- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
In vitro Assays for Measuring Endothelial Permeability by Transwells and Electrical Impedance Systems
Published: Vol 7, Iss 9, May 5, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2273 Views: 27985
Reviewed by: Yannick DebingKate HannanChris Tibbitt

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
Isolation, BODIPY Labeling and Uptake of Exosomes in Hepatic Stellate Cells
Shubham Shrivastava
Dec 5, 2017 12219 Views

TZA, a Sensitive Reporter Cell-based Assay to Accurately and Rapidly Quantify Inducible, Replication-competent Latent HIV-1 from Resting CD4+ T Cells
Anwesha Sanyal [...] Phalguni Gupta
May 20, 2019 7783 Views

Generation and Implementation of Reporter BHK-21 Cells for Live Imaging of Flavivirus Infection
Jorge L. Arias-Arias and Rodrigo Mora-Rodríguez
Mar 5, 2021 4352 Views
Abstract
Vascular leakage is an important feature in several diseases, such as septic shock, viral hemorrhagic fever, cancer metastasis and ischemia-reperfusion injuries. Thus establishing assays for measuring endothelial permeability will provide insight into the establishment or progression of such diseases. Here, we provide transwell permeability assay and electrical impedance sensing assay for studying endothelial permeability in vitro. With these methods, the effect of a molecule on endothelial permeability could be defined.
Keywords: Endothelial permeabilityBackground
The endothelial barrier is a well-regulated structure, which maintains a minimal and selective permeability to fluid and molecules under normal physiological conditions (Komarova and Malik, 2010). The disruption of the endothelial barrier occurs during exposure to inflammatory cytokines, pathogen infection, or cancer metastasis, which induces the disruption of cytoskeleton, cell-cell junction, or cell-to-matrix attachments. The increase in vascular permeability is an important feature in many diseases, including ischemia-reperfusion injury, sepsis, viral hemorrhagic fevers and cancers. To screen which molecules modulate vascular permeability, it is necessary to establish in vitro systems to test endothelial permeability before expanding to animal studies. There are two available systems to test endothelial permeability in vitro, transwell permeability assay and electrical impedance sensing devices (Bischoff et al., 2016). The transwell permeability assays directly detect the penetration of macromolecules and the electrical impedance sensing devices measure the cell layer’s tightness for ion flow. Basically, molecules which can be detected by a spectrometer-based absorbance reader can be used in the transwell permeability assay. As a result, the materials required for this assay are relatively easy to prepare. For the electrical impedance sensing assay, we used the xCELLigence Real-Time Cell Analysis (RTCA) systems to measuring endothelial permeability in a 96-well microplate. Compared to transwell permeability assay, electrical impedance sensing device is more sensitive, and is suitable for time-lapse tracking. However, it is also more expensive, and it may not accurately reflect the penetration of molecules through cell-cell junction. As a result, it is more accurate to apply both systems in parallel. Here, we show the protocol for using these two methods to measure the dengue virus nonstructural protein 1-induced endothelial hyperpermeability in vitro (Chen et al., 2016).
Materials and Reagents
- General materials and reagents
- Pipet tips
- Human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC-1) (ATCC, catalog number: CRL-3243 )
- Medium 200 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: M-200-500 )
- 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) (GE Healthcare, HyCloneTM, catalog number: SH30071.03HI )
- Penicillin-streptomycin solution at a concentration of 100 U/ml (Caisson Laboratories, catalog number: PSL01-100ML )
- Endothelial cell growth medium (see Recipes)
- Pipet tips
- Materials and reagents for transwell permeability assay
- Corning 6.5 mm Transwell inserts with 0.4 µm polycarbonate membranes in a 24-well plate (Corning, catalog number: 3413 )
- 96-well plate (clear polystyrene wells, flat bottom) (ExtraGene, catalog number: EL-1190-F )
- Streptavidin-horseradish peroxidase (HRP) (R&D Systems, catalog number: DY998 )
- 3,3’,5,5’-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) substrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T0440 )
- Stop solution (2 N H2SO4 water solution) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 30743 )
- Corning 6.5 mm Transwell inserts with 0.4 µm polycarbonate membranes in a 24-well plate (Corning, catalog number: 3413 )
- Materials and reagents for RTCA
- 96-well E-plate (ACEA BIO, catalog number: 05232368001 )
Equipment
- Forceps
- General equipment: 37 °C cell incubator supplied with 5% CO2 atmosphere
- Transwell permeability assay: VersaMax microplate reader (Molecular Devices, model: VersaMax ELISA Microplate Reader )
- RTCA: xCELLigence RTCA System (ACEA BIO, model: xCELLigence RTCA SP System , catalog number: 00380601030)
Software
- GraphPad Prism software
Procedure
- Transwell permeability assay
- Grow 2 x 105 HMEC-1 cells in 300 µl endothelial growth medium on the membrane of each 6.5 mm transwell insert (Figure 1).
