- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Acute Live/Dead Assay for the Analysis of Toxic Effects of Drugs on Cultured Neurons
Published: Vol 6, Iss 15, Aug 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1889 Views: 13761
Reviewed by: Oneil G. BhalalaAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Real-time IncuCyte® Assay for the Dynamic Assessment of Live and Dead Cells in 2D Cultures
Arlene K. Gidda [...] Sharon M. Gorski
Feb 5, 2025 2868 Views

Time-Lapse Super-Resolution Imaging and Optical Manipulation of Growth Cones in Elongating Axons and Migrating Neurons
Masato Sawada [...] Kazunobu Sawamoto
Mar 20, 2025 2139 Views

Cryopreservation of Bulk-Produced Primary Rat Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells
Hanki Kim [...] Jun Young Choi
Jun 20, 2025 1426 Views
Abstract
The primary culture of central nervous system (CNS) neurons is a popular test system for a rapid, quantitative and reliable assessment of the effects of drugs on central neurons. Consequently, studies on the excitotoxicity of NMDA activation and on intracellular calcium handling machineries with respect to ischemic damage to the brain as well as neurodegenerative diseases have been highly productive (Ankarcrona et al., 1995). This created the need to establish a standard method for assessment of neurotoxicity. Several methods are currently being used, including LDH leakage and MTT assays (Mosmann, 1983; Decker and Lohmann-Matthes, 1988). We have used another common method for assessing acute cell death, the dead/live assay (Slepian et al., 1996). It provides a precise time and concentration evaluation of the process of cell death following exposure to a toxic substance, in our case, zeta-inhibitory peptide (ZIP), previously proposed to act as a selective PKM-zeta antagonist (Ling et al., 2002; Pastalkova et al., 2006; Sadeh et al., 2015). In this assay, we load cells with Calcein-AM, which, upon penetration into live neurons, is converted from a non-fluorescent compound into a highly fluorescent green fluorophore. Subsequently, we expose the neurons to different concentrations of ZIP for various durations, in the presence of propidium iodide (PI) which penetrates dead cells, and count red/green fluorescent cells. This method allows us to examine which cells were alive before, and died after exposure to the toxic substance as well as the time course of cell death.
Keywords: Cultured hippocampal neuronMaterials and Reagents
- 24 well plates (Nunc)
- Rat pups age P0, hippocampus (Figure 1)
- L-15 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Gibco®, catalog number: 21083 )
- Glucose (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Gentamicin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G1272 )
- Trypsine (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Gibco®, catalog number: 150900046 )
- DNase
- Enriched MEM (Minimal Essential Medium, enriched with glucose (0.6%), Glutamax (2 mM), and gentamicin (15 μg/ml) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Gibco®, catalog number: 32360-026 )
- B-27 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Gibco®, catalog number: 17504 )
- Horse serum (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Gibco®, catalog number: 16050 )
- Fetal calf serum (Gibco)
- 5-Fluoro-2-deoxyuridine (FUDR) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F0503 )
- Calcein-AM (Sigma-Aldrich)
- Zeta inhibitory peptide (ZIP) (AnaSpec)
- Scr-ZIP (Anaspec, same amino acids as ZIP, in a scrambled order)
- Propidium iodide (Sigma-Aldrich)
- NaCl (Sigma-Aldrich)
- KCl
- MgCl2 (Sigma-Aldrich)
- CaCl2 (Sigma-Aldrich)
- HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 83264 )
- Standard extracellular medium (see Recipes)
Figure 1. 3D reconstruction of a rodent brain. In green-bilateral hippocampus (reproduced from Allen Brain Atlas)
Equipment
- Biological hood (Haroshet Ltd.)
- 37 °C/5% CO2 humidified incubator (Tuttnauer, model: TUTT2424-2 )
- Confocal laser scanning inverted microscope (Zeiss, model: LSM 510 ), with a 40x oil-immersion objective (1.3 NA)
- Standard desktop centrifuge
- Inverted microscope (Nikon) equipped with phase optics
- Dissecting binocular microscope
Software
- ImageJ
- LSM 510 software
Procedure
- Primary brain cultures
- Wistar Rat pups are decapitated on day of birth (P0), their brains removed and placed in a chilled (4 °C), oxygenated (by bubbling with a pipette tip) Leibovitz L15 medium enriched with 0.6% glucose and gentamicin (20 µg/ml) under a dissecting microscope. The hippocampus is removed and the meninges are carefully peeled off.
- Hippocampal tissue is mechanically dissociated by trituration after incubation with trypsin (0.25%) and DNase (50 µg/ml), for 20 min at 37 °C.
