- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Qualitative and Quantitative Assay for Detection of Circulating Autoantibodies against Human Aortic Antigen
Published: Vol 7, Iss 13, Jul 5, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2367 Views: 10519
Reviewed by: Jia LiPorkodi PanneerselvamAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Protein Turnover Dynamics Analysis With Subcellular Spatial Resolution
Lorena Alamillo [...] Edward Lau
Aug 5, 2025 2406 Views

Immunopeptidomics Workflow for Isolation and LC-MS/MS Analysis of MHC Class I-Bound Peptides Under Hypoxic Conditions
Hala Estephan [...] Eleni Adamopoulou
Nov 20, 2025 1879 Views

Quantitative Proteomics of Nitrosylated Proteins in Melanoma Using the Biotin-Switch Technique Combined With Tandem Mass Tag Labeling
Vipin K. Yadav [...] Sanjay Premi
Dec 5, 2025 1549 Views
Abstract
Increased amount of autoantibodies in human sera are the hallmark of autoimmune diseases (Wang et al., 2015). In case of known antigen, detection of autoantibodies is done using laboratory based methods. However, in most autoimmune diseases, knowledge of self-antigen is still vague. We have developed an ELISA-based quantitative assay to detect the presence of autoantibodies as well as to measure the circulating autoantibodies in the sera of patients suffering from large vessel vasculitis (LVV), an autoimmune disease (Chakravarti et al., 2015). Using this assay, we detected the increase in anti-aortic antibodies in LVV patient’s sera. We have further verified the results by independent biochemical techniques and found the specificity to be > 94% (Chakravarti et al., 2015). This method can be uniquely modified to suit any autoimmune, in particular organ specific, disease and thus has wider applications in the detection and quantification of autoantibodies.
Keywords: ELISABackground
