- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Whole-seed Immunolabeling of Arabidopsis Mucilage Polysaccharides
Published: Vol 7, Iss 11, Jun 5, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2323 Views: 8169
Reviewed by: Marisa RosaAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Enzymatic Starch Quantification in Developing Flower Primordia of Sweet Cherry
Nestor Santolaria [...] Afif Hedhly
Apr 5, 2025 1905 Views

New Approach to Detect and Isolate Rhamnogalacturonan-II in Arabidopsis thaliana Seed Mucilage
Dayan Sanhueza and Susana Saez-Aguayo
Sep 5, 2025 1258 Views

Detailed Method for the Purification of Rhamnogalacturonan-I (RG-I) in Arabidopsis thaliana
Liang Zhang [...] Breeanna R. Urbanowicz
Feb 5, 2026 162 Views
Abstract
In addition to synthesizing and secreting copious amounts of pectic polymers (Young et al., 2008), Arabidopsis thaliana seed coat epidermal cells produce small amounts of cellulose and hemicelluloses typical of secondary cell walls (Voiniciuc et al., 2015c). These components are intricately linked and are released as a large mucilage capsule upon hydration of mature seeds. Alterations in the structure of minor mucilage components can have dramatic effects on the architecture of this gelatinous cell wall. The immunolabeling protocol described here makes it possible to visualize the distribution of specific polysaccharides in the seed mucilage capsule.
Keywords: Arabidopsis thalianaBackground
Since the first comprehensive immunofluorescence analysis of pectin-rich mucilage in Arabidopsis seed coat epidermal cells (Young et al., 2008), additional types of polysaccharides have been detected in this specialized cell wall (Voiniciuc et al., 2015a; 2015b and 2015c). To handle more samples in parallel, I adapted the original protocols (performed in 1.5-ml microcentrifuge tubes; Young et al., 2008; Harpaz-Saad et al., 2011) to a 24-well plate format. I recommend counterstaining seeds with Pontamine S4B, a fluorescent dye that is more specific to cellulose than previous stains (Anderson et al., 2010). By testing for cross-talk between multiple fluorophores and setting clear guidelines for image acquisition and processing, this protocol yields reproducible mucilage phenotypes that can be reliably interpreted.
Materials and Reagents
- Personal protection equipment (safety glasses, lab coat, gloves)
- 1.5 ml snap-cap tubes
- 24-well plate with lid (VWR, catalog number: 734-2325 )
- Plastic Pasteur pipette (VWR, catalog number: LSUK711117S/20 )
- Manual pipettes tips (Eppendorf, Research plus and Repeater plus, or similar style)
- Aluminum foil
- MARIENFELD glass slides, low autofluorescence, L x B x H: 76 x 26 x 1 mm; pre-washed; Ground edges, 90° slides (VWR, catalog number: 631-9464 )
- Precision cover slip glass, thickness No. 1.5H (Marienfeld-Superior, catalog number: 0107222 )
- 15 ml Falcon tubes (VWR, catalog number: 734-0452 )
- Arabidopsis thaliana mature, dry seeds
- Primary antibodies directed against plant cell wall carbohydrates, obtained from:
- CarboSource (http://www.ccrc.uga.edu/~carbosource/CSS_home.html)
- Plant probes (http://www.plantprobes.net/index.php)
- Alexa Fluor® 488 secondary antibodies (against the host of the primary antibody)
- Goat anti-mouse (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Invitrogen, catalog number: A-11001 )
- Goat anti-rat (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Invitrogen, catalog number: A-11006 )
- Clear nail polish
- Sodium phosphate, dibasic (Na2HPO4·2H2O) (Carl Roth, catalog number: 4984.2 )
- Sodium phosphate, monobasic (NaH2PO4·2H2O) (Carl Roth, catalog number: T879.2 )
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA), IgG free (Carl Roth, catalog number: 3737.2 )
- Pontamine S4B (sold as Direct Red 23) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 212490-50G )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Carl Roth, catalog number: P029.1 )
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.0 (see Recipes)
- Blocking solution (see Recipes)
- Antibody solution (see Recipes)
- 0.01% (w/v) S4B in 50 mM NaCl (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Manual pipettes (Eppendorf, models: Research® plus and Repeater® plus ; or similar style)
