- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
In vitro Cell Wall Stress Assay for Fusarium oxysporum
Published: Vol 6, Iss 17, Sep 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1915 Views: 10892
Reviewed by: Zhaohui LiuEmmanuel ZavalzaAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

In Vitro Hyphal Branching Assay Using Rhizophagus irregularis
Takaya Tominaga and Hironori Kaminaka
Aug 20, 2024 2339 Views

Silencing Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Gene Using Chitosan Nanoparticle-Mediated dsRNA Delivery System
Chumei Yan [...] Xianan Xie
Jun 5, 2025 2646 Views

A Reliable In Planta Inoculation and Antifungal Screening Protocol for Rhizoctonia solani-Induced Sheath Blight in Rice
Alinaj Yasin [...] Palash Deb Nath
Nov 5, 2025 1584 Views
Abstract
In this protocol we describe a cell wall stress assay for the fungal pathogen F. oxysporum, based on exposure to the two anionic dyes Calcofluor White (CFW) and Congo Red (CR). Both compounds have been used to exert stress upon the fungal cell wall in vitro (Perez-Nadales and Di Pietro, 2015; Perez-Nadales and Di Pietro, 2011; Leach et al., 2012; Heilmann et al., 2013; Garcia et al., 2015). CFW perturbs chitin assembly, whereas CR interferes with β-glucan synthesis, resulting in cell wall-weakening and activation of the cell wall stress response (Ram and Klis, 2006; Kopecka and Gabriel, 1992; Roncero and Duran, 1985). Presumably, the signaling pathways and cell wall changes associated with this response reflect cell wall homeostasis during normal growth as well as cell wall remodeling events in response to stresses encountered during the fungus-host interactions. The conditions for preparation of CFW and CR culture medium specified in this protocol are based on the paper by Ram and Klis entitled “Identification of fungal cell wall mutants using susceptibility assays based on Calcofluor white and Congo red”, published in Nature protocols (Ram and Klis, 2006). This paper established the optimum conditions for preparation of CFW and CR stock solutions and suggested maintaining the culture medium at a constant pH to avoid acidification, protonation and precipitation of these dyes. This cell wall stress assay has been widely used in our group for the characterization of F. oxysporum mutants in mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway genes involved in cell wall integrity (Perez-Nadales and Di Pietro, 2015; Perez-Nadales and Di Pietro, 2011; Turra et al., 2014).
Materials and Reagents
- Round (90 mm diameter) or square (120 x 120 mm) Petri dishes
- Autoclavable, filtration material [e.g., Miracloth (Merck Millipore, catalog number: 475855 )]
- Calcofluor white fluorescent brightener (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F-3543 )
- Congo red (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 860956 )
- Distilled water
- Potassium hydroxide (KOH) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5958 )
- Glycerol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G5516 )
- Potatoes
- Cloth strainer
- Potato dextrose agar (PDA) (Scharlab, catalog number: 01-483-500 )
- Yeast extract (Merck Millipore, catalog number: 1119261000 )
- Peptone (Merck Millipore, catalog number: 1119311000 )
- Glucose (VWR, Normapur®, catalog number: 50-99-7 )
- Agar (BD, BactoTM, catalog number: 214010 )
- MgSO4·7H2O (Merck Millipore, catalog number: 1058865000 )
- KH2PO4 (Merck Millipore, catalog number: 1048731000 )
- KCl (Merck Millipore, catalog number: 1049330500 )
- NaNO3 (Merck Millipore, catalog number: 1065371000 )
- Sucrose (Merck Millipore, catalog number: 1076875000 )
- Agar (Thermo Fisher Scientific, OxoidTM, catalog number: LP0011 )
- 2-(N-morpholino) ethanesulfonic acid (MES), monohydrate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 69892 )
- Sodium hydroxide (NaOH) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S8045 )
- Potato dextrose broth (PDB) (see Recipes)
- CFW and CR stock solutions (see Recipes)
- CFW stock solutions (20 mg/ml)
- CR stock solutions (50 mg/ml)
- CFW stock solutions (20 mg/ml)
- Fungal growth agar medium (see Recipes)
- YPD agar medium
- PDA agar medium
- Puhalla’s minimal agar medium (MM)
- YPD agar medium
Note: CFW and CR are hazardous and potentially carcinogenic so caution must be taken to avoid skin contact or inhalation of these compounds.
Equipment
- Protection gloves and coat
- Flasks and magnetic stirrer for preparation of solutions
- Neubauer chamber for cell counting
- Microwave
- Autoclave
- Fungal growth incubator
- Water bath
- Laminar flow hood
- Heat plate and cooking pot to boil potatoes
- pH meter
Note: No other special equipment is required.
