- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Flow Cytometry of Lung and Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Cells from Mice Challenged with Fluorescent Aspergillus Reporter (FLARE) Conidia
Published: Vol 6, Iss 18, Sep 20, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1927 Views: 17643
Reviewed by: Shanie Saghafian-HedengrenAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Addressing the Role of Conventional CD8αβ+ T Cells and CD4+ T Cells in Intestinal Immunopathology Using a Bone Marrow–Engrafted Model
Amneh Aoudi [...] Saïdi Soudja
Feb 20, 2024 2968 Views

A Miniaturized Percoll Gradient Method for Isolation of Quiescent Cells of Yeast
Cenxuan Zu [...] Shaolan Zou
Apr 20, 2025 1521 Views

A Method to Inoculate Millet Grain-Colonized Fusarium pseudograminearum on Wheat to Obtain Reproducible Disease Symptoms
Zhe Tang [...] Xin Zhang
Sep 20, 2025 1312 Views
Abstract
Aspergillus fumigatus is a ubiquitous fungal pathogen that forms airborne conidia. The process of restricting conidial germination into hyphae by lung leukocytes is critical in determining infectious outcomes. Tracking the outcome of conidia-host cell encounters in vivo is technically challenging and an obstacle to understanding the molecular and cellular basis of antifungal immunity in the lung. Here, we describe a method that utilizes a genetically engineered Aspergillus strain [called FLARE (Jhingran et al., 2012; Espinosa et al., 2014; Heung et al., 2015)] to monitor conidial phagocytosis and killing by leukocytes within the lung environment at single encounter resolution.
Keywords: FungusMaterials and Reagents
- Cell strainers - 40 μm and 100 μm
- Syringes
- Injector (Modified precision dispensing tips) (Nordson, catalog number: 7018166 )
- 15 ml tubes
- 96-well plate, U-bottom
- Mice: C57BL/6 (Jackson Laboratories, catalog number: 000664 )
- Fungal strains (Af293 and Af293-DsRed) (Jhingran et al., 2012)
- FATAL-plus solution (Vortech Pharmaceuticals Ltd, National Drug Code: 0298-9373-68 )
- BD BBLTM Sabouraud dextrose agar (Emmons), slants (pH 6.9) (100/sp) (BD, catalog number: 221827 )
- PBS (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 14190-144 )
- Tween 20
- Tris base
- NaHCO3
- Na2CO3
- Biotin-XX, SSE (6-((6-((biotinoyl)amino)hexanoyl)amino) hexanoic acid, sulfosuccinimidyl ester, sodium salt) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Molecular ProbesTM, catalog number: B6352 )
- DMSO
- Streptavidin, Alexa Fluor® 633 conjugate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Molecular ProbesTM, catalog number: S-21375 )
- IsothesiaTM, Isoflurane (Henry Schein Animal Health, SKU number: 029405 )
- RBC lysis buffer (Biolegend, catalog number: 420301 )
- DNase I (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 10104159001 )
- Collagenase type IV (Worthington Biochemical, catalog number: LS004189 )
- EDTA
- Mouse BD Fc BlockTM (BD, BD PharmingenTM, catalog number: 553142 )
- Antibodies (listed in Procedure section)
- PBS Tween (0.025%) (see Recipes)
- Tris-chloride (1 M, pH 8) (see Recipes)
- Sodium bicarbonate buffer (0.1 M, pH 9.5) (see Recipes)
- Lung digestion buffer (for each lung) (see Recipes)
- FACS buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Hemocytometer
- Microscope
- Centrifuge
- Plexiglass stand
- Dissection scissors and forceps
- Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) catheters (Exel International, catalog number: 26738 )
- 4-way large bore (lipid resistant) stopcock with rotating male luer lock adapter (Baxter, catalog number: 2C6204 )
- gentleMACS tissue dissociator, MACSMix tube rotator and C tubes (Miltenyi Biotech)
- Automated cell counter or hemocytometer
- Flow cytometer capable of analyzing at least 7 fluorescent parameters (such as BD LSRII). The 532 or 561 nm (but not 488 nm) laser excites DsRed fluorescence and the 633 nm laser excites Alexa Fluor 633 fluorescence.
