- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Penetration Assays, Fungal Recovery and Pathogenicity Assays for Verticillium dahliae
Published: Vol 7, Iss 4, Feb 20, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2133 Views: 11687
Reviewed by: Arsalan DaudiGazala AmeenVenkatasalam Shanmugabalaji

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Rice Ragged Stunt Virus Propagation and Infection on Rice Plants
Chao Zhang [...] Jianguo Wu
Oct 20, 2018 6505 Views

Botrytis cinerea in vivo Inoculation Assays for Early-, Middle- and Late-stage Strawberries
Piao Yang [...] Ye Xia
Oct 20, 2023 2775 Views
Abstract
Verticillium dahliae is a soil-borne phytopathogenic fungus that infects host roots and proliferates in vascular tissues. The great loss of economically important crop caused by V. dahliae has raised worldwide concern, however, little is known about the mechanism of its pathogenicity (Klosterman et al., 2011; Yadeta and Thomma, 2013). Our recent work has shown that V. dahliae develops hyphopodium as an infection structure to breach plant root cell wall (Zhao et al., 2016). Here, we provide a detailed protocol to analyze the penetration ability and the pathogenicity of V. dahliae as well as recover fungal hyphae from infected cotton stems developed from our previous studies (Zhang et al., 2016a and 2016b; Zhao et al., 2016). Cellophane membrane has been used in inducing appressorium development of foliar pathogens but not root pathogens (Bourett and Howard, 1990). We adopted the method of using the cellophane membrane to induce and assess the development of hyphopodium. Hopefully, it will greatly promote the research of molecular events involved in recognition of the host that regulate infectious development. This protocol is also helpful to identify the key component controlling the pathogenicity of V. dahliae and widen our understanding of the mechanism of plant-microbe interaction.
Keywords: Verticillium dahliaeBackground
The cellophane membrane has been widely used to study the development of infection structure in foliar pathogens (Bourett and Howard, 1990; Kleemann et al., 2012; Gu et al., 2014), we firstly adopt this method to induce infection structure in root pathogen of V. dahliae, which is a simple and efficient method to study the hyphopodium development. Also, we previously developed a novel unimpaired root dip-inoculation method to assess the pathogenicity of V. dahliae in cotton (Gao et al., 2010). The regular procedure for infection of plants with the soil-borne pathogen is to uproot soil-grown plants, incubate the roots in a conidial suspension, and then replant the plants in fresh soil. Our inoculation method avoids damaging the roots and is convenient for operation, which combined the protocol of fungal recovery from stem facilitates the pathogenicity study of soil-borne pathogens that colonize the vascular tissues.
Materials and Reagents
- Protection gloves (Medicom, catalog number: 1174D )
- Protection coat (Medicom, catalog number: 8018 )
- Cellophane membrane (DINGGUO CHANGSHENG, catalog number: XH444-1 )
- Round (90 mm diameter) Petri dishes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 101VIRR )
- Sterilized gauze (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 22-415-469 )
- Pot for cotton growth (Shantou Xing Lv Yuan, dimensions: 300 x 200 x 100)
- Sterilized pipette tips (Corning, Axygen®, catalog number: TF-1005-WB-L-R-S )
- 50 ml conical tubes (Corning, catalog number: 430828 )
- Cotton seeds (Nongqishi Agricultural Institute, cv. Xinluzao NO.16)
- Potato tubers
- Glycerol
- Distilled water (Milli-Q) (EMD Millipore, catalog number: QTUM00ICP )
- 70% (v/v) ethanol (EtOH in ddH2O)
- 30% H2O2 (ALADDIN, catalog number: H112519 )
- Glucose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V900392 )
- Agar (BD, BactoTM, catalog number: 214010 )
- Sodium nitrate, NaNO3 (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 106537 )
- Potassium dihydrogen phosphate, KH2PO4 (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 104873 )
- Potassium phosphate dibasic, K2HPO4 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V900050 )
- Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, MgSO4·7H2O (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 105886 )
- Potassium chloride, KCl (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 104933 )
- Sodium citrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V900095 )