Software
- SPSS 15.0 for Windows® (LEAD Technologies Inc.)
Procedure
A major requirement for this protocol is to experimentally establish the optimum concentration of CFW or CR to be used. This may be influenced by several parameters, including size of the inoculum, genetic background of the strains and composition of the growth medium. The wild type strain used in our laboratory was Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. lycopersici (strain 4287/FGSC 9935). Appropriate CFW and CR concentration should be sublethal for the wild-type or reference strain used in the experiment. We typically define this parameter by inoculating serial dilutions of conidia in the form of spots on plates containing CFW and CR, with concentrations in the range of 10-200 μg/ml of CFW and 5-600 μg/ml of CR.
- Production of fresh microconidia (3-4 d)
Inoculate 50 µl of a -80 °C stock microconidial suspension (in 30% glycerol) into 50 ml of liquid potato dextrose broth (PDB) (see Recipe 1). Grow cultures for 3-4 d at 28 °C with shaking at 170 rpm (Di Pietro and Roncero, 1998). Filter microconidia through one layer of Miracloth, centrifuge and wash with sterile water. Count conidia using a neubauer chamber and adjust to a final concentration of 1 x 107 conidia/ml. - Preparation of stock solutions of CFW (20 mg/ml) and CR (50 mg/ml) (1 h) (see Recipe 2)
- Preparation of growth medium (1-2 h)
Prepare growth agar medium and autoclave (20 min at 120 °C). Cool the medium down to 50-60 °C in a water bath before adding CR and CFW to avoid any potentially harming fumes. Then, add CFW or CR to reach the desired concentrations. This can be done in a laminar flow hood. For F. oxysporum, we suggest to start by testing 4-5 different dye concentrations, in the following range: 10 to 200 μg/ml for CFW and 10 to 600 µg/ml for CR. Additionally, prepare a control plate without the dyes. The plates can be stored overnight, at room temperature and in the dark, to be used the next day. - Preparation of a serial dilution of microconidia (1-2 h)
Prepare a 10-fold serial dilution of freshly-obtained microconidia starting with the 1 x 107 conidia/ml stock solution generated in step 1 (1 x 107, 1 x 106, 1 x 105 and 1 x 104 conidial/ml). Inoculate 2 µl drops of this series on plates containing CFW or CR and a control plate (final concentrations: 2 x 104, 2 x 103, 2 x 102 and 2 x 10 conidia/ml). We typically use square (120 x 120 mm) Petri dishes, to allow sufficient space for growth of the fungal colonies. - Incubation of plates (2-3 d)
Incubate plates at 28 °C in the dark for 2-3 d. - Interpreting and monitoring results
- Sensitivity to CFW and CR should be determined by comparing the extent of colony formation of parental and mutant strains in control and CFW or CR plates. Colony diameter may be measured for quantification of differences in colony growth of the strains tested. For this, inoculate each single strain (a 5 µl drop of a 1 x 107 microconia/ml suspension) on the control and cell wall stress plates, with 5 replicates each. We use round (90 mm diameter) Petri dishes. Incubate the plates at 28 °C for 5 d before scanning and measuring colony diameter.
- Data from three independent experiments, each with five replicates, can then be analyzed with a statistic software such as SPSS 15.0 for Windows®. Kruskal-Wallis analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Mann-Whitney test are used to assess statistically relevant differences among strains at P ≤ 0.05.
- Sensitivity to CFW and CR should be determined by comparing the extent of colony formation of parental and mutant strains in control and CFW or CR plates. Colony diameter may be measured for quantification of differences in colony growth of the strains tested. For this, inoculate each single strain (a 5 µl drop of a 1 x 107 microconia/ml suspension) on the control and cell wall stress plates, with 5 replicates each. We use round (90 mm diameter) Petri dishes. Incubate the plates at 28 °C for 5 d before scanning and measuring colony diameter.
