- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
In vitro mTORC1 Kinase Assay for Mammalian Cells Protocol
Published: Vol 6, Iss 11, Jun 5, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1827 Views: 13574
Reviewed by: HongLok LungShravani MukherjeeAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Purification of Native Acetyl CoA Carboxylase From Mammalian Cells
Yaxue Sun [...] Hongtao Zhu
Feb 20, 2025 2193 Views

Fluorescence Polarization-Based High-Throughput Screening Assay for Inhibitors Targeting Cathepsin L
Keyu Guo [...] Shuyi Si
Jul 20, 2025 2282 Views

Detecting the Activation of Endogenous Small GTPases via Fluorescent Signals Utilizing a Split mNeonGreen: Small GTPase ActIvitY ANalyzing (SAIYAN) System
Miharu Maeda and Kota Saito
Jan 5, 2026 496 Views
Abstract
Historically, mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) was purified from mammalian cells using mild nonionic detergents such as NP-40 and or Triton-X100 that resulted in dissociation of core regulatory components essential for its native kinase activity. Consequently, these older kinase assays required MnCl2 to artificially enhance the weak phosphotransfer activity observed (Bai et al., 2007; Kim et al., 2002). With the use of the zwitterionic detergent 3-[(3-Cholamidopropyl) dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate (CHAPS), the mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) containing Regulatory-associated protein of mTOR (Raptor) and Lst8 (also known as GbetaL) can be successfully purified as a complex. This in vitro kinase assay allows for purification of mTORC1 that resembles its physiological state and retains kinase activity under physiological MgCl2 concentrations (Sancak et al., 2007). The activity of mTORC1 can be further enhanced through the use of hyperactive mutations within the kinase domain of mTOR or inclusion of GTP-bound RAS enriched in brain (Rheb) that is supplemented into the in vitro kinase assays. Rheb is a small-G-protein that binds to and activates mTORC1 to phosphorylate downstream substrates, such as eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-BP1 (4E-BP1) (Burnett et al., 1998), ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) (Kim et al., 2002), Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) (Dodd et al., 2015), and proline-rich Akt substrate of 40 kDa (PRAS40) (Dunlop et al., 2009).
Materials and Reagents
- HEK293E cells
- Plasmids and vectors
- HA-Raptor (Addgene, catalog number: 8513 )
- myc-mTOR (Addgene, catalog number: 1861 )
- Rheb (National Center for Biotechnology Information, Gene, catalog number: 6009 ) cloned into pDEST27 using the gateway cloning system in accordance with manufacturer protocol (Life Technologies, catalog number: 11812-013 )
Note: Currently, it is “Thermo Fisher Scientific, Invitrogen™, catalog number: 11812-013 ”. - GST-4E-BP1/pGEX vectors generated as previously described (Dunlop et al., 2009)
- HA-Raptor (Addgene, catalog number: 8513 )
- Antibodies
- Clone 9E10 anti-Myc antibodies (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M5546 )
- Clone 9B11 anti-Myc antibodies (Cell Signaling Technology, catalog number: 2276 )
- Anti-HA (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 11867431001 )
- Anti-GST (Merck Millipore Corporation, catalog number: 05-782 )
- Clone 9E10 anti-Myc antibodies (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M5546 )
- Cell culture and transfection
- Dulbecco’s modified eagle’s medium (DMEM)
- 10% foetal bovine serum (FBS), EU Approved (South American) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 10270-106 )
- Penicillin-streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15070-063 )
Note: HEK293E cells were cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 1 μg/ml penicillin and 1 µg/ml streptomycin.