- Zinc sulfate heptahydrate, ZnSO4·7H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z4750 )
- Iron(II) sulfate heptahydrate, FeSO4·7H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V900038 )
- Ammonium iron(III) sulfate dodecahydrate, NH4Fe(SO4)2·12H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V900032 )
- Copper(II) sulfate pentahydrate, CuSO4·5H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C7631 )
- Manganese(II) sulfate monohydrate, MnSO4·H2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V900271 )
- Boric acid, H3BO3 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V900267 )
- Sodium molybdate dehydrate, Na2MoO4·2H2O (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 106521 )
- Sucrose (Merck Millipore, catalog number: 107687 )
- Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium including vitamins (Duchefa Biochemie, catalog number: M0222 )
- Potato dextrose agar (PDA) (see Recipes)
- TES (see Recipes)
- Minimal medium (MM) (see Recipes)
- MS liquid medium (see Recipes)
- Czapek-Dox medium (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Heat plate and cooking pot to boil potatoes (Supor, catalog number: SDHC8E15 )
- Flasks and magnetic stirrer for preparation of solutions (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S88850206 )
- Fungal growth incubator (SAIFU, catalog number: MJX-450S )
- 26 °C incubator shaker (Zhicheng, catalog number: ZHWY-2102C )
- Autoclave (Hirayama, catalog number: HVE-50 )
- Clean bench (Zhicheng, catalog number: ZHJH-C1209B )
- Hemocytometer for conidia counting (Qiujing, catalog number: QJ1102 )
- Rotator (Qilinbeier, catalog number: QB-208 )
Procedure
- Penetration assays
- Pipette 20 μl conidial suspension (3 x 107 conidia per ml) of V. dahliae stored at -80 °C in 20% glycerol and plate the suspension culture onto the PDA plate and incubate for 5 days at 26 °C in the dark.
- Prepare Minimal medium (MM medium) and autoclave 20 min at 113 °C. Pour plates after cooling the medium down to 50-60 °C and dry the plates in a clean bench.
- Cut the flat sheet membranes of cellophane into circles of 90 mm diameter and autoclave 20 min at 113 °C. Lay one circle on each MM plate prepared in step A2.
- Use a sterilized pipette tip to inoculate the fungi from step A1 onto the cellophane membrane overlaid on the MM medium. Grow cultures for 3 days at 26 °C in the dark. Then remove the membrane and incubate the medium for 7 days to observe hyphae in the underlying medium for determination of breach of cellophane (Figure 1).

Figure 1. Penetration assay on the cellophane membrane. A. Uncovering the membrane from the MM plates with a colony of V. dahliae at 3 days post inoculation (dpi). B. The colony of V. dahliae on the underlying medium indicating the penetration of cellophane membrane.
- Pipette 20 μl conidial suspension (3 x 107 conidia per ml) of V. dahliae stored at -80 °C in 20% glycerol and plate the suspension culture onto the PDA plate and incubate for 5 days at 26 °C in the dark.
- Pathogenicity assays
Susceptible upland cotton (cv. Xinluzao NO. 16) and strain V592 of V. dahliae were used in our lab for pathogenicity assays.
- Sterilize cotton seeds for 15 min and rinse three times with distilled water. Soak the seeds overnight at room temperature. Germinate seeds in pots filled with wet soil and cover with plastic dome for one week to grow seedlings until two cotyledons are fully expanded.
- Transplant 12 seedlings per pot with MS liquid medium and grow at 26 °C with a 16 h light (8,000 lux)/8 h dark cycle for about 2 weeks before inoculation of V592.
- Streak V592 onto fresh PDA plates (from older PDA plates or glycerol stocks) and incubate for 1 week. Transfer one plate (90 mm) of mycelia by a sterilized blade into 200 ml Czapek-Dox medium with shaking at 200 rpm for 3-4 days at 26 °C in the dark to obtain conidia.
- Prepare the conidial suspension through filtrating the fungal cultures with 4 layers of sterilized gauze to remove mycelia. Measure the concentration of conidia in the suspension using a hemocytometer and adjust to approximately 1 x 107 conidia per ml with Czapek-Dox medium.
- Immerse the roots of seedlings with two true leaves to the conidial suspension from step B4 for 1 h (Figure 2A). Put back the inoculated seedlings to MS liquid medium and supply water once a week.
- Count disease incidence by the percentage of cottons that showed wilting symptom at 30 dpi (Figure 2B). The infection assay was repeated at least three times with 3 pots of cotton each trial.