- Water purification system (Milli-Q or similar style)
- Balance
- Autoclave
- Orbital shaker
- Vortex mixer (Scientific Industries, model: Vortex-Genie 2 ; or similar style)
- Leica TCS SP8 confocal microscope (Leica Microsystems, model: TCS SP8 ) with the following key components:
- DM 5000 upright microscope with manual stage
- HC PL APO 10x/0.40 CS (Leica Microsystems, catalog number: 15506285 ) objective
- Compact LIAchroic AOTF unit with 488 nm and 552 nm solid state lasers
- SP8 Scan Head with LIAchroic beam splitters for filter-free spectral detection
Note: Alternatively, use a conventional confocal microscope equipped with filter-based detection. Filters designed for green fluorescent proteins (GFP) and red fluorescent proteins (RFP) are generally suitable for the acquisition of Alexa Fluor® 488 and Pontamine S4B signals, respectively. In this protocol, the emission of fluorophores was detected in 500-530 nm and 590-700 nm ranges. - Two fluorescence photomultipliers and one transmitted light detector
- Scan optics module HIVIS with rotation
- Computer for image acquisition and processing
Software
- Leica Application Suite X (LAS X) software for image acquisition
- Fiji is just ImageJ (Fiji) image processing package (https://fiji.sc/)
Procedure
- Antibody selection and ordering
- Based on previous publications or the WallBioNet antibody heatmap (http://glycomics.ccrc.uga.edu/wall2/antibodies/antibodyHome.html; Pattathil et al., 2010), select at least one primary antibody directed against the mucilage component of interest. Note the animal host used to produce the antibody, the polysaccharide cross-reactivity, and the epitope structure for carbohydrate antigen (if known).
Example: CCRC-M30 is a mouse monoclonal antibody directed against Arabidopsis thaliana seed mucilage, and primarily binds this pectin-rich substrate from a diverse panel of 54 plant polysaccharides (Pattathil et al., 2010).
Note: If using the 2F4 antibody (Liners et al., 1989) or His-tagged carbohydrate-directed modules (e.g., CBM3a; Blake et al., 2006), alternative solutions or additional labeling steps must be prepared, respectively (Voiniciuc et al., 2013 and 2015b). - Order the primary antibody of interest and the corresponding Alexa Fluor® 488 secondary antibody.
Example: For CCRC-M30, use the goat-anti-mouse antibody. - Primary antibodies should be aliquoted into 1.5 ml tubes and stored at -20 °C. Once a tube is thawed, store it in the dark at 4 °C until it is completely used up.
- Based on previous publications or the WallBioNet antibody heatmap (http://glycomics.ccrc.uga.edu/wall2/antibodies/antibodyHome.html; Pattathil et al., 2010), select at least one primary antibody directed against the mucilage component of interest. Note the animal host used to produce the antibody, the polysaccharide cross-reactivity, and the epitope structure for carbohydrate antigen (if known).
- Preparing seeds for immunolabeling
- Label the lid of a 24-well plate with the name of the samples that will be analyzed. Always include at least one negative control.
Example: Wild-type seeds that will be prepared alongside the samples of interest except that the primary antibody is omitted. - Fill each well of the plate with 500 µl of ultrapure water (18.2 MΩ cm at 25 °C) using a repeater pipette.
- To each well, add around 20 Arabidopsis dry, mature seeds.
Note: Seeds stored in small paper bags can be directly transferred to the wells, minimizing the risk of contamination. For more detailed instructions about seed harvesting and storage conditions for mucilage analysis, see the protocol by (Voiniciuc and Günl, 2016). - Cover the 24-well plate with the lid and incubate for 5 min on horizontal shaker. For all shaking steps, use an orbital shaker at 100 rpm and room temperature (~23 °C).
- Using a 1,000 µl pipette, remove 470 µl of water from each well.
Note: This removes the non-adherent mucilage from the seeds. Tilt the plate and pipette carefully to avoid removing any seeds along with the liquid. - Add 100 µl of the fresh blocking solution using a repeater pipette.
- Cover the plate with the lid and shake for 30 min.
- Remove 100 µl of blocking solution with a 200 µl pipette.
