- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Isolating and Measuring the Growth and Morphology of Pro-embryogenic Masses in Araucaria angustifolia (Bertol.) Kuntze (Araucariaceae)
Published: Vol 6, Iss 23, Dec 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2031 Views: 9596
Reviewed by: Scott A M McAdamAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

A Novel Imaging Protocol for Investigating Arabidopsis thaliana Siliques and Seeds Using X-rays
Brylie A. Ritchie [...] Ansul Lokdarshi
Oct 5, 2023 2190 Views

Direct Plant Regeneration From Immature Male Inflorescence of Banana (Musa spp.)
Pradeep Chand Deo
Oct 20, 2025 1438 Views

A Simple Protocol for Periodic Live Cell Observation of Flagellate Stages in the Lichen Alga Trebouxia
Enrico Boccato [...] Mauro Tretiach
Jan 20, 2026 189 Views
Abstract
Embryogenic suspension cultures of Araucaria angustifolia (Bertol.) Kuntze (Araucariaceae) can be used as a model to test the effects of compounds added to the culture medium on the cellular growth and morphology of Pro-Embryogenic Masses (PEMs). PEMs are formed by embryogenic and suspensor-type cells. To measure changes in the cellular growth of embryogenic cultures, we performed sedimented cell volume (SCV) quantification, which is a non-destructive method. Morphological analysis by microscopy allowed for the observation of growth and development of PEMs and the alterations in embryogenic and suspensor-type cells. The methods used here provide an efficient means for monitoring the cellular growth of PEMs and identifying morphological changes during the development of embryogenic cultures. These studies can also be combined with biochemical and molecular analyses, such as proteomics, to further investigate embryo growth and morphology.
Keywords: Somatic embryogenesisBackground
Silveira et al. (2006) used SCV measurements to analyze the effects of exogenous polyamines on the morphological changes of A. angustifolia PEMs and Osti et al. (2010) tested the effect of different nitric oxide donors on cellular growth and PEM morphology. Recently, Douétts-Peres et al. (2016) studied the effect of a cellular growth inhibitor on cellular growth and PEM morphology using SCV, fresh and dry weight, PEM area, and individual diameters of embryogenic-type cells, including the length and width of the suspensor-type cells. In addition, alterations to cellular growth and morphology in response to endogenous compounds, such as polyamines, nitric oxide and specific proteins have been evaluated using this method (Silveira et al., 2006; Osti et al., 2010; Douétts-Peres et al., 2016).
Materials and Reagents
- Falcon tube rack (Kasvi, catalog number: K30-1552 )
- 12-well cell culture plates - disposable (TPP, catalog number: 92012 )
- Manual pipette 200 µl tips (Corning, Axygen®, catalog number: T-200-Y )
- Manual pipette 1,000 µl tips (Corning, Axygen®, catalog number: T-1000-B )
- Aluminum foil
- Glass slides (Kasvi, catalog number: K5-7101 )
- Cover slips (Kasvi, catalog number: K5-2450 )
- Falcon tubes, 50 ml (Kasvi, catalog number: K19-0050 )
- Embryogenic suspension cultures of A. angustifolia, induced according to the methodology established by Steiner et al. (2005)
- Cellulase (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 22178 )
- Potassium nitrate (KNO3) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000944 )
- Calcium chloride dihydrate (CaCl2·2H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000199 )
- Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate (MgSO4·7H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V001861 )
- Potassium chloride (KCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000104 )
- Potassium dihydrogen phosphate (KH2PO4) (EMD Millipore, catalog number: 104873 )
- MnSO4·H2O (Labsynth, catalog number: S2036 )
- ZnSO4·7H2O (Labsynth, catalog number: S1072 )
- Boric acid (H3BO3) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 31146 )
- Potassium iodide (Kl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000130 )
- Cobalt(II) chloride hexahydrate (CoCl2·6H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: V000213 )
- CuSO4·5H2O (Labsynth, catalog number: S1054 )
- Sodium molybdate dihydrate (Na2MoO4·2H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M1651 )
- FeSO4·7H2O (Labsynth, catalog number: S1057 )
- Na2EDTA (Labsynth, catalog number: E2005 )
- Myo-inositol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: I17508 )
- Nicotinic acid (Labsynth, catalog number: A1043 )
- Pyridoxine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9755 )
- Thiamine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T4625 )
- L-glutamine (Labsynth, catalog number: G1011 )
- Sucrose (Labsynth, catalog number: 2731 )
- MSG culture medium (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Cell dissociation sieve-screens, 150 mesh (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: CD1-1KT ) sterilized by autoclave (121 °C, 30 min)
- Chamber flow (or its equivalent) (Pachame, model: PA 220 )
- Adapted glass Erlenmeyer flasks (custom-made) (Figure 1), sterilized by autoclave (121 °C, 30 min). This adjustment to the flask can be performed by a company that produces laboratory glassware, fusing a glass tube to an Erlenmeyer flask
- Ruler
- Orbital shaker (or its equivalent) (Cientec Equipamentos para Laboratório, model: CT-165 )
- Analytical balance (or its equivalent) (Shimadzu, model: BL3200H )
- Spatula sterilized by autoclave (121 °C, 30 min) (VWR, catalog number: 231-2233 )
- AxioPlan light microscope (Carl Zeiss, model: AxioPlan )
- Manual pipettes (or their equivalent) (Eppendorf, catalog numbers: 3120000062 and 3120000054 )
- Forced air circulation drying oven (or its equivalent) (Ethik Technology, model: 420-6D )
- AxioCam MRC5 digital camera (Carl Zeiss, model: AxioCam )
- Desktop computer
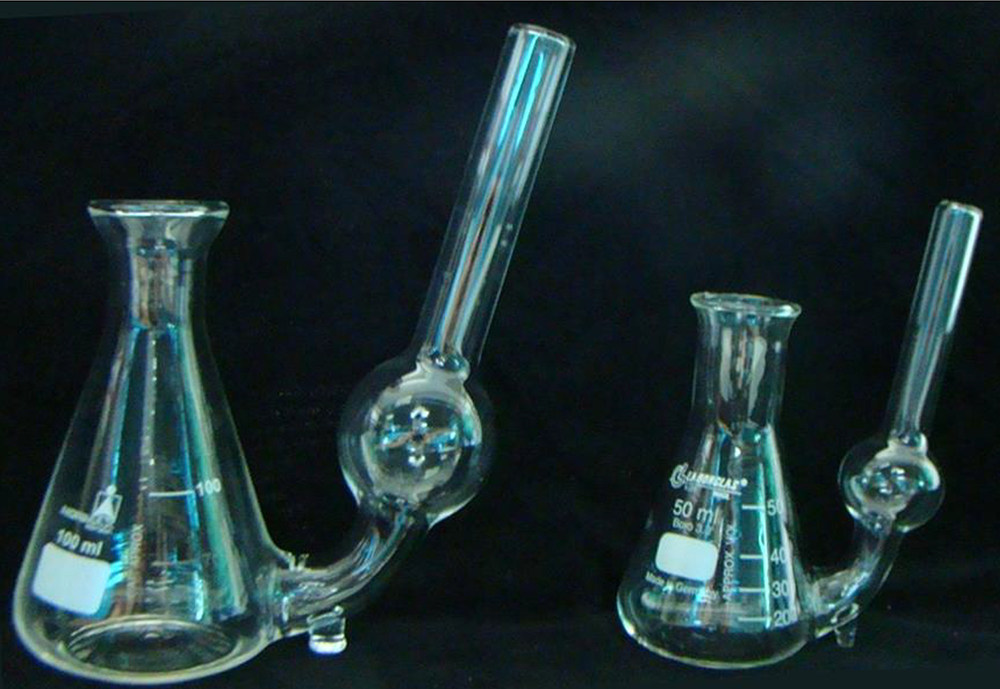

Figure 1. Adapted Erlenmeyer flasks (100 and 50 ml) used in SCV analyses. For an adapted Erlenmeyer flask of 100 ml capacity, we used 25 ml of culture medium and 500 mg of fresh cells. For an adapted Erlenmeyer flask with 50 ml capacity, we used 10 ml of culture medium and 200 mg of fresh cells, with a ratio of 20 mg fresh cells to 1 ml of culture medium.
