- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
A Reliable Assay to Evaluate the Virulence of Aspergillus nidulans Using the Alternative Animal Model Galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera)
(*contributed equally to this work) Published: Vol 7, Iss 11, Jun 5, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2329 Views: 11154
Reviewed by: Valentine V TrotterShahin S. AliAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

In Vitro Hyphal Branching Assay Using Rhizophagus irregularis
Takaya Tominaga and Hironori Kaminaka
Aug 20, 2024 2288 Views
Silencing Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Gene Using Chitosan Nanoparticle-Mediated dsRNA Delivery System
Chumei Yan [...] Xianan Xie
Jun 5, 2025 2606 Views

A Reliable In Planta Inoculation and Antifungal Screening Protocol for Rhizoctonia solani-Induced Sheath Blight in Rice
Alinaj Yasin [...] Palash Deb Nath
Nov 5, 2025 1527 Views
Abstract
The greater wax moth Galleria mellonella has emerged as an effective heterologous host to study fungal pathogenesis and the efficacy of promising antifungal drugs (Mylonakis et al., 2005; Li et al., 2013). Here, a methodology describing the Aspergillus nidulans infection in G. mellonella larvae, along with insect survival analysis, is reported. This protocol allowed the distinction between virulent A. nidulans strains (such as TNO2A3), which induced high larval mortality rates, to those in which gene deletion was accompanied by reduced pathogenicity such as ∆gcsA and ∆sdeA (Fernandes et al., 2016).
Keywords: Aspergillus nidulansBackground
G. mellonella is an inexpensive model, easy to handle and its innate immune response shares functional similarities with the mammalian immune system. Additionally, larvae and mice infected with fungal mutant strains exhibited similar survival rates (Brennan et al., 2002). Therefore, larvae constitute a convenient animal host to substitute the use of vertebrates in fungal pathogenesis analysis. Despite all the advantages of the insect model, only a few reports have shown the effect of Aspergillus infection in G. mellonella. This protocol describes an efficient methodology to analyze Aspergillus nidulans pathogenesis in G. mellonella larvae.
Materials and Reagents
- Sterile toothpick
- Inoculation loop (microstreaker) (Thermo Fischer Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: SL1S )
- 200-1,000 µl pipette tips (Corning, Axygen®, catalog number: T-1000-B )
- 2-20 µl pipette tips (Corning, Axygen®, catalog number: T-200-Y )
- 15 ml conical tube (Greiner Bio One International, catalog number: 188271 )
- Miracloth filter, pore size 22-25 µm (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 475855 )
- 20 ml syringe (BD, catalog number: 302830 )
- 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube (Corning, Axygen®, catalog number: MCT-150-R )
- Gloves
- Weighing paper
- Glass wool (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 18421 )
- 280 ml plastic boxes
- Galleria mellonella larvae
- Aspergillus nidulans strains (TNO2A3 strain is available commercially in Fungal Genetics Stock Center as #A1149; ∆sdeA and ∆gcsA mutants can be provided by us upon request)
- Sterile deionized water
- Yeast extract (BD, BactoTM, catalog number: 212750 )
- Glucose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G8270 )
- Agar (BD, BactoTM, catalog number: 214010 )
- Uridine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: U3750 )
- Uracil (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: U0750 )
- Zinc sulfate heptahydrate (ZnSO4·7H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000283 )
- Boric acid (H3BO3) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000263 )
- Manganese(II) chloride tetrahydrate (MnCl2·4H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 221279 )
- Iron(II) sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO4·7H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000119 )
- Cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate (CoCl2·6H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000213 )
- Copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO4·5H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000118 )
- Ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000122 )
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000114 )
- 10 N sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution
- Ethanol
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000106 )
- Potassium chloride (KCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9541 )
- Sodium phosphate dibasic (Na2HPO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000317 )
- Potassium phosphate monobasic (KH2PO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000225 )
- Hydrogen chloride (HCl)
- Honey (Local supermarket)
- Glycerol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000123 )
- Milk (Local supermarket)
- Wheat germ (Local supermarket)
- Wheat flour (Local supermarket)
- Wheat bran (Local supermarket)
- Complete media (YUU media) for A. nidulans growth (see Recipes)
- Trace elements solution for Aspergillus (see Recipes)
- 70% ethanol solution (see Recipes)
- PBS buffer (see Recipes)
- Artificial diet for Galleria mellonella (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 100 x 10 mm glass Petri dishes (Corning, PYREX®, catalog number: 3160-100 )
- Autoclave (Prismatec, model: CS-18 )
- Laminar flow cabinet (TROX Technik, model: TLF-A1 )
- 250 ml beaker (Roni Alzi, catalog number: 2-570 )
- Blunt tipped tweezer (EMD Millipore, catalog number: XX6200006P )
- Bunsen burner/lighter
- Hemocytometer (Hausser Scientific, catalog number: 3500 )
- Optical microscope with a 100x objective (American Optical Corporation)
- 10 µl Hamilton 700 series cemented syringe (Hamilton, catalog number: 80300 )
- Analytical balance (Denver Instrument, model: XL-410 , catalog number: 8515.1)
- Spatula (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z282774 )
- Graduated cylinder (Roni Alzi, catalog number: 2-950 )
- Glass bottle (Corning, PYREX®, catalog number: 1395-1L )
- Manual adjustable pipette (200-1,000 µl, Pipetman P1000) (Gilson, catalog number: F123602 )
- Manual adjustable pipette (2-20 µl, Pipetman P20) (Gilson, catalog number: F123600 )
- Thermostatic incubators (Fanem®, model: 515 )
Software
- GraphPad Prism 7.0 program (GraphPad Software; https://www.graphpad.com/)
Procedure
- Fungal growth and conidia isolation
- Prepare the culture media (solid YUU media) for A. nidulans growth and heat-sterilize by autoclaving at 121 °C for 20 min. Cool the media at room temperature until it turns pleasant to touch.