Procedure
- Preparation of FLARE conidia
- Harvest conidia from 7-10 days old slants (Sabouraud dextrose agar slants) grown at 37 °C by adding 10 ml ice-cold PBST (0.025% Tween-20 in PBS) and pipetting multiple times with gentle scrapping.
Note: Maintain conidia at 4 °C or on ice for all subsequent steps unless otherwise stated. All infection and animal studies need to be performed following biosafety level 2 (BSL2). - Filter the conidial suspension sequentially through a 100 μm and a 40 μm cell strainer to eliminate hyphal fragments. Centrifuge the filtered suspension at 400 x g for 5 min. Discard the supernatant and resuspend the conidial pellet in 10 ml PBST.
- Count the conidia using a hemocytometer and adjust the final concentration to 5-6 x 108 conidia per ml.
- Centrifuge desired amount of conidial suspension at 400 x g for 5 min, discard supernatant and resuspend the pellet in 50 mM NaHCO3 (pH 9.5) maintaining the final concentration as 5 x 108 conidia per ml.
- Add 0.5 mg/ml Biotin-XX, SSE (6-((6-((biotinoyl)amino)hexanoyl)-amino) hexanoic acid), sulfosuccinimidyl ester, sodium salt (stock 50 mg/ml in DMSO) to the conidial suspension and incubate with rotation in the dark.
Note: A minimum of 2 h incubation is recommended for efficient biotinylation. This step can be extended for up to 12 h (O/N incubation). The tubes containing biotinylated conidia should be covered with aluminum foil at all times. - Centrifuge and decant the supernatant. Neutralize unbound biotin by resuspending the pellets and incubating conidia in 0.1 M Tris-HCl (pH 8.0) for 30 min with constant rotation.
- Repeat step A6 and resuspend the biotinylated conidia in (indicate volume) PBS containing 0.02 mg/ml AF633-streptavidin (stock 2 mg/ml in PBS). Incubate for 30 min at RT with constant rotation.
- Wash once with PBST and adjust the concentration to 6 x 107 per ml for intratracheal challenge.
Note: Check the labeling efficiency by flow cytometry before using the FLARE conidia for experiments (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Labeling efficiency of FLARE conidia. Flow plots depict fluorescence intensity of (A) unlabeled, (B) AF633-labeled, (C) DsRed-labeled, and (D) FLARE conidia in AF633 (X-axis) and DsRed (Y-axis) channels using a BD LSR II flow cytometer equipped with 532 nm and 633 nm lasers.
- Harvest conidia from 7-10 days old slants (Sabouraud dextrose agar slants) grown at 37 °C by adding 10 ml ice-cold PBST (0.025% Tween-20 in PBS) and pipetting multiple times with gentle scrapping.
- Murine intratracheal challenge with FLARE conidia
- Adjust conidial suspension at 6 x 108/ml. Load a 1 ml syringe fitted with a curved blunt-ended, 20 gauge precision tip (Figure 2; lower syringe) with 50 μl conidial suspension (typical inoculum: 3 x 107 conidia) and expel any air bubbles. The inoculum volume should not exceed 75 μl.

Figure 2. Curved blunt-ended 20 G tip used to administer conidia intratracheally. The injection syringe (lower syringe) was fabricated from a straight 20 G syringe (upper syringe) by applying heat via a Bunsen burner. - Anaesthetize mice using an isoflurane unit that pumps a mixture of isoflurane (3.5%, vol/vol) and oxygen in an anesthesia chamber.
- Confirm anesthesia by monitoring breathing rate and by toe pinch. Once anesthetized, immobilize the mouse in an upright position on an angled plexiglass stand by hooking its incisors onto a rubber band. Secure the mouse torso with a second rubber band (Figure 3).

