- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Metabolite Profiling of Mature Arabidopsis thaliana Seeds Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS)
Published: Vol 6, Iss 21, Nov 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1981 Views: 12513
Reviewed by: Tie LiuArsalan DaudiAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Isolation of Intact Vacuoles from Arabidopsis Root Protoplasts and Elemental Analysis
Chuanfeng Ju [...] Zhenqian Zhang
Mar 5, 2023 2068 Views

Analysis of Modified Plant Metabolites Using Widely Targeted Metabolite Modificomics
Jianing Zhang [...] Jun Yang
Apr 5, 2025 1474 Views

High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Quantification of Glyphosate, Aminomethylphosphonic Acid, and Ascorbate in Culture Medium and Microalgal Cells
Juan Manuel Ostera [...] Gabriela Malanga
Apr 5, 2025 1193 Views
Abstract
Metabolite profiling using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) permits the annotation and quantification of a relatively wide variety of metabolites, covering a wide range of biochemical groups of metabolites. Lisec et al. (2006) established a method for GC-MS profiling in plants. Based on this protocol, we provide here a detailed GC-MS-based metabolite profiling protocol to identify compounds belonging to several biochemical groups in the primary metabolism of mature Arabidopsis thaliana seeds (Cohen et al., 2014). The protocol uses methoxyamine hydrochloride and N-methyl-N-trimethylsilyltriflouroacetamide (MSTFA) as derivatization reagents, as previous studies indicated these are the most appropriate compounds for profiling of plant metabolites. The protocol is relatively rapid, delivers reproducible results, and can be employed to profile metabolites of many other types of plant tissues with only minor modifications. In this context, developing seeds can serve as an excellent system for studying metabolic regulation, since during their development, a massive synthesis of reserve compounds occurs controlled under tight transcriptional regulation and associated with temporally distinct metabolic switches.
Materials and Reagents
- 2 ml microfuge safe seal lock-cap tubes (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 72-695-500 )
- 1.5 ml microfuge safe seal lock-cap tubes (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 72-690-001 )
- Mature dry Arabidopsis thaliana (ecotype Colombia-0) seeds
- Liquid nitrogen
- HPLC-grade methanol (Merck Millipore, catalog number: 67-56-1 )
- HPLC-grade chloroform (Merck Millipore, catalog number: 67-66-3 )
- HPLC-grade water (Avantor Performance Materials, J.T. Baker, catalog number: 7732-18-5 )
- Pyridine (Merck Millipore, catalog number: 110-86-1 )
- DL-norleucine internal standard (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N1398 )
- Methoxyamine hydrochloride (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 226904 )
- N-methyl-N-trimethylsilyltriflouroacetamide (MSTFA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 24589-78-4 )
- n-alkanes mixture (see Recipes)
n-Dodecane (C12) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 44010 )
n-Pentadecane (C15) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 76509 )
n-Octadecane (C18) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 74691 )
n-Nonadecane (C19) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 74158 )
n-Docosane (C22) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 43942 )
n-Octacosane (C28) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 74684 )
n-Dotriacontane (C32) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 44253 )
n-Hexatriacontane (C36) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 52919 ) - Pre-cooled (4 °C) extraction buffer containing DL-norleucine internal standard solution (see Recipes)
- Methoxyamine hydrochloride derivatization reagent (see Recipes)
- n-alkanes time standards mix solution (see Recipes)
- N-methyl-N-trimethylsilyltriflouroacetamide (MSTFA) derivatization reagent + pre-mixed n-alkanes time standards (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Vacuum desiccator
- Liquid nitrogen dewar
- Table-top centrifuge (able to reach 20,817 x g at 4 °C) (Eppendorf)
- Table-top vortex (Benchmark Scientific Inc.)
- CentriVap benchtop centrifugal vacuum concentrator (Labconco)
- Benchtop multi-Therm heat-shaker (Benchmark Scientific Inc.)
- GC-MS system (Agilent Technologies, model: 7890A ) coupled with a mass selective detector and a Gerstel multipurpose sampler MPS2S (or any other GC-MS system)
- DB-5ms capillary column (30 m, 0.25 mm i.d., and 0.25 μm thickness) (or any other column suitable for primary metabolic profiles) (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: 122-5532G )
- VF-5ms capillary column (30 m + 10 m EZ-guard, 0.25 mm i.d., and 0.25 μm thicknesses) or any other column suitable for primary metabolic profiles (Agilent Technologies, catalog number: CP9013 )
- 10 mm Certified Clear Screw Thread Kit: 2 ml Thermo ScientificTM NationalTM 10 mm wide opening screw thread vials and inserts manufactured from clear glass + PTFE/silicone septa (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: CERT4010-91 ).