- Transfer approximately 15 ml of the melted culture media to a sterile Petri dish. Let the agar plate solidify and air-dry for 20 min at room temperature.
Note: From this step to the end of Procedure B, it is recommended to work in a laminar flow cabinet. - From a stock culture (usually stored in slant culture tubes or Petri dishes containing solid media), pick a small quantity of fungal mycelia using a sterile inoculation loop or a sterile toothpick. Transfer the loop/toothpick content to solid YUU media (prepared in step A2) by gently streaking back and forth. Make sure that mycelium is equally distributed throughout the plate, instead of performing streak plating procedure. Incubate the culture at 37 °C for 2 days or until colonies are grown.
- Transfer 1 ml of PBS buffer to the surface of A. nidulans culture grown in solid YUU media (after step A3). Using the pipette tip, suspend the fungal cells and transfer the suspension to a sterile 15 ml conical tube. To obtain enough conidia, repeat this step with fresh PBS buffer at least 5 times, increasing the suspension volume to ≥ 5 ml.
- Fill a 250 ml beaker with approximately 200 ml of 70% ethanol solution. Immerse the tweezer in ethanol solution and carefully flame it in a Bunsen burner or in a lighter. Repeat this procedure 3 x and cool the tweezer for 2-3 min at room temperature.
- Using the flamed tweezer, insert a Miracloth filter or a small amount of the glass wool into the end of a sterile 20 ml syringe and isolate A. nidulans conidia by filtering the fungal suspension. Collect the filtrate in a new and sterile 15 ml conical tube.
Note: The steps A3-A6 are shown in the Video 1 (Aspergillus growth and conidia isolation).Video 1. Manipulation of A. nidulans for growth and isolation of conidia. This video shows step-by-step the manipulation of A. nidulans for growth and recovery in YUU (solid media), and isolation of the conidia by filtration using a syringe containing Miracloth filter or glass wool. - Transfer 10 µl of the conidial suspension to a hemocytometer and, under a 100x objective of an optical microscope, count the number of A. nidulans conidia. The concentration of conidia/ml can be estimated through the sum of cells x 10,000/number of counted squares.
Notes: - Conidia should be uniformly distributed throughout the hemocytometer and the suspension should be diluted enough in order that cells do not overlap on the grids.
- The fungal suspension should contain at least 108 conidia/ml, so the volume of fungal suspension used is ≤ 10 µl. This is required to maintain the volume of G. mellonella hemolymph nearly to constant, as fungal suspension will be injected in larva body cavity (as described in Procedure B). If the conidial concentration obtained is inferior to 108 conidia/ml, harvest more A. nidulans mycelia (described in step A4) and repeat the filtration and counting.
