, L., Liu, X. and Zhu, J. K. (2014). Multigeneration analysis reveals the inheritance, specificity, and patterns of CRISPR/Cas-induced gene modifications in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(12): 4632-4637.
- Hahn, F., Mantegazza, O., Greiner, A., Hegemann, P., Eisenhut, M. and Weber, A. P. (2017). An efficient visual screen for CRISPR/Cas9 activity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci 8: 39.
- Heigwer, F., Kerr, G. and Boutros, M. (2014). E-CRISP: fast CRISPR target site identification. Nat Methods 11(2): 122-123.
- Hofgen, R. and Willmitzer, L. (1988). Storage of competent cells for Agrobacterium transformation. Nucleic Acids Res 16(20): 9877.
- Jinek, M., Chylinski, K., Fonfara, I., Hauer, M., Doudna, J. A. and Charpentier, E. (2012). A programmable dual-RNA-guided DNA endonuclease in adaptive bacterial immunity. Science 337(6096): 816-821.
- Lei, Y., Lu, L., Liu, H. Y., Li, S., Xing, F. and Chen, L. L. (2014). CRISPR-P: a web tool for synthetic single-guide RNA design of CRISPR-system in plants. Mol Plant 7(9): 1494-1496.
- Liang, G., Zhang, H., Lou, D. and Yu, D. (2016). Selection of highly efficient sgRNAs for CRISPR/Cas9-based plant genome editing. Sci Rep 6: 21451.
- Mao, Y., Zhang, H., Xu, N., Zhang, B., Gou, F. and Zhu, J. K. (2013). Application of the CRISPR-Cas system for efficient genome engineering in plants. Mol Plant 6(6): 2008-2011.
- Norris, S. R., Meyer, S. E. and Callis, J. (1993). The intron of Arabidopsis thaliana polyubiquitin genes is conserved in location and is a quantitative determinant of chimeric gene expression. Plant Mol Biol 21(5): 895-906.
- Pacher, M. and Puchta, H. (2016). From classical mutagenesis to nuclease-based breeding - directing natural DNA repair for a natural end-product. Plant J.
- Paul, J. W., 3rd and Qi, Y. (2016). CRISPR/Cas9 for plant genome editing: accomplishments, problems and prospects. Plant Cell Rep 35(7): 1417-1427.
- Qiu, P., Shandilya, H., D'Alessio, J. M., O'Connor, K., Durocher, J. and Gerard, G. F. (2004). Mutation detection using Surveyor nuclease. Biotechniques 36(4): 702-707.
- Salomon, S. and Puchta, H. (1998). Capture of genomic and T-DNA sequences during double-strand break repair in somatic plant cells. EMBO J 17(20): 6086-6095.
- Sambrook, J. and Russell, D. W. (2006). The inoue method for preparation and transformation of competent E. coli: "ultra-competent" cells. CSH Protoc 2006(1).
- Schiml, S., Fauser, F., and Puchta, H. (2014). The CRISPR/Cas system can be used as nuclease for in planta gene targeting and as paired nickases for directed mutagenesis in Arabidopsis resulting in heritable progeny. Plant J 80: 1139-1150.
- Schiml, S. and Puchta, H. (2016). Revolutionizing plant biology: multiple ways of genome engineering by CRISPR/Cas. Plant Methods 12: 8.
- Semenova, E., Jore, M. M., Datsenko, K. A., Semenova, A., Westra, E. R., Wanner, B., van der Oost, J., Brouns, S. J. and Severinov, K. (2011). Interference by clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat (CRISPR) RNA is governed by a seed sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(25): 10098-10103.
- Weigel, D. and Glazebrook, J. (2009). Quick miniprep for plant DNA isolation. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2009(3): pdb prot5179.
- Xie, K. and Yang, Y. (2013). RNA-guided genome editing in plants using a CRISPR-Cas system. Mol Plant 6(6): 1975-1983.
- Xie, K., Zhang, J. and Yang, Y. (2014). Genome-wide prediction of highly specific guide RNA spacers for CRISPR-Cas9-mediated genome editing in model plants and major crops. Mol Plant 7(5): 923-926.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Hahn, F., Eisenhut, M., Mantegazza, O. and Weber, A. P. M. (2017). Generation of Targeted Knockout Mutants in Arabidopsis thaliana Using CRISPR/Cas9. Bio-protocol 7(13): e2384. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2384.
Category
Plant Science > Plant molecular biology > DNA > Mutagenesis
Molecular Biology > DNA > Mutagenesis
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