- 37 °C 5% CO2, in a humidified incubator. The tissue is washed 3x with 2 ml of the L15 medium by centrifugation and passed to the plating medium. This consists of 1 ml minimum essential medium (MEM, Earl salts) containing 5% heat-inactivated horse serum (HS), 5% fetal calf serum, and B-27 (1 µl/1ml), enriched with 0.6% glucose, gentamicin (20 µg/ml), and 2 mM glutamax (enriched MEM). Cell number can either be determined by counting trypan blue-stained cells on a Neurobauer (Boeco, Germany), or estimated, assuming that each hippocampus contains appx. 1 million cells. About 105 cells in 1 ml medium are plated in each well of a 24-well plate, onto a hippocampal glial feeder layer which is grown on the glass for 2 weeks prior to the plating of the neurons (Papa et al., 1995, Goldin et al., 2001).
- Cells are left to grow in the humidified incubator at 37 °C, 5% CO2 for 4 days, at which time the medium is changed to 10% HS in enriched MEM, plus a mixture of 5´-fluoro-2-deoxyuridine/uridine (FUDR) (20 µg and 50 µg/ml, respectively), to block glial proliferation. Four days later the medium is replaced by 1ml 10% HS in MEM which does not contain FUDR, and no further changes are made.
Note: We routinely use Wistar rats, but the procedure should be applicable to other rat strains and with small modifications, also to mouse cultures. The procedure is similar in other brain areas, and the neocortex or striatum have been used successfully using this method. We did not try cerebellar or spinal cord cultures. We use P0 rat pups, and this protocol is useful until P4-5, beyond that the yield of viable cells is reduced dramatically.
- Wistar Rat pups are decapitated on day of birth (P0), their brains removed and placed in a chilled (4 °C), oxygenated (by bubbling with a pipette tip) Leibovitz L15 medium enriched with 0.6% glucose and gentamicin (20 µg/ml) under a dissecting microscope. The hippocampus is removed and the meninges are carefully peeled off.
- Viability assay
- Cells are incubated in standard extracellular medium at room temperature and imaged on a stage of a Zeiss LSM 510 laser scanning confocal microscope, with a 40x oil-immersion objective (1.3 NA).
- Cultures are initially loaded in 1 ml standard recording medium with 2 µM Calcein-AM for 30 min, and imaged in 1.8 ml of standard medium in the presence of PI (2.5 µM). A new vile of ZIP or Scr-ZIP (a scrambled peptide used as control) was used each day, diluted to a final concentration of 1mM and kept at -4 °C, or control medium are added at 5-10 min after onset of imaging.
- Two-channel images [Calcein-AM/Propidium Iodide (PI)] are acquired, where green (488 nm) and red (545 nm) fluorescent cells represent live and dead cells, respectively.
- Time-lapse imaging of cultures is performed at room temperature for 90 min at 4 min intervals. Several fields of view per coverslip are imaged repeatedly. Survival probability is calculated as [[no. live cells (cells stained green) (attime t)/no. live cells (t = 0)]*100]. Cells that either lose their color (Calcein-AM leaked out) or gain red staining (PI entering the cell) were not regarded as live (Figure 2). No co-staining of red and green is detected. Neurons can easily be distinguished from glial cells, in that the latter group consists of large flat cells, whereas the neuronal somata are more compact and 3-dimensional.
- Standard imaging software (ImageJ) is used to count the number of live cells for each image.