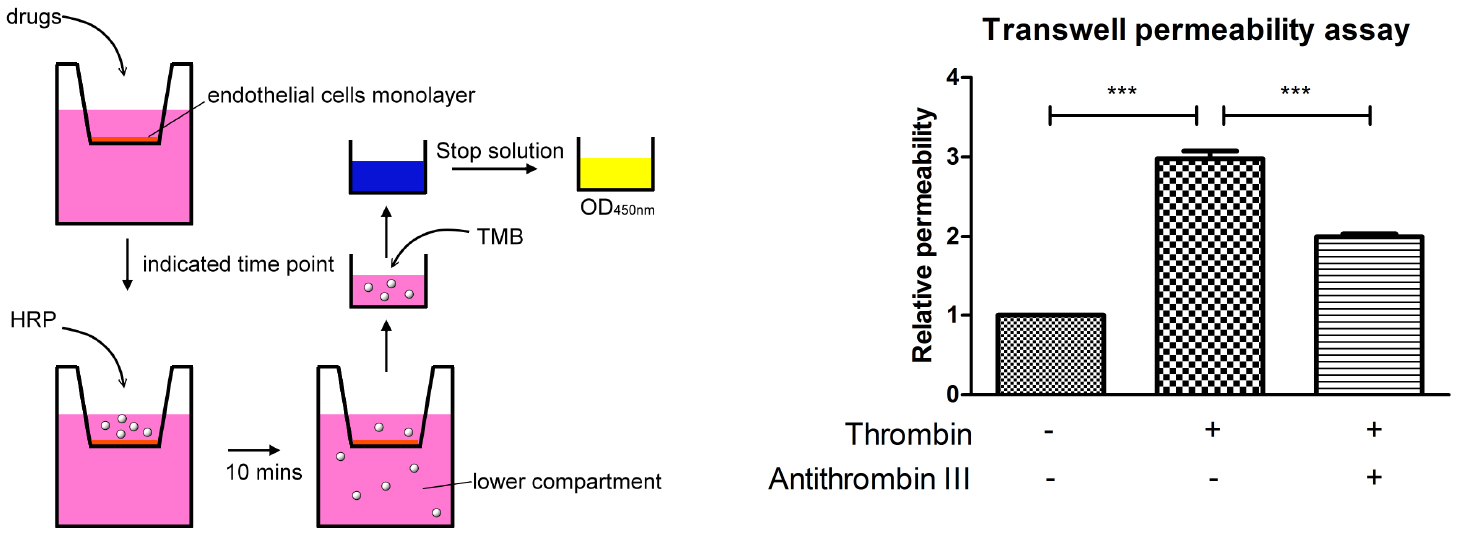
Figure 1. A schematic outline procedure and typical results of transwell permeability assay - Fill the 24-well plate with 1 ml endothelial growth medium.
- Transfer the inserts to the wells with medium by using forceps, and then cover the plate with the lid. The sterilization of the forceps is not necessary, although treating with 80% ethanol is recommended.
- Incubate the plate in a 37 °C incubator for two days.
- Aspirate the medium from the top and bottom chamber, then replace with the same volume of fresh Medium 200 medium as described above.
Note: Every movement in this step should be done carefully and slowly as to not activate the endothelial cells. Pipet tips should not touch the membrane. Refill the chambers with fresh medium in a dropwise manner to avoid shear flow. - Put the plate back into the 37 °C incubator for another two days.