- Use 106 A. nidulans conidia to each larva infection. Transfer the volume of conidial suspension containing 106 conidia x the number of larvae in the experimental group to a new 1.5 ml microcentrifuge tube. Reserve an equivalent volume of PBS to the control group.
- Prepare the culture media (solid YUU media) for A. nidulans growth and heat-sterilize by autoclaving at 121 °C for 20 min. Cool the media at room temperature until it turns pleasant to touch.
- Injection of Aspergillus nidulans conidia in Galleria mellonella larvae
- Obtain the G. mellonella larvae after oviposition of the adult moths reared at the insectarium. Insects should be maintained inside plastic boxes, with small holes on its cover. Provide enough artificial diet (ad libitum) for the larvae to be able to dig their tunnels within the diet (Figures 1A and 1B). The development of instars (shown in Figure 1C) should occur after 20-30 days at 21 °C and in the dark.
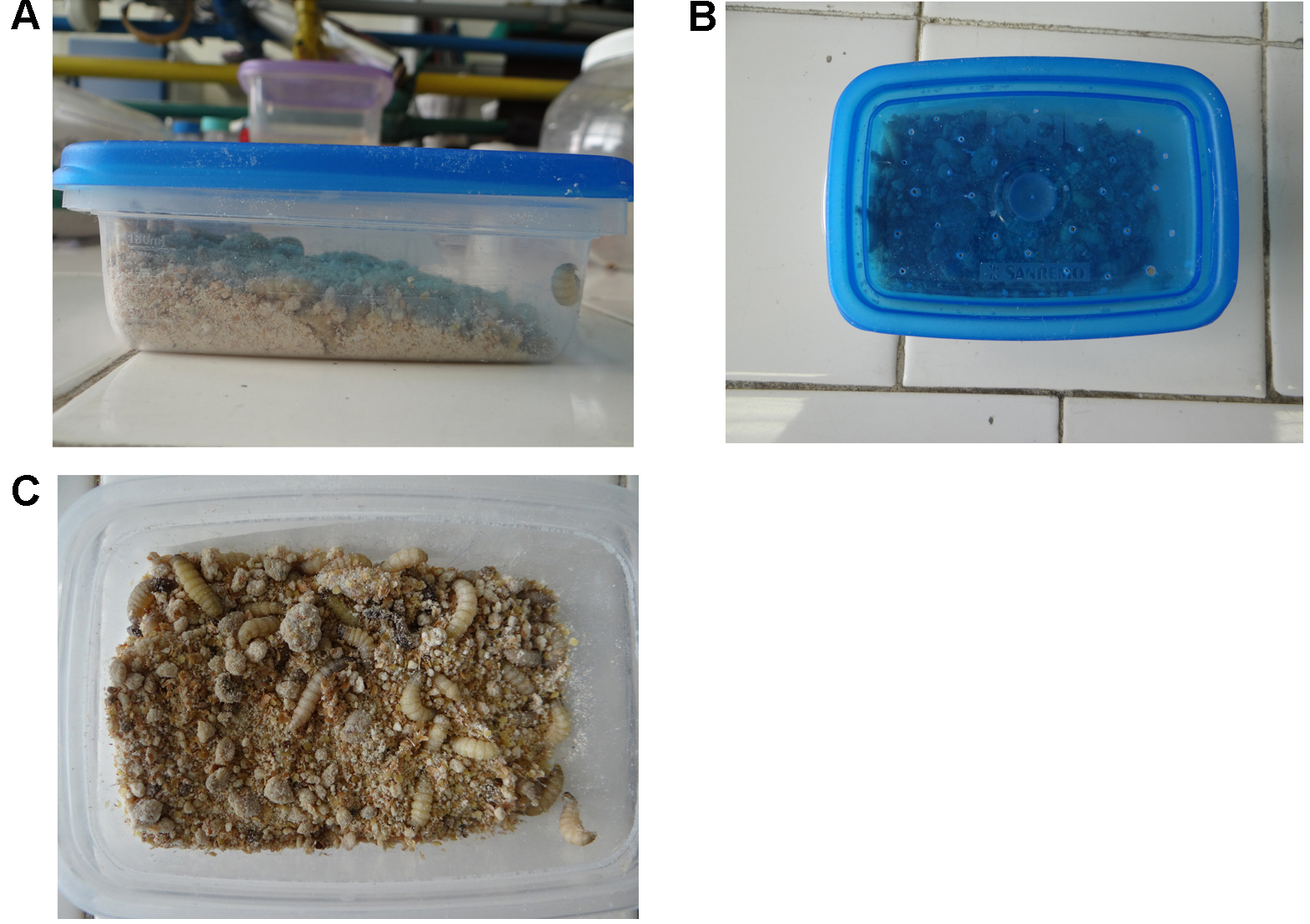
Figure 1. Maintenance and development of G. mellonella instars include incubation in aerated plastic boxes containing ad libitum artificial diet - Using gloves to avoid bacterial contamination and a blunt tipped tweezer, manually select 10-20 healthy G. mellonella larvae, from the last instar with similar size (15-20 mm) and weight (approximately 0.2 g) for each experimental group. Place up to 10 larvae into a sterile 100 x 10 mm Petri dish without any food.
Notes:- Creamy colored insects, which do not exhibit any grey pigmentation and are responsive to the tweezer touch, can be defined as healthy. Grey colored larvae should be discarded.
- Provide enough larvae for the experimental conditions and for two different control groups. The first control group may include larvae that are inoculated with PBS buffer, to monitor deaths provoked by physical injury. The insects of the second control group should not receive any injection.
- Creamy colored insects, which do not exhibit any grey pigmentation and are responsive to the tweezer touch, can be defined as healthy. Grey colored larvae should be discarded.
- Wash the 10 µl Hamilton syringe by aspirating and discarding the 70% ethanol solution. Repeat this procedure at least 3 times.
- Remove the residual ethanol by washing the syringe with room temperature sterile water.
- Using the Hamilton syringe, aspirate 10 µl of fungal suspension, which contains 106 A. nidulans conidia (obtained in the step A8).
- Gently, pick a G. mellonella larva with one hand and firmly hold it by its back using your index and thumb fingers (Figure 2).
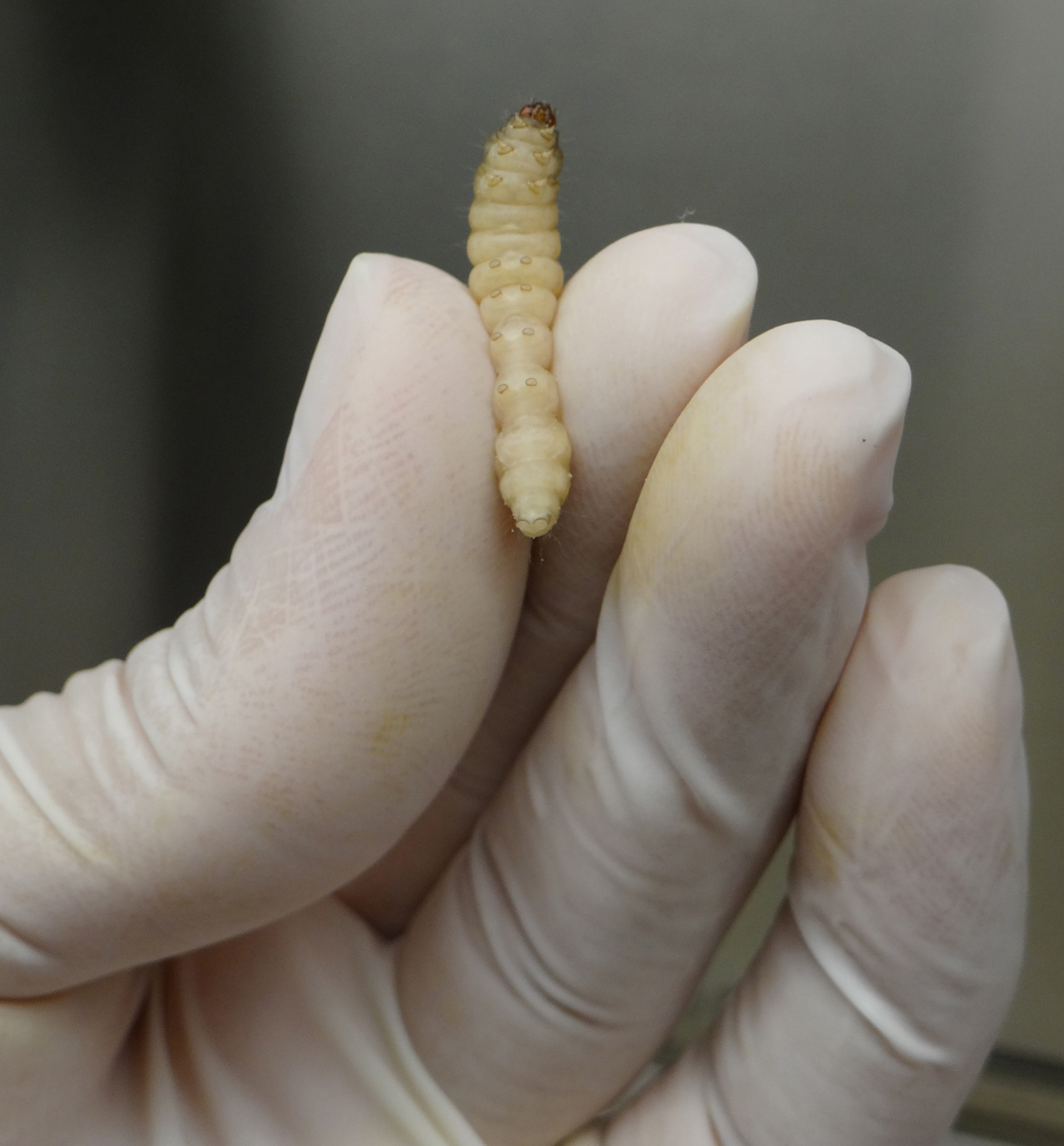
Figure 2. Handling G. mellonella larva for A. nidulans infection - Carefully insert the needle of the Hamilton syringe into the larva last left pro-leg and slowly inject the volume corresponding to 106 A. nidulans conidia in the insect hemolymph (Figure 3).