There are about 80-100 autoimmune diseases wherein immune cells recognize a self-protein as a foreign antigen, and get activated to generate humoral response. Though the trigger for most autoimmune diseases remains a mystery, presence of higher levels of antibodies in the patient’s sera is very common (Wang et al., 2015). Some of the examples include antibodies against neutrophil cytoplasmic antigens in small vessel vasculitis, myelin basic protein in multiple sclerosis, glutamate decarboxylase in type 1 diabetes etc. (Wang et al., 2015). Limited knowledge of autoantigen in most autoimmune diseases presents a challenge for both the detection of disease as well as understanding the pathogenesis. However, ability to detect autoantibodies in the sera provides a diagnostic and prognostic advantage. Discovering a reliable autoantigen in autoimmune diseases are needed to make better clinical decisions. LVV is a spectrum of autoimmune diseases affecting aorta or its primary branch vessels. Like many others, its etiology and cure are not known (Buttgereit et al., 2016). We have developed a qualitative and quantitative assay to detect the presence of autoantibody in the human sera targeting against the human aortic antigen. Our assay provides a tool to find autoantigen in any affected/damaged tissue and in any disease model. We looked for the presence of autoantigen in the human thoracic aortic aneurysms using patients’ sera and tested the specificity of the assay by comparing the sera obtained from related subsets of autoimmune or non-immune diseases. We utilized discarded aortic tissues from aortic reconstruction surgeries and made soluble extracts of aorta to set up the assay (Figure 1). Using this method we performed a high throughput screen for detecting autoantibody in more than 100 sera against aortic antigen (Chakravarti et al., 2015).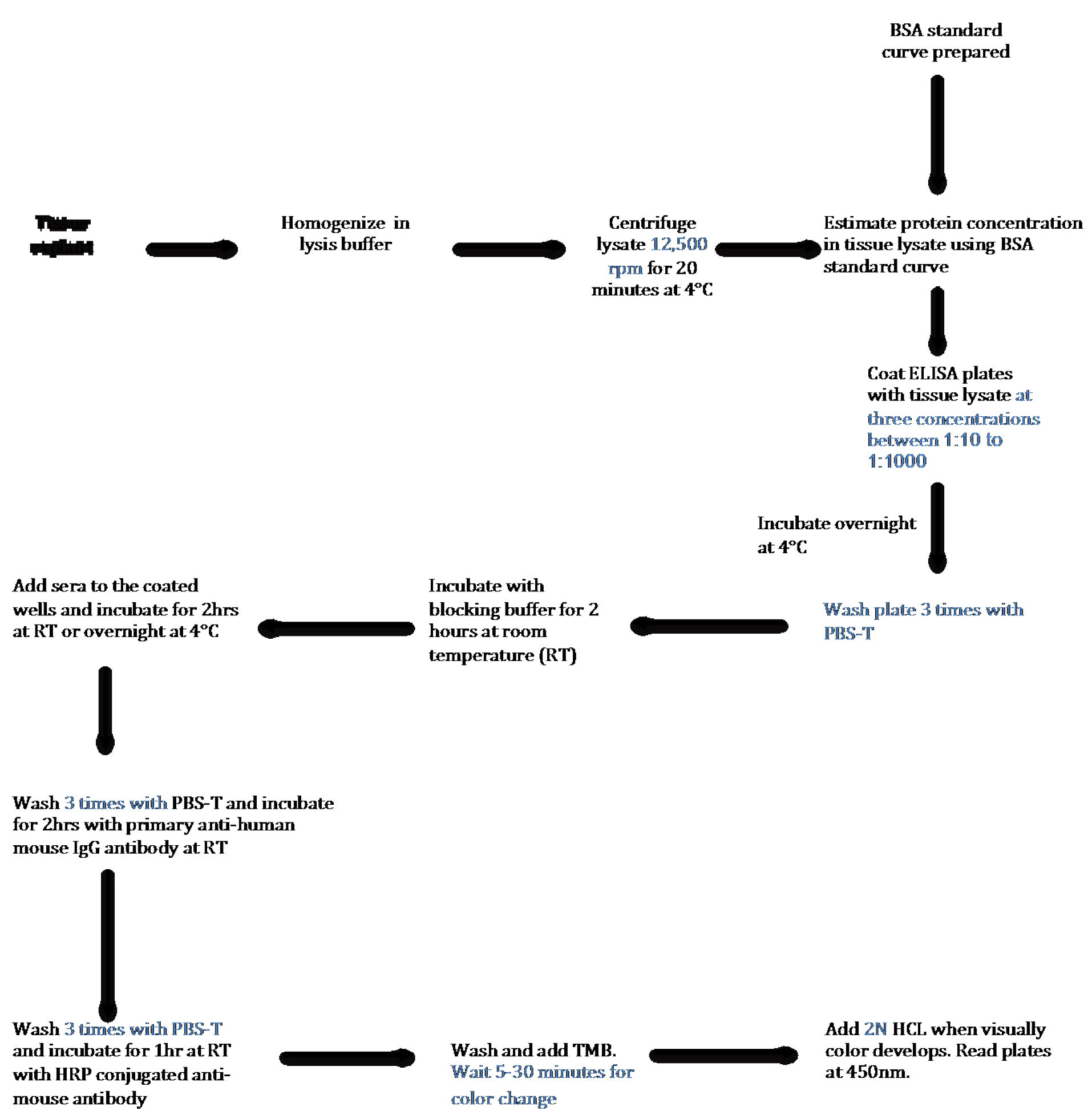
Figure 1. Schematic Flow Diagram of ELISA to detect autoantibody in human tissue lysates. Step-by-step outline of the method used to detect and quantify autoantibodies present in the sera against antigen present in tissue.