Figure 3. Anaesthetized mouse that is immobilized in preparation for intratracheal administration of conidia. - Gently grasp the tongue on one side (typically right hand) using forceps and then grasp tongue with gloved left thumb and forefinger, opening the jaw and flexing the jaw forward. With the right hand guide the syringe containing inoculum over the tongue towards its trachea until a hub of the catheter has been inserted into oral cavity (Figure 4). Push the plunger to deliver inoculum and withdraw the syringe quickly to avoid suffocation. There should be no resistance to delivering the inoculum.
Note: A video demonstration of murine intratracheal administration can be seen at Hasenberg et al. (2011).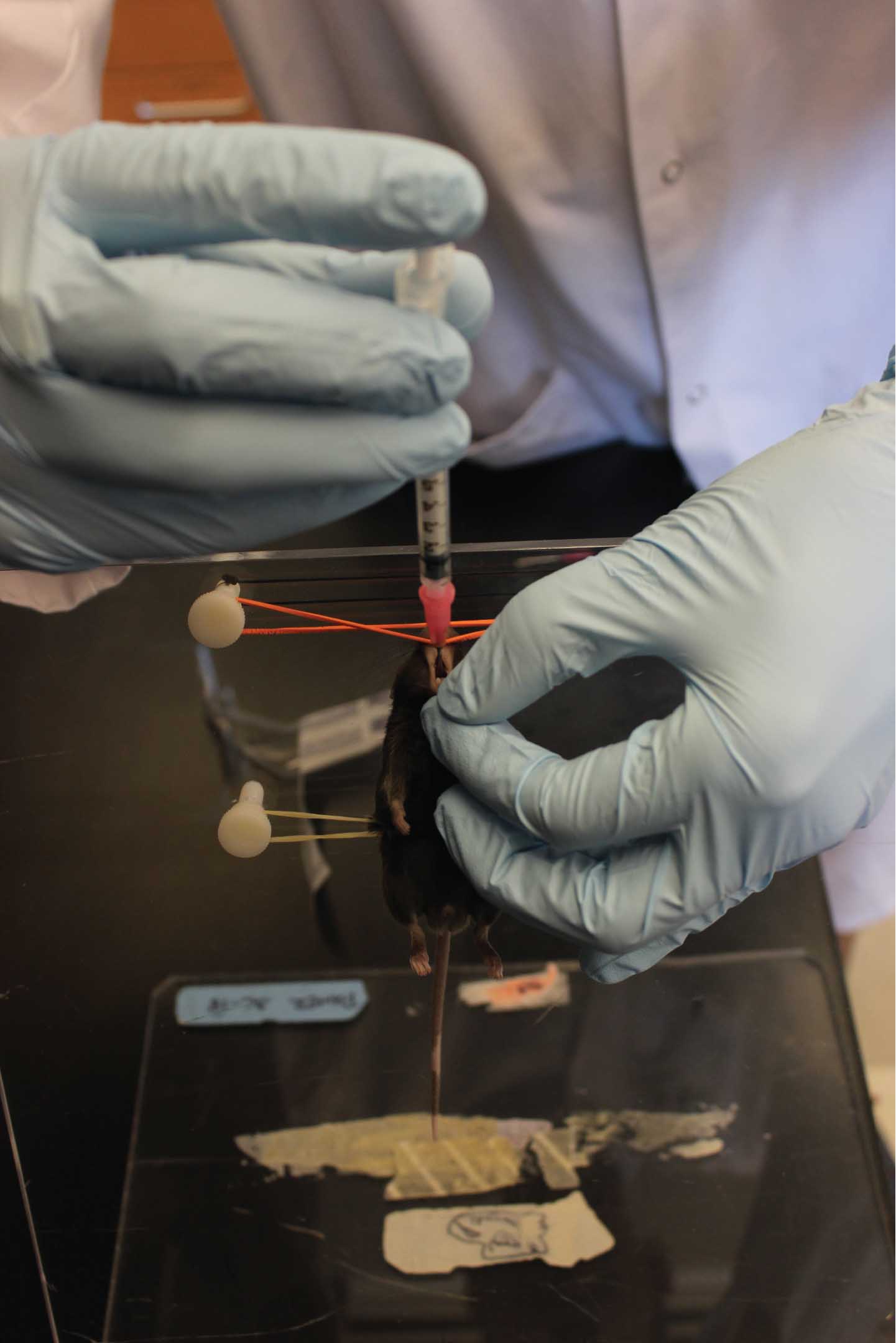
Figure 4. Intratracheal administration of conidia. - Remove the mouse from the plexiglass stand and place it back into its original cage. Monitor the mouse until it starts moving and then proceed to the next mouse. Once all mice are inoculated and regained conscious, return the cage to the rack.
