- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Cycloheximide Assays to Measure Protein Degradation in vivo in Plants
Published: Vol 6, Iss 17, Sep 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1919 Views: 20386
Reviewed by: Tie LiuYuko KuritaAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Assessing Metabolite Interactions With Chloroplastic Proteins via the PISA Assay
Anna Karlsson [...] Elton P. Hudson
May 5, 2025 2020 Views

Advancing 2-DE Techniques: High-Efficiency Protein Extraction From Lupine Roots
Sebastian Burchardt [...] Emilia Wilmowicz
Oct 5, 2025 1779 Views

Quantitative Analysis of the Arabidopsis Leaf Secretory Proteome via TMT-Based Mass Spectrometry
Sakharam Waghmare [...] Rucha Karnik
Nov 20, 2025 2035 Views
Abstract
The half-life of a protein is a characteristic property, and can be modulated by post-translational modifications, changes in subcellular localization, and/or interaction with other proteins or ligands. As one determinant of its steady-state level, a protein’s degradation represents an important distinguishing attribute relevant to its biological function. Because protein longevity cannot be elucidated from bioinformatics analyses, it must be determined empirically. Here we describe two approaches for in vivo half-life determination in plants: 1. pooled-seedling degradation assays monitoring either tagged versions of the protein (luciferase fusions or other epitope tags) or following the endogenous protein; 2. single-seedling degradation assays using luciferase fusion proteins. The advantages of these approaches are their simplicity and low cost.
Keywords: Protein degradationMaterials and Reagents
- 60 x 15 mm sterile Petri dishes (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 353002 )
- Microfuge tubes
- Pipet tips
- White polystyrene flat-bottom 96-well plates (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 12-566-619 )
- PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) Western protein blotting membrane (Sigma-Aldrich, Amersham HybondTM, catalog number: GE10600023 )
- Clear adhesive plate film (USA-Scientific, catalog number: 2921-7810 )
- X-ray film (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, catalog number: 34091 )
- Plant lines expressing protein of interest, either from transgene or from endogenous locus
- Cycloheximide (CHX) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C1988 )
- Primary antibody [example, anti-HA-HRP (3F10) (Sigma-Aldrich, Roche, catalog number: 12158167001 )]
- Secondary antibody (horseradish peroxidase-linked) (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 1662408EDU )
- Tween-20 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9416 )
- Bleach (sodium hypochlorite) (VWR International, Chlorox®, catalog number: 89501-620 ) or from a grocery or drugstore, such as Chlorox bleach
- Murashige and Skoog basal salts with micronutrients (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M5524 )
- Sucrose
- MES [2-(N-morpholino)ethanesulfonic acid] free acid (Merck Millipore, Calbiochem®, catalog number: 475893 )
- Nicotinic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N4126 )
- Thiamine-HCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T4625 )
- Pyroxidine-HCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9755 )
- Myo-inositol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: I1525 )
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher Scientific, catalog number: P250 )
- Bacto agar (BD, Difco, catalog number: 214010 )
- Parafilm (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 13-374-10 )
- Liquid nitrogen
- Potassium phosphate monobasic (KH2PO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9791 )
- Potassium phosphate dibasic (K2HPO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P3786 )
- Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), disodium dehydrate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S311 )
- β-mercaptoethanol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M6250 )
- Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P7626 )
- Tricine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T0377 )
- Magnesium chloride hexahydrate (MgCl2) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher Scientific, catalog number: M33 )
- BSA (bovine serum albumin) for protein standard curve (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A7030 )
- Adenosine 5’-triphosphate disodium salt hydrate (ATP) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A2383 )