- 200 μl MicroSert glass inset (31 x 5 mm) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: C4012-465 )
- 1 ml clear glass high recovery reaction vials with attached 13-425 open top phenolic screw-cap + PTFE/silicone septa (WHEATON, catalog number: W986294NG )
- 20 ml pre-assembled EPA vials + PTFE screw-caps (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: B7800-20 )
Procedure
- Extraction of metabolites from Arabidopsis thaliana seeds (Figures 1A1-1A8)
- Weight 20 mg of mature dry Arabidopsis thaliana seeds and place them into 2 ml lock-cap microfuge tubes (Figure 1A1). Seeds were harvested at full maturity at the end of desiccation period. Following collection, the seeds were allowed to fully-dry under vacuum desiccation for another 3 d. Please see Note 1 for seed stock, desiccation processes and replicate recommendations.
- Insert small metal grinding balls into each tube and place tubes in liquid nitrogen (Figure 1A2).
- Insert tubes into a 4 °C pre-cooled ball mill plastic adaptors and immediately place the adaptors in the ball mill. Homogenize samples for 4 min at 24 Hz and transfer the samples back into the liquid nitrogen (Figure 1A3).
- Add 1 ml of 4 °C pre-cooled extraction buffer containing the DL-norleucine internal standard (see Recipes) and vortex vigorously (Figure 1A4). Please see Note 2 for safety recommendations.
- Centrifuge samples on a 4 °C pre-cooled table-top centrifuge for 10 min at 20,817 x g. This step permits the separation of polar supernatant (methanol/water) and non-polar (chloroform) phases (Figure 1A5).
- Collect the supernatant into new 2 ml lock-cap microfuge tubes and add 300 μl of HPLC-grade chloroform and 300 μl of HPLC-grade water. Vortex vigorously each sample for 10 sec to allow water and chloroform thoroughly mixed, and centrifuge samples on a 4 °C pre-cooled table-top centrifuge for 10 min at 20,817 x g (Figure 1A6).
- Collect 300 μl aliquots from the supernatant into new 1.5 ml lock-cap microfuge tubes (Figure 1A7).
- At this stage, the 300 μl aliquots can be immediately transferred into -80 °C for future analyses without being derivatized (Figure 1A81). In case derivatization takes place, dry 300 μl aliquots using a CentriVap benchtop centrifugal vacuum concentrator for 5-6 h at 25 °C (Figure 1A82).

Figure 1. Workflow of extraction metabolites from Arabidopsis thaliana seeds
- Weight 20 mg of mature dry Arabidopsis thaliana seeds and place them into 2 ml lock-cap microfuge tubes (Figure 1A1). Seeds were harvested at full maturity at the end of desiccation period. Following collection, the seeds were allowed to fully-dry under vacuum desiccation for another 3 d. Please see Note 1 for seed stock, desiccation processes and replicate recommendations.
- Derivatization using methoxyamine hydrochloride and N-methyl-N-trimethylsilyltriflouroacetamide (MSTFA) reagents (Figures 2B1-2B5)
- Methoxymate the dry aliquots by re-suspending the pellet in 40 μl of methoxyamine hydrochloride solution (see Recipe 2) (Figure 2B1).
Note: Methoxyamine hydrochloride reagent is extremely toxic, thus, derivatization process must be handled with the highest care under the fume hood. - Transfer the whole amount of samples into reaction vials (Figure 2B2).
- Incubate reaction vials for 2 h at 37 °C in order to protect carbonyl moieties (Figure 2B3).
- Trimethylsilylate acidic protons by adding 70 μl of N-methyl-N-trimethylsilyltriflouroacetamide (MSTFA) containing pre-mixed n-alkanes time standards (see Recipes) and incubate reaction vials for 30 min at 37 °C (Figure 2B4). The addition of n-alkanes allows the determination of retention time indices.
Note: MSTFA reagent is extremely toxic, thus, derivatization process must be handled with the highest care under the fume hood. - Cool reaction vials in room temperature and transfer the whole amount of samples (approximately 110 μl) into inserts placed in GC-MS running vials (Figure 2B5).