- Adjust conidial suspension at 6 x 108/ml. Load a 1 ml syringe fitted with a curved blunt-ended, 20 gauge precision tip (Figure 2; lower syringe) with 50 μl conidial suspension (typical inoculum: 3 x 107 conidia) and expel any air bubbles. The inoculum volume should not exceed 75 μl.
- Tissue harvest
- Euthanize mice by injecting sodium pentobarbital solution, 300 mg/kg body weight via the intraperitoneal route. When the mouse is euthanized (4-6 min), exsanguinate the animal by making an incision in abdominal aorta to minimize blood contamination during BAL procedures.
- Expose trachea by dissecting out tissues from neck and make a minute incision into the trachea to allow the passage of 18 G lavage catheter through it (Figure 5).
- Insert a BALF catheter into the mouse trachea and repeatedly inject 0.5 ml of ice cold PBS/5% FBS (from the “input” syringe filled with 3 ml of PBS/5% FBS) and then aspirate BALF from the inflated lungs into the initially unfilled “output” syringe via a 3-way stopcock. Typically, we inject a total of 3 ml and recover 2.5 ml of BALF in the output syringe. The 3-way stopcock is adjusted after each injection and aspiration step to ensure that BALF is captured in the output syringe.
- Transfer BALF into empty tubes and store on ice.
- Collect lungs in tubes containing 2 ml ice cold PBS and store on ice.

Figure 5. BALF harvest using a 3-way stopcock.
- Euthanize mice by injecting sodium pentobarbital solution, 300 mg/kg body weight via the intraperitoneal route. When the mouse is euthanized (4-6 min), exsanguinate the animal by making an incision in abdominal aorta to minimize blood contamination during BAL procedures.
- Lung processing
- Transfer lungs into gentleMACS C tubes each containing 5 ml of freshly prepared lung digestion buffer.
- Attach the tubes onto the gentleMACS dissociator and run program “m_lung_01” to dissociate lung samples. Incubate the tubes for 45 min at 37 °C on the MACS mix tube rotator to allow digestion.
- Bring the tubes back to the gentleMACS dissociator and run program “m_lung_02, which completes preparation of single cell suspension of lung samples.
- Briefly spin tubes (300 x g for 1 min) to bring cells at the bottom and using a pipette, transfer the contents into fresh 15 ml tubes.
Note: All subsequent steps are to be performed at 4 °C unless otherwise mentioned. - Centrifuge the tubes at 300 x g for 5 min, discard supernatant and lyse RBCs by resuspending pellet in 1 ml of 1x RBC lysis buffer for 5 min at RT.
- Following RBC lysis, add 9 ml of ice cold 5% FBS/PBS to each tube and pass the entire 10 ml lung suspension through a 100 μm cell strainer into fresh 15 ml tubes.
- Centrifuge tubes, discard supernatant and resuspend cells in 2 ml ice cold 5% FBS/PBS.