Materials and Reagents
- 5 ml sterile polystyrene round bottom tubes (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 352008 )
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf tubes (USA Scientific, catalog number: 1615-5500 )
- 15 ml centrifuge tubes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 339650 )
- Greiner 96 well, F-Bottom, clear microplate (Greiner Bio One International, catalog number: 655001 )
- 200 μl pipette tip (USA Scientific, catalog number: 1111-1700 )
- 1,250 μl pipette tip (USA Scientific, catalog number: 1112-1720 )
- Immulon 2 HB: high affinity protein binding plates (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 3455 )
- Paper towel
- Human Specimen
Note: Human tissue explant as well as sera should be collected under institutionally approved IRB protocol. - Protease
- Phosphatase inhibitor (PhosSTOP) (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 04906837001 )
- Protein Assay dye (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 5000006 )
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A9418 )
- Phosphate-buffered saline-Tween (PBS-T) (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP293810 )
- Antibodies:
- Ultra-TMB (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 34029 )
- 2 N HCl (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: SA431-500 )
- Tris buffer, pH 7.4 (Fischer Scientific, catalog number: BP152-1 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, product number: S9888 )
- Triton X-100 (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 1610407 )
- Sodium orthovanadate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S6508 )
- Sodium fluoride (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 919 )
- Glycerophosphate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G9422 )
- Sodium pyrophosphate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P8010 )
- Non-fat dry milk powder (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 1706404 )
- Cell lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- Blocking buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 2-20 μl pipettes (Alkali Scientific, catalog number: P9280-20U )
- 20-200 μl pipettes (Alkali Scientific, catalog number: P9280-200U )
- Scissors (Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 08-951-20 )