Software
- AxioVision Rel. 4.8 software (Carl Zeiss, AxioVision)
Procedure
- SCV analysis
- First, in the flow chamber, separate the embryogenic suspension cultures from the medium using the cell dissociation sieve (150 mesh screens) (Figure 2A).
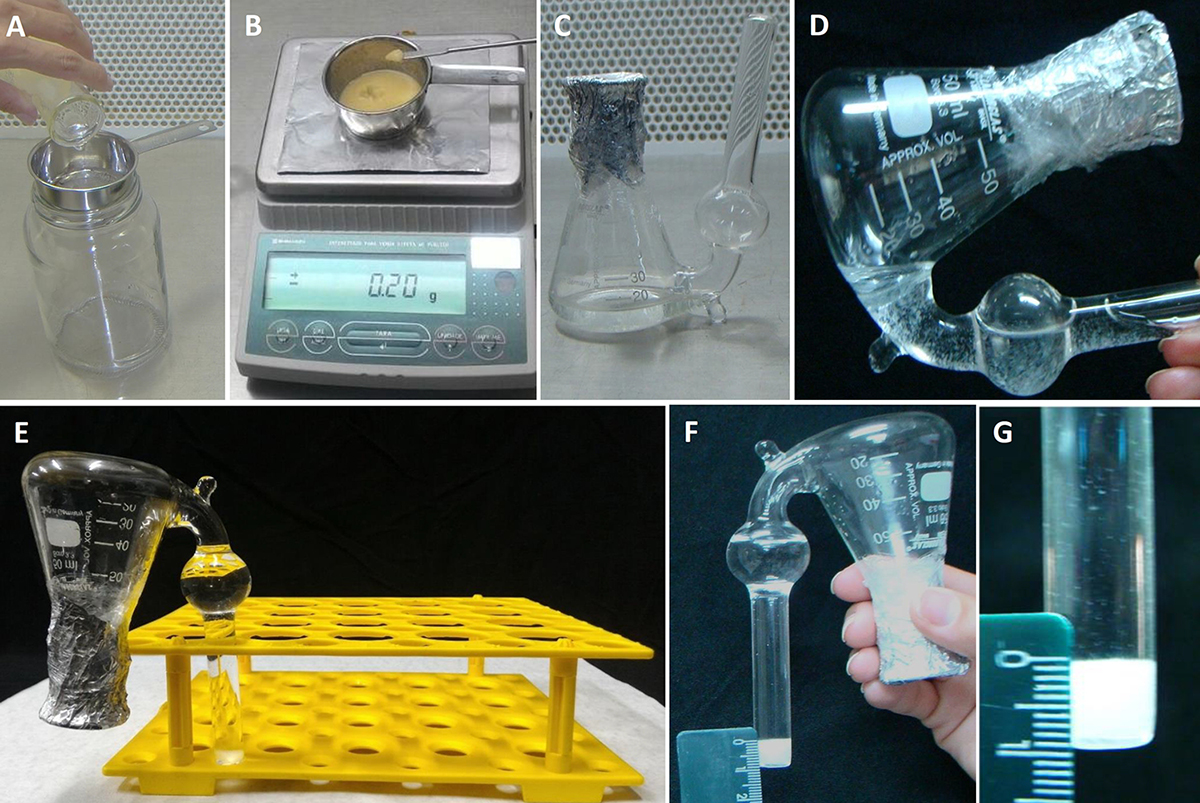
Figure 2. SCV analysis procedures. A. Separation of cells from the culture medium using the sieve; B. Sampling the cells (in terms of fresh weight) for the SCV analyses; C. Adapted Erlenmeyer flask containing the culture medium with inoculated cells; D. Transferring the cells and culture medium to the lateral side tube of the adapted Erlenmeyer flask for SCV measurement; E. Erlenmeyer flask held upright for 15 min; F and G. Details of SCV measurement using the ruler. - Then, place 200 mg of culture (fresh weight) consisting of separated cells in an adapted Erlenmeyer flask (Figure 1) containing 10 ml of the culture medium containing the required testing treatments (Figures 2B and 2C).
- To measure the initial SCV, transfer the entire contents of the flask (culture medium and cells) to the adapted tube outside of the Erlenmeyer flask (Figure 2D). Keep upright in a Falcon tube rack (Figure 2E) for 15 min.
- After this time, measure the initial SCV using a ruler (Figures 2F and 2G).
- Later, return the entire contents (culture medium + cells) into the Erlenmeyer flask by carefully inverting to make sure to return most of the cells into the Erlenmeyer flask (Figure 2C). Keep the adapted Erlenmeyer flasks on a horizontal shaker (100 rpm in the dark at 25 ± 2 °C).
- To determine PEM growth, repeat the measurement procedures every three days until the PEMs reach the decline phase.
Notes:
- A cellular growth curve (Figure 3) is performed to identify the phases of cellular growth of the embryogenic cultures in suspension. This identification can be used to establish the sampling points for the assessment of morphology and for biochemical studies.
- If an Erlenmeyer flask of 100 ml capacity is used, we suggest the following proportion: 25 ml of culture medium used for every 500 mg of fresh cells.