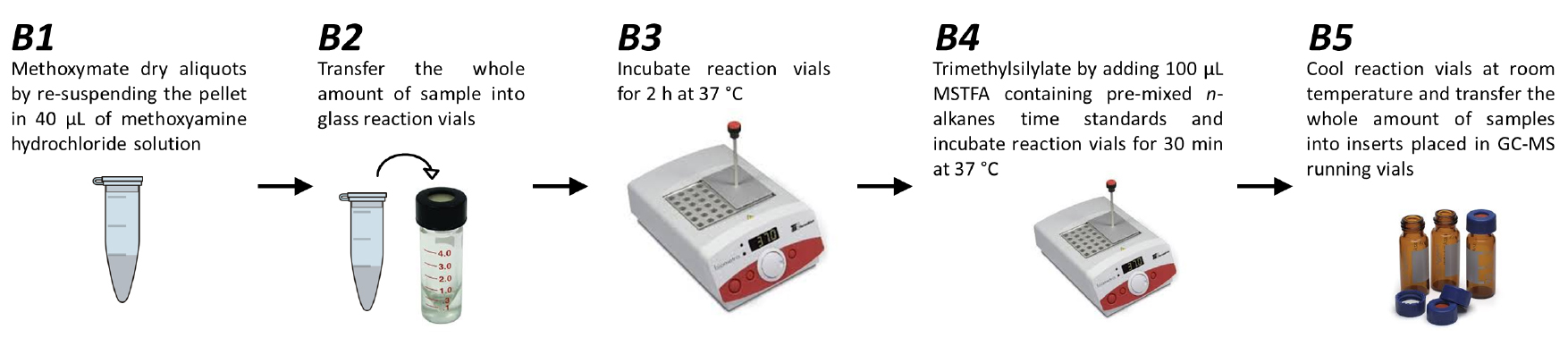
Figure 2. Workflow of derivatization processes
- Methoxymate the dry aliquots by re-suspending the pellet in 40 μl of methoxyamine hydrochloride solution (see Recipe 2) (Figure 2B1).
- GC-MS analysis (Figure 3C)
- Analyses were carried out on a GC-MS system (Agilent, model: 7890A) coupled with a mass selective detector (Agilent, model: 5975c) and a Gerstel multipurpose sampler MPS2S (Figure 3C). The analysis was performed under the conditions described in Table 1, whereby the DB-5ms capillary column (together with a duraguard, DG) were used to quantify soluble and protein-bound amino acids, and the VF-5ms capillary column was used to quantify sugars, sugar acids, sugar alcohols, tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle intermediates and organic acids. The VF-5ms capillary column was used as it can reach a higher temperature, thus, allowing better separation of metabolites within chromatographs.