- Table top centrifuge (Labnet International, model: PrismRTM R, catalog number: C2500-R )
- Orbital shaker (Benchmark Scientific, model: BT302 )
- Refrigerator
- Plate reader (BMG LABTECH, model: FLUstar Omega )
- Homogenizer (Thomas Scientific, model: SCILOGEX D160 )
Software
- MS Excel
- GraphPad Prism 7
Procedure
- Making tissue lysates
- Chop tissue into small pieces (as much possible) and place in a sterile round bottom tube on ice.
- Add 5 ml of cold cell lysis buffer (see Recipes) containing protease and phosphatase inhibitors. Homogenize tissue using tissue homogenizer in sterile lysis buffer at cold temperature by keeping the tube covered in ice to prevent protein denaturation.
- Perform 6-8 cycles, 20-30 sec each, of homogenization. After each cycle, wait for 2 min and evaluate suspension manually for the presence of large pieces of tissues (Figure 2).
Note: If the intact tissues pieces are observed, continue homogenization to improve solubilization. Make sure that tissue lysate stays cold during homogenization. - Centrifuge homogenized lysate at 12,000 x g for 20 min under refrigeration at 4 °C. Transfer supernatants to sterile Eppendorf tubes and keep them cold. If needed, lysate can be stored at -80 °C for long-term.
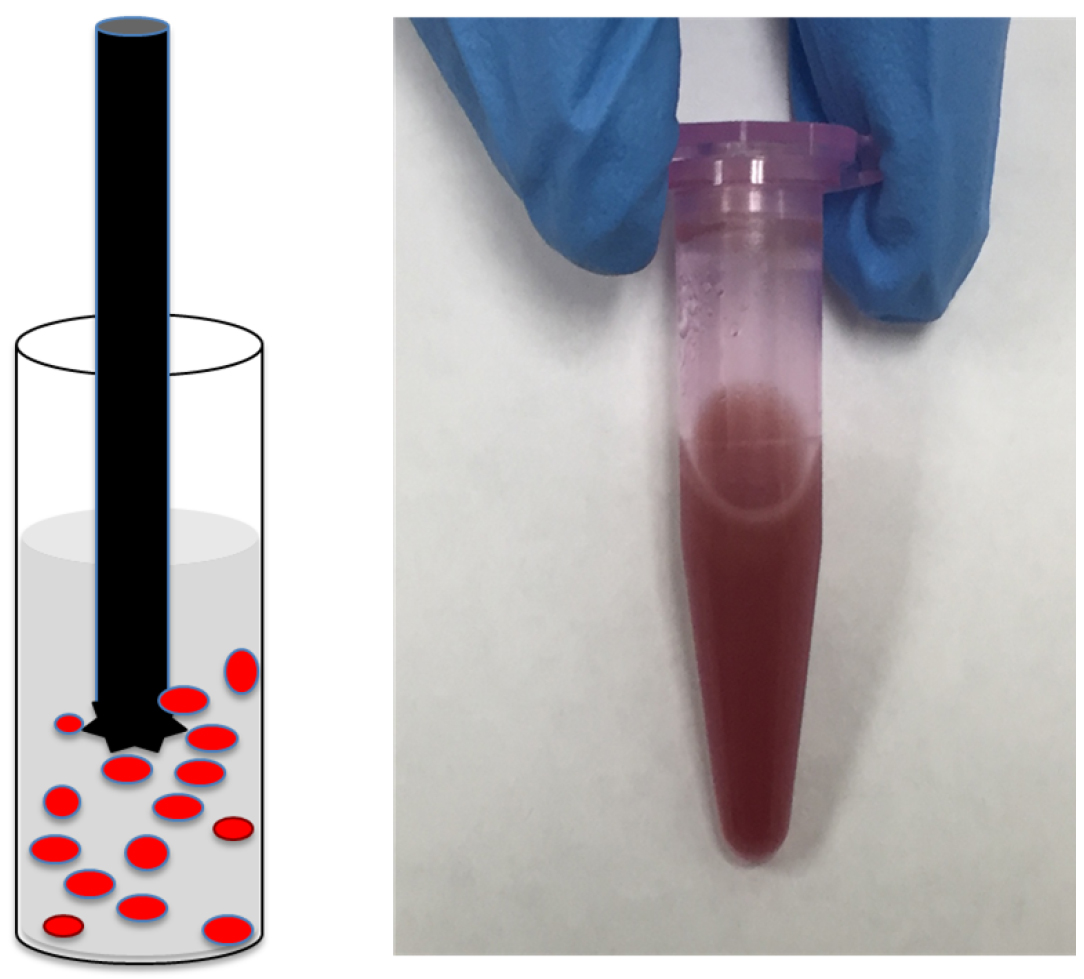
Figure 2. Tissue homogenization. A. Cartoon showing round tube containing red colored pieces of tissue in lysis buffer and a sharp metal homogenizer; B. Representative picture of soluble tissue lysate.
- Chop tissue into small pieces (as much possible) and place in a sterile round bottom tube on ice.
- Measuring protein concentration in tissue lysate
- Pipette a Greiner 96-well plate with 200 µl of pre-diluted (1:5) Bio-Rad Protein Assay dye into each well corresponding to a sample.
Note: BSA standards and tissue lysate usually measured in the same plate, however separated here for clarity. - First, prepare a protein standard curve using BSA concentration in the range of 0-1 mg/ml at the increment of 0.1 mg/ml. To each well containing assay dye, add 1 µl of BSA solution mixing solution with pipette tip, and incubate for 5 min. Each concentration of BSA is assayed in triplicate. Absorbance of wells is measured using plate reader at 595 nm. Wells containing no protein solution (no BSA) are used as blank for subtraction from the actual samples. Average absorbance (blank subtracted average of triplicates) and respective concentrations of BSA samples are plotted in an excel file to obtain the linear equation (Figure 3).