Representative data
Figure 1 shows the sensitivity of several F. oxysporum MAPK pathway mutants to CFW and CR (Perez-Nadales and Di Pietro, 2011). In F. oxysporum, the Fmk1 MAPK pathway is essential for plant infection (Di Pietro et al., 2001). This experiment revealed that Msb2, a signaling mucin receptor functioning upstream of Fmk1 and also the Fmk1 MAPK are required for cell wall integrity in F. oxysporum under these conditions.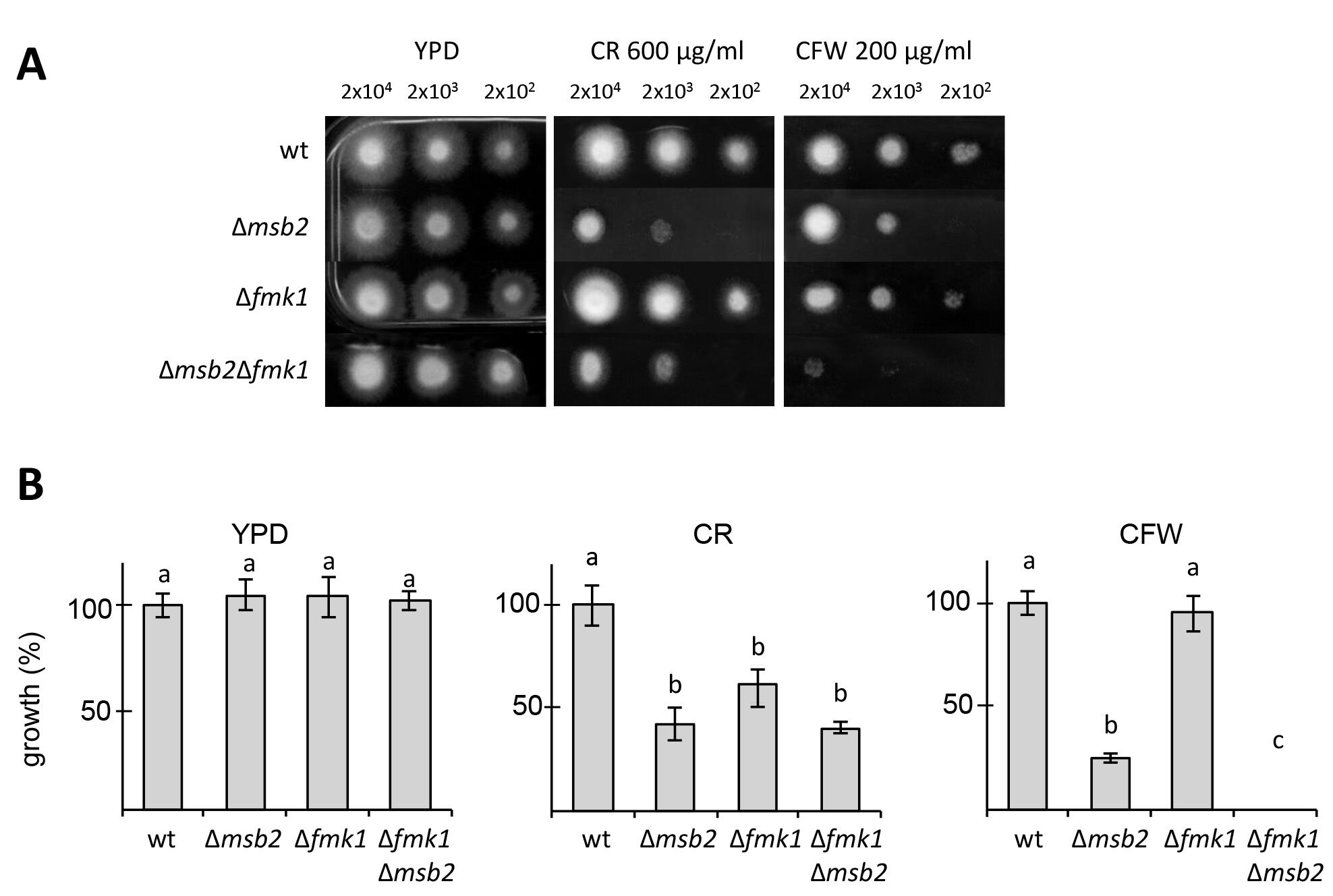
Figure 1. Cell wall stress assay for F. oxysporum. A. Plates containing YPD medium or YPD medium supplemented with CR or CFW were spot-inoculated with the indicated strains and amounts of microconidia, incubated for three days at 28 °C and photographed. B. Colony diameter of the indicated media was measured at day 3 post-inoculation and plotted relative to the wild-type strain (100%). Error bars represent standard deviations calculated from five independent plates. Values with the same letter are not significantly different according to Mann–Whitney test (P ≤ 0.05).
Notes
- During handling, CFW and CR solutions should always be protected from light by wrapping the containers in aluminum foil. As a precaution to prevent possible inactivation of CFW and CR by light, the plates should be incubated in the dark.
Recipes
- Potato dextrose broth (PDB)
- Boil 200 g of pealed potatoes in 1 L of distilled water for 60 min
- Filtrate through a cloth strainer
- Add 20 g of glucose and add up to 1 L distilled water
- Sterilize by autoclaving 20 min at 120 °C
- Boil 200 g of pealed potatoes in 1 L of distilled water for 60 min
- CFW and CR stock solutions
- CFW stock solutions (20 mg/ml)
We use the following diluting solution (Ram and Klis, 2006):
20 mg/ml CFW
0.5% (w/v) KOH
83% (v/v) glycerol
Note: We recommend preparing 20-30 ml of this solution prior to the experiment and store it at room temperature. On the day of the experiment, CFW can be freshly added to this solution reach a final stock concentration of 20 mg/ml. - CR stock solutions (50 mg/ml)
Note: CR is in the di-sodium form and is readily dissolved in water.