- Tris base (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T1503 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S3014 )
- IGEPAL CA-630 [Octylphenoxy poly (ethyleneoxy) ethanol] (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: I8896 ), a nonionic, non-denaturing detergent replacement for Nonidet P-40
- MG132 (Benzyloxycarbonyl-L-Leucyl-L-Leucyl-L-Leucinal) (Peptides International, catalog number: IZL-3175-v )
- Complete mini protease inhibitor EDTA-free tablet (Sigma-Aldrich, Roche, catalog number: 4693159001 )
- Protein concentration assay (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 5000006 )
- Chemiluminescent western blot development kit (SuperSignal West Pico or Dura Extended duration substrate) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 34077 and 34075 , respectively)
- D-Luciferin potassium salt (Gold Biotechnology, catalog number: LUCK-100 )
- Growth media (GM) (see Recipes)
- Luciferase extraction buffer (see Recipes)
- Luciferase assay buffer (see Recipes)
- Protein extraction buffer for Western blot assays (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Plate reading spectrophotometer for protein determination assay (Thermo Fisher Scientific)
- Refrigerated centrifuge (Eppendorf)
- SDS-PAGE gel apparatus and power supply (Thermo Fisher Scientific)
- Porcelain mortar and pestle for protein extraction (Thermo Fisher Scientific)
- Western transfer apparatus (Thermo Fisher Scientific)
- Plate reading luminometer (Berthold Technologies)
- Flatbed scanner (Hewlett-Packard)
- X-ray film developer, either a set of tanks or trays, or an automatic machine
- Orbital shaker for Western blot incubation (Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Software
- Excel and another statistical package such as GraphPad Prism or Stata
- NIH ImageJ 1.36 (http://rsb.info.nih.gov/ij/)
- ImageQuant 1.0 software (http://www.gelifesciences.com/webapp/wcs/stores/servlet/catalog/en/GELifeSciences-us/products/AlternativeProductStructure_16016/29000605)
Procedure
- Pooled seedling cycloheximide in vivo degradation protocol (see Notes)
This protocol is called the pooled seedling degradation assay because populations of seedlings are grown in multiple Petri plates and the protein/activity measured from an extract of one plate of seedlings harvested at a specific time after addition of the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide (CHX) represents a single time point (see Figure 1, top). An important aspect of this assay to emphasize is that degradation occurs in vivo and the amount of protein remaining at specific time points is determined after termination of degradation, protein extraction and detection. CHX is an effective protein synthesis inhibitor for intact seedlings (Ramos et al., 2001). The degradation rate and then subsequently the half-life of any protein can be measured and derived from data obtained in the pooled seedling CHX assay as long as there is the ability to detect the protein, either by enzyme assay or antibody detection. Multiple plates at each time point can be included in the analysis, and the same extract (time-point) sampled multiple times. Finally, the experiment should be repeated with independently grown seedlings.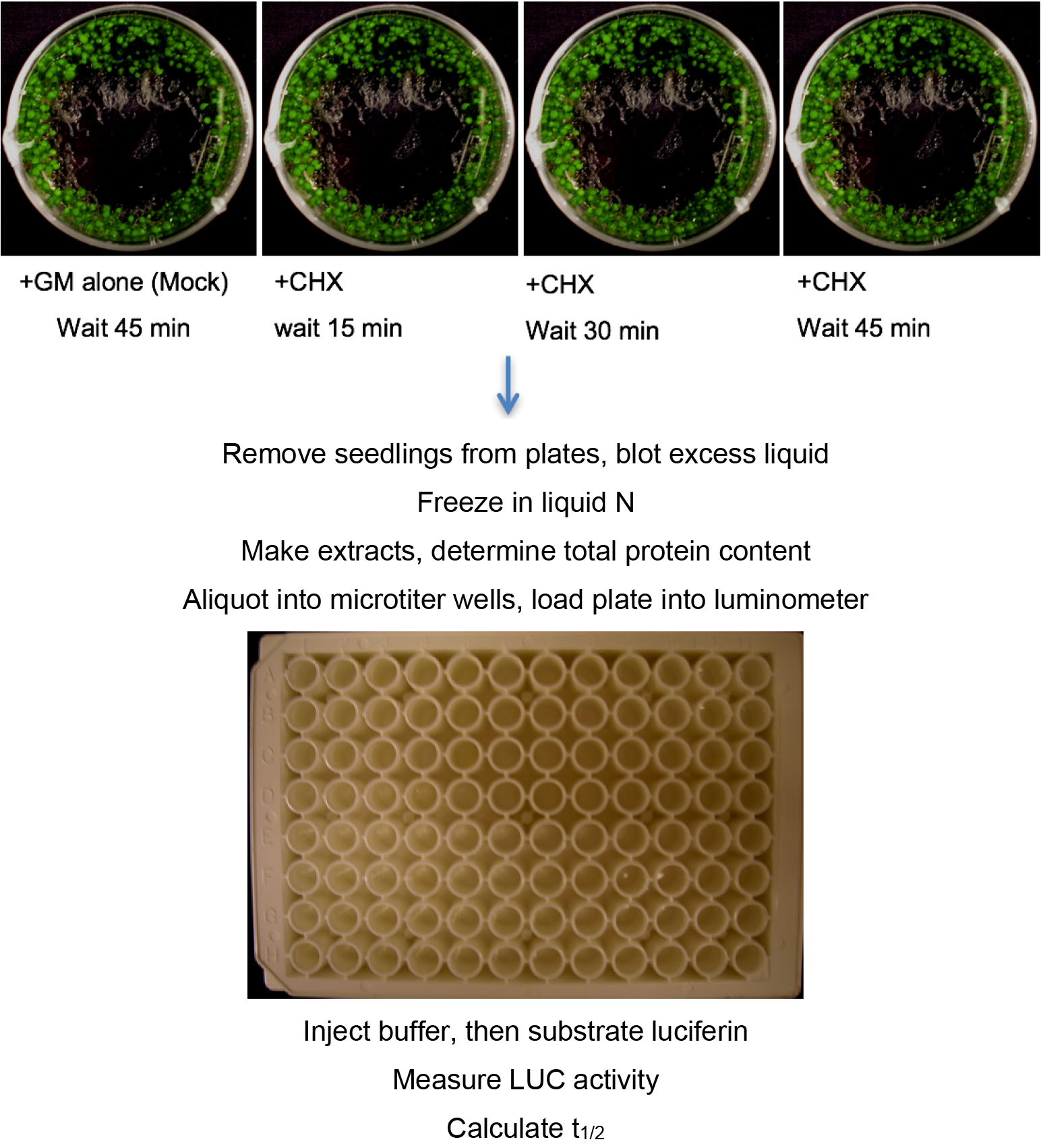
Figure 1. Procedure for pooled seedling assay, analyzed using LUC fusions. For Western analysis initial procedure is the same, but extract is analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with antibody of choice rather than aliquoted into a microplate and analyzed in a luminometer.- ~2 mg of Arabidopsis seeds (weighed out) are placed in a microfuge tube and surface-sterilized by a 10 min treatment with 300 μl of a fresh (less than 2 weeks old) solution of 30% commercial bleach + 0.1% Tween-20, followed by 2 sterile water rinses (typically, 800 μl each) to remove the bleach. The seeds are then suspended in 1 ml of liquid growth media (GM) and transferred to 60 x 15 mm sealed (Parafilm) Petri dishes with a pipet tip whose tip was cut to make the opening wider. Seeds are carefully disturbed around the edge of Petri dish. The seeds and liquid should not cover the entire bottom of the plate (Figure 1, top). This reduces the need for excess media. After plating, seeds are stratified by incubation at 4 °C for 2-3 days in the dark. Plates are then removed from the cold and incubated at 22 °C under constant light (~50-70 μmol sec-1 m-2) for 6 days without shaking. This amount of liquid is sufficient to last 6 days for this amount of seed. If growth is more robust, or more seeds are used, then media may need to be added to the plates before day 6 to keep the seedlings sufficiently hydrated. In a sterile hood, open the plate and add a small amount of sterile liquid GM media. Reseal the plate and return to 22 °C under constant light.