Note: Standard equation of linear functions is: Y = MX + C, where Y is absorbance, X is BSA concentration, M is slope and C is intercept on y-axis.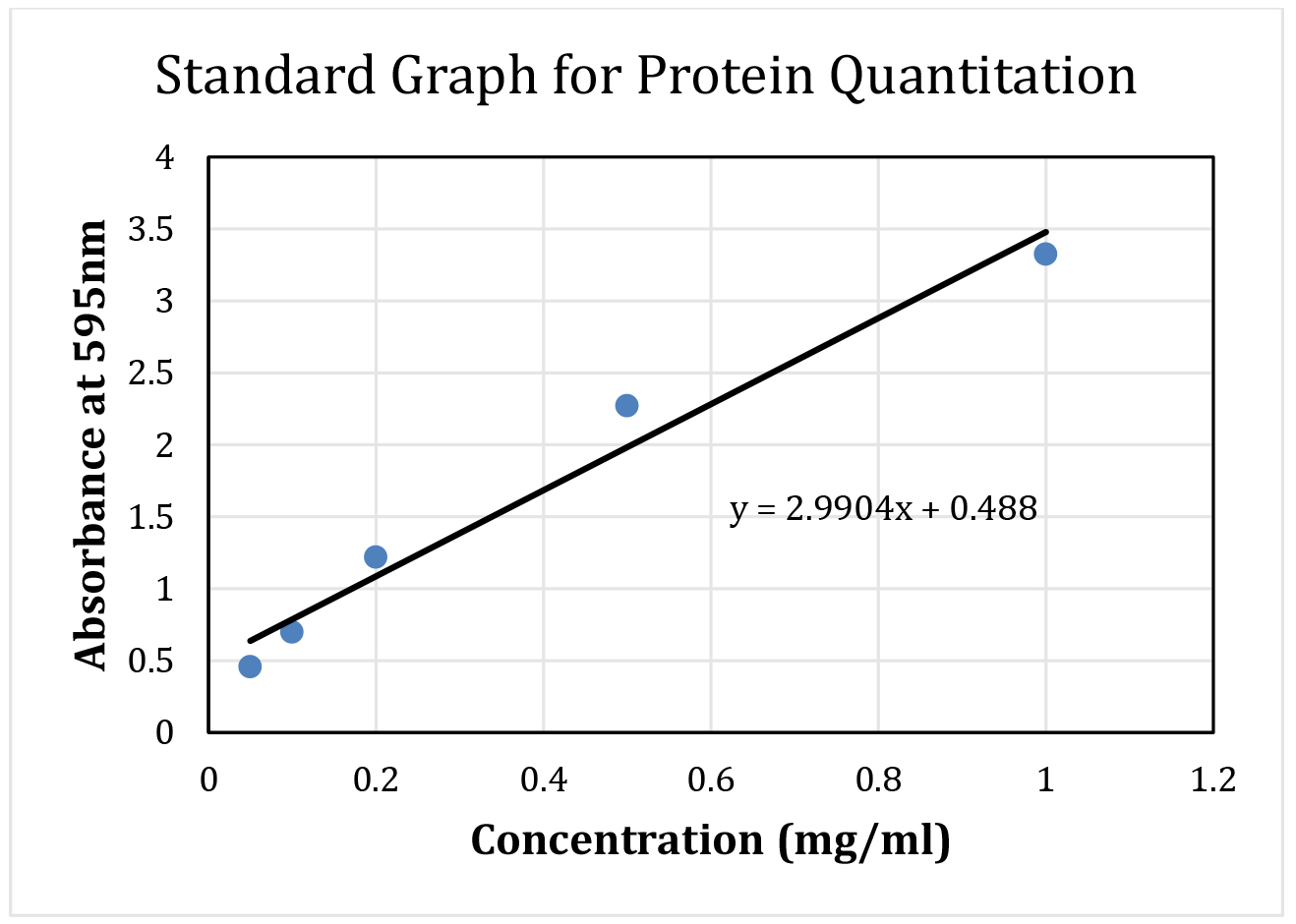
Figure 3. Sample standard curve using BSA with the fitted line and equation. This BSA curve and equation will be used to calculate protein concentration from tissue lysate. - Next, add 1 µl of supernatant from the tissue lysate to each well containing 200 µl of protein assay reagent. In case of high concentration of proteins, dilute tissue lysates in 1:10 or 1:20 with cell lysis buffer before the protein estimation. Measure each sample in triplicate.
- Measure absorbances at 595 nm using plate reader.
- After the blank subtraction, average absorbance values for each sample. Plot final absorbance of each sample on the BSA standard curve to calculate the protein concentrations of the tissue lysate (see step B2). In case tissue lysates are diluted, dilution factor is included for the final calculation.
Note: When calculating the concentration of the sample undergoing ELISA procedure, input the absorbance measured into equation as Y value, and use slope (M) and y-intercept (C) from BSA line equation as constants to calculate protein concentration (X).
- Pipette a Greiner 96-well plate with 200 µl of pre-diluted (1:5) Bio-Rad Protein Assay dye into each well corresponding to a sample.
- ELISA
- Coat Immulon 2 HB plates with 100 µl of soluble tissue lysate by adding in each well. We recommend testing 3 different protein dilutions (ranging from 1:10 to 1:1,000) in PBS buffer for this analysis in triplicate. Use BSA solution of the same protein concentration as tissue lysates. Incubate at 4 °C overnight. In case of any known antigen, use purified proteins of concentrations (5-100 µg/ml) as positive control in the experiment.
- Remove the protein solution by decanting the plate. Wash the wells 3 times with PBS-T (200 µl) by shaking for 5 min at room temperature each time. Tap it upside down on the paper towel to get rid of any retained liquid.
- Block the wells by adding 200 µl of blocking buffer (see Recipes) in each well and incubate for 2 h at room temperature (RT) while shaking at 100 rpm.