- Label the lid of a 24-well plate with the name of the samples that will be analyzed. Always include at least one negative control.
- Primary antibody labeling
- To the ‘no primary antibody’ negative control, add 50 µl of plain antibody solution.
- To each sample, add 50 µl of the primary antibody diluted 1:10 in antibody solution.
Note: Prepare a fresh master mix containing 5 µl of CCRC-M30 antibody plus 45 µl of antibody solution per sample. This dilution works well for most antibodies tested. - Cover the 24-well plate with the lid and shake for 90 min.
- Remove the 50 µl of primary antibody solution with a 200 µl pipette.
Note: Change tips if using two or more primary antibodies on one plate. - Add 300 µl of PBS to each well using a repeater pipette.
- Gently mix seeds in the PBS wash solution by manually shaking the plate twice. Discard the wash solution using a plastic Pasteur pipette, without removing seeds.
- Perform four additional PBS washes by repeating steps C5 and C6.
- To the ‘no primary antibody’ negative control, add 50 µl of plain antibody solution.
- Secondary antibody labeling
- After removing the final wash solution, add 100 µl of the appropriate secondary antibody diluted 1:100 in antibody solution with a repeater pipette.
Example: For CCRC-M30 labeling, add a freshly prepared mixture of 1 µl of Alexa Fluor® 488 goat-anti-mouse antibody and 99 µl of antibody solution to each sample. - Shake the 24-well plate, covered with the lid and wrapped in aluminum foil, for 90 min.
- Remove the 100 µl of secondary antibody solution with a 200 µl pipette.
Note: Change tips if using different secondary antibodies on one plate. - Add 300 µl of PBS to each well using a repeater pipette.
- Gently mix seeds in the PBS wash solution by manually shaking the plate twice. Discard the wash solution using a plastic Pasteur pipette, without removing seeds.
- Perform four additional PBS washes by repeating steps D4 and D5.
- After the final wash, seeds can be stored in 300 µl of PBS in the dark at 4 °C overnight, or used immediately for the following steps.
Note: Keep the seeds in the 24-well plate, until they are ready to be transferred to a glass slide for confocal imaging.
- After removing the final wash solution, add 100 µl of the appropriate secondary antibody diluted 1:100 in antibody solution with a repeater pipette.
- Seed counterstaining (Optional)
- The distribution of carbohydrates epitopes in mucilage capsules is best examined relative to seed surfaces counterstained with Pontamine S4B.
Note: The choice of the counterstain is important for the interpretation of the results. S4B specifically binds cellulose microfibrils unlike the commonly used Calcofluor stain, which also fluoresces in the presence of pectic galactan, xylan, and galactomannan (Anderson et al., 2010). - To each well, add 300 µl of fresh 0.01% (w/v) Pontamine S4B in 50 mM NaCl.
- Shake the 24-well plate, covered with the lid and wrapped in aluminum foil, for 30 min.
- Remove the S4B solution with a plastic Pasteur pipette.
- Add 300 µl of water to each well using a repeater pipette.
- Gently mix seeds with the water by manually shaking the plate twice. Discard the wash solution using a plastic Pasteur pipette, without removing seeds.
- Perform two additional water washes by repeating steps E5 and E6.
- The seeds are ready to image and can be transferred to a glass slide (one per sample) using a plastic Pasteur pipette or a 1,000 µl pipette.
- A cover slip glass (thickness No. 1.5H) is placed over each drop containing seeds, and additional water is added (if necessary). If samples will be stored for more than 60 min, the cover slips should be sealed to glass slides with nail polish to limit evaporation.
- The distribution of carbohydrates epitopes in mucilage capsules is best examined relative to seed surfaces counterstained with Pontamine S4B.
- Image acquisition and processing
- Examine each glass slide containing whole seeds using a 10x objective equipped on a Leica TCS SP8 confocal system.
Note: Other microscopes that can excite and detect the emission of green and red fluorescent proteins (GFP and RFP) are also suitable. - Initialize the confocal hardware and the Leica Application Suite X (LAS X) software to begin the image acquisition. Turn on the 488 nm and 552 nm solid state lasers.
- Use transmitted light and the manual stage controls to focus on a seed of interest.