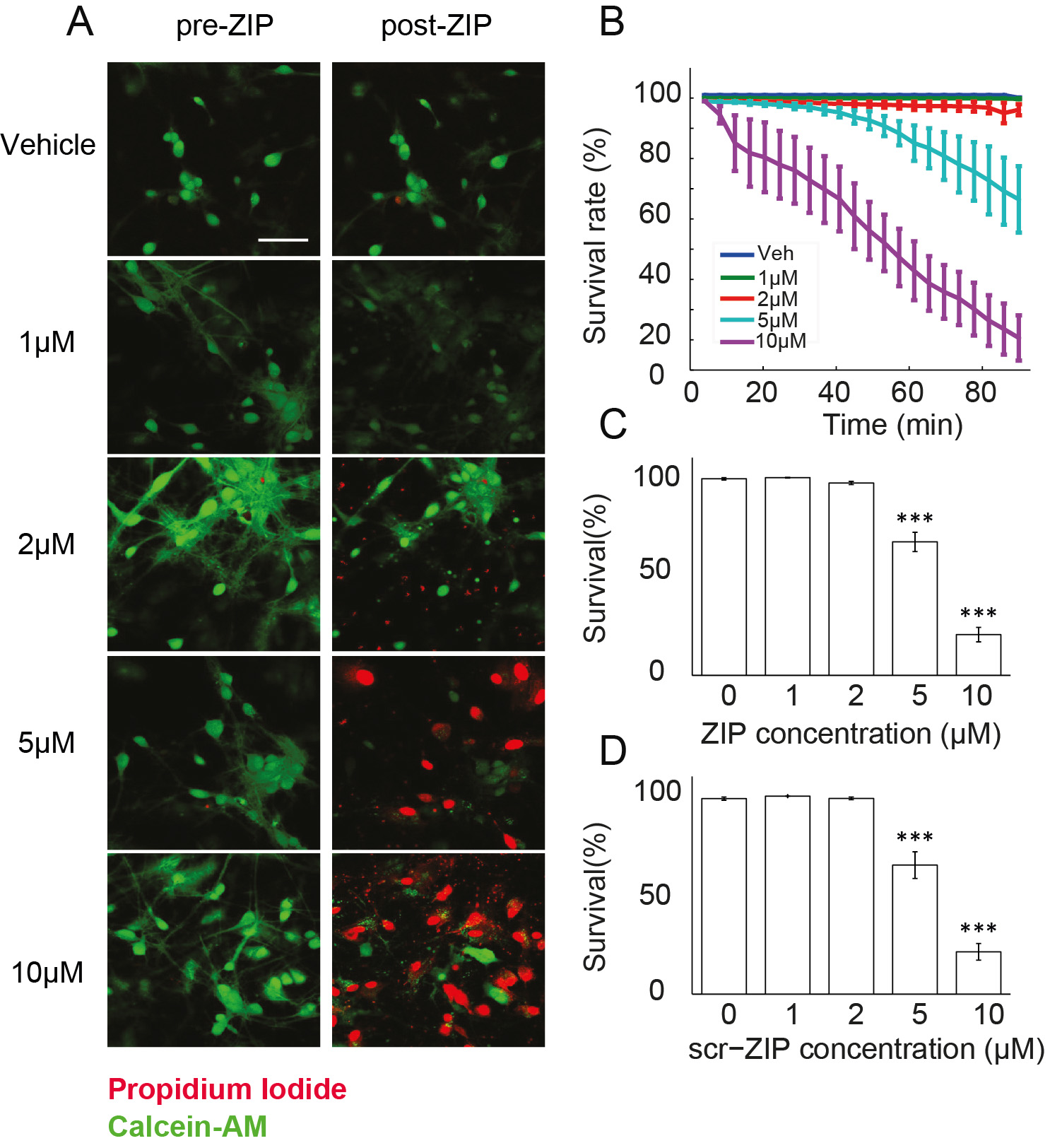
Figure 2. Measuring viability of hippocampal cultures in response to ZIP application. A. Viability of cultured hippocampal neurons was determined using Calcein-AM (green) and propidium iodide (red). Cultures were exposed to different doses of ZIP [Vehicle (0 µM)/1 µM/2 µM/5 µM/10 µM]. Scale bar, 50 µm; B. Dose response curve was constructed from time-lapse images taken in 4 min intervals (Figure 3) to assess the rate of cellular death following treatment with ZIP; C. Bar graph summarizes total change in culture viability (n = 22 coverslips, 3,544 cells, values are mean ± SEM, 90 min post ZIP-treatment vs. viability pre-treatment, paired t-test, ***P < 0.005); D. Scr-ZIP induces similar changes in culture viability. Bar graphs summarize total change in culture viability (n = 13 coverslips, 2,365 cells, 90 min post scr-ZIP-treatment vs. viability pre-treatment, paired t-test, ***P < 0.005). (Adapted from Sadeh et al., 2015)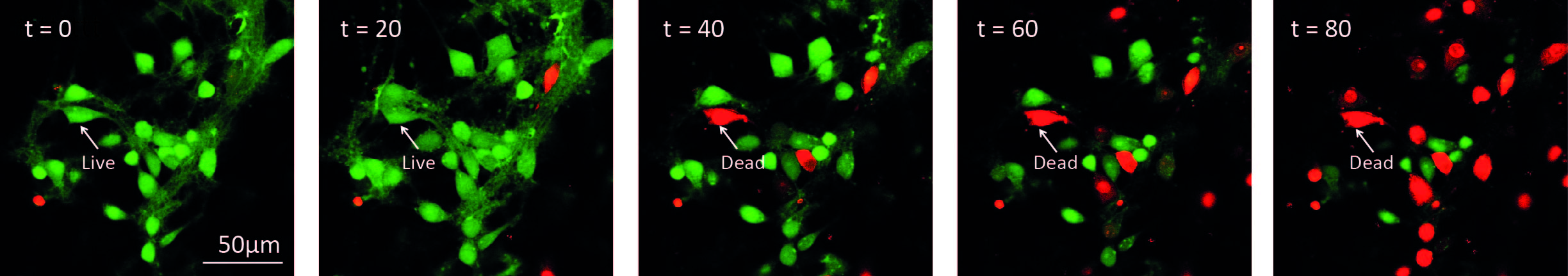
Figure 3. Illustration of time-lapse imaging of hippocampal cultures. Cells were loaded with Calcein-AM and Imaged in the presence of propidium iodide. 10 μM ZIP was added to the culture at t = 0. A cell was considered alive in the cell count as long as it retained green fluorescence.