- Remove the blocking buffer by decanting.
- Add 200 µl of diluted sera (typical dilutions range from 1-10-1:1,000) in the blocking buffer. We recommend using 3 dilutions of each sera to figure out the best dilutions for subsequent experiments. Also include no sera control for tissue lysate coated wells.
Note: Frozen sera should always be thawed on ice before making dilutions. - Incubate the plate on shaker at 100 rpm for 2 h at RT or overnight at 4 °C.
- Remove sera and wash wells 3 times with PBS-T. Tap it upside down on a paper towel to get rid of any retained liquid.
- Add 200 µl of mouse anti-human IgG antibody, the primary antibody, diluted with blocking buffer in the ratio of 1:5,000. Shake the plate at RT for 2 h at 100 rpm.
- Remove the primary antibody and wash the plate 3 times with PBS-T as in step C7.
- Add 200 µl of anti-mouse IgG conjugated with HRP (diluted in blocking buffer at 1:3,000) and shake the plate for 1 h at RT.
- Remove the secondary antibody by decanting the plate and wash the plate as in step C7.
Note: While performing washing step, prepare the plate reader for plate reading. Set up the program for the wells to be read at 450 nm. - Add 100 µl of ultra-TMB and observe the blue color development. Depending upon the antigen (protein concentration of tissue lysates) and autoantibodies (sera dilutions), some wells may change color to blue before others. Change of color in 5-30 min is desirable. Very quick change of color would require lowering the amount of tissue lysates or increasing the serum dilution. If color change is very slow, takes more than 60 min, increasing the tissue lysates or decreasing the sera dilution, may be needed.
- As desirable change in color is achieved, add 100 µl of 2 N HCl to each well that will change the color to yellow (Figure 4).
- Read plate at 450 nm and note absorbance in each well.
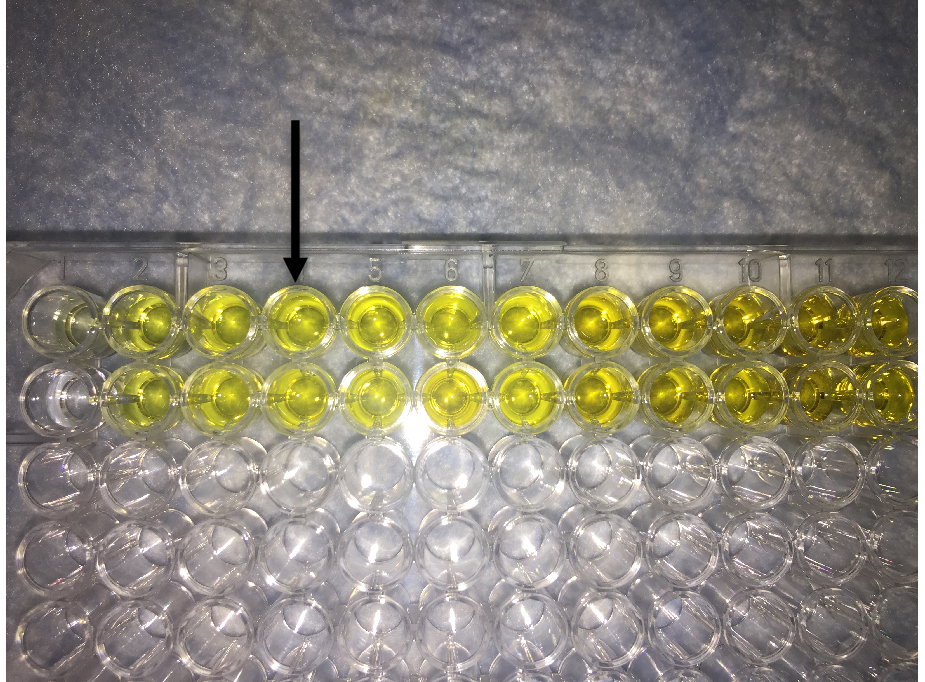
Figure 4. Image showing final readout of ELISA. Addition of HCL to the TMB containing well changes the color of solution from blue to yellow. Arrow shows the desirable intensity of yellow color that should be within the linear range of absorbance of the plate reader.