- Simultaneously excite Alexa Fluor® 488 and S4B using 488 nm and 552 nm solid state lasers, and acquire their signals using two fluorescence photomultipliers (PMT; PMT 1 = 500-530 nm; PMT 2 = 590-700 nm).
Note: Only use simultaneous acquisition, if there is no significant cross-talk between two or more fluorophores. Otherwise, the confocal system should be used in sequential scanning mode. Figure 1 shows that the aforementioned parameters can separate Alexa Fluor® 488 and S4B.
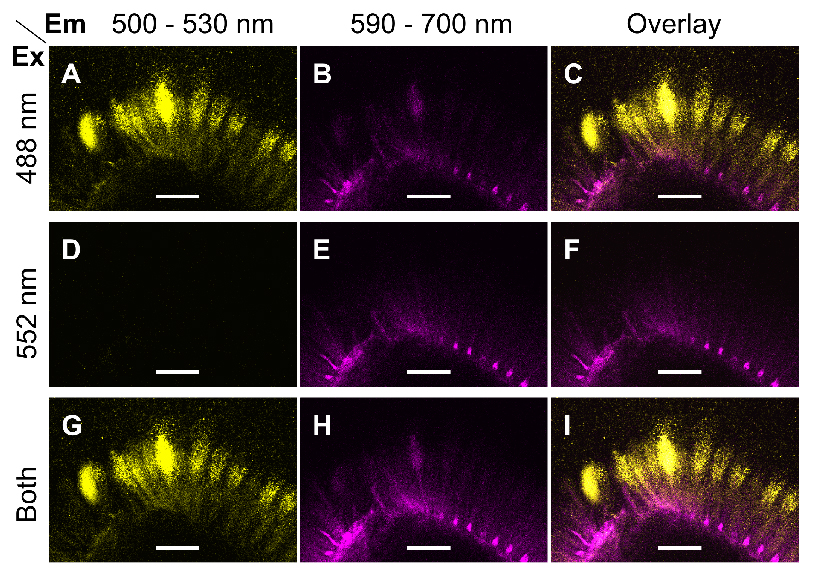
Figure 1. Excitation and emission parameters to detect two fluorophores. A-I. Single optical sections of the same region of mucilage around a wild-type (Col-0) seed immunolabelled with CCRC-M30 and counterstained with S4B. Fluorescent signals were acquired using distinct Excitation (Ex) and Emission (Em) parameters. Images were processed in Fiji. Bars = 75 µm. - Briefly compare the fluorescence of the different samples and controls prepared, then set the final acquisition settings (e.g., scan format, power of each laser, gain of each detector) for the whole experiment.
Example: Figure 2 shows the CCRC-M30 and S4B labeling of Col-0 wild-type and muci21-1 mutant seeds. In contrast to these samples, no mucilage fluorescence was detected using the same acquisition settings around wild-type seeds prepared without the CCRC-M30 primary antibody and the S4B dye.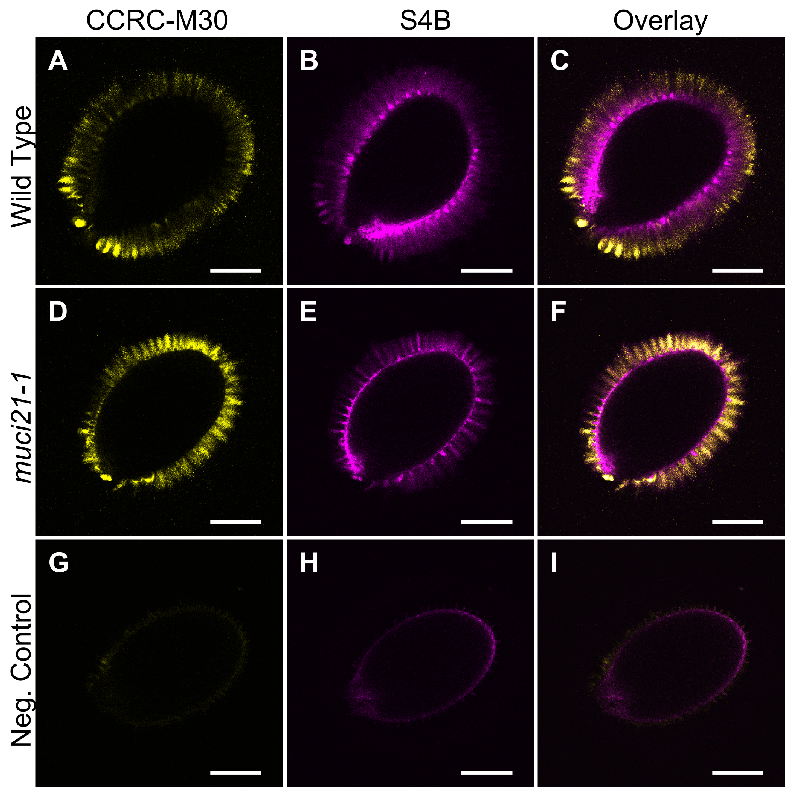
Figure 2. Pectin and cellulose distribution around wild-type and muci21-1 seeds. A-I. Single optical sections of three different seeds imaged using identical acquisition parameters and processed in paralleled in Fiji. The negative control (G to I) represents wild-type (Col-0) seeds incubated without the CCRC-M30 primary antibody and the S4B counterstain. Bars = 200 µm. - Acquire Z-stacks of multiple seeds for each sample using identical acquisition settings. Use the scan field rotation to analyze all seeds from a similar orientation.
- The acquired Leica confocal images (.lif file format) can be loaded in the Fiji image processing package for processing and/or exporting images for publication (Schindelin et al., 2012).
- Examine each glass slide containing whole seeds using a 10x objective equipped on a Leica TCS SP8 confocal system.
Recipes
- Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.0