- Move the inserts to empty wells with forceps, and wait for 5 min to observe whether medium from the upper chambers leaks into the lower chamber. If there is no leak, then proceed to the next steps. If there is a leak repeat steps A6-A7 and wait till the cells are confluent. The endothelial cells must be fully confluent to ensure the formation of cell-cell junctions and a good endothelial barrier. In general, the cells form confluent monolayer after 5 days of incubation.
- Repeat step A5 and add the desired stimulation to the medium in the top chambers. The stimulation can be cytokines (TNF-α), molecules which induce inflammatory responses (lipopolysaccharide, histamine), or recombinant proteins (thrombin, dengue virus nonstructural protein 1).
- Incubate the plate in the 37 °C incubator for desired time period. This assay works best when the cells are stimulated between 10 min to 24 h. Here we show the result of stimulating the endothelial cells with thrombin for 30 min (Figure 1).
- Before measuring the permeability of the endothelial monolayer, prepare medium containing streptavidin-HRP (15 µl streptavidin-HRP per 1 ml of serum-free medium).
- Aspirate medium in top chambers and refill them with streptavidin-HRP-containing medium.
Note: As mentioned in step A6, every movement should be gentle and careful, and pipet tips should not touch the membrane. - Add 1 ml serum-free medium in each well of a new 24-well plate. And then put the inserts in.
- Cover the plate, and place the plate in the 37 °C incubator.
- After incubation for 5 min, the inserts are removed, and 20 µl of media from the lower chamber is transferred to a new 96-well plate. Every condition should be aliquoted in triplicate.
- Add 50 µl TMB substrate into each well of the 96-well plate, and wait 5 min at room temperature for the reaction to stabilize. After incubation, TMB substrate should turn blue. If there is no change in the color, extend the incubation time. However, the incubation time should not exceed 20 min.
- Add 25 µl stop solution into each well, and acquire the absorption at 450 nm with an ELISA reader.
A schematic outline procedure and typical results are shown in Figure 1.
- Grow 2 x 105 HMEC-1 cells in 300 µl endothelial growth medium on the membrane of each 6.5 mm transwell insert (Figure 1).
- RTCA
- Grow 1 x 104 HMEC-1 cells in each well of a 96-well E-plate, and fill the well with 100 µl of endothelial growth medium.
- Place the plate in the xCELLigence RTCA System, which is set up in a 37 °C incubator.
- Set the program to detect the resistance every hour and monitor when the cells have grown to confluency. In general, the cells grow to confluency after incubating for 2 days, so we suggest checking the cell index curve after 36 h of incubation.
- After the cell index curve stabilizes, refresh the medium, and wait 2 h for the cell index curve to stabilize again.
- Add the desired stimulation into each well. Every condition should be done in triplicate.
- Put the plate back into the xCELLigence RTCA System in the 37 °C incubator.
- Set up the desired detection period and time interval, and start the recording.
The typical results of RTCA are shown in Figure 2.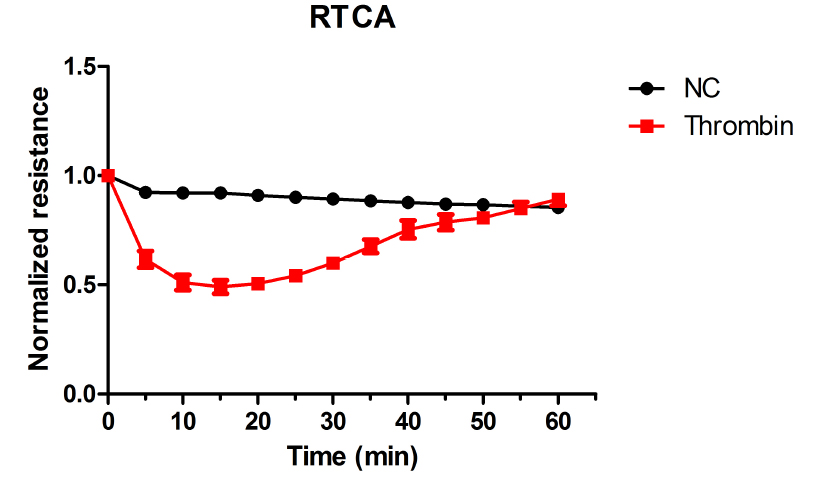
Figure 2. Thrombin-induced endothelial permeability increase as detected by RTCA
- Grow 1 x 104 HMEC-1 cells in each well of a 96-well E-plate, and fill the well with 100 µl of endothelial growth medium.