Prepare CR in sterile double-distilled water at a stock concentration of 50 mg/ml
- CFW stock solutions (20 mg/ml)
- Fungal growth agar medium
The composition of the growth medium for this cell wall stress test may vary depending on the purpose of the experiment. We have used in our assays complete media such as YPD or potato dextrose agar (PDA) and Puhalla’s minimal medium (Puhalla, 1985). All media are prepared in distilled water.- YPD agar medium
3 g/L yeast extract
10 g/L peptone
20 g/L glucose
15 g/L Bacto agar - PDA agar medium
3.9% PDA, w/v - Puhalla’s minimal agar medium (MM)
0.5 g/L MgSO4·7H2O
1 g/L KH2PO4
0.5 g/L KCl
2 g/L NaNO3
30 g/L Sucrose
Add 15 g/L of oxoid agar
- YPD agar medium
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the SIGNALPATH Marie Curie Research Training Network (MRTN-CT-2005-019277) and by grants BIO2008-04479-E, EUI2009-03942, and BIO2010-15505 from the Spanish Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación.
References
- Di Pietro, A. and Roncero, M. I. (1998). Cloning, expression, and role in pathogenicity of pg1 encoding the major extracellular endopolygalacturonase of the vascular wilt pathogen Fusarium oxysporum. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 11(2): 91-98.
- Di Pietro, A., Garcia-MacEira, F. I., Meglecz, E. and Roncero, M. I. (2001). A MAP kinase of the vascular wilt fungus Fusarium oxysporum is essential for root penetration and pathogenesis. Mol Microbiol 39(5): 1140-1152.
- Garcia, R., Botet, J., Rodriguez-Pena, J. M., Bermejo, C., Ribas, J. C., Revuelta, J. L., Nombela, C. and Arroyo, J. (2015). Genomic profiling of fungal cell wall-interfering compounds: identification of a common gene signature. BMC Genomics 16: 683.
- Heilmann, C. J., Sorgo, A. G., Mohammadi, S., Sosinska, G. J., de Koster, C. G., Brul, S., de Koning, L. J. and Klis, F. M. (2013). Surface stress induces a conserved cell wall stress response in the pathogenic fungus Candida albicans. Eukaryot Cell 12(2): 254-264.
- Kopecka, M. and Gabriel, M. (1992). The influence of Congo red on the cell wall and (1----3)-beta-D-glucan microfibril biogenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Microbiol 158(2): 115-126.
- Leach, M. D., Budge, S., Walker, L., Munro, C., Cowen, L. E. and Brown, A. J. (2012). Hsp90 orchestrates transcriptional regulation by Hsf1 and cell wall remodelling by MAPK signalling during thermal adaptation in a pathogenic yeast. PLoS Pathog 8(12): e1003069.
- Perez-Nadales, E. and Di Pietro, A. (2015). The transmembrane protein Sho1 cooperates with the mucin Msb2 to regulate invasive growth and plant infection in Fusarium oxysporum. Mol Plant Pathol 16(6): 593-603.
- Perez-Nadales, E. and Di Pietro, A. (2011). The membrane mucin Msb2 regulates invasive growth and plant infection in Fusarium oxysporum. Plant Cell 23(3): 1171-1185.
- Puhalla, J. E. (1985). Classification of strains of Fusarium oxysporum on the basis of vegetative compatibility. Can J Bot 63(2):179-183.
- Ram, A. F. and Klis, F. M. (2006). Identification of fungal cell wall mutants using susceptibility assays based on Calcofluor white and Congo red. Nat Protoc 1(5): 2253-2256.
- Roncero, C. and Duran, A. (1985). Effect of Calcofluor white and Congo red on fungal cell wall morphogenesis: in vivo activation of chitin polymerization. J Bacteriol 163(3): 1180-1185.
- Turra, D., Segorbe, D. and Di Pietro, A. (2014). Protein kinases in plant-pathogenic fungi: conserved regulators of infection. Annu Rev Phytopathol 52: 267-288.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Pérez-Nadales, E. and Di Pietro, A. (2016). In vitro Cell Wall Stress Assay for Fusarium oxysporum. Bio-protocol 6(17): e1915. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1915.
Category
Microbiology > Antimicrobial assay > Antifungal assay
Microbiology > Microbe-host interactions > Fungus
Biochemistry > Other compound > Antimicrobial
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










