- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Salinity and Drought Treatment Assays in Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.)
Published: Vol 6, Iss 17, Sep 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1918 Views: 10476
Reviewed by: Arsalan DaudiJian ChenMohan TC

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

A Plate Growth Assay to Quantify Embryonic Root Development of Zea mays
Jason T. Roberts [...] David M. Braun
Oct 20, 2023 2256 Views

Detection and Quantification of Programmed Cell Death in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: The Example of S-Nitrosoglutathione
Lou Lambert and Antoine Danon
Aug 5, 2024 1589 Views

Enzymatic Starch Quantification in Developing Flower Primordia of Sweet Cherry
Nestor Santolaria [...] Afif Hedhly
Apr 5, 2025 1897 Views
Abstract
Salinity and drought are the two main factors that cause fiber yield and quality losses in kenaf. It is reported that salinity and drought can affect more than 10% of arable land and cause a global decline in the average yields of major crops by more than 50%. Therefore, understanding plant tolerance of drought and salinity is of fundamental importance and has become the focus of intensive research. This protocol describes a simple and reproducible protocol to imitate natural salinity and drought stress under soil conditions. Even though the water-culture method is most frequently used for salinity and drought treatments, the soil-culture method in this study was more applicable to studying natural stress conditions.
Keywords: SalinityMaterials and Reagents
- Sterile Petri dishes (JET, catalog number: TCD010090 )
- Sterile filter paper (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z241091 )
- Seeds: kenaf (cv Fuhong 992) [conserved in the Key Laboratory for Genetics, Breeding and Multiple Utilization of Crops of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (China)].
- Sterile water (sterilized for 20 min at 121 °C/1 atm using an autoclave)
- Sterile soil (Fafard® growing mix 1-PV/C-1PV, Sun Gro Horticulture Canada Ltd.) (sterilized for 30 min at 121 °C/1 atm using an autoclave)
- Sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) solution (15%) (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent, catalog number: 7681-52-9 )
- Potassium nitrate (KNO3) (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent, catalog number: 7757-79-1 )
- Ammonium dihydric phosphate (NH4H2PO4) (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent, catalog number: 7722-76-1 )
- Ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent, catalog number: 6484-52-2 )
- Calcium nitrate [Ca(NO3)2·4H2O] (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent, catalog number: 13477-34-4 )
- Magnesium sulphate (MgSO4·7H2O) (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent, catalog number: 10034-99-8 )
- Ethylene diamine-N,N bis (2 hydroxyphenylacetic acid) Ferric sodium complex (Fe-EDDHA) (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent, catalog number: 16455-61-1 )
- Boric acid (H3BO3) (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent, catalog number: 10043-35-3 )
- Manganese chloride (MnCl2·4H2O) (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent, catalog number: 7773-01-5 )
- Zinc sulphate (ZnSO4·7H2O) (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent, catalog number: 7446-20-0 )
- Copper sulphate (CuSO4·5H2O) (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent, catalog number: 7758-98-7 )
- Sodium molybdate (Na2MoO4·2H2O) (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent, catalog number: 10102-40-6 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sinopharm Chemical Reagent, catalog number: 7647-14-5 )
- PEG6000 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 81260 )
- 5% (v/v) sodium hypochlorite(see Recipes)
- Hoagland solution (see Recipes)
- 200 mM sodium chloride (NaCl) solution (see Recipes)
- 20% (w/v) PEG6000 solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Plastic pots (10 cm diameter and 8 cm depth)
- Clean bench (Suzhou AirTech , AirTech®, model: SW-CJ-1FD )
- Growth chamber (Yihengyiqi Shanghai, Blue pard®, model: MGC-300A )
- Autoclave (TOMY, model: SX-500 )
- Precision balance (± 0.001)
- Timer control
Procedure
- Seed germination and culture
- Rinse the seeds under running water for 10 min, and then sterilize the seeds with 5% sodium hypochlorite for 10 min, and subsequently wash the seeds three times with sterile water (Figure 1A).
- Place the sterilized seeds in Petri dishes on filter paper saturated with sterile water, and maintain the seeds in complete darkness at 28 °C until germination (about 3 days) (Figure 1B and 1C).
- Transfer 3-5 days old seedlings to separate sterilized soil pots.
- Maintain the plants in growth chambers at 28 °C for 16 h with light and 26 °C for 8 h without light, 60% relative humidity, ~450 μmol m-2 s-1 light intensity, and supplement 100 ml 1/4 Hoagland solution to soil once a day (Figure 1D).
- Allow plants to grow up to 3-10 leaves stage (about 4 weeks) for salinity and drought treatments assays.
- Rinse the seeds under running water for 10 min, and then sterilize the seeds with 5% sodium hypochlorite for 10 min, and subsequently wash the seeds three times with sterile water (Figure 1A).