- Coat Immulon 2 HB plates with 100 µl of soluble tissue lysate by adding in each well. We recommend testing 3 different protein dilutions (ranging from 1:10 to 1:1,000) in PBS buffer for this analysis in triplicate. Use BSA solution of the same protein concentration as tissue lysates. Incubate at 4 °C overnight. In case of any known antigen, use purified proteins of concentrations (5-100 µg/ml) as positive control in the experiment.
Data analysis
- Since all of our samples are tested in triplicate, we averaged the absorbance obtained for each of our patient samples.
- All the samples were clustered in the set of diseases (e.g., sera of patients with large vessel vasculitis or healthy).
- Absorbance of each sera under each set was plotted in a chart (Figure 5).
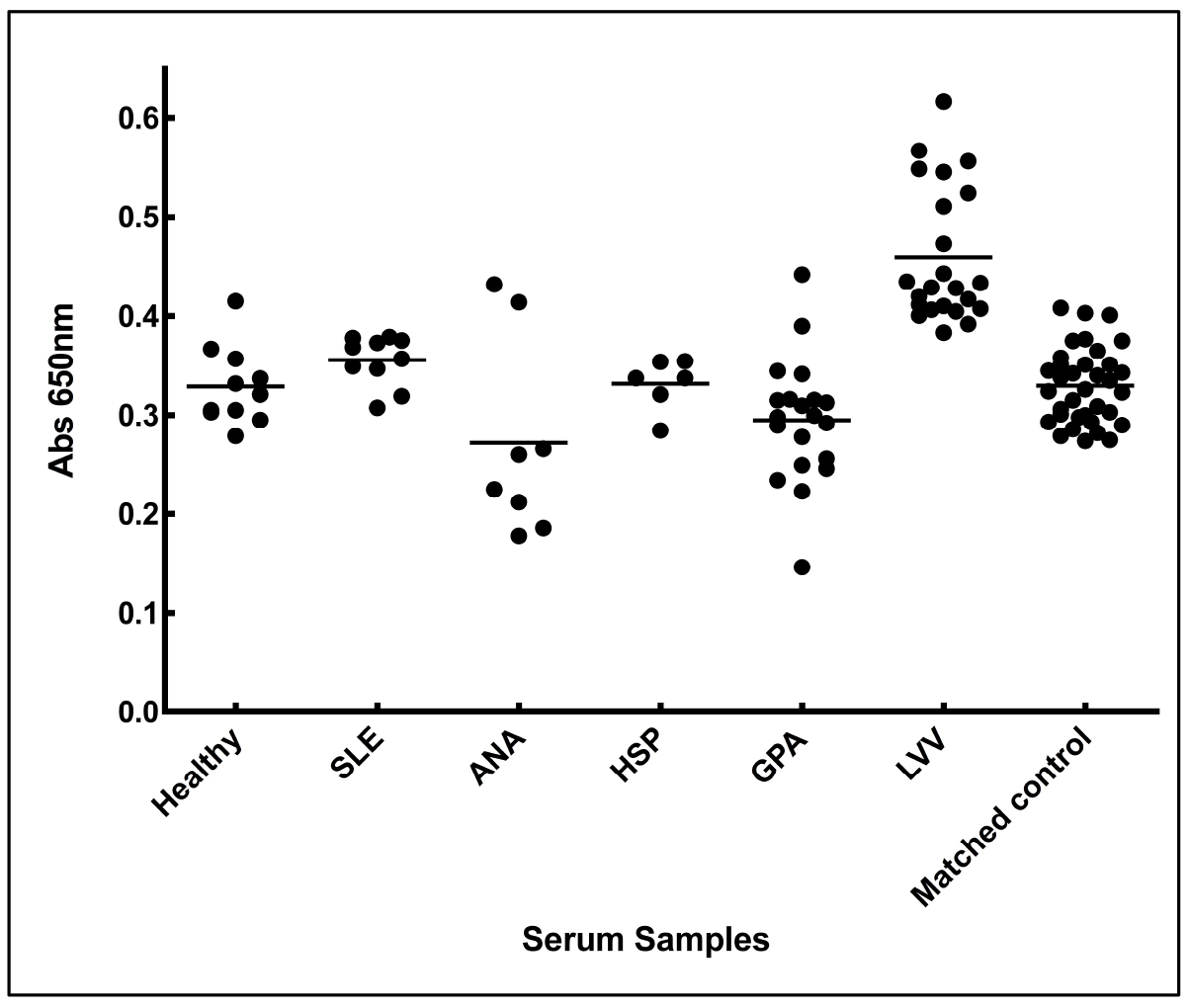
Figure 5. Increased anti-aortic antigen antibody levels in the sera from LVV patient. Sera from patients of LVV (large vessel vasculitis), SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus), ANA (antinuclear antibody) positive, HSP (Henoch-Schonlein purpura), GPA (granulomatosis with polyangitis), matched controls (thoracic aortic aneurysmal control), and healthy individuals were tested for the presence of antibodies against aortic proteins. Adopted from Chakravarti et al., 2015. - Mean absorbance of each set of sera was plotted using column graphs and average option in the GraphPad Prism 7.