Data analysis
- For the transwell permeability assay, the resultant absorption intensity values should be normalized over control (e.g., time zero, vehicle control). In order to determine the relative permeability. Each experiment should be repeated more than 3 times, then statistics can be performed using GraphPad Prism software and relevant statistical protocols. Here we show the result which is analyzed with one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni’s multiple comparison test as post-test (Figure 1).
- For RTCA, the cell index of every time point should be normalized over the time zero to determine the relative cell index. The average cell index is calculated and plotted verse time.
Notes
- Other types of endothelial cells, such as HUVECs or hCMEC/D3, can also be used for either assays; however, pre-coating the membranes or plates with substrates such as fibronectin, collagen, gelatin, and/or laminin may be required to promote cell adhesion.
- The integrity of the endothelial monolayer is crucial for the accuracy of either method, so shear flow should always be avoided when handling the cells. For RTCA, as the electrode of 96-well E-plate is very fragile and sensitive, it should always be handled with care. Pipet tips should not touch the electrode on the plate thus avoiding any disruption of the endothelial monolayer. Hands should not touch the electrode beneath the plate as well, as it might disrupt the detection of the resistance. After trypsinizing and washing, the E-plate could be reused (Stefanowicz-Hajduk et al., 2016). An E-plate can be reused at least 3 times without affecting data reproducibility in previous literature and in our experiences (Stefanowicz-Hajduk et al., 2016).
Run a pretest program before use. If it shows errors in detecting electrical resistance, the E-plate is unsuitable for further assays.
Recipes
- Endothelial cell growth medium
Medium 200 supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and penicillin-streptomycin solution at a final concentration of 100 U/ml
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan (102-2320-B-006-025-MY3) (105-2321-B-006-023 and the Center of Infectious Disease and Signaling Research of NCKU, Tainan, Taiwan). This protocol is a modification of those published by Chuang et al. (2011) and Bao Dang et al. (2013).
References
- Bao Dang, Q., Lapergue, B., Tran-Dinh, A., Diallo, D., Moreno, J. A., Mazighi, M., Romero, I. A., Weksler, B., Michel, J. B., Amarenco, P. and Meilhac, O. (2013). High-density lipoproteins limit neutrophil-induced damage to the blood-brain barrier in vitro. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 33(4): 575-582.
- Bischoff, I., Hornburger, M. C., Mayer, B. A., Beyerle, A., Wegener, J. and Furst, R. (2016). Pitfalls in assessing microvascular endothelial barrier function: impedance-based devices versus the classic macromolecular tracer assay. Sci Rep 6: 23671.
- Chen, H. R., Chuang, Y. C., Lin, Y. S., Liu, H. S., Liu, C. C., Perng, G. C. and Yeh, T. M. (2016). Dengue virus nonstructural protein 1 induces vascular leakage through macrophage migration inhibitory factor and autophagy. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 10(7): e0004828.
- Chuang, Y. C., Lei, H. Y., Liu, H. S., Lin, Y. S., Fu, T. F. and Yeh, T. M. (2011). Macrophage migration inhibitory factor induced by dengue virus infection increases vascular permeability. Cytokine 54(2): 222-231.
- Komarova, Y. and Malik, A. B. (2010). Regulation of endothelial permeability via paracellular and transcellular transport pathways. Annu Rev Physiol 72: 463-493.
- Stefanowicz-Hajduk, J., Adamska, A., Bartoszewski, R. and Ochocka, J. R. (2016). Reuse of E-plate cell sensor arrays in the xCELLigence Real-Time Cell Analyzer. Biotechniques 61(3): 117-122.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Chen, H. and Yeh, T. (2017). In vitro Assays for Measuring Endothelial Permeability by Transwells and Electrical Impedance Systems. Bio-protocol 7(9): e2273. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2273.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial cell biology > Cell-based analysis > Reporter assay
Cell Biology > Cell-based analysis > Transport
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









