- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Primary Neuron-glia Culture from Rat Cortex as a Model to Study Neuroinflammation in CNS Injuries or Diseases
Published: Vol 6, Iss 8, Apr 20, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1788 Views: 11927
Reviewed by: Soyun KimPengpeng LiHong-guang Xia

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Microfluidic Cultures of Basal Forebrain Cholinergic Neurons for Assessing Retrograde Cell Death by Live Imaging
Srestha Dasgupta [...] Wilma J. Friedman
Jan 5, 2025 1861 Views

Time-Lapse Super-Resolution Imaging and Optical Manipulation of Growth Cones in Elongating Axons and Migrating Neurons
Masato Sawada [...] Kazunobu Sawamoto
Mar 20, 2025 2143 Views

Cryopreservation of Bulk-Produced Primary Rat Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells
Hanki Kim [...] Jun Young Choi
Jun 20, 2025 1427 Views
Abstract
Primary neuron-glia cultures are commonly used in vitro model for neurobiological studies. Here, we provide a protocol for the isolation and culture of neuron-glial cells from cortical tissues of 1-day-old neonatal Sprague-Dawley pups. The procedure makes available an easier way to obtain the neuron and glia. In this culture system, neuron-glia cultures consisted of approximately 37% neurons, 51% astrocytes, 7% microglia, and a small percentage (<5%) of other cells after fourteen days in vitro. Primary neuron-glia cultures is a simplified in vitro model for studies focusing on interactions between neurons and glia cells. Activated glial cells, mainly astrocytes and microglia, are histopathological hallmarks of acute injury of the central nervous system (CNS) or chronic neurologic diseases (Hirsch and Hunot, 2009; Lee et al., 2009; Minghetti, 2005). Inflammatory mediators (e.g., nitric oxide, reactive oxygen species, proinflammatory cytokines, and chemokines) released by activated glia can directly or indirectly cause neuronal damage or neurodegeneration. Neuroinflammation is a common mechanism of various neurological diseases leading to neurodegeneration. The advantages of neuron-glia cultures are that: (1) Cultured cells can bypass complicated physiological interactions (such as leukocyte infiltration, blood-brain barrier, reflex or other systemic regulation) in vivo to allow direct observation of neuroinflammation caused by various CNS insults (hypoxia, ischemia, trauma. infection, neurotoxins, chronic stress or diseases); (2) Unlike cell lines that are mostly derived from tumor cells, primary cultured neuron-glia system is closer to the cell population ratio in vivo and can mimic the in situ microenvironment; and (3) Cultures can be prepared from various brain regions (e.g., cortex, hippocampus, mesencephalon…etc.) and allow an opportunity to examine the regional difference in the susceptibility to neurodegeneration following neuroinflammation caused by various CNS insults (Kim et al., 2000). The following protocol is an example for primary rat cortical neuron-glia culture preparation (Huang et al., 2015; Huang et al., 2014; Huang et al., 2012; Huang et al., 2009).
Keywords: Primary neuron-glia cultureMaterials and Reagents
- Tissue culture dishes (60 x 15 mm) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P5237 )
- Tissue culture dishes (100 x 20 mm) (Nunc, catalog number: 172958 )
- Screw cap centrifuge tube (50 ml) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: BR114821 )
- 24-well plates (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: CLS 3527 )
- Pipette tips (10 μl, 200 μl and 1,000 μl) (Shineteh instruments co ltd., catalog number: PT4-W10 , PT1-Y200 and PT5-W10 )
- Neonatal Sprague-Dawley pups (1-day-old)
- Trypan blue (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15250061 )
- Hanks’ Balanced Salt solution (HBSS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 55021C )
- Sodium bicarbonate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S5761 )
- Pyruvate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P2256 )
- HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3375 )
- Bovine Serum Albumins (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A9418 )
- DMED powder (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 12100-046 )
- DMED/F-12, HEPES, no phenol red (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 11039-021 )
- Penicilline/Stretomycin (100x) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15140-122 )
- 100 mM Sodium pyruvate solution (100x) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 11360-070 )
- MEM non-essential amino acids solution (100x) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 11140-050 )
- Fetal bovine serum (FBS) (NQBB, catalog number: A6806-11 )
- Hank’s solution (see Recipes)
- Dulbecco's modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) (see Recipes)
- Serum-free medium (100 ml) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 37 °C, 5% CO2 incubator (Water Jacketed Laboratory CO2 Incubator)
- Stereo microscope (Shineteh instruments co., catalog number: IH1-ZM150A )
- Biological Inverted microscope (OLYMPUS CORPORATION, model: IX71 )
- Mini micro centrifuge (Shineteh instruments co., catalog number: IC-MINIMAX )
- Centrifuge (Hermle, catalog number: Hermle Z232K )
- Water bath (Bioman Scientific Co Ltd, catalog number: SWB-20-1 )
- Counting chamber (Shineteh instruments co., catalog number: PT14-901001 )
- Operating scissors STR (Shineteh instruments co., catalog number: ST-014 )
- Iris scissors STR (Shineteh instruments co., catalog number: ST-S009 )
- Dressing forceps (Shineteh instruments co., catalog number: ST-D114 )
- Iris forceps (Shineteh instruments co., catalog number: ST-I510 )
- Tweezers forceps (Shineteh instruments co ltd., catalog number: ST-NO5 )
- Pipetman (Gilson, catalog number: P10 , P200 and P1000)
- Pipet-aid (Thomas Scientific, FlaconTM, catalog number: 0410C04 )
- Pipets (10 ml) (Tseng Hsiang Life Science ltd., catalog number: SP-1-C )
- Ice bucket (Shineteh instruments co ltd., catalog number: PA8-4 )
Procedure
- Primary neuron-glia cultures are prepared from cortical tissues of 1-day-old neonatal Sprague-Dawley pups.