- Count cells in an automated cell counter, transfer 200 μl cell suspension (approx. 2-5 million cells) in a U-bottom, 96-well plate and prepare for staining with fluorescent antibodies.
- Transfer lungs into gentleMACS C tubes each containing 5 ml of freshly prepared lung digestion buffer.
- BALF processing
- Spin tubes containing BALF at 300 x g for 5 min, discard supernatant and transfer the pellets in a U-bottom, 96-well plate for staining with fluorescent antibodies.
- Spin tubes containing BALF at 300 x g for 5 min, discard supernatant and transfer the pellets in a U-bottom, 96-well plate for staining with fluorescent antibodies.
- Flow cytometry of lung and BALF cell suspension
- Resuspend the lung and BALF samples in 50 μl of FACS buffer containing Fc block in 1:100 dilution, incubate at 4 °C for 10 min.
- Wash the cells once in FACS buffer and add 50 μl of stain cocktail mix containing antibodies (purchased from ebiosciences/BD/AbD serotec) listed below:
- Ab staining cocktail for lung neutrophils and Ly6Chi monocytes (Figure 6)
CD45.2 (clone 104) - PerCP-Cy5.5
Ly6G (1A8) - FITC
Ly6C (clone AL-21) - PE-Cy7
Ly6B.2 (clone 7/4) - AF700
CD11b (clone M1/70) - Pacific Blue
Neutrophils: CD45.2+Ly6G+Ly6CloCD11b+Ly6B.2+
Monocytes: CD45.2+Ly6G-Ly6ChiCD11b+Ly6B.2+
Figure 6. Gating strategy to measure conidial uptake and killing by Ly6Chi monocytes and neutrophils in lung tissue. In the right column, the red gate consists of leukocytes with live conidia, the blue gate leukocytes with dead conidia, and the black gate bystander leukocytes that contain no conidia. - Ab staining cocktail for lung macrophages and CD11b+ DCs (Figure 7)
CD45.2 (clone 104) - PerCP-Cy5.5
CD103 (2E7) - FITC
CD11c (HL3) - PE-Cy7