- Mix 5.34 g of sodium phosphate, dibasic (30 mM final concentration) and 3.12 g of sodium phosphate, monobasic (20 mM final concentration)
- Add 900 ml of purified water and stir to dissolve the salts
- Check that pH = 7.0 and adjust if necessary
- Fill to 1,000 ml with water, stir once again and autoclave
Note: The sterile solution is stable for at least 1 year.
- Blocking solution
- Weigh 0.5 g of BSA in a 15 ml Falcon tube and fill to 10 ml with PBS
- Vortex mix until the BSA is completely dissolved
Note: Make this solution fresh every time.
- Antibody solution
- Weigh 0.1 g of BSA in a 15 ml Falcon tube and fill to 10 ml with PBS
- Vortex mix until the BSA is completely dissolved
Note: Make this solution fresh every time.
- 0.01% (w/v) S4B in 50 mM NaCl
- Dissolve 0.5 g of Pontamine S4B per 10 ml of ultrapure water to prepare a 5% (w/v) concentrated stock solution, which is stable in the dark at 4 °C for several months
- Dissolve 5.84 g of NaCl in 100 ml of ultrapure water, and autoclave to prepare a 100 mM NaCl concentrated stock. The sterile solution is stable for at least 1 year
- For each experiment, prepare a fresh 0.01% (w/v) S4B in 50 mM NaCl master mix containing 0.6 μl of 5% (w/v) of S4B, 150 μl of 100 mM NaCl and 149.4 μl of ultrapure water per sample
Acknowledgments
This protocol was briefly described by (Voiniciuc et al., 2015a), and was modified from the (Young et al., 2008; Harpaz-Saad et al., 2011) methods. I performed this work in the laboratory of Dr. Björn Usadel at Forschungzentrum Jülich with support from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC PGS-D3 grant).
References
- Anderson, C. T., Carroll, A., Akhmetova, L. and Somerville, C. (2010). Real-time imaging of cellulose reorientation during cell wall expansion in Arabidopsis roots. Plant Physiol 152(2): 787-796.
- Blake, A. W., McCartney, L., Flint, J. E., Bolam, D. N., Boraston, A. B., Gilbert, H. J. and Knox, J. P. (2006). Understanding the biological rationale for the diversity of cellulose-directed carbohydrate-binding modules in prokaryotic enzymes. J Biol Chem 281(39): 29321-29329.
- Harpaz-Saad, S., McFarlane, H. E., Xu, S., Divi, U. K., Forward, B., Western, T. L. and Kieber, J. J. (2011). Cellulose synthesis via the FEI2 RLK/SOS5 pathway and cellulose synthase 5 is required for the structure of seed coat mucilage in Arabidopsis. Plant J 68(6): 941-953.