Notes:- Avoid using too much force not to puncture the larva and leak the hemolymph. In such situation, select another larva.
- The steps B3-B7 are shown in the Video 2 (Injecting A. nidulans conidia in G. mellonella larvae)
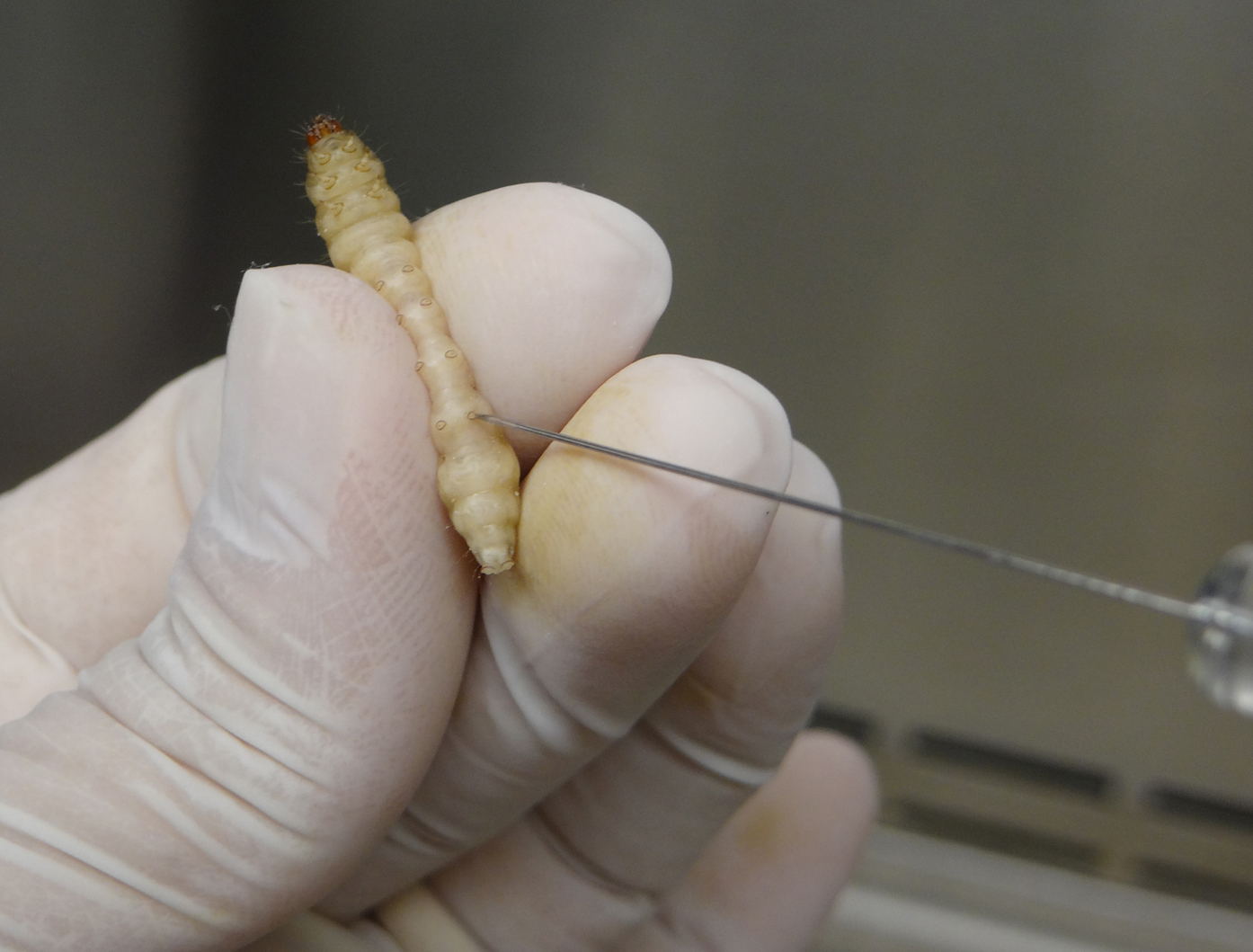
Figure 3. Inoculation of G. mellonella by injection of fungal suspension in the larval last left pro-legVideo 2. G. mellonella infection with A. nidulans conidia. This video shows all steps, from the washing of Hamilton syringe to inoculation by A. nidulans conidia injection. In all experiments, inoculation was performed in the last left pro-leg.
- Avoid using too much force not to puncture the larva and leak the hemolymph. In such situation, select another larva.
- Place the larvae of each experimental group in a new sterile Petri dish. After manipulating all larvae, incubate them in the dark at 28 °C.
