- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Dot Blot Analysis of N6-methyladenosine RNA Modification Levels
Published: Vol 7, Iss 1, Jan 5, 2017 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2095 Views: 29480
Reviewed by: Antoine de MorreeXiaoyi ZhengVaibhav B Shah

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Separation of Microspores from Anthers of Lilium longiflorum (Lily) and Subsequent RNA Extraction
Ming-Che Liu [...] Co-Shine Wang
Feb 20, 2015 10529 Views
Low-cost and High-throughput RNA-seq Library Preparation for Illumina Sequencing from Plant Tissue
Marta Bjornson [...] Pingtao Ding
Oct 20, 2020 8287 Views

A Highly Efficient System for Separating Glandular and Non-glandular Trichome of Cucumber Fruit for Transcriptomic and Metabolomic Analysis
Lei Sun [...] Xingwang Liu
Jan 5, 2025 1459 Views
Abstract
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is the most prevalent internal modification of eukaryotic messenger RNA (mRNA). The total amount of m6A can be detected by several methods, such as dot blot analysis using specific m6A antibodies and quantitative liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) (Fu et al., 2014; Shen et al., 2016). Here we describe the method for fast detection of total m6A levels in mRNA by dot blot analysis using a specific m6A antibody.
Keywords: Dot blotBackground
Dot blot analysis for detecting total m6A levels in mRNA is relatively easy, fast, and cost-effective as compared to other methods, such as two-dimensional thin layer chromatography and LC-MS/MS. This approach can be used, in a qualitative manner, to evaluate temporal and spatial changes in m6A levels in various plant tissues or plants at different developmental stages. This is particularly useful for initial examination of changes in m6A levels in relevant mutants prior to detailed investigations by other complex and quantitative approaches.
Materials and Reagents
- Amersham Hybond-N+ membrane (GE Healthcare, catalog number: RPN203B )
- Plastic wrap
- Amersham Hyperfilm ECL (GE Healthcare, catalog number: 28906835 )
- Total RNA
- Dynabeads® mRNA Purification Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, AmbionTM, catalog number: 61006 )
- RNase-free water
- Anti-m6A antibody (Synaptic Systems, catalog number: 202 003 )
- Goat anti-rabbit IgG-HRP (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, catalog number: sc-2004 )
- ECL Western Blotting Substrate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 32106 )
- 1x phosphate buffered saline (1x PBS), pH 7.4
- Tween 20 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9416 )
- Non-fat milk (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 1706404 )
- Wash buffer (see Recipes)
- Blocking buffer (see Recipes)
- Antibody dilution buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: NanoDropTM 2000 Spectrophotometer )
- Heat block
- Stratalinker 2400 UV Crosslinker (Stratalinker)
- Shaker
Software
- ImageJ
Procedure
- mRNA purification
- Isolate mRNA from total RNA using the Dynabeads® mRNA Purification Kit following the manufacturer’s instructions. For one dot blot assay, we recommend to purify at least 20 μg of total RNA.
- Determine the concentration of purified mRNA with NanoDrop and make a serial dilution of mRNA to 50 ng/μl, 10 ng/μl and 2 ng/μl using RNase-free water.
- Isolate mRNA from total RNA using the Dynabeads® mRNA Purification Kit following the manufacturer’s instructions. For one dot blot assay, we recommend to purify at least 20 μg of total RNA.
- Dot blotting
- Denature the serially diluted mRNA at 95 °C to disrupt secondary structures in a heat block for 3 min.
- Chill on ice immediately after denaturation to prevent the re-formation of secondary structures of mRNA.
- Drop 2 μl of mRNA directly onto the Hybond-N+ membrane optimized for nucleic acid transfer (Figure 1).
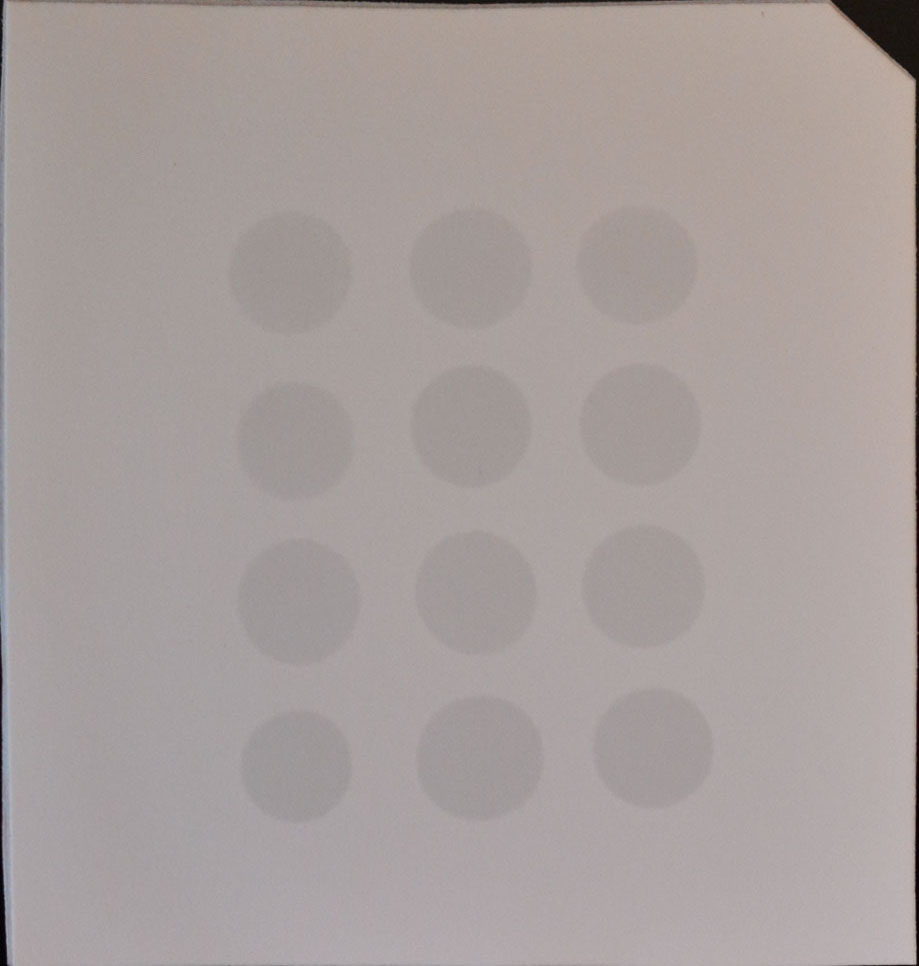