- Dulbecco’s modified eagle’s medium (DMEM)
- Insulin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: I9278 )
- Rapamycin (EMD Millipore Corporation, catalog number: 553210 )
- Chemicals of analytical grade
- HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3375 )
- EDTA (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 431788 )
- β-glycerophosphate (disodium salt, pentahydrate) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 50020 )
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S7653 )
- Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M8266 )
- Adenine triphosphate (ATP) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A26209 )
- Leupeptin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: L5793 )
- Antipain (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 10791 )
- Benzamidine (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 12072 )
- Pepstatin A (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5318 )
- Sodium vanadate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 289361 )
- Dithiothreitol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 43815 )
- Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 78830 )
- Wortmannin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: W1628 )
- 3-[(3-Cholamidopropyl)dimethylammonio]-1-propanesulfonate hydrate (CHAPS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 226947 )
- HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3375 )
- mTOR lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- Low salt mTOR wash buffer (see Recipes)
- High salt mTOR wash buffer (see Recipes)
- mTOR wash buffer (see Recipes)
- 3x mTOR kinase assay buffer (see Recipes)
- Rheb lysis buffer (see Recipes)
- Rheb storage buffer (see Recipes)
- Phosphate buffered saline (see Recipes)
- mTOR assay start buffer (see Recipes)
- Protease inhibitors (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Thermomixer heating block (Eppendorf AG, model: Eppendorf thermomixer® compact )
- Refrigerated mini centrifuge (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo Scientific™, model: Heraeus and Fresco 17 centrifuge )
- StuartTM SB2 fixed speed rotator (Bibby Scientific Limited, Stuart Scientific)
Procedure
Note: An overview of the whole procedure can be found in Figure 1.
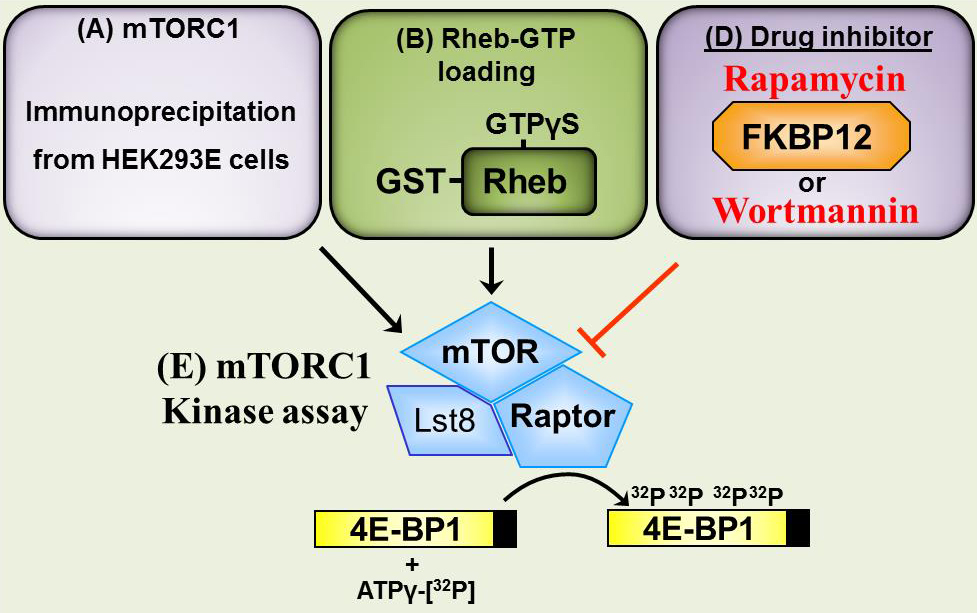
Figure 1. mTOR in vitro kinase assay. As described in the “Procedure”, preparation of (A) mTORC1 complexes, (B) Rheb-GTP and (D) drug inhibitors (rapamycin/FKBP12 and wortmannin) and incubation of mTORC1 substrate (4E-BP1) within the mTORC1 kinase assay (E).
- Generating mTOR/raptor complexes from HEK293E cells
- HEK293E cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% foetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1%, 100 μg/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin.
- 75 cm2 flasks of 80% confluent HEK293E cells were either co-transfected with 5 µg Myc-tagged mTOR and 5 µg HA-tagged Raptor constructs or transfected with a GST-tagged Rheb construct using the calcium phosphate transfection method (1 x 75 cm2 flask of HEK293E cells is sufficient for three mTOR kinase assays). Cells were harvested 36 h post-transfection. Cells are treated with 10 µg/ml insulin for 30 min prior to lysis. This dose is sufficient to stimulate mTORC1 signaling and ensure that the active complex is purified as previously demonstrated (Dunlop et al., 2009).
- Stimulate cells with 100 nM insulin for 15 min then lyse the cells in 1 ml of mTOR lysis buffer supplemented with protease inhibitors and 0.3% CHAPS (w/v).
- Centrifuge at 16,200 x g for 8 min at 4 °C (refrigerated mini centrifuge).