Note: Larvae can also be incubated at 37 °C to mimic human body temperature. - After 24 h of infection, gently touch the larvae with the blunt tipped tweezers to evaluate survival. Alive larvae (shown in Figure 4A) should respond quickly to touch, while absence of movement associated with a grey/dark pigmentation characterize dead larvae (present in 4B). Record the number of alive and dead larvae every 24 h in each experimental group. After approximately 10 days, larvae turn into pupa.
Notes: - Disposal of all animals used in the experiment should be done after autoclaving/decontamination of the Petri dishes containing the larvae.
- This step is shown in the Video 3 (Analysis of larvae survival).
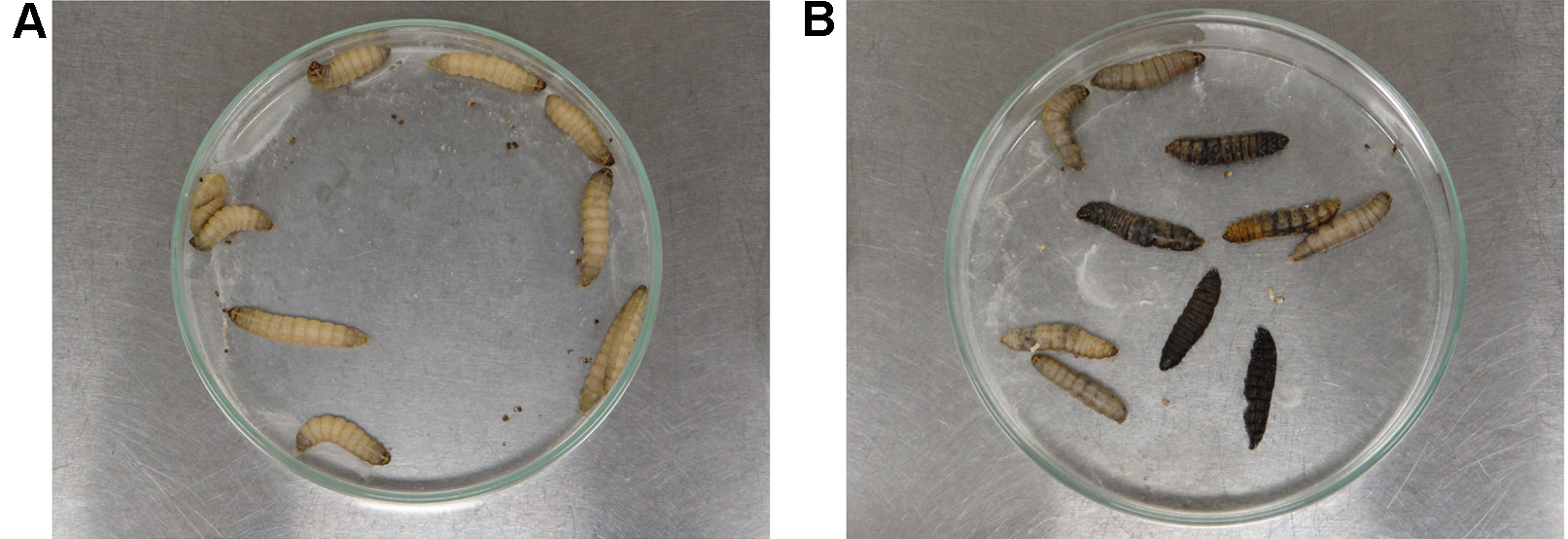
Figure 4. Analysis of the larvae survival after A. nidulans infection. Alive instars (panel A) exhibit creamy pigmentation and show movement response under stimulation. Dead instars exhibit grey/dark pigmentation and are unresponsive to touch.Video 3. Evaluation of G. mellonella survival after A. nidulans infection. After A. nidulans inoculation, G. mellonella larvae were daily analyzed for unresponsiveness to stimulation (dead larvae).
- Obtain the G. mellonella larvae after oviposition of the adult moths reared at the insectarium. Insects should be maintained inside plastic boxes, with small holes on its cover. Provide enough artificial diet (ad libitum) for the larvae to be able to dig their tunnels within the diet (Figures 1A and 1B). The development of instars (shown in Figure 1C) should occur after 20-30 days at 21 °C and in the dark.
Data analysis
- Data analysis of G. mellonella survival using GraphPad Prism 7.0.
- Open the GraphPad Prism 7.0 as a new project. A free trial of the software is available online (https://www.graphpad.com/).
- On the New Table and Graph window, select Survival table where each row tabulates the survival or censored time of a subject (Figure 5).
Figure 5. The selection of ‘Survival table’ in GraphPad Prism initial menu - Record the experimental data in ‘Data Tables’ by inserting, in the x-axis, time measurement of the experiment (days) and, in the y-axis, the number of dead larvae per day for each experimental group.