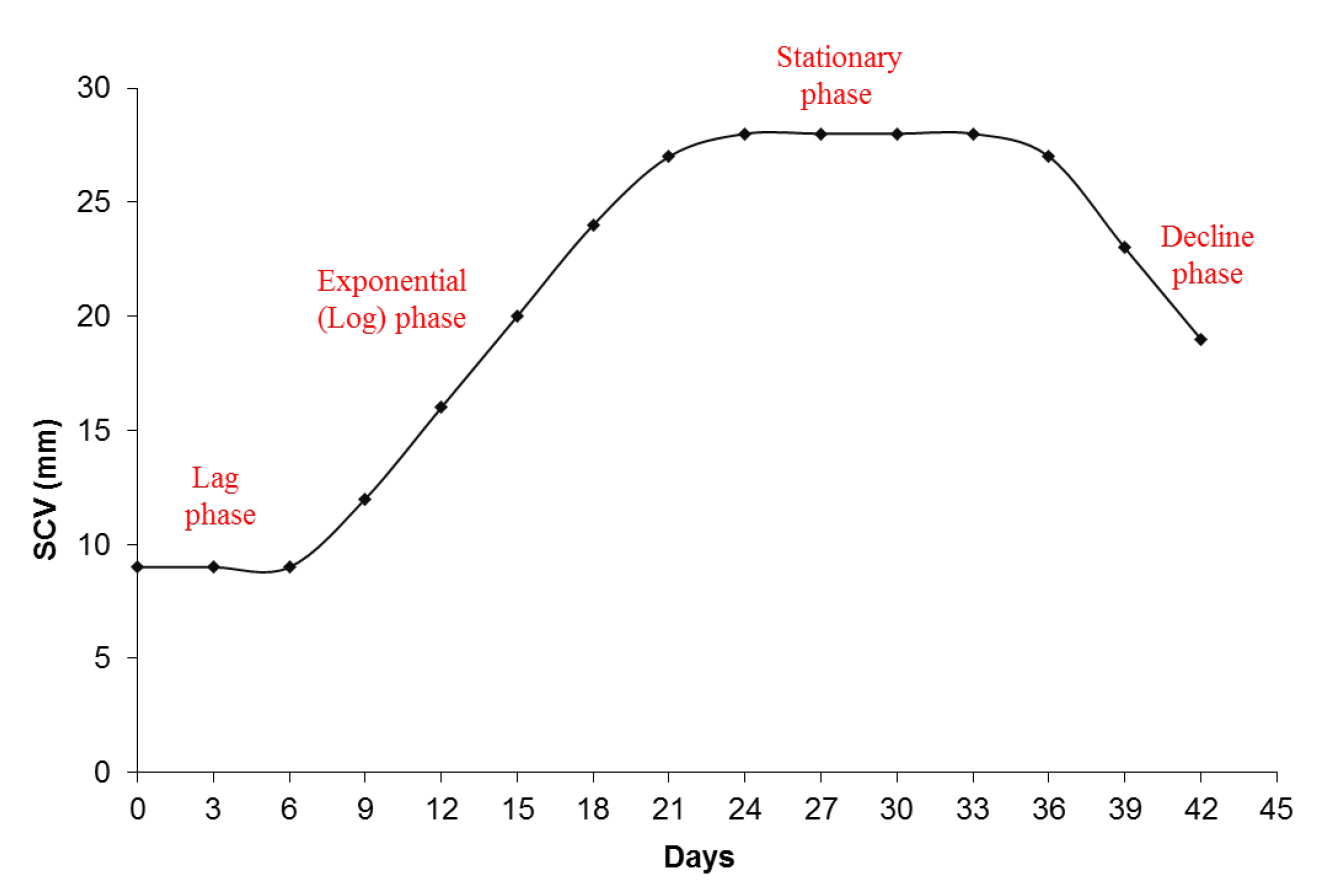
Figure 3. Graphic representation of the cellular growth by SCV. A cellular growth curve by SCV analysis from embryogenic suspension cultures of A. angustifolia in MSG culture medium showing the different phases during incubation.
- First, in the flow chamber, separate the embryogenic suspension cultures from the medium using the cell dissociation sieve (150 mesh screens) (Figure 2A).
- Fresh and dry weight measurement
- Use 12-well cell culture plates for this analysis.
- In a flow chamber, separate the cells from the suspension cultures using a sieve to collect only the cells; discard the culture medium (Figure 2A).
- Next, use the analytical balance (Figure 2B) to weigh the cells and place 60 mg fresh cells into each well of the cell culture plate, which should contain 2 ml of culture medium per well (Figure 4A).
- Close the cell culture plates and keep on a horizontal shaker for incubation (100 rpm in the dark at 25 ± 2 °C).
- To measure the fresh weight on specific days (established by the growth curve, for example), take the cell culture plate and carefully remove the liquid culture medium using a pipette (Figure 4B). Repeat this procedure for each individual well.
- Use a spatula to collect all the solid contents of the cell culture from each well (Figure 4C), separately, on a piece of pre-weighed aluminum foil.
- Measure the fresh weight of cells using an analytical balance (Figure 4D). Dry the samples at 70 °C for 48 h. Then, measure the samples plus aluminum foil again on the analytical balance. It is necessary to subtract the weight of the aluminum foil (pre-weighed) to obtain the dry weight.
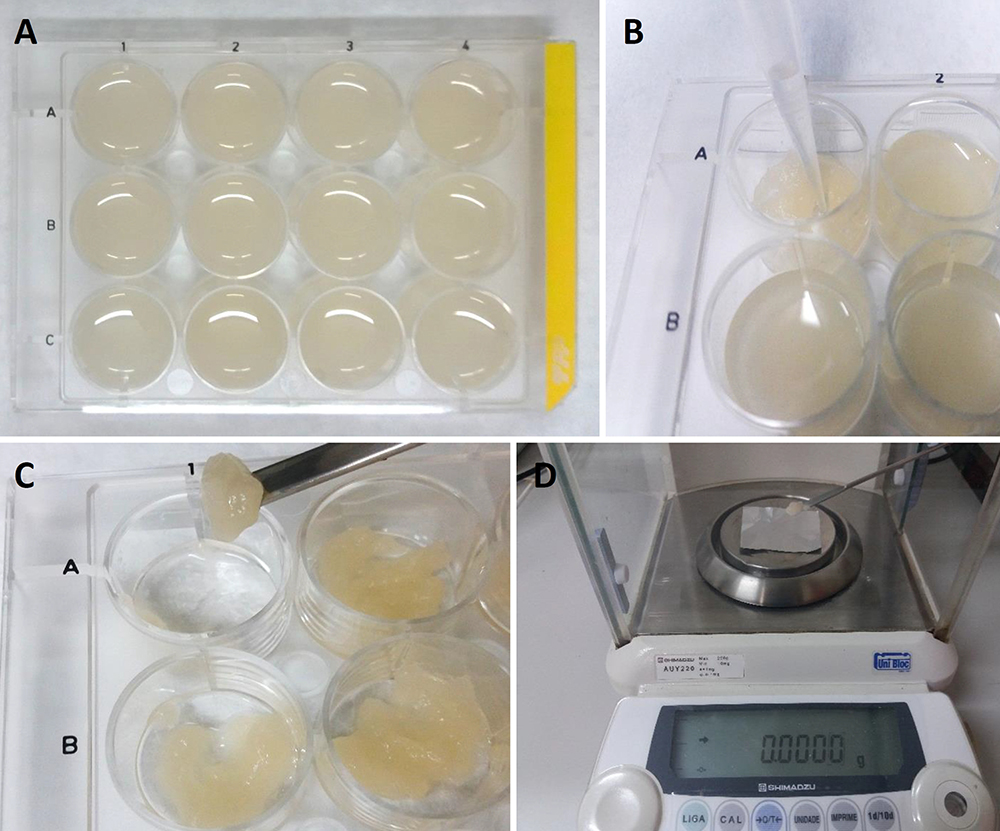
Figure 4. Measurement of fresh weight using 12-well cell culture plates. A. 12-well cell culture plates with cellular culture; B. Removal of liquid culture medium using a pipette; C. Collection of the cells from each well using a spatula; D. Measurement of the fresh weight with an analytical balance using pre-weighed aluminum foil.
