- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
High Fat Diet-induced Breast Cancer Model in Rat
Published: Vol 6, Iss 13, Jul 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1852 Views: 8715
Reviewed by: Masahiro MoritaPooja MehtaAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Generation and Maintenance of Patient-Derived Endometrial Cancer Organoids
Mali Barbi [...] Semir Beyaz
Oct 20, 2024 2069 Views

Temporally and Spatially Controlled Age-Related Prostate Cancer Model in Mice
Sen Liu [...] Qiuyang Zhang
Jan 5, 2025 2713 Views

An Optimized Protocol for Simultaneous Propagation of Patient-derived Organoids and Matching CAFs
Jenny M. Högström and Taru Muranen
Jan 20, 2025 4459 Views
Abstract
Obesity has been linked to breast cancer progression but the underlying mechanisms remain obscure. Being overweight or obese for a woman at the time she is diagnosed with breast cancer is linked to a high risk of recurrence regardless of treatment factors. In rodents, high body weight is also associated with increased incidence of spontaneous and chemically induced tumors. To study the complex interaction between the mammary epithelia and the microenvironment, with a focus on the mechanism underlying the role obesity plays in the regulation of the cancer stem cell traits and the development of mammary cancer in vivo, we have established a diet-induced obesity (DIO) rat model of breast cancer (Chang et al., 2015).
Keywords: ObesityMaterials and Reagents
- 40 µm cell strainer (STEMCELL Technologies, catalog number: 27305 )
- Female Sprague-Dawley rats (Envigo, Harlan Laboratories, catalog number: Sprague Dawley® SD®)
- 1 ml, 26 G x 3/8 in. BD Tuberculin syringe with detachable needle, slip tip (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 309625 )
- N-methylnitrosourea (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N1517 )
- Sodium chloride (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S7653 )
- 10% neutral formalin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: HT501128 )
- EpiCultTM-B Mouse Medium Kit (STEMCELL Technologies, catalog number: 05610 )
- 10x Gentle Collagenase/Hyaluronidase (STEMCELL Technologies, catalog number: 07919 )
- Hanks’ balanced salt solution modified (HBSS) (STEMCELL Technologies, catalog number: 37150 )
- Trypsin-EDTA
- Ammonium chloride (NH4Cl) (STEMCELL Technologies, catalog number: 07800 )
- 40 µm cell strainer (STEMCELL Technologies, catalog number: 27305)
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Corning, catalog number: 35-011-CV )
- Flow Cytometry Stain Buffer (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 554656 )
- FITC-conjugated anti-OBR antibody (aa956-986, polyclonal antibody) (Lifespan Biosciences, catalog number: LS-C261832 )
- Regular rat chow diet (Envigo, catalog number: 8604 ) (see Recipes)
- Western diet (Research Diets, catalog number: D12079B ) (see Recipes)
- 0.9% saline (see Recipes)
- N-methylnitrosourea solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Dual-energy x-ray absorptometry (Lunar Corporation, model: Lunar PIXImus II Densitometer )
- Cell analyzer (BD Biosciences, model: BD FACSCanto II )
Software
- BD FACSDiva and FCS Express Flow Cytometry Software
Procedure
- Obesity-induced breast cancer
- Obtain twenty-day-old outbred Sprague-Dawley rats from Harlan Laboratories.
- Wean pups 24 h after arrival and maintain in a temperature and light controlled animal facility.
- Give the animals ad libitum access to water and assign randomly to either a regular rat chow diet or a Western diet after grouped.
- At 54 days old, group the animals according to their body fat composition determined by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). The average percent body fat mass of rats on the lean rat chow diet would be half of that on the obese Western diet. The example of body composition analysis from DEXA scans is shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Body composition analysis from DEXA scans. Animals in the Western-obese group showed a significant increase in fat mass compared to animals in the Western-lean group. Values represent mean ± SEM. n = 9 animals per group. Asterisk indicates P < 0.05, double asterisk indicates P < 0.0001 (from Chang et al., 2015).