- Cells are incubated in standard extracellular medium at room temperature and imaged on a stage of a Zeiss LSM 510 laser scanning confocal microscope, with a 40x oil-immersion objective (1.3 NA).
Notes
- The method allows us to distinguish between cells that were already dead before the onset of drug treatment (those stained with PI but not stained earlier with Calcein-AM), those that died during and after the treatment (initially stained with Calcein-AM) and those which survived the damage (stained only with Calcein-AM).
- In addition the procedure allows distinguishing between neurons and glia, based on their different morphology.
- Additional stain for glia is possible with the use of selective live glia stains (Nimmerjahn et al., 2004).
- Finally, the time-lapse imaging of the cells allows to trace the course of cell death in the neuronal population (e.g., Figure 3).
Recipes
- Standard extracellular medium (filtered and stored in 0-4 °C refrigerator for up to 1 mo.)
pH = 7.4, 32 mOsm
129 mM NaCl
4 mM KCl
1 mM MgCl2
2 mM CaCl2
10.5 mM glucose
10 mM HEPES
Acknowledgments
Adapted from “Zeta Inhibitory Peptide, a Candidate Inhibitor of Protein Kinase Mζ, Is Excitotoxic to Cultured Hippocampal Neurons” (Sadeh et al., 2015).
References
- Ankarcrona, M., Dypbukt, J. M., Bonfoco, E., Zhivotovsky, B., Orrenius, S., Lipton, S. A. and Nicotera, P. (1995). Glutamate-induced neuronal death: a succession of necrosis or apoptosis depending on mitochondrial function. Neuron 15(4): 961-973.
- Decker, T. and Lohmann-Matthes, M. L. (1988). A quick and simple method for the quantitation of lactate dehydrogenase release in measurements of cellular cytotoxicity and tumor necrosis factor (TNF) activity. J Immunol Methods 115(1): 61-69.
- Goldin, M., Segal, M. and Avignone, E. (2001). Functional plasticity triggers formation and pruning of dendritic spines in cultured hippocampal networks. J Neurosci 21(1): 186-193.
- Ling, D. S., Benardo, L. S., Serrano, P. A., Blace, N., Kelly, M. T., Crary, J. F. and Sacktor, T. C. (2002). Protein kinase Mzeta is necessary and sufficient for LTP maintenance. Nat Neurosci 5(4): 295-296.
- Mosmann, T. (1983). Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65(1-2): 55-63.
- Papa, M., Bundman, M. C., Greenberger, V. and Segal, M. (1995). Morphological analysis of dendritic spine development in primary cultures of hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 15(1 Pt 1): 1-11.
- Pastalkova, E., Serrano, P., Pinkhasova, D., Wallace, E., Fenton, A. A. and Sacktor, T. C. (2006). Storage of spatial information by the maintenance mechanism of LTP. Science 313(5790): 1141-1144.
- Sadeh, N., Verbitsky, S., Dudai, Y. and Segal, M. (2015). Zeta Inhibitory Peptide, a Candidate Inhibitor of Protein Kinase Mzeta, Is Excitotoxic to Cultured Hippocampal Neurons. J Neurosci 35(36): 12404-12411.
- Slepian, M. J., Massia, S. P. and Whitesell, L. (1996). Pre-conditioning of smooth muscle cells via induction of the heat shock response limits proliferation following mechanical injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 225(2): 600-607.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Sadeh, N., Oni-Biton, E. and Segal, M. (2016). Acute Live/Dead Assay for the Analysis of Toxic Effects of Drugs on Cultured Neurons. Bio-protocol 6(15): e1889. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1889.
-
Sadeh, N., Verbitsky, S., Dudai, Y. and Segal, M. (2015). Zeta Inhibitory Peptide, a Candidate Inhibitor of Protein Kinase Mzeta, Is Excitotoxic to Cultured Hippocampal Neurons. J Neurosci 35(36): 12404-12411.
Category
Neuroscience > Cellular mechanisms > Cell isolation and culture
Cell Biology > Cell viability > Cell death
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link