- Use 12-well cell culture plates for this analysis.
- Slide preparation for PEM morphology studies
- First, in the flow chamber, separate the embryogenic suspension cultures from the medium using the cell dissociation sieve (150 mesh screens) (Figure 2A).
- Then, 1,200 mg of separated cells, fresh weight (Figure 2B), should be placed into an Erlenmeyer flask (250 ml capacity) containing 60 ml of the culture medium containing the required testing treatments. Three flasks for each treatment should be maintained for three biological replicates.
- Place the flasks on a horizontal shaker during incubation (100 rpm in the dark at 25 ± 2 °C).
- For analyzing the incubation results on specific days, in a flow chamber, take a sample of PEMs from the liquid culture medium using the modified pipette tip. It is necessary to remove the end of the pipette tip (Figures 5A and 5B) to prevent the disruption of PEMs. The pipette tips must be sterilized before use.
- Put a drop of the PEM culture on a glass slide (Figure 5C), and cover with a cover slip.
- Observe under an optical microscope.
Notes:
- The remaining cells in the flask could be returned to the horizontal shaker for use on the next day of analysis. If you do not continue the incubation, and the cells will be discarded, it is not necessary to use a sterilized pipette tip for sampling.
- The PEMs can alternatively be incubated in an Erlenmeyer flask with a smaller volume (keeping the ratio of 20 mg fresh cells for 1 ml of culture medium).
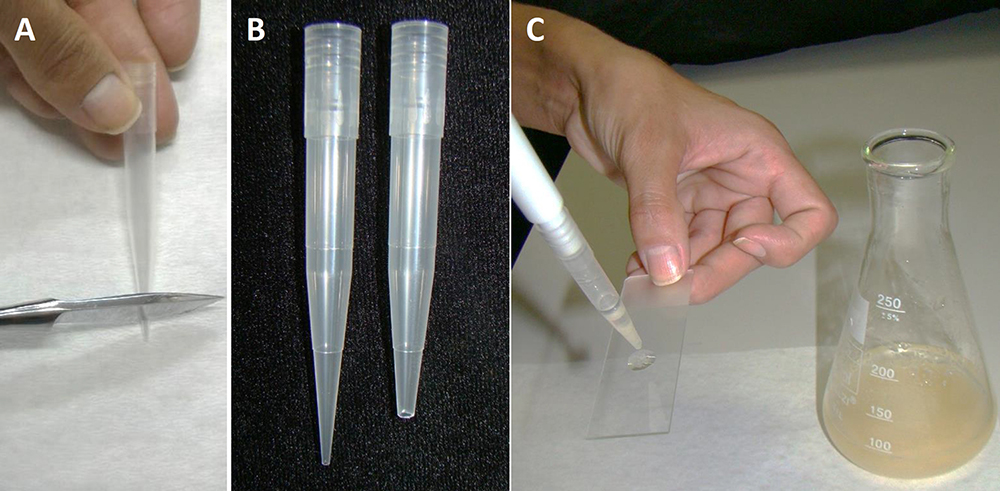
Figure 5. Slide preparation of PEMs from embryogenic suspension culture. A. Removal of the end of a tip; B. Comparison of the tip before and after cutting; C. Plating with a drop of PEMs in suspension culture.
- First, in the flow chamber, separate the embryogenic suspension cultures from the medium using the cell dissociation sieve (150 mesh screens) (Figure 2A).
- Slide preparation for isolated embryogenic and suspensor-type cells
- First, dissociate the PEMs to obtain embryogenic and suspensor-type cells by incubating the PEM suspension culture in culture medium with 0.1% (w/v) cellulase (Sigma-Aldrich).
- Keep the samples incubating in cellulase for 3 h on a rotary shaker (100 rpm) in the dark at 25 ± 2 °C.
- After incubation, transfer the cells to a Falcon tube and wash with a new culture medium that is cellulose free. Remove the culture medium carefully with a pipette and repeat this procedure three times.
- To visualize the cells with an optical microscope, follow the procedure described in Procedure C used to prepare slides using a modified pipette tip.
- First, dissociate the PEMs to obtain embryogenic and suspensor-type cells by incubating the PEM suspension culture in culture medium with 0.1% (w/v) cellulase (Sigma-Aldrich).
- Image capture
- To capture images for morphological analysis, we use AxioVision Rel. 4.8 software according to the following procedures (other comparable image analysis software should suffice):
- Open the software AxioVision Rel. 4.8, and in the Tool Bar, select: View>Toolbars>Standard.
- To view the image on the screen: click the ‘Live’ option.
- Set in the software the specifications of the objective and ocular you are using to capture the image using the ‘Snap’ option.
- When saving the image, choose the .zvi format.
- Open the software AxioVision Rel. 4.8, and in the Tool Bar, select: View>Toolbars>Standard.
- To capture images for morphological analysis, we use AxioVision Rel. 4.8 software according to the following procedures (other comparable image analysis software should suffice):
- Procedure for morphological measurement and analysis
- Area measurement
- Open the image in the microscope software.
- Choose the options: View>Toolbars>Measure.
- To measure the area, use the tool options, ‘outline’ or ‘outline spline’.
- Then, draw a closed shape around the embryonal head (Figures 6A and 7). When the form is closed, the area appears on the figure in µm2. This value is used for area analyses.
- Repeat this operation with several samples of embryonal head and suspensor-type cell images.