Note: If no larva dies on a given time point, it is not necessary to add number ‘0’ in this respective time. Record only the days/hours in which larvae death occurred by inserting number ‘1’ for each dead animal. If more than one animal in the group died in a time point, repeat the same day in a subsequent row and insert ‘1’ as many as necessary. In the data table shown below (Figure 6), days 7, 8, 9 were not included since no larval death was observed.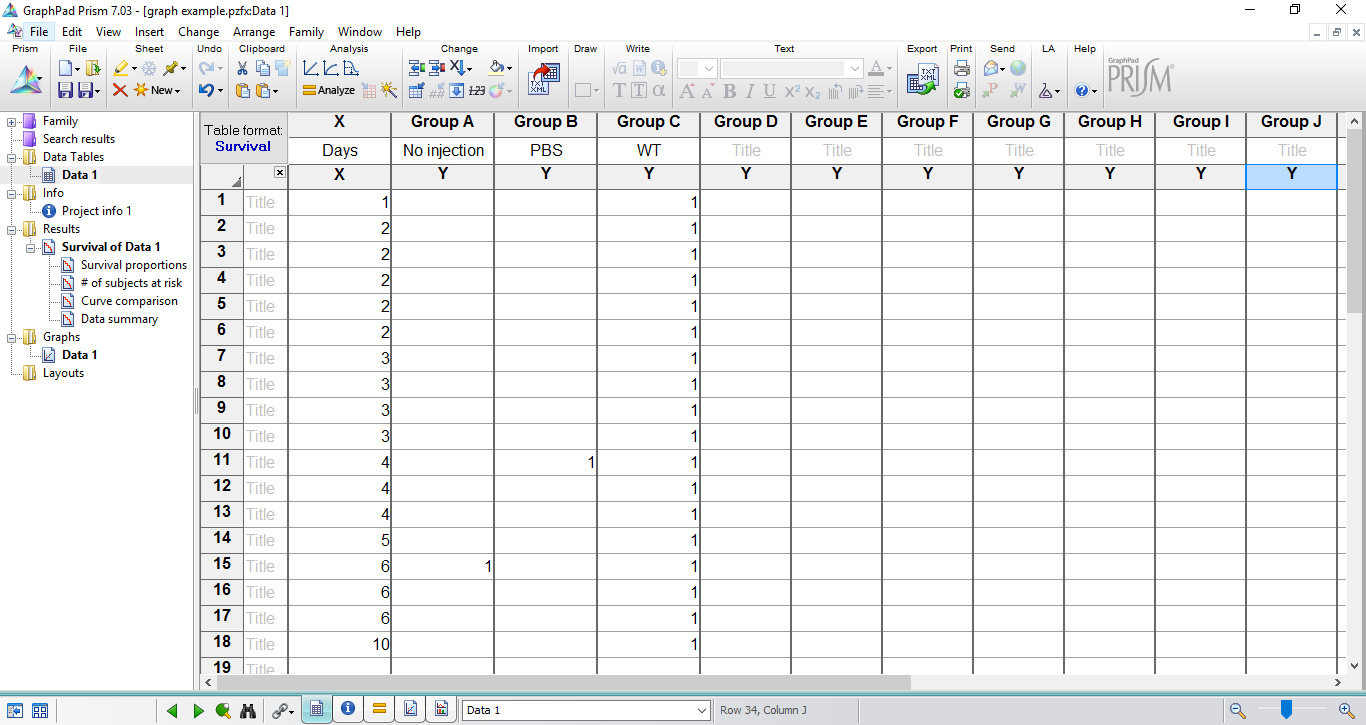
Figure 6. Table fills with the experimental data in survival data table - In the last time point of the experiment, score 0 to each alive larva in the respective group. If more than one animal in the group remained alive, repeat the same day/hour in a subsequent row and insert ‘0’ as many as necessary (Figure 7).
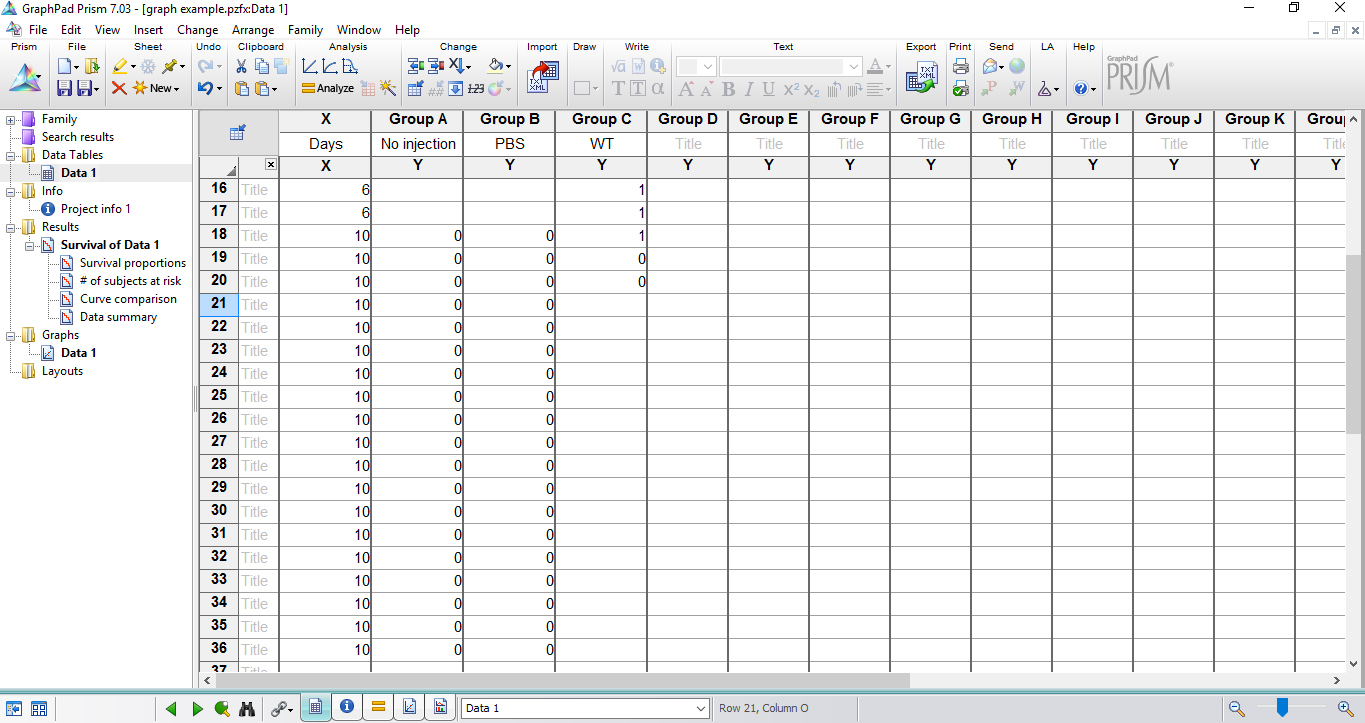
Figure 7. The registering of each alive larva by the end of the experiment - GraphPad Prism automatically analyzes statistical significance by using Kaplan-Meier survival curves. Open the ‘Results Table’ in the same project to check statistical significance (Figure 8).