- Salinity and drought treatments
- For salinity treatment, prepare 200 mM sodium chloride solution in Hoagland nutrient medium and supplement 100 ml of this solution to 10 pots individually once a day (Figure 1D).
- For drought treatment, prepare 20% (w/v) PEG6000 solution in Hoagland nutrient medium and supplement 100 ml of this solution to 10 pots individually once a day (Figure 1D).
- Harvest 3 treated leaves from each plant at different time points (e.g., 6, 12 and 24 h). Untreated samples were collected at the same interval as a control. Three biological replicates were obtained from each treatment (Figure 1E).
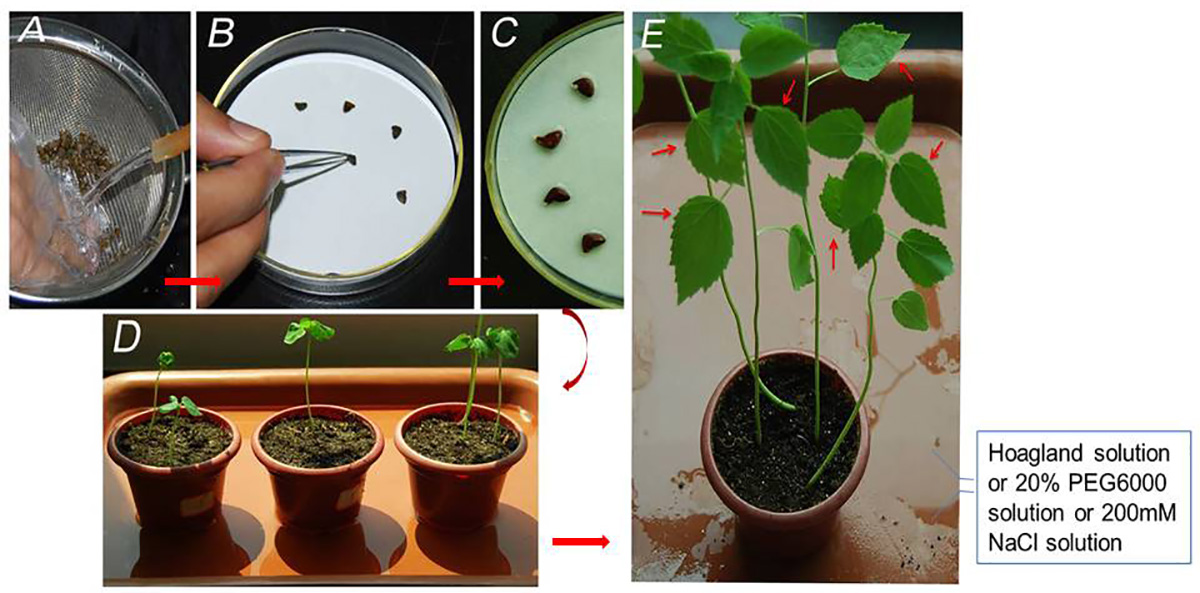
Figure 1. Example of experimental procedure. A. Seeds rinsed under running water; B. Sterilized seeds on saturated filter paper in Petri dishes; C. Germinated seeds; D. Seedlings at cotyledon stage; E. Harvesting leaf samples (about 4 weeks) as pointed by red arrows after salinity and drought treatments.
- For salinity treatment, prepare 200 mM sodium chloride solution in Hoagland nutrient medium and supplement 100 ml of this solution to 10 pots individually once a day (Figure 1D).
Data analysis
RNA was isolated and used for selection reliable reference gene (such as ACT, 18S rRNA, EF1α) for Real-Time PCR (RT-qPCR) assay under salinity and drought stress, and this section was stated clearly in our paper (Niu et al., 2015).
Notes
- Soil is sterilized for at least 30 min at 121 °C/1 atm using an autoclave.
- Polyethylene glycol (PEG) is a flexible, water-soluble polymer, and it can be used to create high osmotic pressure. Therefore, it is used for applying osmotic pressure in plants to induce water deficit.
- The same aged leaves should be taken from each sample type. Also use at least three individual lines from each treatment for analysis.
- The volume of supplement is depended on the size of pots, watering frequency, and plant species. It is recommended that a series of assays should be done for a given plant species before stress treated.
Recipes
- Hoagland solution
Note: Hoagland solution is based on Hoagland No.2 solution (Hoagland et al., 1950) (Table 1).