Figure 6. Measurement scheme of PEMs and isolated cells. A. Area analysis of embryonal head and suspensor-type cells from non-dissociated PEMs; B. Diameter, length and width analysis of dissociated embryogenic and suspensor-type cells.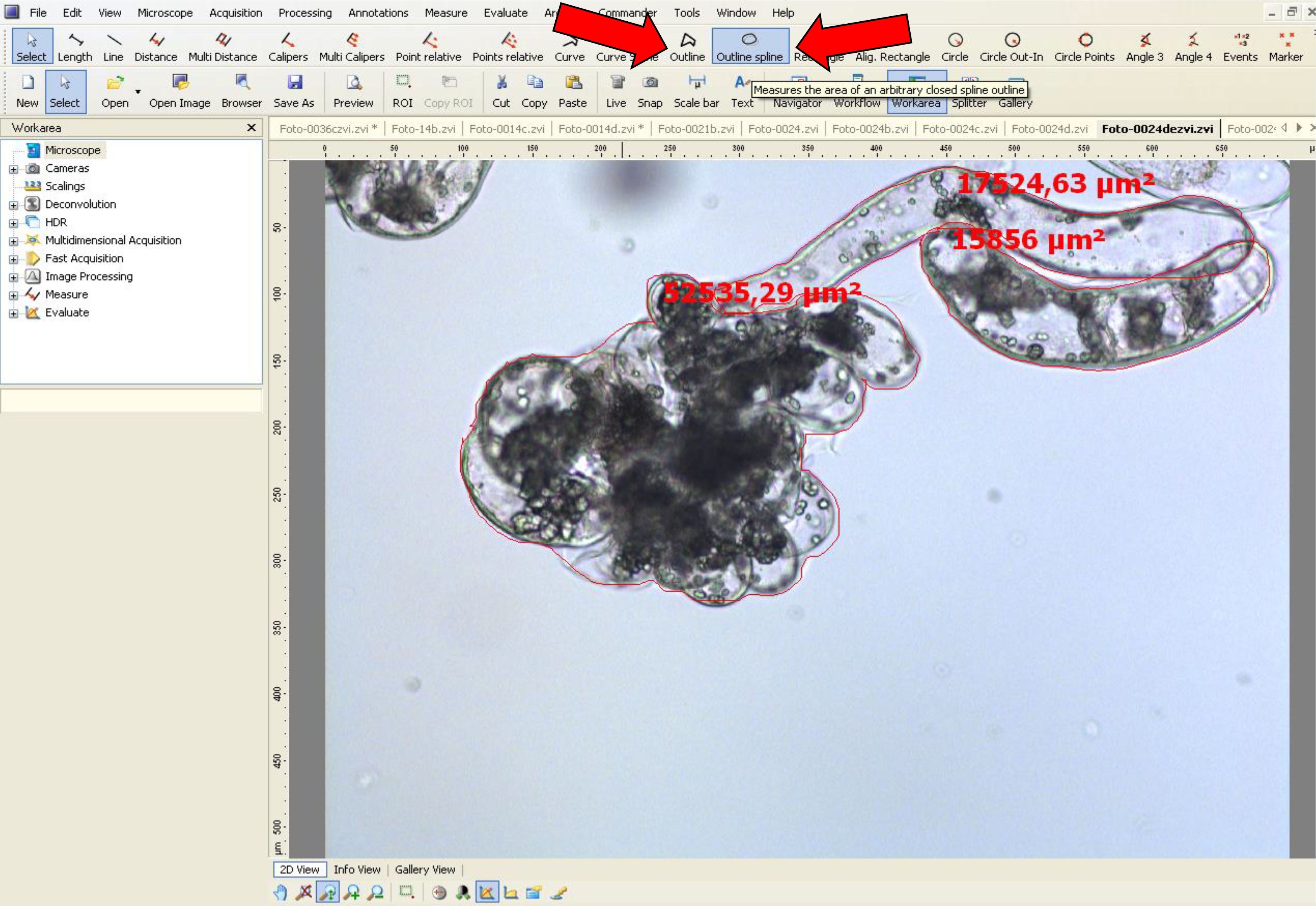
Figure 7. Area measurement procedure for non-dissociated PEMs using AxioVision software. Arrows (red) indicate the tool options used.
- Open the image in the microscope software.
- Diameter, width and length measurement
- Open the image in the microscope software.
- Choose the options: View>Toolbars>Measure
- To measure the area, use the tool option ‘length’.
- Then, using the ‘length’ tool, measure the embryogenic-type cells to obtain the diameter data (see red line in Figure 6B and black line in Figure 8).
- Using the ‘length’ tool, measure the length and width in suspensor-type cells, as shown by a black line in Figure 8.
- Repeat this operation with several samples of dissociated embryogenic and suspensor cells.
- Open the image in the microscope software.
Notes:
- In Araucaria, as embryogenic-type cells are isodiametric, the size was measured based on the diameter, and as suspensor-type cells are elliptic and elongated, the size was measured using the length and width (at the middle of the cell) (Figure 8).
- If the suspensor-type cells are curved, the ‘curve spline’ tool can be used as shown in Figure 9.