Figure 1. Example of mRNA dots on a membrane
- Crosslink spotted mRNA to membrane in a Stratalinker 2400 UV Crosslinker twice using the Autocrosslink mode (1,200 microjoules [x100]; 25-50 sec).
- Wash the membrane in 10 ml of wash buffer in a clean washing tray, which is unnecessary to be RNase-free, for 5 min at room temperature with gentle shaking to wash off the unbound mRNA.
- Incubate the membrane in 10 ml of blocking buffer for 1 h at room temperature with gentle shaking.
- Incubate the membrane with anti-m6A antibody (1:250 dilution; 2 μg/ml) in 10 ml of antibody dilution buffer overnight at 4 °C with gentle shaking.
- Wash the membrane three times for 5 min each in 10 ml of wash buffer with gentle shaking.
- Incubate the membrane with goat anti-rabbit IgG-HRP (1:10,000 dilution; 20 ng/ml) in 10 ml of antibody dilution buffer for 1 h at room temperature with gentle shaking.
- Wash the membrane four times for 10 min each in 10 ml of wash buffer with gentle shaking.
- Incubate the membrane with 3 ml of ECL Western Blotting Substrate for 5 min in darkness at room temperature. Please note that the volume of ECL solution added is dependent on the size of the membrane. According to the manufacturer’s instructions, 0.125 ml ECL solution per cm2 of the membrane is recommended.
- Wrap the membrane in plastic wrap and expose with Hyperfilm ECL for a proper exposure period.
- Develop the film.
Data analysis
As dot blot analysis is a semi-quantitative approach, the analysis should be repeated through the above procedures using independent biological materials. Only the repeatable changes in m6A levels observed in independent materials as compared to the wild-type control are considered ‘positive’ results, which may be further investigated by other quantitative approaches. In addition, the signals from the dot blot images can be quantified by ImageJ and the statistical analysis should be based on at least three biological replicates.
Representative data
For representative data, please see the paper of Shen et al., 2016.
Notes
This protocol is also applicable to detect other types of RNA modifications if the corresponding specific primary antibodies and secondary antibodies are available.
Recipes
- Wash buffer
1x PBS
0.02% Tween-20 - Blocking buffer
1x PBS
0.02% Tween-20
5% non-fat milk - Antibody dilution buffer
1x PBS
0.02% Tween-20
5% non-fat milk
Note: It is unnecessary to use RNase-free water to prepare the above solutions.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Academic Research Fund (MOE2015-T2-1-002) from the Ministry of Education-Singapore, the Singapore National Research Foundation Investigatorship Programme (NRF-NRFI2016-02), and the intramural research support from National University of Singapore and Temasek Life Sciences Laboratory.
References
- Fu, Y., Dominissini, D., Rechavi, G., and He, C. (2014). Gene expression regulation mediated through reversible m6A RNA methylation. Nat Rev Genet 15(5): 293-306.
- Shen, L., Liang, Z., Gu, X., Chen, Y., Teo, Z.W., Hou, X., Cai, W.M., Dedon, P.C., Liu, L., and Yu, H. (2016). N6-methyladenosine RNA modification regulates shoot stem cell fate in Arabidopsis. Dev Cell 38(2): 186-200.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Shen, L., Liang, Z. and Yu, H. (2017). Dot Blot Analysis of N6-methyladenosine RNA Modification Levels. Bio-protocol 7(1): e2095. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2095.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > RNA > RNA extraction
Molecular Biology > RNA > RNA detection
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link