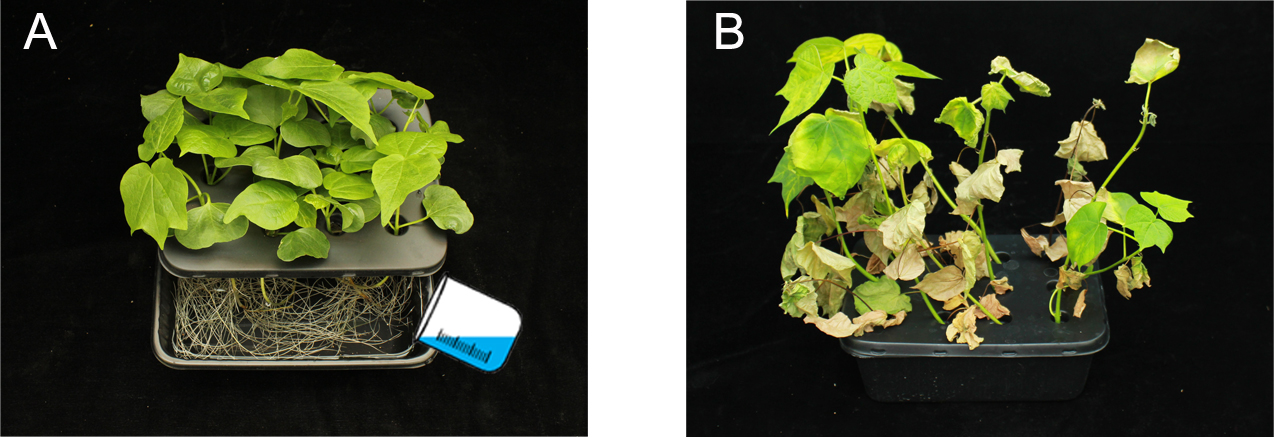
Figure 2. Pathogenicity assay of V. dahliae. A. Root-dip inoculation of cotton seedling with conidia suspension. B. Representative disease symptom in cotton at 30 dpi of V. dahliae.
- Sterilize cotton seeds for 15 min and rinse three times with distilled water. Soak the seeds overnight at room temperature. Germinate seeds in pots filled with wet soil and cover with plastic dome for one week to grow seedlings until two cotyledons are fully expanded.
- Fungal recovery
To identify the colonization of V. dahliae in vascular tissues, we isolate the inoculated cotton stems to recover the fungi.- Cut the stem above cotyledons of cotton at 30 days post inoculation (Figure 3).
- Sterilize the stem sections for 1 min in 70% ethanol within a 50 ml conical tube followed by 60 min in 40 ml of 10% (v/v) H2O2 (dilute the 30% [v/v] H2O2 with distilled water). Revolve the tube on the rotator at 20 rpm during this process.