MHC Class II (M5/114.15.2) - AF700
CD11b (clone M1/70) - Pacific Blue
Macrophages: CD45.2+CD11c+MHCIIvar Autofluorescent cells
CD11b+ DCs: CD45.2+CD11c+MHCIIvar CD103-CD11b+
Figure 7. Gating strategy to measure conidial uptake and killing by CD11b+ DCs and macrophages in lung tissue. In the right column, the red gate consists of leukocytes with live conidia, the blue gate leukocytes with dead conidia, and the black gate bystander leukocytes that contain no conidia. - Ab staining cocktail for BALF neutrophils and alveolar macrophages (Figure 8)
CD45.2 (clone 104) - PerCP-Cy5.5
Ly6G (1A8) - FITC
CD11c (HL3) - PE-Cy7
Ly6B.2 (clone 7/4) - AF700
CD11b (clone M1/70) - Pacific Blue
Neutrophils: CD45.2+Ly6G+CD11c-CD11b+Ly6B.2+
Alveolar macrophages: CD45.2+Ly6G- CD11b-Ly6B.2-CD11c+Note: Leave the AF633 and DsRed channels open in all FLARE experiments. Leukocytes that are AF633+DsRed+ harbor live conidia, leukocytes that are AF633+DsRed- harbor dead conidia and leukocytes that are AF633-DsRed- represent bystander population (Jhingran et al., 2012).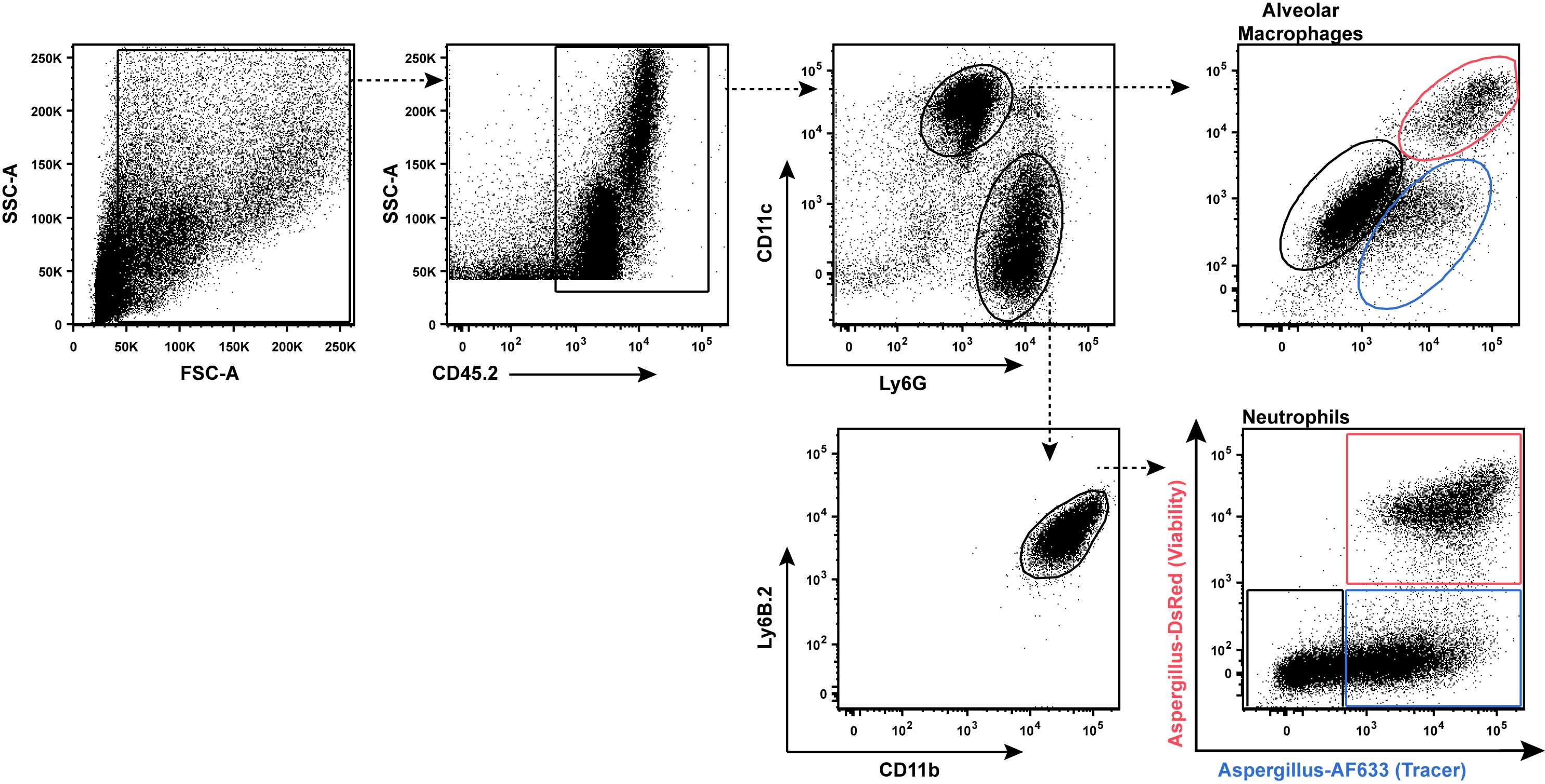
Figure 8. Gating strategy to measure conidial uptake and killing by BALF neutrophils and alveolar macrophages. In the right column, the red gate consists of leukocytes with live conidia, the blue gate leukocytes with dead conidia, and the black gate bystander leukocytes that contain no conidia.
- Ab staining cocktail for lung neutrophils and Ly6Chi monocytes (Figure 6)
- Incubate in the dark at 4 °C for 20 min. Wash once, resuspend in FACS buffer and analyze with flowcytometry within 1 h. We do not recommend fixing samples as we observed DsRed fluorescent intensity was significantly lower if samples were fixed with 1% PFA and analyzed 24 h later.