Table 1. Hoagland solution composition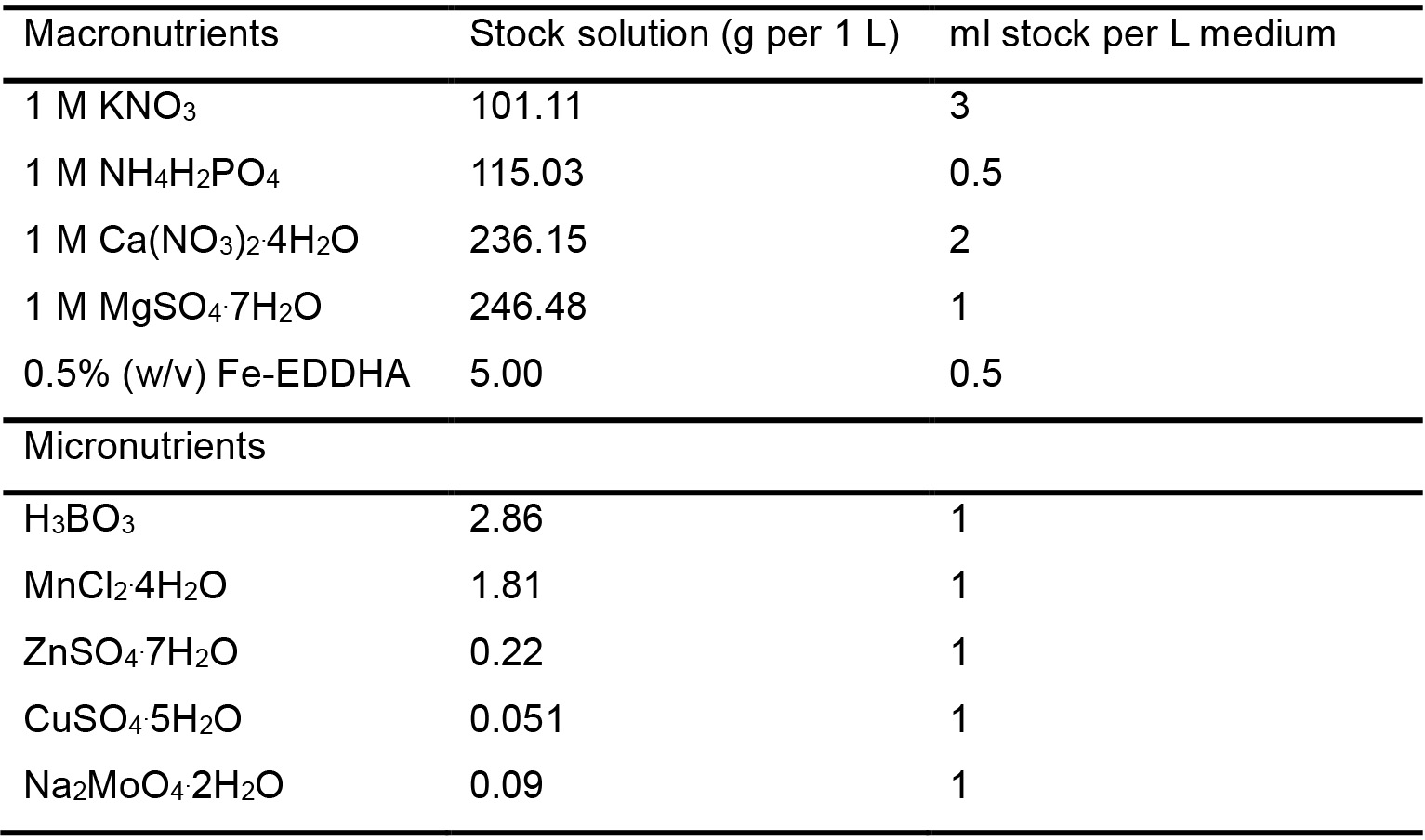
- 5% (v/v) sodium hypochlorite
Add 33 ml 15% NaClO solution in the distilled water to get a final volume of 100 ml - 20% (w/v) PEG6000 solution
Dissolve 20 g PEG6000 in distilled water
Dilute with distilled water to get a final volume of 100 ml, and mix - 200 mM sodium chloride solution
Dissolve 11.7 g NaCl in 1 L distilled water
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the 948 project of the Agricultural Department of China (2013-Z70), the National bast fiber germplasm resources project of China (K47NI201A) and National bast fiber research system of China (CARS-19-E06). This protocol was adapted from our recent publications (Niu et al., 2015).
References
- Hoagland, D. R., Arnon, D. I. (1950). The water-culture method for growing plants without soil. California Agriculture Experiment Station 347: 34.
- Niu, X., Qi, J., Chen, M., Zhang, G., Tao, A., Fang, P., Xu, J., Onyedinma, S. A. and Su, J. (2015). Reference genes selection for transcript normalization in kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) under salinity and drought stress. Peer J 3: e1347.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Niu, X., Chen, M., Tao, A. and Qi, J. (2016). Salinity and Drought Treatment Assays in Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.). Bio-protocol 6(17): e1918. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1918.
Category
Plant Science > Plant physiology > Abiotic stress
Plant Science > Plant physiology > Plant growth
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