- On the evening of the 6th day, open the plates, remove any remaining liquid and replace the media with 900 μl fresh sterile GM. Reseal the plates with fresh Parafilm. This step, as well as the initiation of the degradation experiments, should be conducted at the same time of day to control for circadian effects on degradation.
- On the morning of the 7th day, add 100 μl of 2,000 μg/ml cycloheximide (CHX) stock (CHX powder is dissolved in liquid GM media. Stock should be less than 2 weeks old stored at 4 °C) to the plates of seedlings, and incubate under same conditions for at least three time periods: as examples - 15, 30, and 45 min (for very short-lived proteins) or 1, 2 and 4 h (for more stable proteins). To mix in the added CHX, rock the plate in your hand with a circular motion for 15 sec. Mix with hand again during the time-course. Intermediate times can also be used (see Notes 1 and 2). The minus CHX controls (the mock samples) are represented by dishes of seedlings treated with addition of 100 μl GM alone for the maximum time. We recommend 3 plates (biological replicates) for the mock at each time-point in the experiment. In our hands, protein levels in control incubations were not different from samples harvested at the start of time course.
- After the appropriate time, remove seedlings from the plate, blot dry with a Kimwipe or a paper towel, and quick-freeze in liquid nitrogen. After all samples are obtained, they should be processed as quickly as possible.
- When ready to process the samples (in our hands, storage of tissue for LUC assays at -80 °C for more than a few days results in variable activity, and thus tissue should be processed soon after collection), grind the seedlings in ~200 µl luciferase extraction buffer, if quantifying the protein of interest by luciferase assay, or in ~200 µl protein extraction buffer, if quantifying protein by Western blot.
- Clear the samples by centrifugation at 15,000 x g in a refrigerated centrifuge (4 °C) for 20 min, and transfer the supernatant to a clean tube pre-chilled on ice. Quantify the protein concentration in each sample using a Bradford assay or equivalent method.
Note: For the remainder of the protocol, follow the appropriate directions for either the luciferase assay or Western blot assay. [Luciferase assay (see Figure 1 for outline of protocol, including luciferase assays)] - Transfer 10 µl of the extract for each sample into a well of a white, polystyrene flat-bottomed 96-well plate. Arrange the samples in the plate so that they can be measured in technical triplicates or at a minimum in duplicate.
- Program the luminometer to inject 100 µl of luciferase assay buffer into each well, followed by 40 µl of 0.5 mM luciferin (loaded into one of the injector reservoirs). Measure the luminescence (in relative light units, RLU) for 8 sec. Set up the program to inject the buffer, followed by luciferin, and immediately measure. Each luminometer has a procedure to set up for injection of a solution (in this case should be luciferin) and for length of time to collect light emission. Please read the instructions that comes with your particular make and model.
- Calculate the RLU/µg protein by using the data from the luminometer and the protein quantification assay for each sample.
- Average the RLU/µg protein for the mock samples, and use this to normalize the RLU/µg protein for the other time-points.
- Linearize the data by calculating the natural log (ln) of the normalized RLU/µg protein.
- Plot the natural log (ln) of the normalized RLU/µg protein versus time, with the averaged mock sample as the 0 time-point, and perform a linear regression to determine the slope of this line. We generally force the line through the origin. Divide ln (0.5) by the slope to determine the half-life. We recommend having 3 biological replicates for each time-point, and three technical replicates for each biological replicate. The linear regression represents all of these replicates combined for a single experiment. See Figure 2 for the graph of sample data.