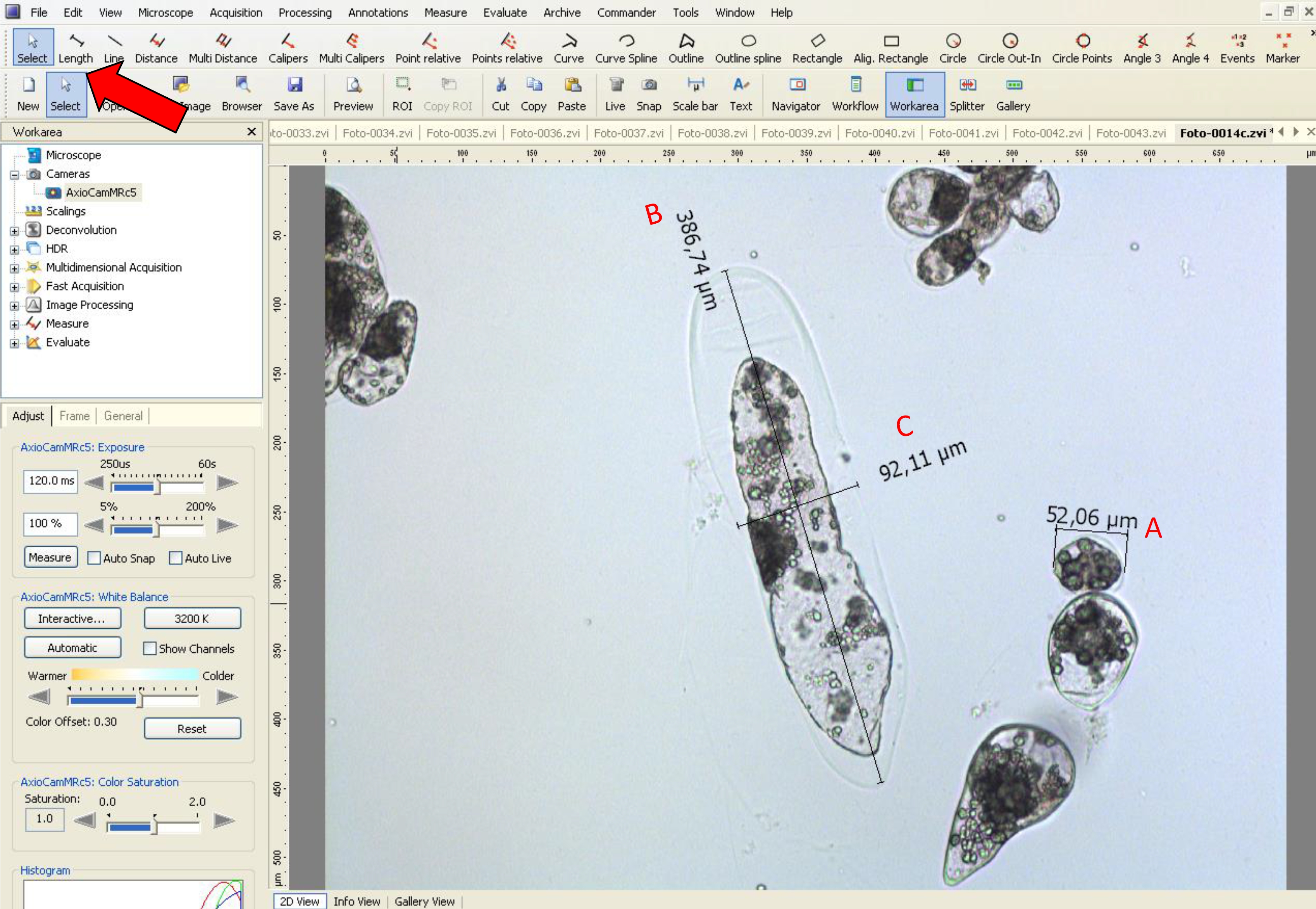
Figure 8. Measurement of diameter, width and length of embryogenic and suspensor-type cells using AxioVision LE software. The red arrow indicates the tool used for A. diameter analysis of embryogenic-type cells, B. length and C. width in suspensor-type cells.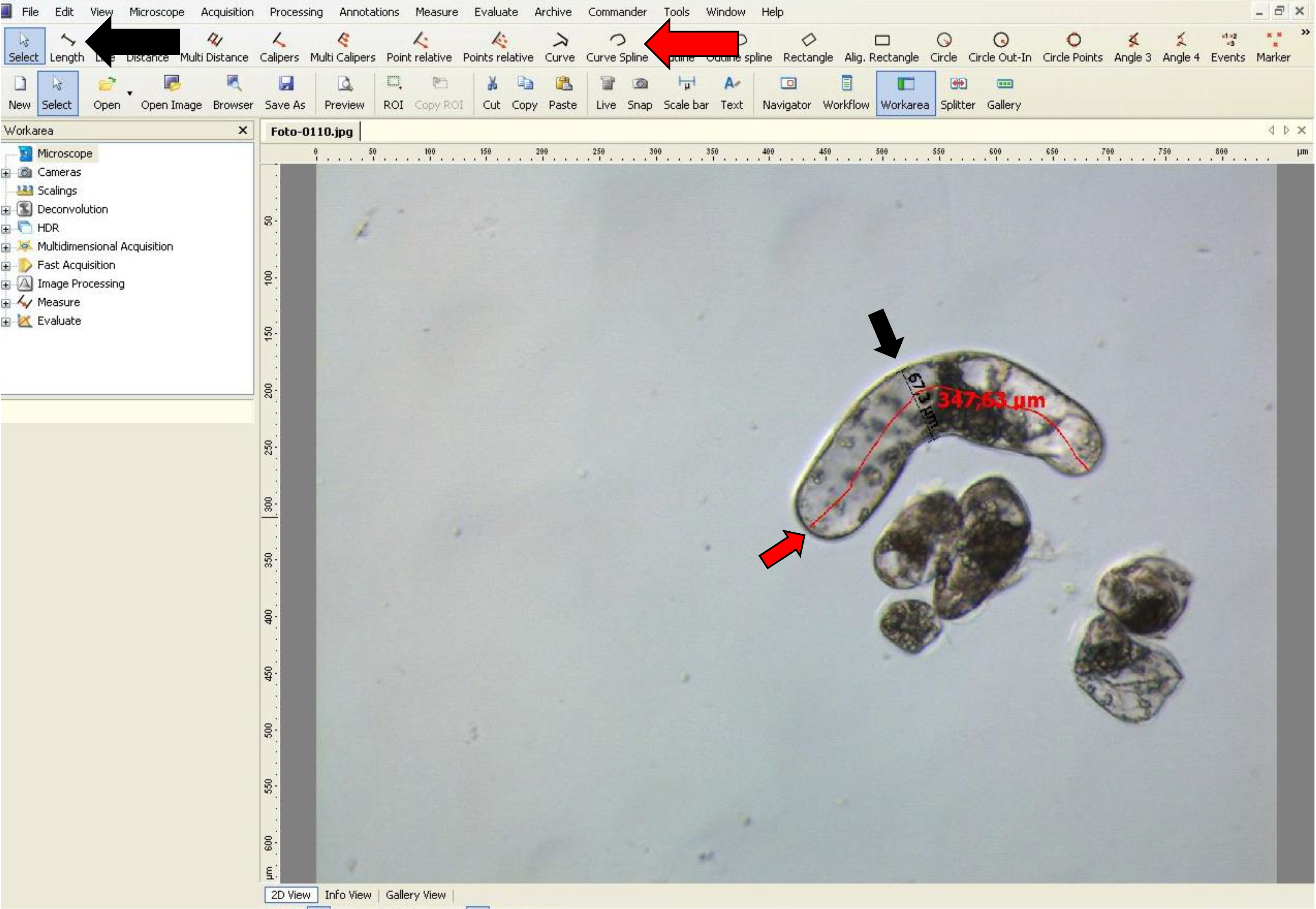
Figure 9. Width and length measurementsof suspensor-type cells using AxioVision software. The red arrow indicatesthe ‘Curve spline’ tool used for length of curved suspensor-type cells, and theblack arrow indicates the ‘Length’ tool used for width of these cells.
- Area measurement
Data analysis
- For the analysis of area, diameter, length and width, the values of different samples can be processed and presented in a graph format. Additionally, the data can be subjected to analysis of variance (ANOVA) and mean separation tests (such as Tukey or SNK) by using an appropriate statistical software.