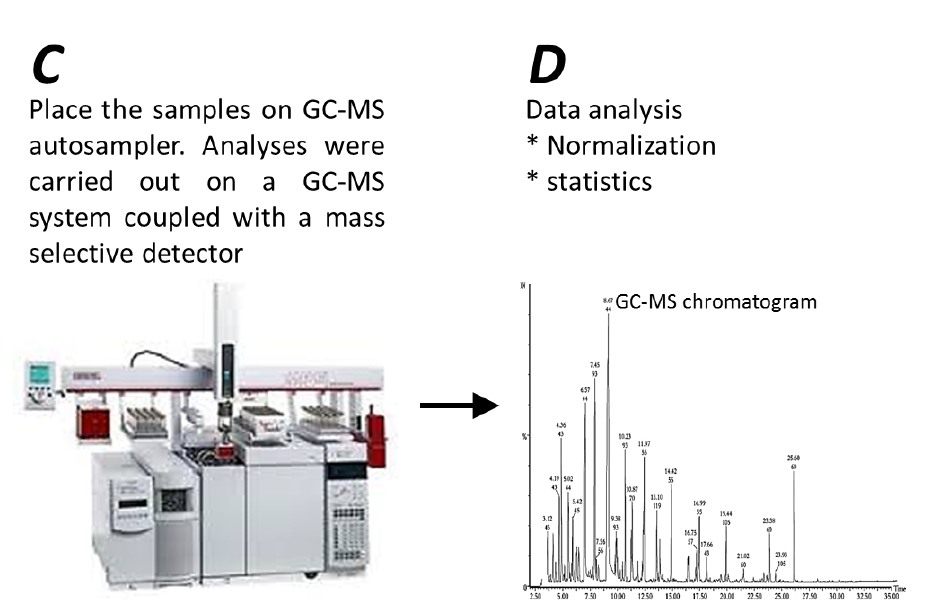
Figure 3. Workflow of GC-MS running and Data analysis
Table 1. GC-MS metabolite profiling conditions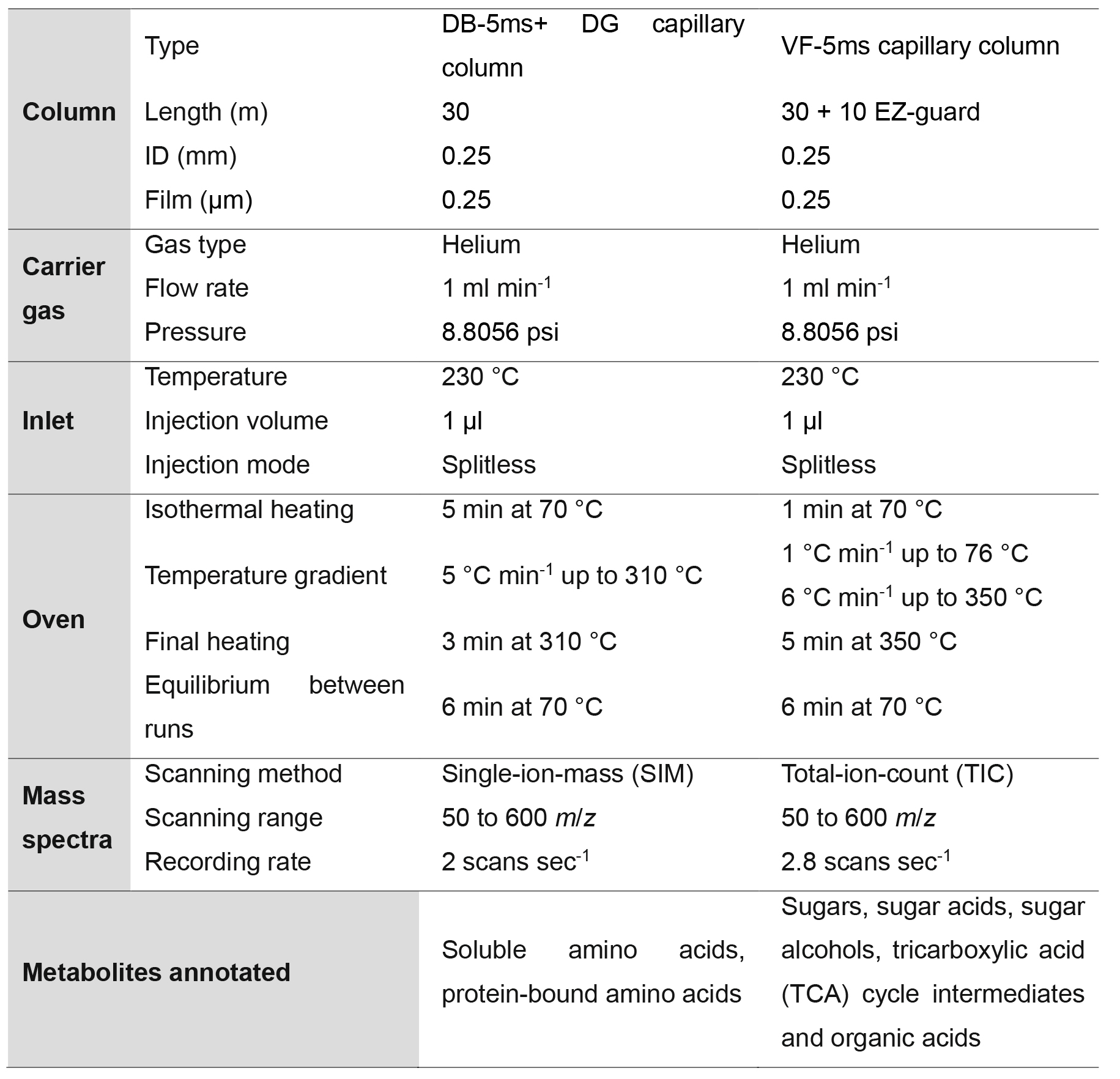
- Analyses were carried out on a GC-MS system (Agilent, model: 7890A) coupled with a mass selective detector (Agilent, model: 5975c) and a Gerstel multipurpose sampler MPS2S (Figure 3C). The analysis was performed under the conditions described in Table 1, whereby the DB-5ms capillary column (together with a duraguard, DG) were used to quantify soluble and protein-bound amino acids, and the VF-5ms capillary column was used to quantify sugars, sugar acids, sugar alcohols, tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle intermediates and organic acids. The VF-5ms capillary column was used as it can reach a higher temperature, thus, allowing better separation of metabolites within chromatographs.