- Incubate lysates with 3 μl of Myc- or HA-antibodies (the mTORC1 complex can be purified with either HA-raptor or myc-mTOR immunoprecipitation) for 1.5 h at 4 °C with rotation.
- Make a 50% volume ratio mix of Protein G plus mTOR lysis buffer, add 40 μl to each tube and incubate for 1 h at 4 °C with rotation (StuartTM SB2 fixed speed rotator).
- Wash immunoprecipitates with 0.5 ml of the following buffers supplemented with protease inhibitors:
- 1x low salt mTOR wash buffer (supplemented with 0.3% w/v CHAPS)
- 2x high salt mTOR wash buffer (supplemented with 0.3% w/v CHAPS)
- 2x mTOR wash buffer
- 1x low salt mTOR wash buffer (supplemented with 0.3% w/v CHAPS)
- Split immunoprecipitates equally into three Eppendorf tubes for the in vitro kinase assay.
- HEK293E cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% foetal bovine serum (FBS) and 1%, 100 μg/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin.
- Preparing GTP-bound Rheb
Human Rheb (Gene ID: 6009) cloned into pDEST27, which contains an N-terminal GST-tag.- Transfect four 75 cm2 flasks of 80% confluent HEK293E cells with GST-Rheb-pDEST27 (10 µg DNA per flask), using standard calcium phosphate transfection procedures (Schalm et al., 2002).
- Grow HEK293E cells over-night in the presence of 10% (v/v) FBS till fully confluent (6-7 x 106 cells).
- Lyse HEK293E cells in 1 ml Rheb lysis buffer supplemented with 0.3% (w/v) CHAPS (plus protease inhibitors).
Note: Reducing agents (such as DTT) should be omitted as this will interfere with GST-purification. Incubate lysates on ice for 30 min to facilitate lysis. - Incubate pre-cleared lysates (after centrifugation at 16,200 x g for 10 min at 4 °C) with immobilized 40 μl of a 50% volume ratio mix of Rheb lysis buffer and glutathione-sepharose beads, incubate for 2 h at 4 °C with rotation.
- Wash the glutathione-sepharose beads twice with 0.5 ml Rheb lysis buffer and then once with 0.5 ml Rheb storage buffer supplemented with protease inhibitors.
- Elute GST-Rheb from the glutathione-sepharose beads in 50 µl Rheb storage buffer supplemented with of 10 mM glutathione (pH readjusted back to 8.0).
- Incubate eluted GST-Rheb protein at 30 °C for 10 min with either 10 mM EDTA and 1 mM GDP to generate inactive Rheb-GDP, or 10 mM EDTA and 0.1 mM non-hydrolysable GTPγS to generate active Rheb-GTP. To tightly bind the guanine nucleotide to Rheb, add MgCl2 to a final concentration of 20 mM. Incubate on ice until use.
- Generating dephosphorylated 4E-BP1 protein for positive control substrate
- Transform BL21 (DE3) pLys bacteria with GST-tagged 4E-BP1/pGEX plasmid (4E-BP1 GeneID, 1978) using standard transformation methods.
- Grow bacteria until OD600 is 0.6-0.8, add isopropyl-β D-thiogalactoside (IPTG) to give a final concentration of 0.5 mM and incubate for 3 h at 30 °C to induce expression. Pellet cells by centrifugation at 1,500 x g for 30 min at 4 °C.
- Lyse bacteria with a freeze/thaw cycle in 10 ml of PBS supplemented with 10 mM EDTA, 0.1% (v/v) Triton and protease inhibitors.
- Use pulse sonication to shear bacterial DNA [3 x 5 sec cycles on full power (30 μm)]. Centrifuge at 16,200 x g for 10 min at 4 °C, then purify GST-4E-BP1 from the bacterial supernatant using glutathione-sepharose beads.
- Dephosphorylate GST-4E-BP1 protein using 50 U shrimp alkaline phosphatase, washed in PBS, 10 mM EDTA, 0.1% (v/v) Triton X-100. Elute in 10 mM reduced glutathione in PBS (pH 7.6).
- Desalt the eluent using a HiTrap Desalting Column in accordance with manufacturer protocol.
- Resolve using SDS-PAGE and stain with Coomassie Brilliant Blue to check the purity and concentration against known bovine serum albumin (BSA) standards.