- After the rats are sacrificed, their brains are quickly removed aseptically. Under the stereo surgical microscope, the blood vessels and meninges are removed by tweezers.
- Cerebral cortices (6~8 pups cerebral cortices/tube) are dissected under sterile conditions and kept on ice in conical tube containing 10 ml of Hank’s solution (without Ca2+ or Mg2+).
- Remove Hank’s solution and add 15 ml of warm (37 °C) Dulbecco's modified Eagle’s media (DMEM) containing 10% heat-inactivated FBS to 50 ml conical tube.
- Cortical cells are dissociated by trituration using a 10 ml pipette (about 15 times). Cells are centrifuged at 4 °C (1,500 x g) for 5 min to pellet cells.
- After centrifugation, cells are re-suspended in 10 ml of DMEM containing 10% heat-inactivated FBS.
- Dilute cells for counting by adding 20 μl of cells to 180 μl of culture medium (10x dilution).
- Add 10 μl of the above cell dilution to a hemocytometer. Cells are counted in the 1 mm center square.
- Cell density is determined by the average of the 5 randomly selected squares. To calculate the total # of cells/ml = (the average count per square) x (the dilution factor) x (105/ml).
- Dilute the 10 ml stock to make a final concentration of 5 x 105 cells/ml.
- To each well of 24-well culture plates 5 x 105 cells are seeded in 0.5 ml of culture medium.
- The cultures are incubated at 37 °C in a humidified atmosphere of 5% CO2 and 95% air.
- Culture medium is replenished five days after plating, and is changed every three days thereafter.
- The neuron-glial cells become confluent 10-12 days after plating.
- Fourteen days in vitro (DIV14), the cultures are used for experiment. The cell composition is determined by immunostaining, followed by cell counting. The neuron-glia cultures consisted of approximately 37% ± 0.8% neurons, 51% ± 1.5% astrocytes, and 7% ± 7.7% microglia (Figure 1). In addition, cultures also consist of a small percentage (<5%) of other cells including oligodendrocytes, fibroblast and endothelial cells (data not shown).
- The characterization of neuronal phenotypes is shown in Figure 2.
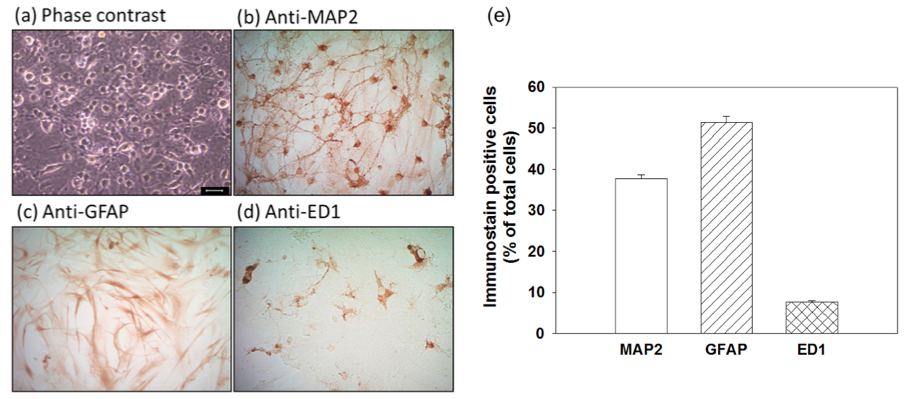
Figure 1. The composition of cell types in primary cortical neuron-glia cultures. Phase contrast photomicrograph of the primary cortical neuron-glia cultures in vitro (DIV14) (a), and representative immunocytochemically-stained photomicrographs using antibodies against (neuronal) dendritic marker microtubule associated protein 2 (MAP2) (b), astrocytic marker glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) (c) or pan-macrophage lysosomal antigen (ED1) as a phagocytic marker for activated microglia (d). Percentage of immunostain positive cells of neurons (MAP2+), astrocytes (GFAP+) and activated microglia (ED1+) cells in cultures (e). Scale bar = 25 μm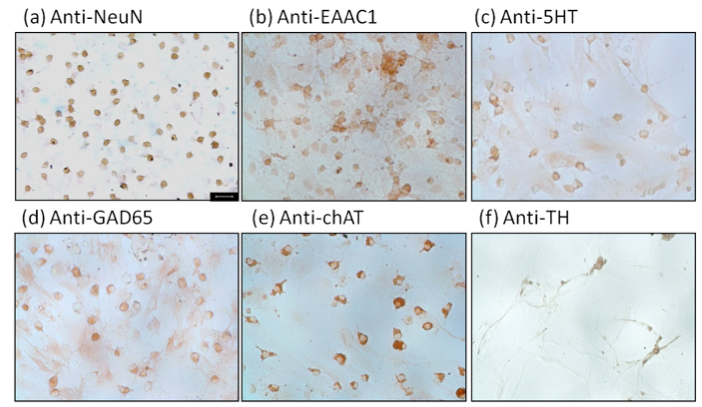
Figure 2. Characterization of neuronal phenotype by immunocytochemical staining. Cultures were stained using antibodies against (a) neuronal marker neuronal nuclei antigen (NeuN) on 14 days in vitro (DIV 14), (b) excitatory amino acid carrier 1 (EAAC1) for glutamatergic neurons, (c) 5-hydroxytryptamine (5HT) for serotonergic neurons, (d) glutamate decarboxylase 65 (GAD 65) for GABAergic neurons, (e) choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) for cholinergic neurons, and (f) tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) for catecholaminergic neurons. Scale bar = 25 μm