- Liners, F., Letesson, J. J., Didembourg, C. and Van Cutsem, P. (1989). Monoclonal antibodies against pectin: Recognition of a conformation induced by Calcium. Plant Physiol 91(4): 1419-1424.
- Martin, C. and Blatt, M. (2013). Manipulation and misconduct in the handling of image data. Plant Cell 25(9): 3147-3148.
- Pattathil, S., Avci, U., Baldwin, D., Swennes, A. G., McGill, J. A., Popper, Z., Bootten, T., Albert, A., Davis, R. H., Chennareddy, C., Dong, R., O'Shea, B., Rossi, R., Leoff, C., Freshour, G., Narra, R., O'Neil, M., York, W. S. and Hahn, M. G. (2010). A comprehensive toolkit of plant cell wall glycan-directed monoclonal antibodies. Plant Physiol 153(2): 514-525.
- Schindelin, J., Arganda-Carreras, I., Frise, E., Kaynig, V., Longair, M., Pietzsch, T., Preibisch, S., Rueden, C., Saalfeld, S., Schmid, B., Tinevez, J. Y., White, D. J., Hartenstein, V., Eliceiri, K., Tomancak, P. and Cardona, A. (2012). Fiji: an open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat Methods 9(7): 676-682.
- Voiniciuc, C. (2016). Quantification of the mucilage detachment from Arabidopsis seeds. Bio-protocol 6: e1802.
- Voiniciuc, C., Dean, G. H., Griffiths, J. S., Kirchsteiger, K., Hwang, Y. T., Gillett, A., Dow, G., Western, T. L., Estelle, M. and Haughn, G. W. (2013). Flying saucer1 is a transmembrane RING E3 ubiquitin ligase that regulates the degree of pectin methylesterification in Arabidopsis seed mucilage. Plant Cell 25(3): 944-959.
- Voiniciuc, C. and Günl, M. (2016) Analysis of monosaccharides in total mucilage extractable from Arabidopsis seeds. Bio-protocol 6: e1801.
- Voiniciuc, C., Günl, M., Schmidt, M. H. and Usadel, B. (2015a). Highly branched xylan made by IRREGULAR XYLEM14 and MUCILAGE-RELATED21 links mucilage to Arabidopsis seeds. Plant Physiol 169: 2481-2495.
- Voiniciuc, C., Schmidt, M. H., Berger, A., Yang, B., Ebert, B., Scheller, H. V., North, H. M., Usadel, B. and Gunl, M. (2015b). MUCILAGE-RELATED10 produces galactoglucomannan that maintains pectin and cellulose architecture in Arabidopsis seed mucilage. Plant Physiol 169(1): 403-420.
- Voiniciuc, C., Yang, B., Schmidt, M. H., Günl, M., Usadel, B. (2015c). Starting to gel: how Arabidopsis seed coat epidermal cells produce specialized secondary cell walls. Int J Mol Sci 16: 3452-3473.
- Voiniciuc, C., Zimmermann, E., Schmidt, M. H., Gunl, M., Fu, L., North, H. M. and Usadel, B. (2016). Extensive natural variation in Arabidopsis seed mucilage structure. Front Plant Sci 7: 803.
- Young, R. E., McFarlane, H. E., Hahn, M. G., Western, T. L., Haughn, G. W. and Samuels, A. L. (2008). Analysis of the Golgi apparatus in Arabidopsis seed coat cells during polarized secretion of pectin-rich mucilage. Plant Cell 20(6): 1623-1638.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Voiniciuc, C. (2017). Whole-seed Immunolabeling of Arabidopsis Mucilage Polysaccharides. Bio-protocol 7(11): e2323. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2323.
- Voiniciuc, C., Gunl, M., Schmidt, M. H. and Usadel, B. (2015). Highly Branched Xylan Made by IRREGULAR XYLEM14 and MUCILAGE-RELATED21 Links Mucilage to Arabidopsis Seeds. Plant Physiol 169(4): 2481-2495.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Carbohydrate
Cell Biology > Tissue analysis > Tissue staining
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