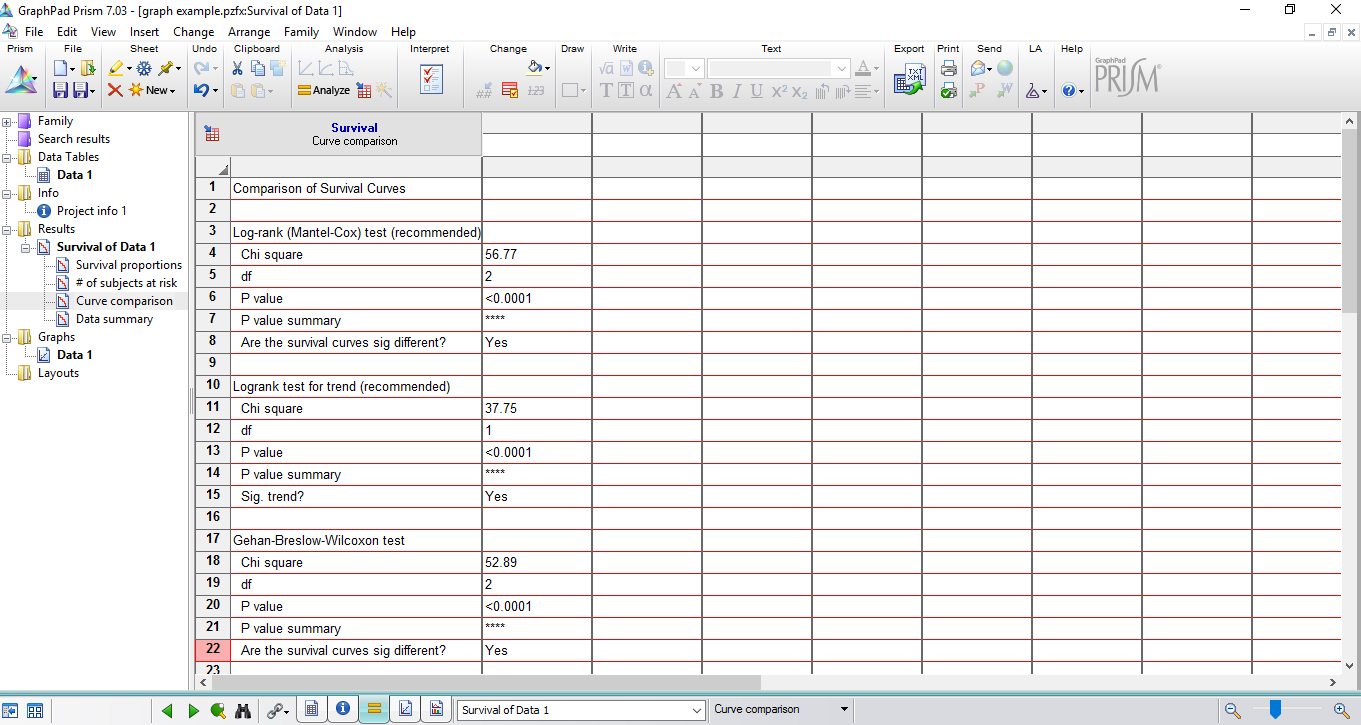
Figure 8. Results table showing the analysis of statistical significance - GraphPad Prism also automatically creates data graph, which can be easily edited (Figure 9).
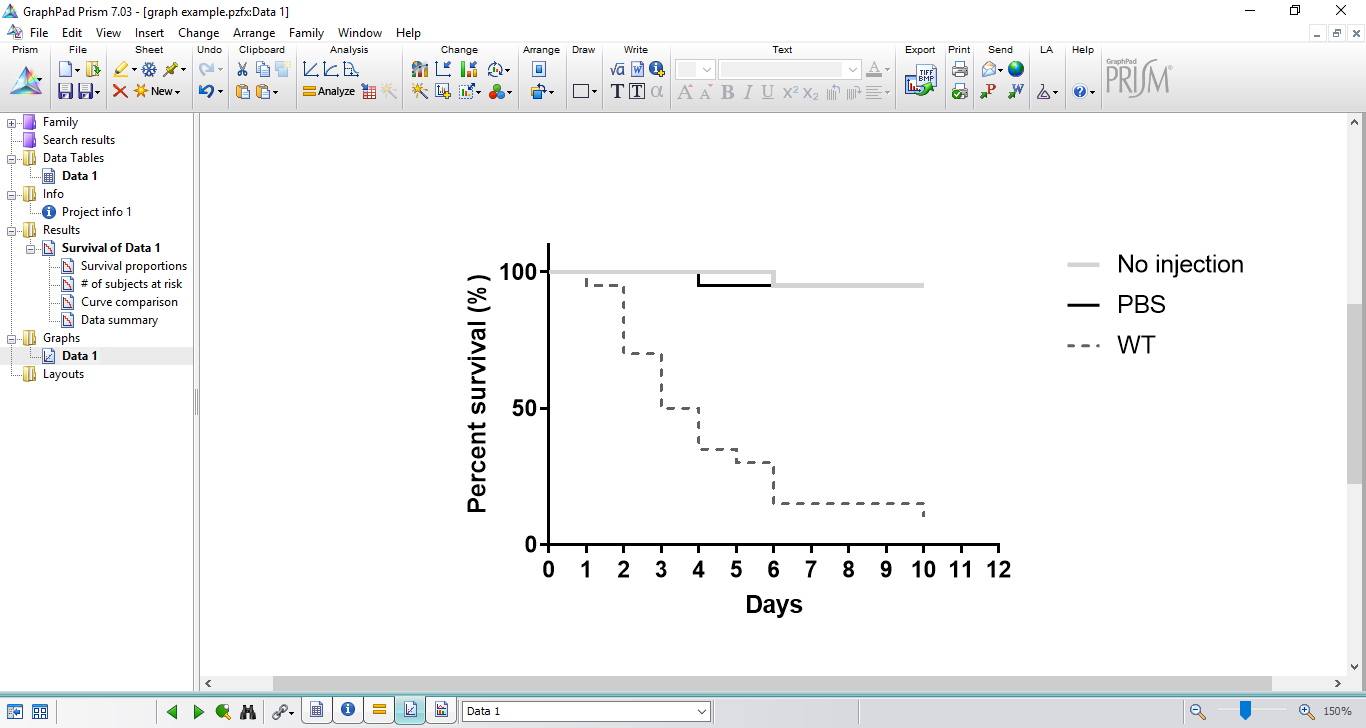
Figure 9. Illustration of a survival graph created by GraphPad Prism - For project presentation or manuscript submission, data graph can be edited and exported in several formats. On project window, select ‘export’ on file attributions.