- Data analysis (Figure 3D)
- Peak finding, peak integration and retention time correction were performed with the Agilent GC/MSD Productivity ChemStation package (http://www.agilent.com).
- The corresponding mass spectra and retention time indices were compared with standard substances and commercially available electron mass spectrum libraries available from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (http://www.nist.gov/) and Max Planck Institute for Plant Physiology, Golm, Germany (http://www.mpimp-golm.mpg.de/).
- Integrated peaks of mass (m/z) fragments were normalized against the DL-norleucine internal standard signal. The relative peaks of the DL-norleucine internal standard should be of similar height/area among all samples (see representative ion chromatograms appear in Figure 4).
- Following internal standard normalization, anomalous values were excluded from the metabolite dataset based on the calculated relative peak area of every metabolite. Representative total-ion-chromatograms (TIC) appear in Figure 5 shows differential peak areas from overlaid chromatograms from seeds of wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana (Colombia-0) against two transgenic lines.
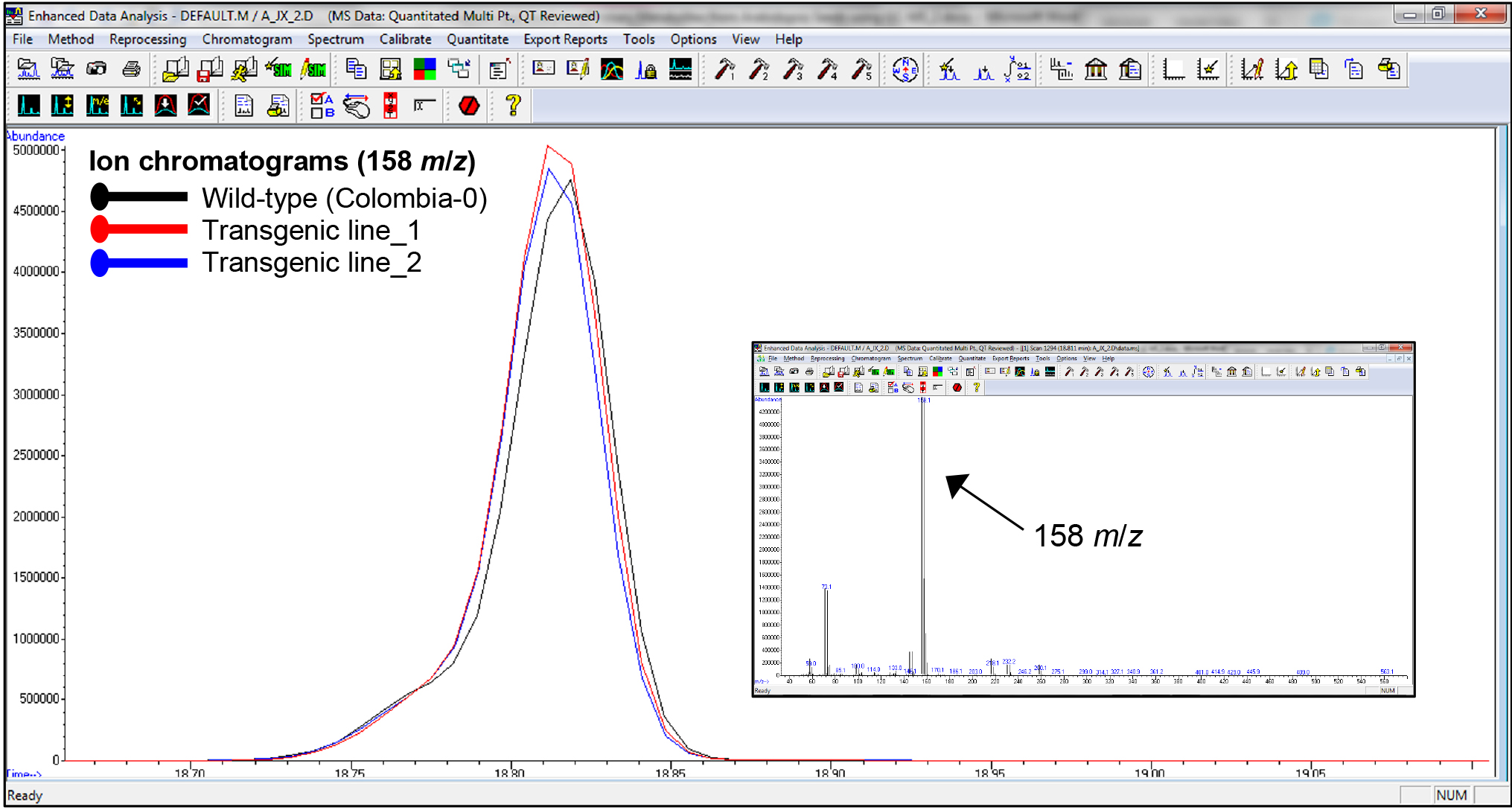
Figure 4. Representative ion chromatograms of wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana seeds (ecotype Colombia-0) and seeds from two transgenic lines. Ion chromatograms (large square) show similar peaks underlying the characteristic 158 m/z mass fragment (small square) of the DL-norleucine internal standard.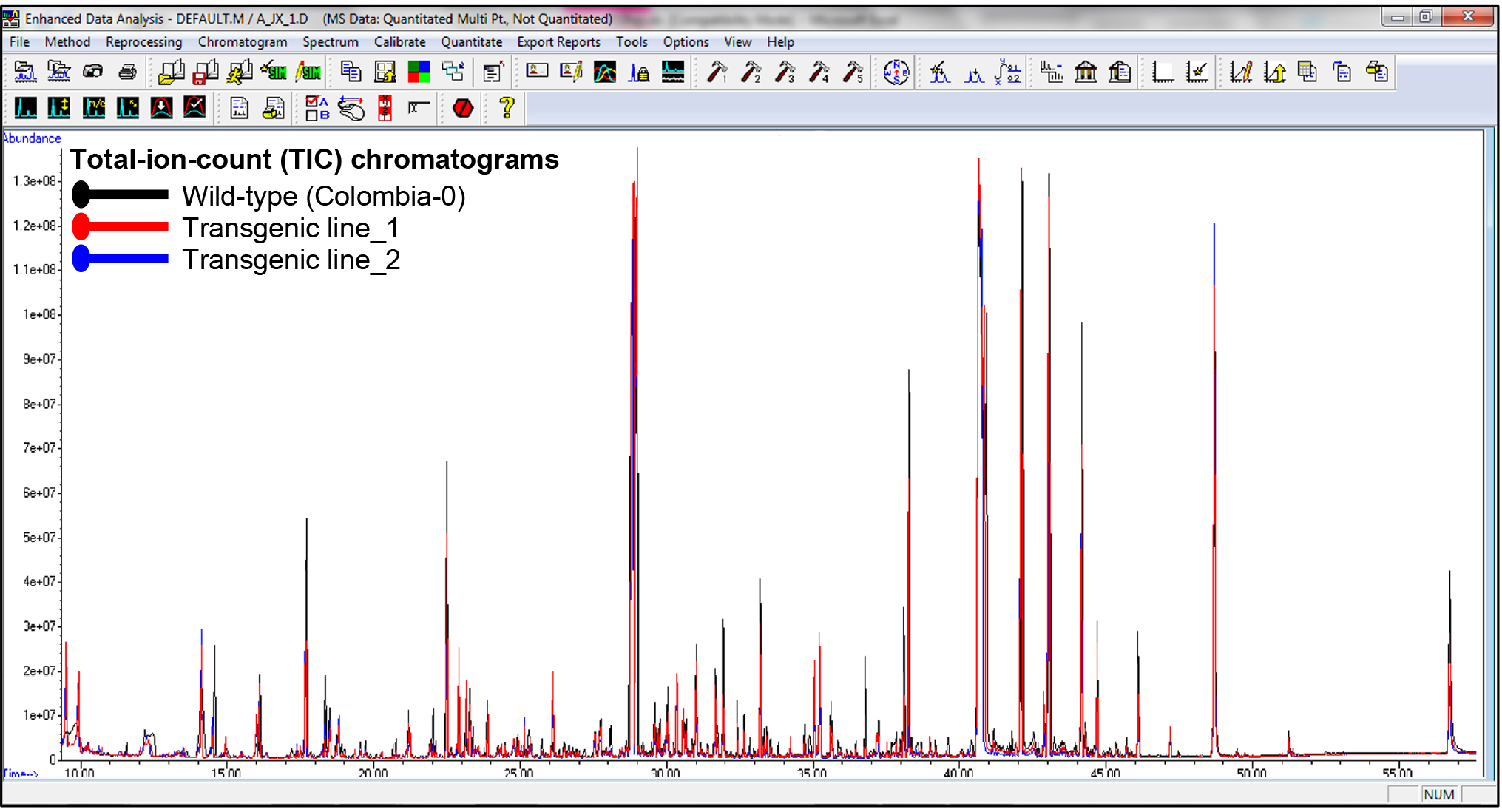
Figure 5. Representative total-ion-count (TIC) chromatograms of wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana seeds (ecotype Colombia-0) and seeds from two transgenic lines. Differences are shown in various peaks between the wild-type and transgenic lines.