Note: Western blot assay (perform 1-6 as above, then continue with 7). See Figure 3 for sample data for Western blot analysis.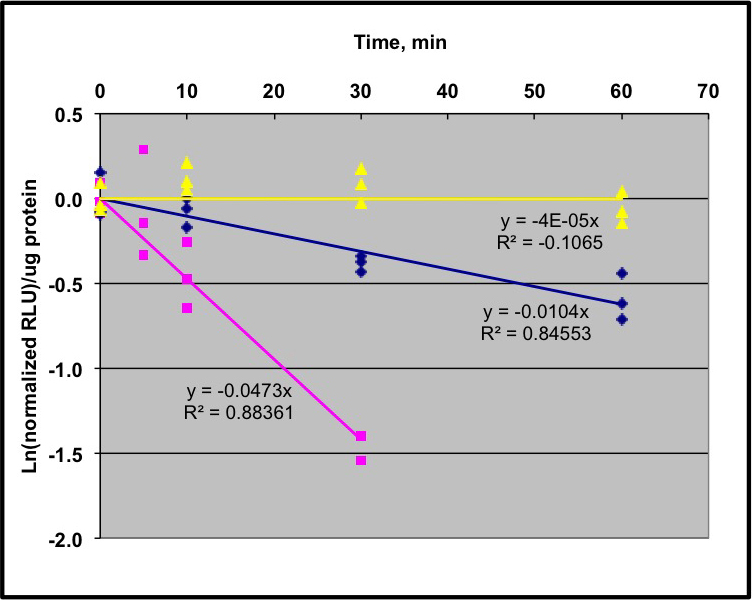
Figure 2. Sample data from a pooled seedling degradation assay using LUC fusions. Protocol as described in text and shown in Figure 1 was used to analyze 3 different transgenic lines. Two lines are expressing IAA1:LUC fusion in two different Arabidopsis thaliana Col-0 genetic backgrounds; wild type (magenta line) and cul1-7 (blue line). Data were analyzed as described in the text and regression lines indicated in the figure. The half-life of IAA1-LUC in the wild type line is 14 min, and in cul1-7 is ~70 min. A transgenic line expressing unfused luciferase shows no detectable degradation in this time period (yellow line). Adapted from data obtained in Gilkerson et al. (2007). - After protein quantification, load equal total protein for each time-point onto standard polyacrylamide gels for SDS-PAGE. The amount of total protein applied to the gel depends on the abundance of the protein, which has to be determined empirically. Proteins are transferred from the gel to a PVDF membrane for antibody visualization. The exact conditions for protein visualization using antibodies depend on the antibody and the expression of the protein. For example, there are multiple chemiluminescent detection kits with different sensitivities.
- When film is used, blots should be scanned using a flat-bed scanner without auto-toning and saved as 8-bit gray-scale tagged-image-file-format images. After scanning and capturing an image, perform spot densitometry using NIH ImageJ 1.36 without background correction to quantify the amount of protein at each time-point. For detailed instructions on use of ImageJ for spot densitometry, we recommend the website “Analyzing gels and westerns with ImageJ” (http://lukemiller.org/index.php/2010/11/analyzing-gels-and-western-blots-with-image-j/).
- Normalize the amount of protein at the various times to the amount without CHX. Calculate the natural log of that normalized value to linearize the data. The ln(normalized band intensity) should be plotted against time, and the slope of this line used to calculate the half-life by the following equation: t1/2 = [ln(0.5)]/slope. Data for all blots should be combined to draw a single line for the final half-life calculations. Linear regression analysis should be performed to calculate the 95% confidence interval for the slope of the line.
- This experiment should be repeated at least 3 times and each sample analyzed twice as technical replicates. See Figure 3 for sample Western blot analysis.