Recommended band-pass filter setting:
DsRed (PE): 586/15
PerCP-Cy5.5: 695/40
FITC: 530/30
PE-Cy7: 780/60
AF700: 720/40
Pacific Blue: 450/50
AF633 (APC): 660/20
- Resuspend the lung and BALF samples in 50 μl of FACS buffer containing Fc block in 1:100 dilution, incubate at 4 °C for 10 min.
Recipes
- PBS Tween (0.025%)
0.025% Tween 20 (v/v, 2.5 ml from 10% stock)
1,000 ml PBS (pH 7.4)
Filter sterilize and store at 4 °C - Tris-chloride (1 M, pH 8)
121.14 g Tris base
Dissolve in 800 ml Milli Q water
Adjust pH to 8.0 using 10 N HCl
Adjust volume to 1,000 ml and store at 4 °C - Sodium bicarbonate buffer (0.1 M, pH 9.5)
8.40 g NaHCO3
3.56 g Na2CO3
Dissolve in 1,000 ml Milli Q water and store at 4 °C - Lung digestion buffer (for each lung)
5 ml 5% FBS/PBS (pH 7.4)
2.2 mg/ml collagenase type IV
100 μg/ml DNase I - FACS buffer
0.5% BSA (2.5 g)
0.1 mM EDTA (100 μl from 0.5 M stock)
500 ml 1x PBS (pH 7.4)
Store at 4 °C
Acknowledgments
The studies were performed with support from the following funding agencies and grants: The Lucille Castori Center for Microbes, Inflammation, and Cancer (CMIC) postdoctoral fellowship to A.J., NIH grants R01 AI093808 and R21 AI105617 to T.M.H. T.M.H. is an Investigator in the Pathogenesis of Infectious Diseases supported by the Burroughs Wellcome Fund. This research was funded in part through the NIH/NCI Cancer Center Support Grant P30 CA008748.
References
- Espinosa, V., Jhingran, A., Dutta, O., Kasahara, S., Donnelly, R., Du, P., Rosenfeld, J., Leiner, I., Chen, C. C., Ron, Y., Hohl, T. M. and Rivera, A. (2014). Inflammatory monocytes orchestrate innate antifungal immunity in the lung. PLoS Pathog 10(2): e1003940.
- Hasenberg, M., Kohler, A., Bonifatius, S., Jeron, A. and Gunzer, M. (2011). Direct observation of phagocytosis and NET-formation by neutrophils in infected lungs using 2-photon microscopy. J Vis Exp (52).
- Heung, L. J., Jhingran, A. and Hohl, T. M. (2015). Deploying FLAREs to visualize functional outcomes of host-pathogen encounters. PLoS Pathog 11(7): e1004912.
- Jhingran, A., Mar, K. B., Kumasaka, D. K., Knoblaugh, S. E., Ngo, L. Y., Segal, B. H., Iwakura, Y., Lowell, C. A., Hamerman, J. A., Lin, X. and Hohl, T. M. (2012). Tracing conidial fate and measuring host cell antifungal activity using a reporter of microbial viability in the lung. Cell Rep 2(6): 1762-1773.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Jhingran, A., Kasahara, S. and Hohl, T. M. (2016). Flow Cytometry of Lung and Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid Cells from Mice Challenged with Fluorescent Aspergillus Reporter (FLARE) Conidia . Bio-protocol 6(18): e1927. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1927.
- Heung, L. J., Jhingran, A. and Hohl, T. M. (2015). Deploying FLAREs to visualize functional outcomes of host-pathogen encounters. PLoS Pathog 11(7): e1004912.
Category
Immunology > Immune cell staining > Flow cytometry
Microbiology > in vivo model > Fungi
Immunology > Host defense > Murine
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link