- Peak finding, peak integration and retention time correction were performed with the Agilent GC/MSD Productivity ChemStation package (http://www.agilent.com).
Notes
- In the case of Arabidopsis, mature dry seeds can be collected from fully-matured plants at the end of desiccation, usually 4-6 weeks after germination on soil (depending on irrigation light and humidity growing conditions). WT ecotypes and mutant lines can be ordered by several different public seed collections such as the SALK Institute for Biological Studies (http://www.salk.edu/) or RIKEN (http://www.riken.jp/en/). The availability of Arabidopsis T-DNA mutant lines can be checked in the websites of T-DNA Express: Arabidopsis Gene Mapping Tool (http://signal.salk.edu/cgi-bin/tdnaexpress) or The Arabidopsis Information Resource (https://www.arabidopsis.org/). We recommend desiccating seeds under vacuum as desiccation under heat in an oven might induce too harsh conditions triggering some metabolic changes. We recommend using at least 5 biological replicates from each genotype/treatment. Apart from biological replicates, at least one blank sample containing no biological material should be prepared and subjected to all extraction and derivatization protocols.
- Extraction buffer and both methoxyamine hydrochloride and MSTFA derivatization reagents are extremely toxic, thus, apart for seeds sampling and weighting procedures, all extraction and derivatization processes must be performed with extreme care under fume hood.
Recipes
- Pre-cooled (4 °C) extraction buffer containing DL-norleucine internal standard solution
- Prepare a 2.5:1:1 mixture of HPLC-grade methanol, HPLC-grade chloroform and HPLC-grade water (v:v:v). The extraction buffer must be prepared freshly before the extraction.
- For preparation of DL-norleucine internal standard solution, dissolve 2 mg of DL-norleucine in 1 ml of HPLC-grade water and vortex vigorously. Mix 7 μl of internal standard per 1 ml of extraction buffer.
- Internal standard tube should be stored at -20 °C when unused. The internal standard allows the normalization of peaks in case of material loss during extraction procedures.
- Methoxyamine hydrochloride derivatization reagent
- Dissolve 20 mg methoxyamine hydrochloride in 1 ml of pyridine at room temperature.
- This reagent needs to be prepared freshly before the experiment.
- n-alkanes time standards mix solution
- Dissolve 2 μl or 2 mg of soluble or solid n-alkane, respectively, in 1 ml of pyridine in separate 20 ml glass vials with Teflon screw-caps (Table 2).
- For the preparation of n-alkanes time standards mix solution, transfer 500 μl from each C12 to C32 n-alkane solutions and 1,000 μl from the C36 n-alkane solution (as the C36 peak can be observed better at this concentration) into a new 20 ml glass vial and vortex vigorously (Table 2).
- All separate n-alkane vials and n-alkanes time standards mix solution vial should be stored at -20 °C when unused.