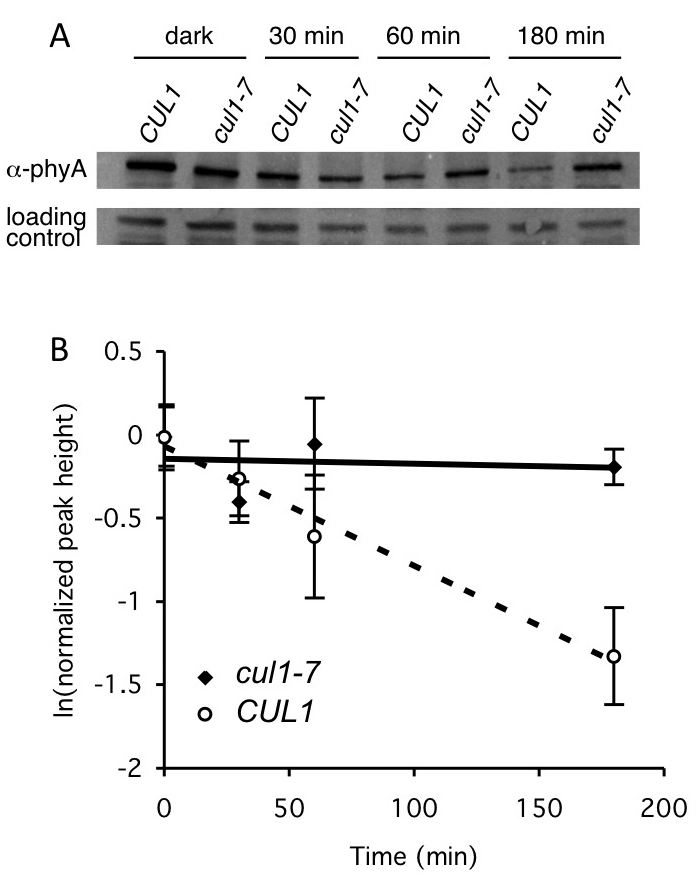
Figure 3. Example of pooled seedling degradation assay using Western blot analysis. The stability of native phytochrome A (PhyA) was assessed in 2 different genetic backgrounds, wild-type (CULLIN 1) and cul1-7, defective in a type of ubiquitin E3 ligase. Seeds were germinated in 1 ml liquid GM and dark-grown for four days (to allow PhyA accumulation). Cycloheximide was added (with the exception of the dark mock control), and seedlings exposed to 20 μmol/m-2 s-1 red light for the indicated times, then flash frozen. PhyA is degraded in the light. Protein extracts were made, and 40 μg total protein were separated by SDS-PAGE. A. PhyA levels at different times were determined by immunoblotting with an anti (α)-PhyA antibody. A cross reactive band was included as a loading control. B. Quantification of PhyA degradation in cul1-7. ImageQuant 1.0 software was used to quantify relative PhyA levels from the Western blot analyses described in (A). Values represent averages ± SD from a total of at least three Western blots from three independent experiments. T1/2 = 96 min in CUL1. PhyA is not degraded appreciably in cul1-7. This is Figure 7 from Gilkerson et al. (2009). Reprinted with permission from Genetics Society of America, which holds the copyright.
- ~2 mg of Arabidopsis seeds (weighed out) are placed in a microfuge tube and surface-sterilized by a 10 min treatment with 300 μl of a fresh (less than 2 weeks old) solution of 30% commercial bleach + 0.1% Tween-20, followed by 2 sterile water rinses (typically, 800 μl each) to remove the bleach. The seeds are then suspended in 1 ml of liquid growth media (GM) and transferred to 60 x 15 mm sealed (Parafilm) Petri dishes with a pipet tip whose tip was cut to make the opening wider. Seeds are carefully disturbed around the edge of Petri dish. The seeds and liquid should not cover the entire bottom of the plate (Figure 1, top). This reduces the need for excess media. After plating, seeds are stratified by incubation at 4 °C for 2-3 days in the dark. Plates are then removed from the cold and incubated at 22 °C under constant light (~50-70 μmol sec-1 m-2) for 6 days without shaking. This amount of liquid is sufficient to last 6 days for this amount of seed. If growth is more robust, or more seeds are used, then media may need to be added to the plates before day 6 to keep the seedlings sufficiently hydrated. In a sterile hood, open the plate and add a small amount of sterile liquid GM media. Reseal the plate and return to 22 °C under constant light.
- Single seedling CHX in vivo degradation assays using luciferase (LUC) fusions
This protocol is called the single seedling degradation assay because degradation of a LUC fusion protein is measured separately in individual seedlings, and the individual degradation kinetics are pooled afterward to obtain a single half-life. In our laboratory, the only proteins that have been analyzed using this protocol have been proteins expressed as fusions with the reporter protein luciferase (typically from Firefly). Because the luciferase substrate is cell-permeable, luciferase activity can be detected in an intact seedling as light emission after incubation with luciferin, and this light emitted can be quantitated in a luminometer (Gilkerson et al., 2009). In plants, the half-life of unfused LUC was determined to be ~70 min when intact plants are provided the substrate luciferin and degradation measured in vivo (Gilkerson et al., 2009). Therefore, in these in vivo assays the half-life of a protein (peptide)-LUC fusion protein has to be shorter than 70 min or else the degradation rate determined will be driven primarily by the luciferase portion of the fusion protein. However, if degradation of the protein (peptide)-LUC fusion is more rapid than 70 min, then the degradation rate observed results from the degradation determinants present in the protein (peptide) co-expressed with LUC, not simply from LUC amino acids alone.- Seeds from plants expressing LUC fusions are surface sterilized (step A1) and imbibed in water for 2 days at 4 °C in the dark. An individual seed is placed in one microtiter well of a white, polystyrene, flat-bottomed, 96-well plate containing 200 µl solid GM media. Plates are sealed with clear adhesive plate film and placed in continuous white light for 7-10 days at room temperature (Figure 4).