- SCV analysis: examples of results obtained from SCV analysis can be observed in Figure 1 of Silveira et al. (2006), Figure 2 of Osti et al. (2010) and Figure 4 of Douétts-Peres et al. (2016).
- Fresh and dry weight analysis: Figure 5 of Douétts-Peres et al. (2016) is an example of fresh and dry weight measurement.
- Cell size determination: Area measurement of the embryonal head and suspensor-type cells described here (Figure 6) can be observed in Figure 7 of Douétts-Peres et al. (2016). In addition, the diameter of embryogenic-type cells and the width and length of suspensor-type cells can be observed in Figure 8 of Douétts-Peres et al. (2016).
Recipes
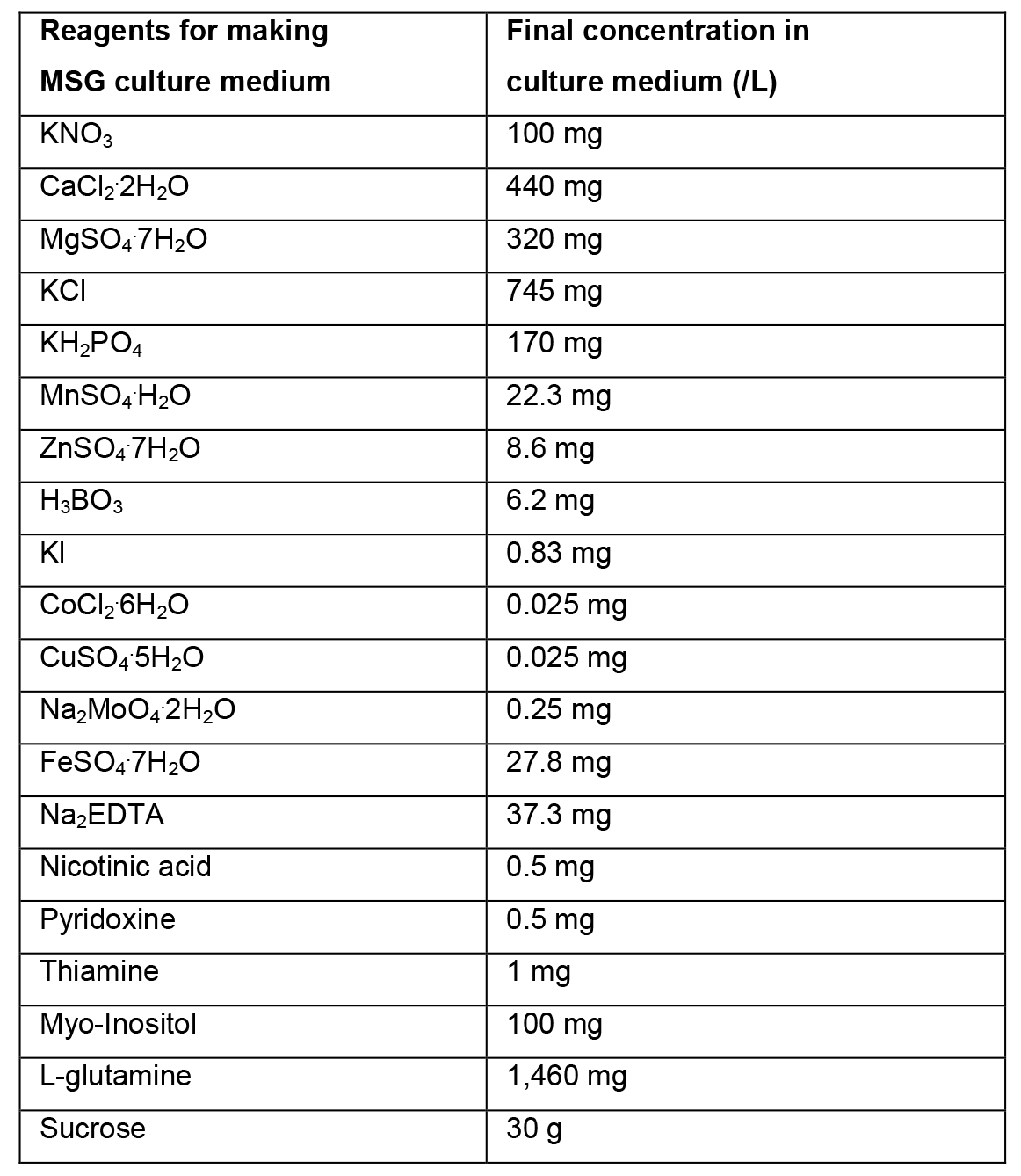
- MSG culture medium (1 L) (Becwar et al., 1989)
- Preparation of liquid MSG culture medium
- To prepare 1 L of liquid MSG culture medium, weigh 30 g of sucrose and dissolve in ~500 ml of distilled water.
- Add 100 ml solution A, 5 ml solution B, 10 ml solution C and 2 ml solution D. Add 1,460 mg of L-glutamine.
- Dissolve all reagents. Adjust the volume with distilled water to 1 L. Mix the culture medium and adjust the pH to 5.7. Sterilize in an autoclave for 15 min at 121 °C.