- Rinse the stems three times with sterilized water for 3 min each time and culture at 26 °C on PDA medium in the dark. The colonies of V. dahliae can grow on the stems within 1 week (Figure 3).
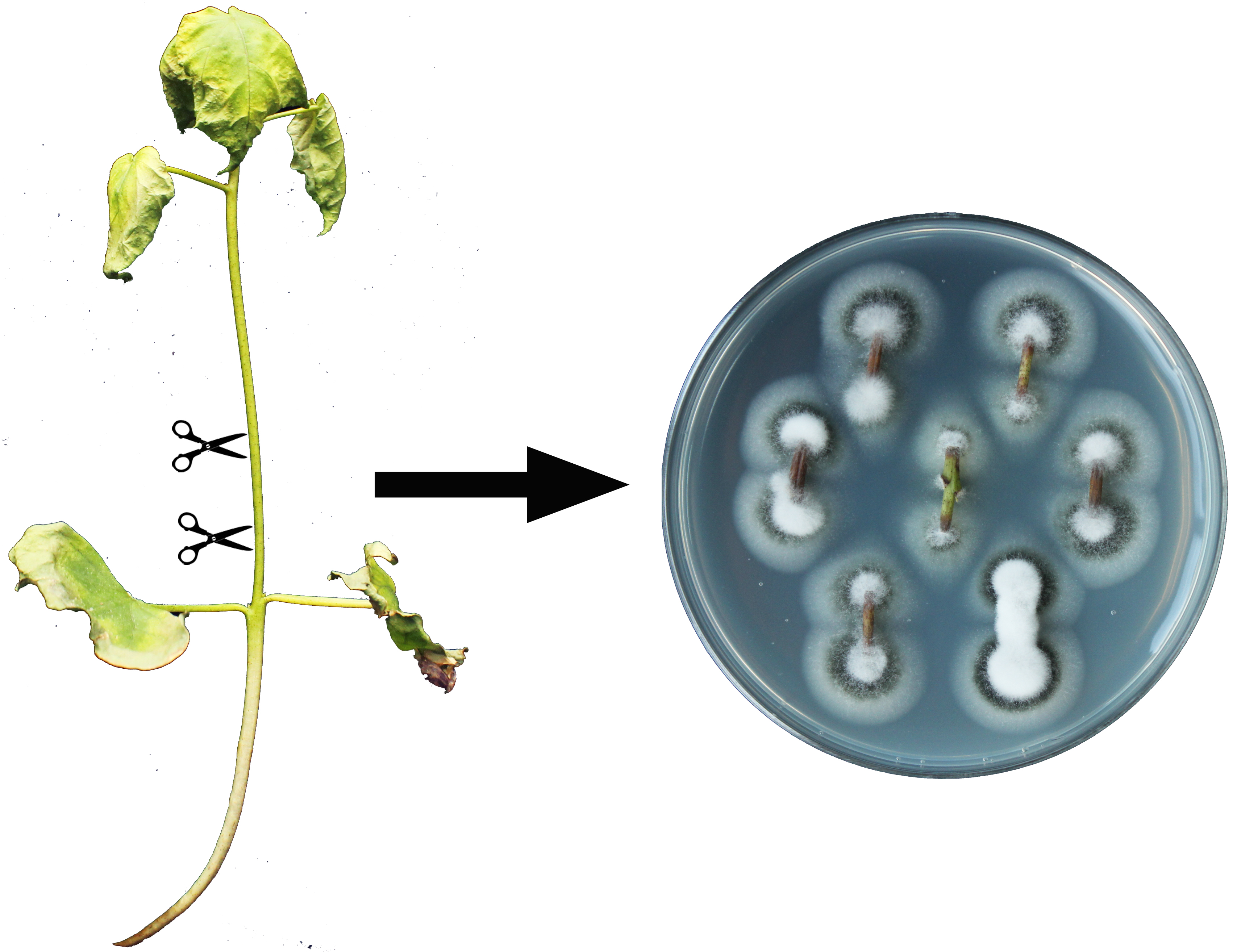
Figure 3. Recovery of V. dahliae from the infected stem of cotton
- Cut the stem above cotyledons of cotton at 30 days post inoculation (Figure 3).
Data analysis
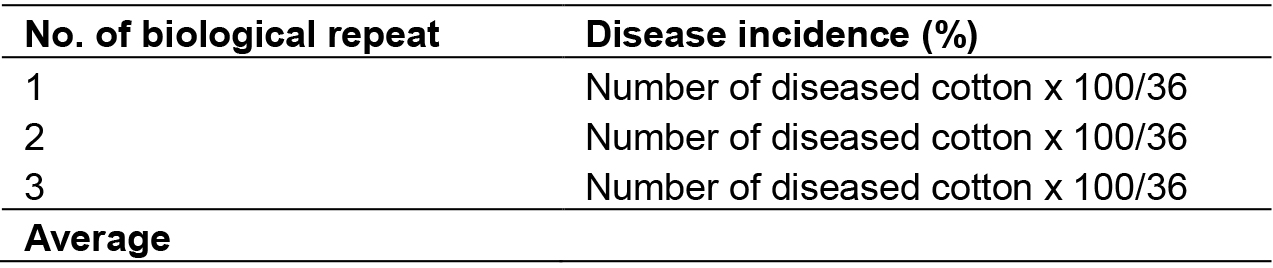
Data from at least three biological repeats were obtained and one-way ANOVA was used to analyze the disease incidence with Microsoft Excel (Table 1).
Table 1. Analysis of disease incidence. Disease incidence was counted by the percentage of diseased cottons in 3 pots of infected cottons (3 x 12, total 36 cottons). Assay was repeated 3 times.
Notes
- Each of cellophane membranes should be separated by a filter paper to prevent adhesion during autoclaving.
- To prevent shrinkage of the cellophane membrane, it is soaked into sterilized water firstly before putting on MM plate.