- Student’s t-test can be used to compare statistically significant differences between two sets of sera. We preferred two-tailed test to provide stringency to our analysis. Alternatively one can use Mann-Whitney test (parametric option).
- In case of a known antigen, use purified antigen coated plate and known amount of commercial antibodies to prepare a standard curve to facilitate quantification of autoantibodies in the sera. In case where details of antigen are not known, this assay provides a semi-quantitative assay to compare different sets, however exact quantitation can’t be made.
Notes
- This method, when tested with other biochemical analysis, shows significant sensitivity (> 94%). However, it is always recommended to include a positive control and negative control in his assay. Positive control can be a known antigen and antibody (we used commercial antibody to 14-3-3 proteins that we suspected to be present in aorta), on the other hand, we used no sera added as our negative control and blank for absorbance subtraction. Having internal controls allows us to correlate amongst different sets of experiments.
- When comparing human samples, it is common to compare disease vs. normal (or healthy). In our case, we compared autoantibodies in the sera set from patients with LVV with other rheumatic diseases (e.g., GPA, RA, HSP, SLE etc.), patients having thoracic aortic aneurysms due to non-inflammatory causes (e.g., bicuspid valve, matrix disorder etc.), and healthy individuals. This provided additional layers for comparison and strengthened our analysis.
- To verify if the LVV patient has increased autoantibody against aortic protein(s), we performed western analysis and immunohistological analysis, as detailed elsewhere (Chakravarti et al., 2015).
Recipes
- Cell lysis buffer
50 mM Tris buffer, pH 7.4
150 mM NaCl
0.1% Triton X-100
1 mM sodium orthovanadate
10 mM sodium fluoride
10 mM glycerophosphate
5 mM sodium pyrophosphate - Blocking buffer
5% Non-fat dry milk powder
PBS-T
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to American Heart Association Scientist Development Grant (15SDG2308025) and the University of Toledo start-up funds to RC. The protocol and result are adopted from our previously published work (Chakravarti et al., 2015) which was carried out at Cleveland Clinic.
References
- Buttgereit, F., Dejaco, C., Matteson, E. L. and Dasgupta, B. (2016). Polymyalgia rheumatica and giant cell arteritis: a stematic review. JAMA 315(22): 2442-2458.
- Chakravarti, R., Gupta, K., Swain, M., Willard, B., Scholtz, J., Svensson, L. G., Roselli, E. E., Pettersson, G., Johnston, D. R., Soltesz, E. G., Yamashita, M., Stuehr, D., Daly, T. M. and Hoffman, G. S. (2015). 14-3-3 in thoracic aortic aneurysms: identification of a novel autoantigen in large vessel vasculitis. Arthritis Rheumatol 67(7): 1913-1921.
- Wang, L., Wang, F. S. and Gershwin, M. E. (2015). Human autoimmune diseases: a comprehensive update. J Intern Med 278(4): 369-395.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Veerman, B. and Chakravarti, R. (2017). Qualitative and Quantitative Assay for Detection of Circulating Autoantibodies against Human Aortic Antigen. Bio-protocol 7(13): e2367. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2367.
Category
Immunology > Antibody analysis > Antibody detection
Biochemistry > Protein > Quantification
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link