Table 2. Preparation of n-alkanes time standards mix solution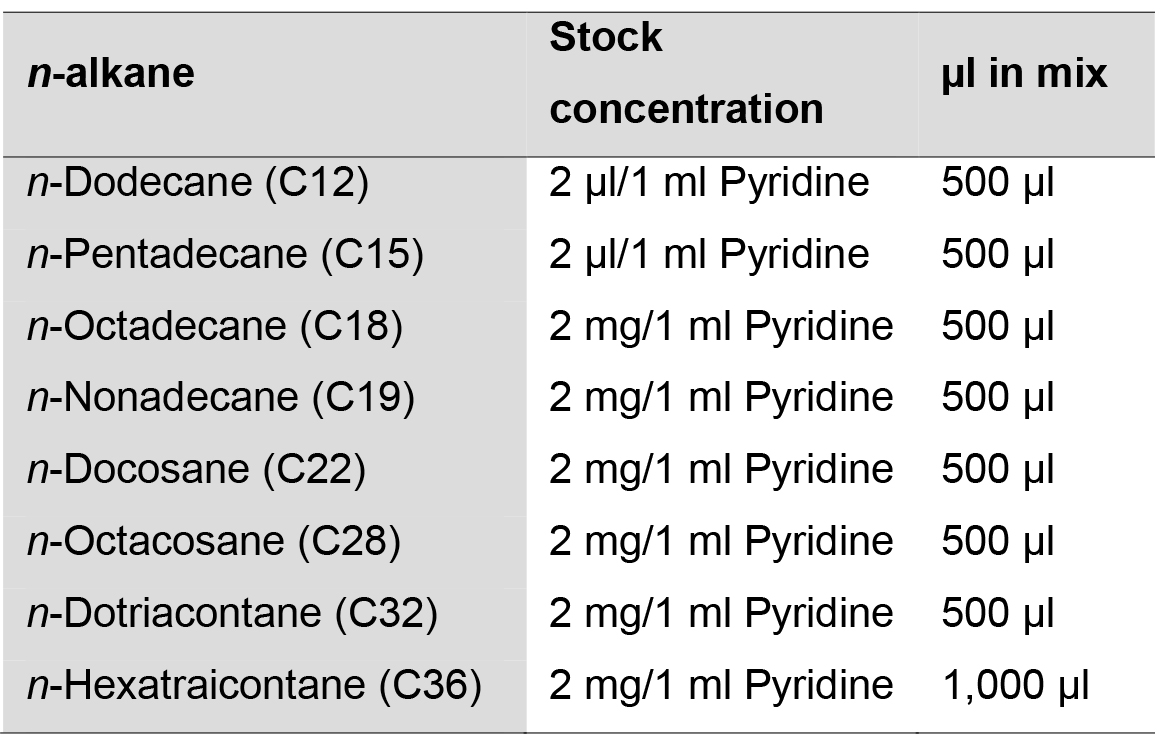
- N-methyl-N-trimethylsilyltriflouroacetamide (MSTFA) derivatization reagent + pre-mixed n-alkanes time standards
Calculate the amount of MSTFA needed for the analysis (70 μl per sample) and add 7 μl per 70 μl MSTFA of pre-mixed n-alkanes time standards mix solution directly into the MSTFA mixture. n-alkanes time standards mix solution should be gently warmed up at 70 °C prior addition into the MSTFA mixture.
Note: This reagent needs to be prepared freshly before the experiment. For example: an experiment of 50 samples would require 3.5 ml of MSTFA (70 μl x 50 samples) mixed with 350 μl of pre-warmed n-alkanes time standards mix solution (7 μl x 50 samples).
Acknowledgments
This is a detailed protocol of the analyses performed in Cohen et al. (2014). Both are fundamentally based on Lisec et al. (2006) with modifications made to profile Arabidopsis thaliana seeds. We would like to acknowledge the Israel Science Foundation for supporting this research (ISF grants #231-09 and #1004/15).
References
- Cohen, H., Israeli, H., Matityahu, I. and Amir, R. (2014). Seed-specific expression of a feedback-insensitive form of CYSTATHIONINE-γ-SYNTHASE in Arabidopsis stimulates metabolic and transcriptomic responses associated with desiccation stress. Plant Physiol 166(3): 1575-1592.
- Lisec, J., Schauer, N., Kopka, J., Willmitzer, L. and Fernie A.R. (2006). Gas chromatography mass spectrometry-based metabolite profiling in plants. Nat Protoc 1(1):387-396.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Cohen, H., Matityahu, I. and Amir, R. (2016). Metabolite Profiling of Mature Arabidopsis thaliana Seeds Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS). Bio-protocol 6(21): e1981. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1981.
- Cohen, H., Israeli, H., Matityahu, I. and Amir, R. (2014). Seed-specific expression of a feedback-insensitive form of CYSTATHIONINE-γ-SYNTHASE in Arabidopsis stimulates metabolic and transcriptomic responses associated with desiccation stress. Plant Physiol 166(3): 1575-1592.
Category
Plant Science > Plant metabolism > Metabolite profiling
Systems Biology > Metabolomics > Seed
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Other compound
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