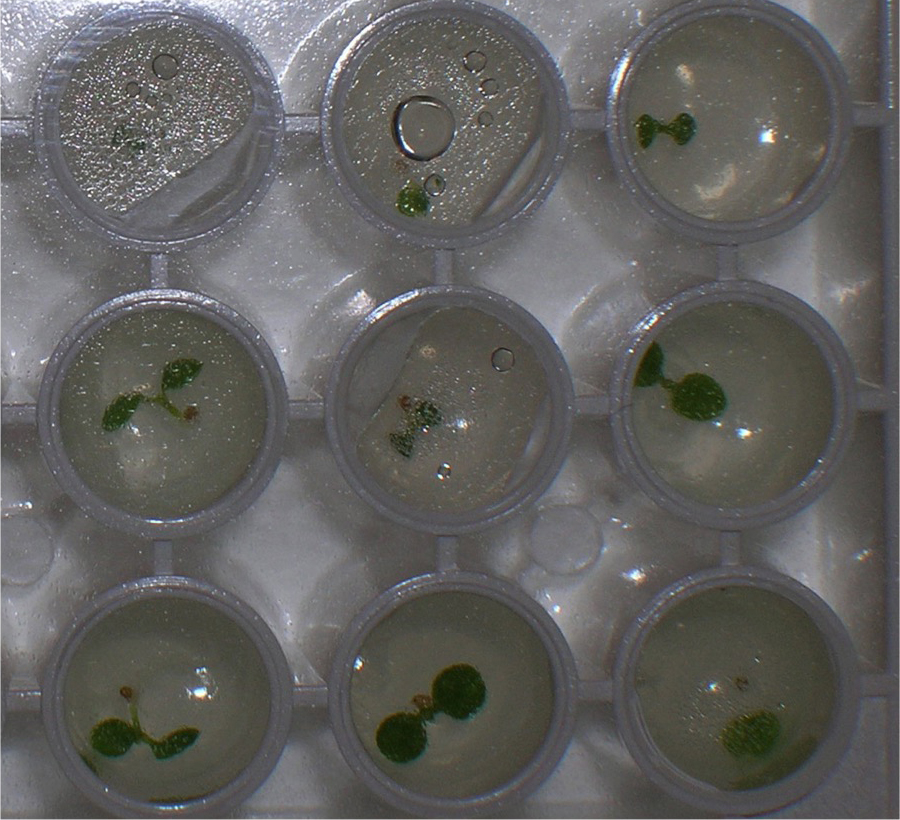
Figure 4. Close-up view of a 96-well microtiter plate with one Arabidopsis seedling in each well. In vivo LUC activity can be measured in a luminometer after addition of the substrate, luciferin. - After incubation, 50 µl of 1 mM luciferin is added to each well and the plates are incubated with slow rocking in the dark (covered with foil) for 60 min at room temperature. Then 20 µl of a 2,000 µg/ml solution of CHX is added to each well and the plate immediately put in the luminometer for measurement. Light emission was monitored over a time-course, with measurements taken every 15 min.
- The luminometer measures (here suggest measuring for 8 sec at each time point) relative light units (RLU) emitted from individual seedlings and the data are stored in an Excel spreadsheet.
- Data analysis. The time interval between each recording is determined by the number of minutes at the start of the first measurement, designated time 0. The RLU (relative light units) at each time-point is normalized to the zero time-point measurement. To linearize the data, the ln(normalized RLU) is calculated for each individual seedling. Calculate the slope of degradation line for each seedling using the slope function in Excel. Use the following formula to calculate the half-life: half-life (min) = ln(0.5)/slope. Average the half-lives for all the seedlings and determine the descriptive statistics (standard deviation, standard error, 95% confidence). See Figure 5 for sample data.
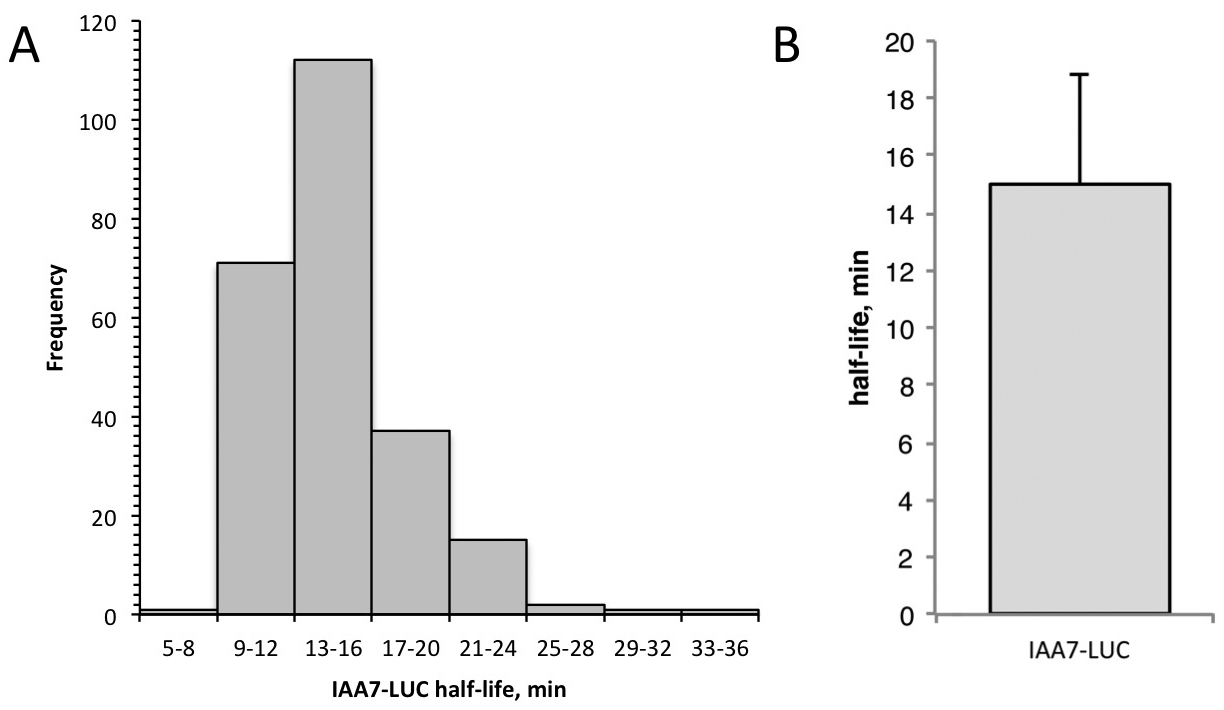
Figure 5. Sample data from single seedling degradation assay. A. Frequency distribution for IAA7-LUC half-lives determined in 240 individuals by the single-seedling assay. B. Half-life of IAA7-LUC is 15.0 min, determined using single-seedling assay data shown in (A). Error bar is standard deviation.