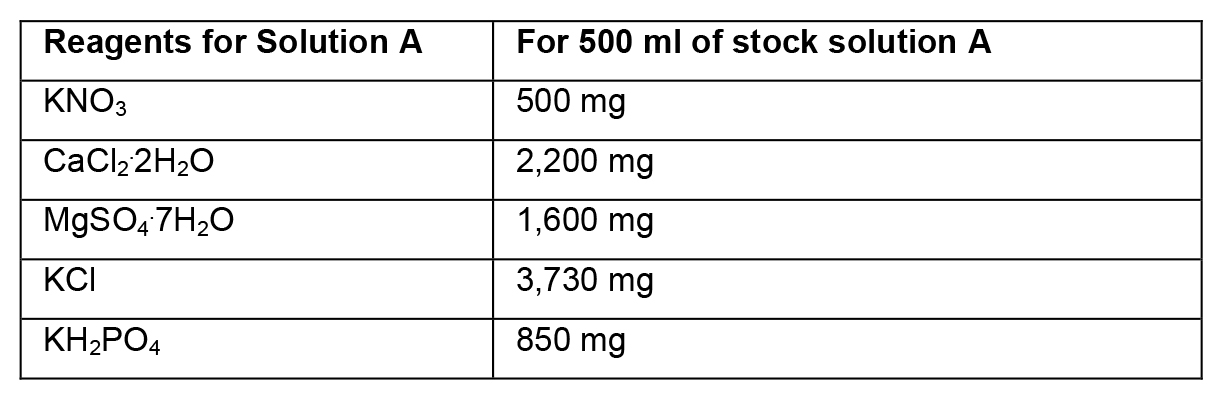
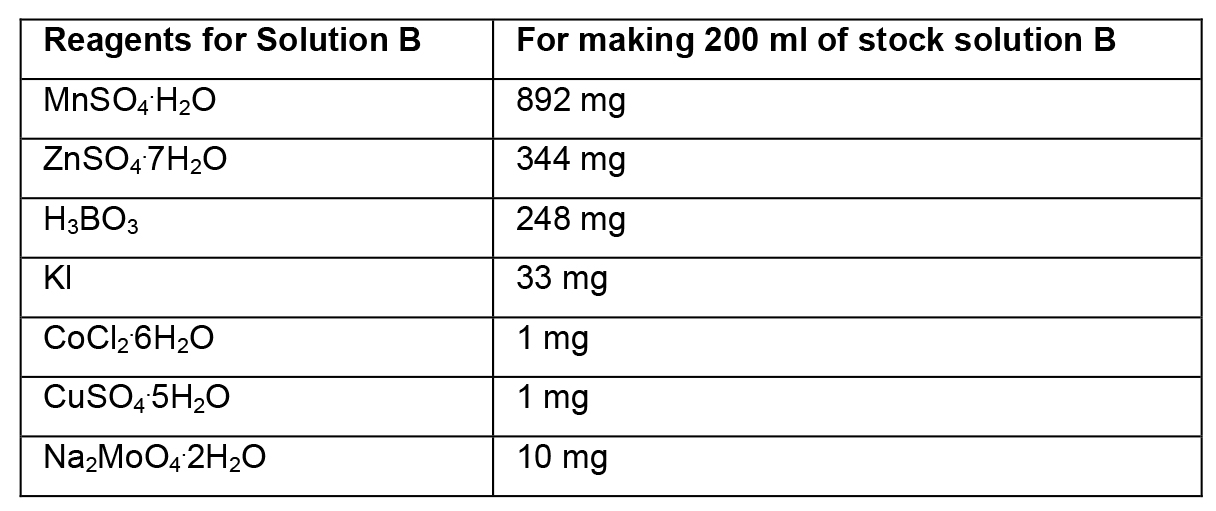
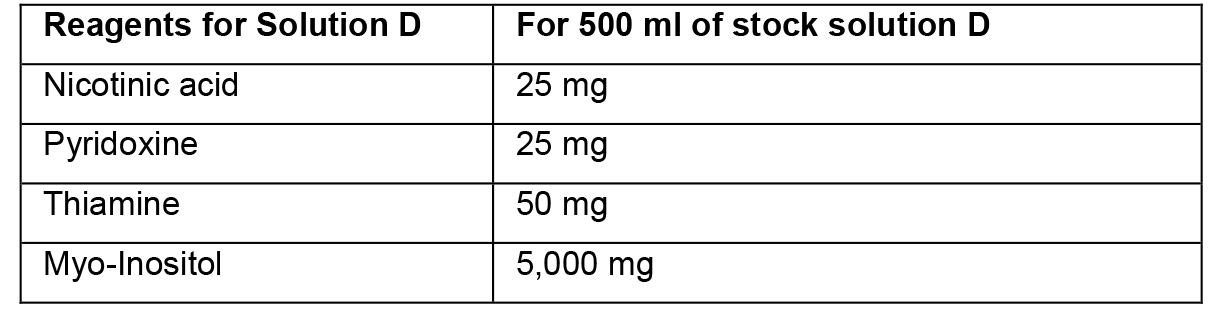
- Preparation of stock solutions
- To prepare stock solutions A, B and D, weigh the reagents in an analytical balance, dissolve in distilled water, and make up the final volume with distilled water.
- To prepare stock solution C, weigh each reagent and add separately to ~150 ml of heated distilled water (~45 °C). Then, mix the two solutions and adjust the final volume to 500 ml. Protect this solution from light.

Acknowledgments
This work was supported by FAPERJ (Foundation for Research Support of the State of Rio de Janeiro) and CNPq (National Counsel of Technological and Scientific Development). The VCS method presented was derived from Silveira et al. (2006).
References
- Becwar, M. R., Noland, T. L. and Wyckoff, J. L. (1989). Maturation, germination, and conversion of Norway spruce (Picea abies L.) somatic embryos to plants. In vitro Cell Dev 25(6): 575-580.
- Douétts-Peres, J. C., Cruz, M. A., Reis, R. S., Heringer, A. S., de Oliveira, E. A., Elbl, P. M., Floh, E. I., Silveira, V. and Santa-Catarina, C. (2016). Mps1 (Monopolar Spindle 1) protein inhibition affects cellular growth and pro-embryogenic masses morphology in embryogenic cultures of Araucaria angustifolia (Araucariaceae). PLoS One 11(4): e0153528.
- Osti, R. Z., Andrade, J. B. R., Souza, J. P., Silveira, V., Balbuena, T. S., Guerra, M. P., Franco, D. W., Floh, E. I. S. and Santa-Catarina, C. (2010). Nitrosyl ethylenediaminetetraacetate ruthenium(II) complex promotes cellular growth and could be used as nitric oxide donor in plants. Plant Sci 178(5): 448-453.
- Silveira, V., Santa-Catarina, C., Tun, N. N., Scherer, G. F. E., Handro, W., Guerra, M. P. and Floh, E. I. S. (2006). Polyamine effects on the endogenous polyamine contents, nitric oxide release, growth and differentiation of embryogenic suspension cultures of Araucaria angustifolia (Bert.) O. Ktze. Plant Sci 171(1): 91-98.
- Steiner, N., Vieira, F. D. N., Maldonado, S. and Guerra, M. P. (2005). Effect of carbon source on morphology and histodifferentiation of Araucaria angustifolia embryogenic cultures. Braz Arch of Bio Technol 48(6): 895-903.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Douétts-Peres, J. C., Silveira, V., Cruz, M. A. L. and Santa-Catarina, C. (2016). Isolating and Measuring the Growth and Morphology of Pro-embryogenic Masses in Araucaria angustifolia (Bertol.) Kuntze (Araucariaceae). Bio-protocol 6(23): e2031. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2031.
- Douétts-Peres, J. C., Cruz, M. A., Reis, R. S., Heringer, A. S., de Oliveira, E. A., Elbl, P. M., Floh, E. I., Silveira, V. and Santa-Catarina, C. (2016). Mps1 (Monopolar Spindle 1) protein inhibition affects cellular growth and pro-embryogenic masses morphology in embryogenic cultures of Araucaria angustifolia (Araucariaceae). PLoS One 11(4): e0153528.
Category
Plant Science > Plant developmental biology > Morphogenesis
Cell Biology > Cell isolation and culture > Cell growth
Cell Biology > Tissue analysis > Tissue isolation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link