- Dephosphorylated 4E-BP1 can be stored at -80 °C in 10 µg/µl aliquots for future use.
- Preparing FKBP12/rapamycin drug/protein complexes to inhibit mTORC1
- Human FKBP12 protein can be expressed and purified using the same protocol to generate GST-4E-BP1 above (omitting the dephosphorylation step C5).
- FKBP12 can also be frozen in 10 µg/µl aliquots at -80 °C for future use.
- To generate FKBP12/rapamycin complexes: Make up 25 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 10 mM MgCl2, 20 mM rapamycin and 0.5 µg FKBP12 in 10 µl final volume (dH2O). Incubate at room temperature in the dark for 5 min, and store on ice until needed.
- Performing mTOR kinase assays
- Make up mTOR/Raptor immunoprecipitates in 3x mTOR kinase assay buffer and add 75 ng of Rheb-GTP and or 2 μl FKBP12/rapamycin as required.
- Incubate for 20 min on ice prior to starting the kinase assay.
- Add 10 μl of mTOR assay start buffer supplemented with 500 μM ATP (freshly added before use) plus 150 ng of purified GST-4E-BP1 or the test substrate to start the assay. Phospho-4E-BP1 (Thr 36/45) levels are used as a positive control and indicate mTOR kinase activity.
- Incubate at 30 °C for 30-60 min in thermomixer heating block, shaking at20 FCS.
- Stop reaction by adding 4x sample buffer.
- Analyse samples using SDS-PAGE and western blotting. An example of representative data is shown in Figure 2.
Representative data
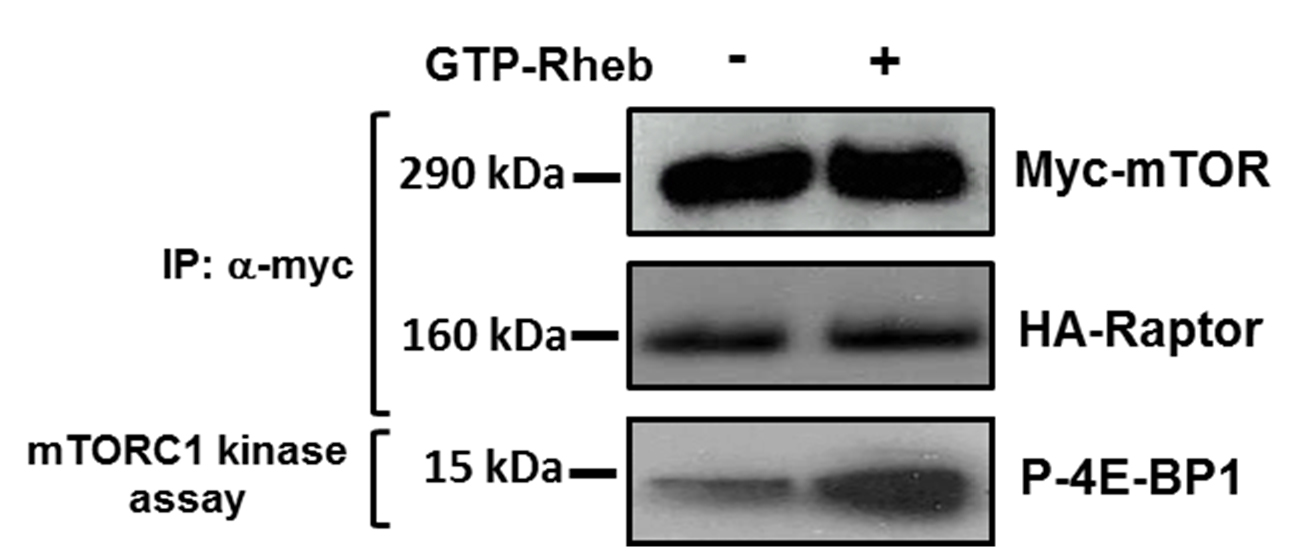
Figure 2. mTORC1 directed phosphorylation of 4E-BP1. Western blotting showing phosphorylation of purified GST-4E-BP1 after in vitro mTORC1 kinase assay performed in the presence and absence of GTP-Rheb. Levels of myc-mTOR and HA-Raptor are shown as controls.