Recipes
- Hank’s solution (1,000 ml)
Reagents Volume Hanks’ balanced salt solution 1,000 ml Sodium bicarbonate 0.35 g Pyruvate 0.11 g HEPES 4.76 g Bovine serum albumins (BSA) 3 g - 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) / Dulbecco's modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) (1,000 ml)
Reagents Volume DMED powder 1 package Sodium bicarbonate 2.2 g Pyruvate 0.11 g HEPES 4.76 g FBS 110 ml - Serum-free medium (100 ml) (drug treatment only)
Reagents Volume DMED/F-12, HEPES, no phenol red 97 ml 100x Penicilline/Stretomycin 1 ml 100x sodium pyruvate solution (100 mM) 1 ml 100x MEM non-essential amino acids solution 1 ml
Acknowledgments
This protocol is adapted from the previously published studies (Huang et al., 2015; Huang et al., 2014; Huang et al., 2009; Kim et al., 2000). These studies were supported in part by grants from the Hsin Sheng Junior College of Medical Care and Management (HSC-103-001 and HSC-104-015) and from Taipei Medical University (03C0720004A) to YNH; and from the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST-104-2923-B-038-001-MY3 and MOST-104-2320-B-038-057-MY3) to JYW, Taiwan.
References
- Hirsch, E. C. and Hunot, S. (2009). Neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease: a target for neuroprotection? Lancet Neurol 8(4): 382-397.
- Huang, Y. N., Ho, Y. J., Lai, C. C., Chiu, C. T. and Wang, J. Y. (2015). 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 attenuates endotoxin-induced production of inflammatory mediators by inhibiting MAPK activation in primary cortical neuron-glia cultures. J Neuroinflammation 12: 147.
- Huang, Y. N., Lai, C. C., Chiu, C. T., Lin, J. J. and Wang, J. Y. (2014). L-ascorbate attenuates the endotoxin-induced production of inflammatory mediators by inhibiting MAPK activation and NF-kappaB translocation in cortical neurons/glia Cocultures. PLoS One 9(7): e97276.
- Huang, Y. N., Wang, J. Y., Lee, C. T., Lin, C. H., Lai, C. C. and Wang, J. Y. (2012). L-Ascorbate attenuates methamphetamine neurotoxicity through enhancing the induction of endogenous heme oxygenase-1. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 265(2): 241-252.
- Huang, Y. N., Wu, C. H., Lin, T. C. and Wang, J. Y. (2009). Methamphetamine induces heme oxygenase-1 expression in cortical neurons and glia to prevent its toxicity. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 240(3): 315-326.
- Kim, W. G., Mohney, R. P., Wilson, B., Jeohn, G. H., Liu, B. and Hong, J. S. (2000). Regional difference in susceptibility to lipopolysaccharide-induced neurotoxicity in the rat brain: role of microglia. J Neurosci 20(16): 6309-6316.
- Lee, Y., Lee, S. R., Choi, S. S., Yeo, H. G., Chang, K. T. and Lee, H. J. (2014). Therapeutically targeting neuroinflammation and microglia after acute ischemic stroke. Biomed Res Int 2014: 297241.
- Minghetti, L. (2005). Role of inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Opin Neurol 18(3): 315-321.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Huang, Y. and Wang, J. (2016). Primary Neuron-glia Culture from Rat Cortex as a Model to Study Neuroinflammation in CNS Injuries or Diseases. Bio-protocol 6(8): e1788. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1788.
Category
Neuroscience > Cellular mechanisms > Cell isolation and culture
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