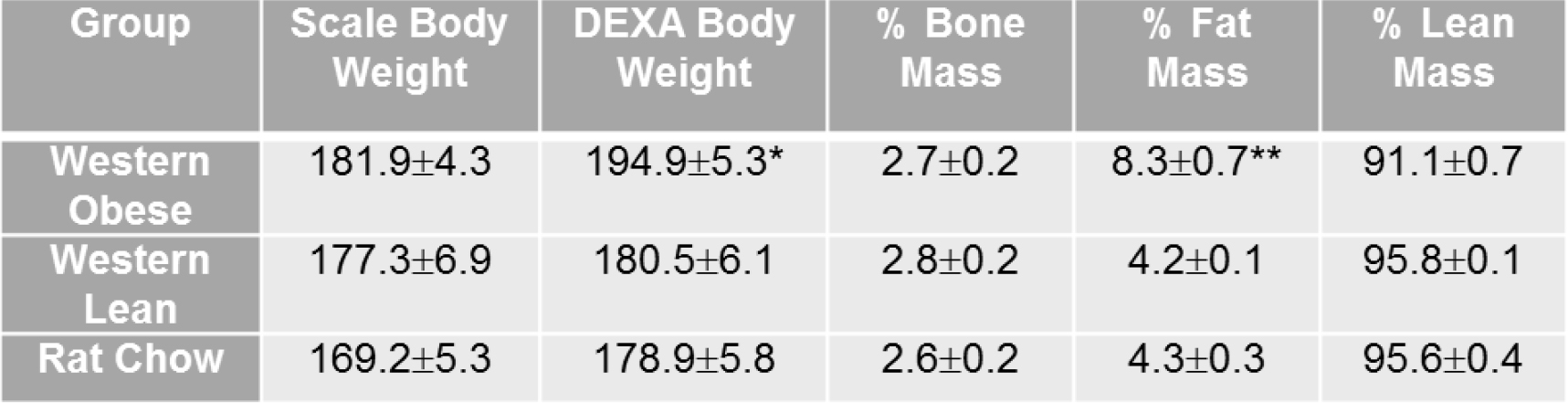
- According to body composition analysis from DEXA scans, place the animals on the Western diet into two groups with rats in the highest tertile being placed in the Western obese group and rats in the lowest tertile being placed in the Western lean group. Three groups would be designated: “Western obesity”, “Western lean” and “Regular chow/diet”.
- Dissolve N-methylnitrosourea immediately before use in 0.9% NaCl and adjust the pH with acetic acid to pH = 4. Prepare fresh solution prior to application.
- At 65 days of age, intraperitoneally inject half of the rats in each group with 50 mg/kg of the chemical carcinogen N-methylnitrosourea and the remaining animals receive 0.9% saline (the amount of the drug to is given per body weight in mg/kg). To reduce the likelihood of piercing an organ, use 26-gauge 3/8-inch-long needles.
- Scarface the rats by 168 days post-injection or when an animal reaches a terminal state as determined by established guidelines (Wallace, 2000).
- Collect intact mammary glands and tumors and flash-freeze in liquid nitrogen or fixed in 10% neutral formalin for histologic evaluation (shown in Figure 1).
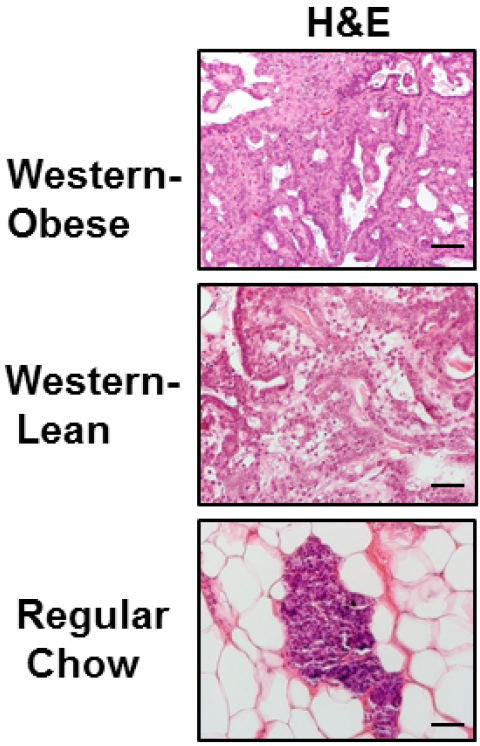
Figure 1. Tumor phenotypes in Western obese animals, Western lean and regular diet fed animals. H&E staining showing normal mammary gland in regular diet-fed rats, aggressive adenocarcinoma in Western-obese animals, and benign adenoma in Western-lean animals (from Chang et al., 2015).