Notes
- It is essential that Rheb is purified from mammalian cells, rather than from bacteria, as proper folding and post-translational modifications (such as prenylation) is required for its activity to enhance mTORC1.
Recipes
Note: All buffers are stored at 4 °C unless otherwise stated.
- mTOR lysis buffer
40 mM HEPES (pH 7.4)
2 mM EDTA
10 mM β-glycerophosphate - Low salt mTOR wash buffer
40 mM HEPES (pH 7.4)
150 mM NaCl
2 mM EDTA
10 mM β-glycerophosphate - High salt mTOR wash buffer
40 mM HEPES (pH 7.4)
400 mM NaCl
2 mM EDTA
10 mM β-glycerophosphate - mTOR wash buffer
25 mM HEPES (pH 7.4)
20 mM KCl - 3x mTOR kinase assay buffer (aliquoted and stored at -20 °C)
X3 stock solution: 75 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 60 mM KCl, 30 mM MgCl2
Add 1:50 dilution of 0.5 M stock of MgCl2 to 25 mM HEPES (pH 7.4), 20 mM KCl - Rheb lysis buffer
40 mM HEPES (pH 7.4)
10 mM glycerophosphate
5 mM MgCl2 - Rheb storage buffer
20 mM HEPES (pH 8.0)
200 mM NaCl
5 mM MgCl2 - Phosphate buffered saline
137 mM NaCl
10 mM phosphate
2.7 mM KCl (pH 7.4) - mTOR assay start buffer (aliquoted and stored at -20 °C)
25 mM HEPES (pH 7.4)
10 mM MgCl2
140 mM KCl, plus 500 μM adenine triphosphate (ATP) added fresh before use - Protease inhibitors (1,000x stock solutions aliquoted and stored at -20 °C)
10 μM leupeptin
2 μM antipain
1 mM benzamidine
1 μg/ml pepstatin
100 μM PMSF
1 mM sodium orthovanadate
1 mM dithiothreitol (DTT not used for GST-purifications)
Acknowledgments
This protocol was adapted as previously reported (Dunlop et al., 2009). This work was supported by an Association for International Cancer Research (AICR) career development award to AT and a Tuberous Sclerosis Association Junior Fellowship to KD.
References
- Bai, X., Ma, D., Liu, A., Shen, X., Wang, Q. J., Liu, Y. and Jiang, Y. (2007). Rheb activates mTOR by antagonizing its endogenous inhibitor, FKBP38. Science 318(5852): 977-980.
- Burnett, P. E., Barrow, R. K., Cohen, N. A., Snyder, S. H. and Sabatini, D. M. (1998). RAFT1 phosphorylation of the translational regulators p70 S6 kinase and 4E-BP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(4): 1432-1437.
- Dodd, K. M., Yang, J., Shen, M. H., Sampson, J. R. and Tee, A. R. (2015). mTORC1 drives HIF-1alpha and VEGF-A signalling via multiple mechanisms involving 4E-BP1, S6K1 and STAT3. Oncogene 34(17): 2239-2250.
- Dunlop, E. A., Dodd, K. M., Seymour, L. A. and Tee, A. R. (2009). Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1-mediated phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E-binding protein 1 requires multiple protein-protein interactions for substrate recognition. Cell Signal 21(7): 1073-1084.
- Kim, D. H., Sarbassov, D. D., Ali, S. M., King, J. E., Latek, R. R., Erdjument-Bromage, H., Tempst, P. and Sabatini, D. M. (2002). mTOR interacts with raptor to form a nutrient-sensitive complex that signals to the cell growth machinery. Cell 110(2): 163-175.
- Sancak, Y., Thoreen, C. C., Peterson, T. R., Lindquist, R. A., Kang, S. A., Spooner, E., Carr, S. A. and Sabatini, D. M. (2007). PRAS40 is an insulin-regulated inhibitor of the mTORC1 protein kinase. Mol Cell 25(6): 903-915.
- Schalm, S. S. and Blenis, J. (2002). Identification of a conserved motif required for mTOR signaling. Curr Biol 12(8): 632-639.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Dodd, K. M. and Tee, A. R. (2016). In vitro mTORC1 Kinase Assay for Mammalian Cells Protocol. Bio-protocol 6(11): e1827. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1827.
Category
Cancer Biology > Cancer biochemistry > Protein
Biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