- Seeds from plants expressing LUC fusions are surface sterilized (step A1) and imbibed in water for 2 days at 4 °C in the dark. An individual seed is placed in one microtiter well of a white, polystyrene, flat-bottomed, 96-well plate containing 200 µl solid GM media. Plates are sealed with clear adhesive plate film and placed in continuous white light for 7-10 days at room temperature (Figure 4).
Notes
- If there is no prior knowledge of the degradation kinetics of the protein of interest, we recommend pilot experiments with one treatment time-point to determine whether the protein is rapidly degraded (with a half-life of less than 1 h) or more slowly, with a half life of > 1 h. For these pilot experiments, the protocol is the same except only 2 plates are needed, one with solvent only added-no cycloheximide (CHX) and one with added CHX. We recommend starting with a 2 h CHX treatment. If the protein is completely absent after 2 h (in the + CHX sample based on normal sample treatment and signal development time), then a short time course is required. If the protein abundance is only slightly reduced, then the longer time courses starting at and after 1 h, such as 1, 2 and 4 h of CHX treatment are required. If protein level is detected, but significantly reduced at 2 h (< 50%), then a time course in the range of 30 min, 1 and 2 h is appropriate. This single time point CHX assay can be repeated until the appropriate range of protein loss is observed.
- To measure protein half-life, once the appropriate times are determined, multiple time points are required. In addition, the protein must be reduced to < 50% of its control value in at least one of the time points. Extrapolation of lines to calculate a half-life is not appropriate, given that complex degradation kinetics can occur; therefore, protein half-life cannot be accurately measured from extrapolating the line past the last time point to reach 50% of initial value, or by using the decay equation to determine half-life if the values used to generate the line derive from protein that has not been significantly reduced in abundance in the time course.
- We also recommend using a rapidly degraded protein as a control protein to monitor the efficacy of the CHX and to verify the procedure and time course. In each experiment, we routinely include a sample of transgenic line expressing a detectable form of Arabidopsis protein indole acetic acid 1 (IAA1) because this protein is very short-lived, with a half-life of ~12-15 min (Ramos et al., 2001; Zenser et al., 2001). Lines expressing either 3xHA-IAA1 (Dreher et al., 2006) or an IAA1-LUC fusion (Zenser et al., 2001; Dreher et al., 2006) have been used. Significant loss of this protein in short time courses and undetectable amounts at longer times (< 1 h, again under specific conditions) are observed and can certify that the CHX treatment was effective in blocking new synthesis. Such transgenic lines are available from the corresponding author upon request.
- CHX assays also work with mature leaf disks floating on GM media using the same pooled seedling assay (a more accurate term in this case would be pooled leaf disc assay) using the same Petri dishes (but with a pre-incubation of 2-4 h after placing on GM). Leaf discs (or punches) are placed on GM media, allowed to incubate for 2-4 h in assay conditions before addition of CHX (or mock) as in step A3.
- Both of the experimental approaches described above take advantage of cycloheximide’s ability to enter cells of intact organs/seedlings and effectively inhibit protein synthesis, properties that have been known for a long time [For examples, see (Delseny et al.,1977; Sluiters-Scholtern, 1973)]. A word of caution. Treatment with cycloheximide for significant lengths of time may lead to secondary effects. If your protein has a modest degradation rate, in the order of hours based on these CHX assays, it is strongly recommended that a different approach confirm the half-life, given the possible secondary effects of prolonged incubation in a protein synthesis inhibitor. For example, degradation of a protein could depend on a short-lived protein that will become depleted during a long CHX chase assay. In this case, the protein will appear stable in CHX assays, while in vivo it could be short-lived. Degradation of the protein could be coupled to ongoing synthesis, which is blocked with CHX treatment. RNA synthesis is affected by CHX, and some genes are induced by cycloheximide (likely due to regulation by short-lived repressors) and while unlikely, these effects could modulate your protein’s longevity. Alternative approaches are pulse-chase experiments (with radiolabeled amino acids, but without CHX), 15N- and D2O-labeling experiments (Yang et al., 2010; Li et al., 2012). For an overview of the topic, see a recent review (Nelson and Millar, 2015).