- Obtain twenty-day-old outbred Sprague-Dawley rats from Harlan Laboratories.
- Isolation of mammary tumor cells for flow cytometry analysis
- Prepare dissociation solution by diluting 1 part 10x Gentle Collagenase/Hyaluronidase mixture with 9 parts Complete EpiCultTM-B Medium supplemented with 5% FBS and placed solution into a 15 ml centrifuge tube.
- Resect and transfer mammary glands or tumors to a sterile petri dish with the 3-5 ml dissociation solution. Mince the tissues with scalpels in a cross-wise pattern until tissues are rendered to a paste. Incubate the tissues overnight (for up to 15 h) at 37 °C.
- After dissociation, centrifuge the cells at 350 x g for 5 min. Discard the supernatant.
- Re-suspend the pellet with a 1:4 mixture of cold Hanks’ balanced salt solution modified (HBSS) supplemented with 2% FBS and ammonium chloride and centrifuged at 350 x g for 5 min.
- Discard the supernatant and add 1-5 ml of pre-warmed 1x Trypsin-EDTA to the partially-dissociated tissue and mix by pipetting.
- Gently pipette up and down with a P1000 micropipettor for 1-3 min.
- Add 10 ml of cold HBSS supplemented with 2% FBS and centrifuge at 350 x g for 5 min.
- Re-suspend the pellet with an additional 10 ml of cold HBSS with 2% FBS, and filter the cell suspension through a 40 µm cell strainer into a new 50 ml centrifuge tube. Centrifuge at 350 x g for 5 min and discard the supernatant.
- Re-suspend the pellet with Flow Cytometry Staining Buffer, and count the cells with hemocytometer or automatic cell counter.
- Aliquot 200 µl of cell suspension (105-106 cells) and stain the cells with FITC-conjugated anti-OBR antibody for 20 min.
- Wash the cells by adding PBS. Use 1 ml for tubes. Pellet the cells by centrifugation at 400-600 x g for 5 min at room temperature. Repeat with two washes and discard supernatant between washes.
- Re-suspend the stained cells in 500 µl Flow Cytometry Staining Buffer.
- Subject the stained cells to flow cytometry analysis and determine the percentage of the cancer stem cell-like OBRhi (high leptin receptor expression, FITC-high) population. Data can be analyzed by BD FACSDiva and FCS Express Flow Cytometry Software. All surgical procedures and animal manipulations are performed under regulations of Purdue Animal Care and Use Committee.
- Prepare dissociation solution by diluting 1 part 10x Gentle Collagenase/Hyaluronidase mixture with 9 parts Complete EpiCultTM-B Medium supplemented with 5% FBS and placed solution into a 15 ml centrifuge tube.
Recipes
- Regular rat chow diet
3.30 kcal/g with 18% protein
5% fat, mainly from corn oil and 57% carbohydrates
- Western diet
4.47 kcal/g with 20% protein
21% fat in the form of anhydrous milk fat, and 50% carbohydrates, 34% sucrose
- 0.9% saline
Add 0.9 g of NaCl to 100 ml of ddH2O in a sterilized glass container and pass through 0.2 µm sterile filter
- N-methylnitrosourea solution
Dissolve immediately before use in 0.9% saline and adjust with acetic acid to pH value 4. Prepare fresh solutions prior to application
Acknowledgments
This protocol was used in Chang et al., (2015). This work was supported by Walther Cancer Foundation-Obesity and Cancer Pilot Grant (I.G. Camarillo and C-J. Chang) and P30 CA023168 to the Purdue University Center for Cancer Research in support of the use of facilities.
References
- Chang, C. C., Wu, M. J., Yang, J. Y., Camarillo, I. G. and Chang, C. J. (2015). Leptin-STAT3-G9a signaling promotes obesity-mediated breast cancer progression. Cancer Res 75(11): 2375-2386.
- Wallace, J. (2000). Humane endpoints and cancer research.ILAR J 41(2): 87-93.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Wu, M. J. and Chang, C. J. (2016). High Fat Diet-induced Breast Cancer Model in Rat. Bio-protocol 6(13): e1852. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1852.
Category
Cancer Biology > General technique > Animal models
Cancer Biology > Proliferative signaling > Tumor formation
Cancer Biology > General technique > Tumor formation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