Recipes
- Complete media (YUU media) for A. nidulans growth
0.5% yeast extract
2% glucose
2% agar
0.1% trace elements solution
5 mM uridine
10 mM uracil- Place a weighing paper on the balance and tare it. Using a spatula, transfer the required mass of each reagent
- Place the agar, uridine and uracil powders directly in the glass container where the culture media will be autoclaved
- Dissolve the yeast extract, glucose and trace elements solution in ¾ of the final volume with deionized water
- Using a graduated cylinder, complete with water to the final volume and transfer this solution to the glass bottle containing the agar, uridine and uracil. Heat-sterilize by autoclaving it at 121 °C for 20 min
Note: Make sure that the total volume of the culture media represents less than 2/3 of the glass container capacity, to avoid spillage during the autoclaving process.
- Place a weighing paper on the balance and tare it. Using a spatula, transfer the required mass of each reagent
- Trace elements solution for Aspergillus
75 mM zinc sulfate heptahydrate
180 mM boric acid
25 mM manganese(II) chloride tetrahydrate
18 mM iron (II) sulfate heptahydrate
6 mM cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate
6 mM copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate
1 mM ammonium molybdate tetrahydrate
140 mM ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid - In the analytical balance, weigh each reagent. Dissolve the powders, following the order above, in 1/8 of the final volume with deionized water
- Heat the solution to 100 °C and then cool it to 60 °C
- Adjust the pH to 6.5-6.8 with a 10 N sodium hydroxide solution
- Chill the solution to room temperature and then add deionized water to the final volume
- 70% ethanol solution
Each 100 ml contains 70 ml of ethanol diluted in 30 ml of distilled water - PBS buffer (according to Sambrook et al., 2005)
137 mM sodium chloride
2.7 mM potassium chloride
10 mM sodium phosphate dibasic
1.8 mM potassium phosphate monobasic- Weigh the reagents and dissolve them in ¾ of the final volume with deionized water
- Adjust the pH for 7.4 with hydrogen chloride and then add deionized water to the total volume
- Divide the solution in smaller aliquots and sterilize by autoclaving for 20 min
- Weigh the reagents and dissolve them in ¾ of the final volume with deionized water
- Artificial diet for Galleria mellonella
120 g of honey
120 g of glycerol
200 g of milk
60 g of yeast extract
100 g of wheat germ
100 g of wheat flour
120 g of wheat bran
Using the analytical balance, weigh each ingredient. Mixture the artificial diet components and heat-sterilize by autoclaving at 121 °C for 20 min
Acknowledgments
Sources of funding for this work were from the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Fundação de Amparo a Pesquisa do Rio de Janeiro (FAPERJ), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES). This protocol is a detailed description of the methodology used in Fernandes et al., 2016.
References
- Brennan, M., Thomas, D. Y., Whiteway, M. and Kavanagh, K. (2002). Correlation between virulence of Candida albicans mutants in mice and Galleria mellonella larvae. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 34(2): 153-157.
- Fernandes, C. M., de Castro, P. A., Singh, A., Fonseca, F. L., Pereira, M. D., Vila, T. V., Atella, G. C., Rozental, S., Savoldi, M., Del Poeta, M., Goldman, G. H. and Kurtenbach, E. (2016). Functional characterization of the Aspergillus nidulans glucosylceramide pathway reveals that LCB Δ8-desaturation and C9-methylation are relevant to filamentous growth, lipid raft localization and Psd1 defensin activity. Mol Microbiol 102(3): 488-505.
- Li, D. D., Deng, L., Hu, G. H., Zhao, L. X., Hu, D. D., Jiang, Y. Y. and Wang, Y. (2013). Using Galleria mellonella-Candida albicans infection model to evaluate antifungal agents. Biol Pharm Bull 36(9): 1482-1487.
- Mylonakis, E., Moreno, R., El Khoury, J. B., Idnurm, A., Heitman, J., Calderwood, S. B., Ausubel, F. M. and Diener, A. (2005). Galleria mellonella as a model system to study Cryptococcus neoformans pathogenesis. Infect Immun 73(7): 3842-3850.
- Sambrook, J., Fristch, E. F. and Maniatis, T. (1989). Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. (2nd edition). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Fernandes, C. M., Fonseca, F. L., Goldman, G. H., Pereira, M. D. and Kurtenbach, E. (2017). A Reliable Assay to Evaluate the Virulence of Aspergillus nidulans Using the Alternative Animal Model Galleria mellonella (Lepidoptera). Bio-protocol 7(11): e2329. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2329.
Category
Microbiology > Microbe-host interactions > Fungus
Microbiology > Microbe-host interactions > In vivo model > Arthropod
Cell Biology > Cell viability > Cell death
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