Recipes
- Potato dextrose agar (PDA)
Boil 200 g of peeled potatoes in 1 L of distilled water for 20 min
Filtrate through 4 layers of gauze
Add 20 g of glucose and 20 g of agar
Distilled water to 1 L
Sterilize by autoclaving 20 min at 113 °C
- TES
50 g/L citrate
50 g/L ZnSO4·7H2O
50 g/L FeSO4·7H2O
13 g/L NH4Fe(SO4)2·12H2O
2.5 g/L CuSO4·5H2O
0.5 g/L MnSO4·H2O
0.5 g/L H3BO3
0.5 g/L Na2MoO4·2H2O
Stored at 4 °C
- Minimal medium
2 g/L glucose
2 g/L NaNO3
1 g/L KH2PO4
0.5 g/L MgSO4·7H2O
0.5 g/L KCl
0.02% (v/v) TES
20 g/L agar
Sterilize by autoclaving 20 min at 113 °C
- MS liquid medium
0.1% (w/v) MS
- Czapek-Dox medium
30 g/L sucrose
3 g/L NaNO3
1 g/L K2HPO4
0.5 g/L MgSO4·7H2O
0.5 g/L KCl
100 mg/L FeSO4·7H2O
Sterilize by autoclaving 20 min at 113 °C
Acknowledgments
This protocol was developed from the following published paper: Bourett and Howard, 1990. This work was supported by grant from the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (XDB11040500) and the China Transgenic Research and Commercialization Key Special Project (2014ZX0800908B).
References
- Bourett, T. M. and Howard, R. J. (1990). In vitro development of penetration structures in the rice blast fungus Magnaporthe grisea. Can J Bot 68(2): 329-342.
- Gao, F., Zhou, B. J., Li, G. Y., Jia, P. S., Li, H., Zhao, Y. L., Zhao, P., Xia, G. X. and Guo, H. S. (2010). A glutamic acid-rich protein identified in Verticillium dahliae from an insertional mutagenesis affects microsclerotial formation and pathogenicity. PLoS One 5(12): e15319.
- Gu, S. Q., Li, P., Wu, M., Hao, Z. M., Gong, X. D., Zhang, X. Y., Tian, L., Zhang, P., Wang, Y., Cao, Z. Y., Fan, Y. S., Han, J. M. and Dong, J. G. (2014). StSTE12 is required for the pathogenicity of Setosphaeria turcica by regulating appressorium development and penetration. Microbiol Res 169(11): 817-823.
- Kleemann, J., Rincon-Rivera, L. J., Takahara, H., Neumann, U., Ver Loren van Themaat, E., van der Does, H. C., Hacquard, S., Stuber, K., Will, I., Schmalenbach, W., Schmelzer, E. and O'Connell, R. J. (2012). Sequential delivery of host-induced virulence effectors by appressoria and intracellular hyphae of the phytopathogen Colletotrichum higginsianum. PLoS Pathog 8(4): e1002643.
- Klosterman, S. J., Subbarao, K. V., Kang, S., Veronese, P., Gold, S. E., Thomma, B. P., Chen, Z., Henrissat, B., Lee, Y. H., Park, J., Garcia-Pedrajas, M. D., Barbara, D. J., Anchieta, A., de Jonge, R., Santhanam, P., Maruthachalam, K., Atallah, Z., Amyotte, S. G., Paz, Z., Inderbitzin, P., Hayes, R. J., Heiman, D. I., Young, S., Zeng, Q., Engels, R., Galagan, J., Cuomo, C. A., Dobinson, K. F. and Ma, L. J. (2011). Comparative genomics yields insights into niche adaptation of plant vascular wilt pathogens. PLoS Pathog 7(7): e1002137.
- Yadeta, K. A. and Thomma, B. P. (2013). The xylem as battleground for plant hosts and vascular wilt pathogens. Front Plant Sci 4(97): 1-12.
- Zhang, T., Jin, Y., Zhao, J. H., Gao, F., Zhou, B. J., Fang, Y. Y. and Guo, H. S. (2016a). Host-induced gene silencing of the target gene in fungal cells confers effective resistance to the cotton wilt disease pathogen Verticillium dahliae. Mol Plant 9(6): 939-942.
- Zhang, T., Zhao, Y. L., Zhao, J. H., Wang, S., Jin, Y., Chen, Z. Q., Fang, Y. Y., Hua, C. L., Ding, S. W. and Guo, H. S. (2016b). Cotton plants export microRNAs to inhibit virulence gene expression in a fungal pathogen. Nat Plants 2(10): 16153.
- Zhao, Y. L., Zhou, T. T. and Guo, H. S. (2016). Hyphopodium-specific VdNoxB/VdPls1-dependent ROS-Ca2+ signaling is required for plant infection by Verticillium dahliae. PLoS Pathog 12(7): e1005793.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Zhao, Y., Zhang, T. and Guo, H. (2017). Penetration Assays, Fungal Recovery and Pathogenicity Assays for Verticillium dahliae. Bio-protocol 7(4): e2133. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2133.
Category
Plant Science > Plant immunity > Disease bioassay
Cell Biology > Tissue analysis > Tissue staining
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