Recipes
- Growth media (GM)
4.3 g/L Murashige and Skoog basal salts with micronutrients
1% sucrose (although likely plant cell culture grade is not essential; other sources likely to be equivalent)
2.5 mM MES free acid
1x B-vitamins (from 100x stock of a mix of the 4 below in water, filter sterilized, stored at 4 °C) containing the 4 items below:
0.5 µg/ml nicotinic acid
1.0 µg/ml thiamine-HCl
0.5 µg/ml pyroxidine-HCl
0.1 µg/ml myo-inositol
Adjust pH to 5.7 with 1 M KOH
Add 8 g/L Bacto agar for solid GM; omit for liquid GM - Luciferase extraction buffer
100 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.8
1 mM EDTA, disodium dehydrate
7 mM β-mercaptoethanol
1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF)
Complete protease inhibitor tablet, 1 tablet/10 ml buffer - Luciferase assay buffer
25 mM tricine, pH 7.8, adjust pH with HCl
15 mM MgCl2
7 mM β-mercaptoethanol
1 mg/ml bovine serum albumin (BSA)
5 mM ATP - Protein extraction buffer for Western blot assays
50 mM Tris, pH 7.2, adjust pH with HCl
150 mM NaCl
0.5% (v/v) IGEPAL CA-630
1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF)
10 μM MG132
Complete mini protease inhibitor EDTA-free tablet, 1 tablet/10 ml buffer
Acknowledgments
These protocols were expanded upon from the previously published material and methods (Gilkerson et al., 2009; Dreher et al., 2006; Gilkerson and Callis, 2014; Gilkerson et al., 2015). This work was supported by NSF (MCB-099100) and DOE (DE-FG02-12ER16077 and DE-SC0002175).
References
- Dreher, K. A., Brown, J., Saw, R. E. and Callis, J. (2006). The Arabidopsis Aux/IAA protein family has diversified in degradation and auxin responsiveness. Plant Cell 18(3): 699-714.
- Delseny, M., Aspart, L. and Guitton, Y. (1977). Effect of the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide on RNA synthesis in radish seedlings. Biochimie 59(1): 51-57.
- Gilkerson, J., Hu, J. H., Brown, J., Jones, A., Sun, T. P. and Callis, J. (2009). Isolation and characterization of cul1-7, a recessive allele of CULLIN1 that disrupts SCF function at the C terminus of CUL1 in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 181(3): 945-963.
- Gilkerson, J. and Callis, J. (2014). A genetic screen for mutants defective in IAA1-LUC degradation in Arabidopsis thaliana reveals an important requirement for TOPOISOMERASE6B in auxin physiology. Plant Signal Behav 9(10): e972207.
- Gilkerson, J., Kelley, D. R., Tam, R., Estelle, M. and Callis, J. (2015). Lysine residues are not required for proteasome-mediated proteolysis of the auxin/indole acidic acid protein IAA1. Plant Physiology 168(2): 708-720.
- Li, L., Nelson, C. J., Solheim, C., Whelan, J. and Millar, A. H. (2012). Determining degradation and synthesis rates of Arabidopsis proteins using the kinetics of progressive 15N labeling of two-dimensional gel-separated protein spots. Mol Cell Proteomics 11(6): M111 010025.
- Nelson, C. J. and Millar, A. H. (2015). Protein turnover in plant biology. Nature Plants 1(3).
- Ramos, J. A., Zenser, N., Leyser, O. and Callis, J. (2001). Rapid degradation of auxin/indoleacetic acid proteins requires conserved amino acids of domain II and is proteasome dependent. Plant Cell 13(10): 2349-2360.
- Sluiters-Scholten, C. M. (1973). Effect of chloramphenicol and cycloheximide on the induction of nitrate reductase and nitrite reductase in bean leaves. Planta 113(3): 229-240.
- Yang, X. Y., Chen, W. P., Rendahl, A. K., Hegeman, A. D., Gray, W. M. and Cohen, J. D. (2010). Measuring the turnover rates of Arabidopsis proteins using deuterium oxide: an auxin signaling case study. Plant J 63(4): 680-695.
- Zenser, N., Ellsmore, A., Leasure, C. and Callis, J. (2001). Auxin modulates the degradation rate of Aux/IAA proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98(20): 11795-11800.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Gilkerson, J., Tam, R., Zhang, A., Dreher, K. and Callis, J. (2016). Cycloheximide Assays to Measure Protein Degradation in vivo in Plants. Bio-protocol 6(17): e1919. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1919.
- Gilkerson, J., Kelley, D. R., Tam, R., Estelle, M. and Callis, J. (2015). Lysine residues are not required for proteasome-mediated proteolysis of the auxin/indole acidic acid protein IAA1. Plant Physiology 168(2): 708-720.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Protein
Biochemistry > Protein > Degradation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










