- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
EdU Based DNA Synthesis and Cell Proliferation Assay in Maize Infected by the Smut Fungus Ustilago maydis
Published: Vol 6, Iss 6, Mar 20, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1761 Views: 10294
Reviewed by: Marisa RosaPablo Bolanos-VillegasDennis Nürnberg

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Quantification of the Composition Dynamics of a Maize Root-associated Simplified Bacterial Community and Evaluation of Its Biological Control Effect
Ben Niu and Roberto Kolter
Jun 20, 2018 10502 Views

Tracking Root Interactions System (TRIS) Experiment and Quality Control
Hassan Massalha [...] Asaph Aharoni
Apr 20, 2019 7345 Views

A Quick Method for Screening Biocontrol Efficacy of Bacterial Isolates against Bacterial Wilt Pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum in Tomato
Heena Agarwal [...] Niraj Agarwala
Nov 20, 2020 5559 Views
Abstract
The basidiomycetous smut fungus Ustilago maydis (U. maydis) infects all aerial parts of its host plant maize (Zea mays L.). Infection is seen in the form of prominent tumorous symptoms after the establishment of a biotrophic interaction with the host, usually around 5-6 days after infection. The fungus colonizes the various developmentally distinct aerial organs at different stages of development. Formation of tumors is coupled with the induction of host cell division. Activation of cell division can be understood as a measure of DNA synthesis which is triggered to induce rapid divisions in host cell. This developed protocol helps in tracking tumor induction in U. maydis by monitoring of DNA synthesis in planta. Infected leaves were treated with 5-ethynyl-2-deoxyuridine (EdU) at several stages of infection in the seedling leaves and labeled. EdU incorporation in the S phase cells, was visualized by attaching a fluorescent tag and non-dividing maize nuclei were stained with propidium iodide (PI). This protocol helped to understand the tumor development in U. maydis by confocal laser scanning microscopy (Kelliher and Walbot, 2011; Redkar et al., 2015)
Keywords: DNA SynthesisMaterials and Reagents
- 1 ml Syringes (Henke Sass-Wolff, catalog number: 5100.200V0 )
- Needles (16 G, 40 mm) (Premier Healthcare & Hygiene, BD microlance, catalog number: 300637 )
Note: A needle of different thickness can be used depending upon the maize variety. - Falcon tubes (15 ml)
- Microcentrifuge tubes
- Click iT EdU imaging kit (Life Technologies, catalog number: 10337 )
Note: Currently, it is “Thermo Fisher Scientific, Molecular ProbesTM, catalog number: 10337”.- 5-ethynyl- 2’-deoxyuridine (EdU)
- Wheat germ Agglutinin-Alexa Fluor 488 (WGA AF 488)
- Dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO)
- Click iT EdU reaction buffer
- Copper sulphate (CuSO4)
- Click iT EdU buffer additive
- Hoechst 33342
- 5-ethynyl- 2’-deoxyuridine (EdU)
- Phosphate buffer saline (PBS, pH 7.4) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 10010023 )
- Permeabilization reagent [e.g. 0.5% Triton X-100 in PBS (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Molecular ProbesTM, catalog number: R37602 )]
- Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A8531 )
- 100% Ethanol
- Propidium iodide (PI) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Molecular ProbesTM, catalog number: P1304MP )
Note: PI is toxic and may cause skin and respiratory irritation. Hence it is good to handle PI in the fume hood with the personal safety protection. - Double distilled water
- 2% BSA in PBS (pH 7.4) (See Recipes)
- Propidium iodide stock solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- EdU Labeling chambers
Note: These plastic chambers are custom made to fit in the desired sample). An image showing the details of this chamber is shown below (Figure 1B). As an alternative to the labeling chambers 50 ml Falcon Tubes can also be used to labeling the leaves by dipping the infected leaf in 10 µM EdU. - Confocal microscope (e.g. Leica Microsystems, model: TCS-SP5 )
- Vacuum Pump
- Rocker
Software
- Leica Imaging Software (Leica)
Procedure
- Preparation of stock solutions
- Allow all the vials to warm to room temperature.
- Add 2 ml DMSO or an aqueous solution to EdU (Molar mass 252.23 g mol-1) to make a 10 mM EdU stock solution. This stock is generally stable for one year when stored at -20 °C.
- Prepare 10x Click-iT EdU reaction buffer by adding 3.6 ml of deionized water to Click iT EdU reaction buffer. Stored at 2-8 °C.
- Prepare Alexa Fluor azide solution by adding 70 μl DMSO to Alexa Fluor 488 Azide. Mix and store well at -20 °C.
- Prepare 10x Click-iT EdU buffer additive by adding 2 ml deionized water to Click iT EdU buffer additive and mix. Stored at -20 °C.
- Allow all the vials to warm to room temperature.
- Labeling cells with EdU and fixation
Note: Ustilago maydis infections are done in the desired maize organ as described previously (Redkar and Doehlemann, 2016).
For seedling samples- The U. maydis seedling or tassel infections are carried out by the syringe inoculation method by injecting the inoculum into the desired maize organ (Redkar and Doehlemann, 2016).
- The EdU labeling is done at the time-point for which DNA synthesis is to be measured. In case of a U. maydis infected seedling the 4 days post infection (dpi) time-point was chosen. In the U. maydis infected seedling the third infected leaf where the first infection symptoms appear is used for the EdU labeling assay.
- This leaf is incubated for 5 h with 10 µM EdU in small chambers (details of which have been previously mentioned) designed for labeling physiologically active leaves, taking care that the 2 cm area below the infection mark which is actively colonized is well immersed (Figure 1A). The labeling is done in the temperature controlled greenhouse to ensure the active imbibition of EdU into the leaf cells.
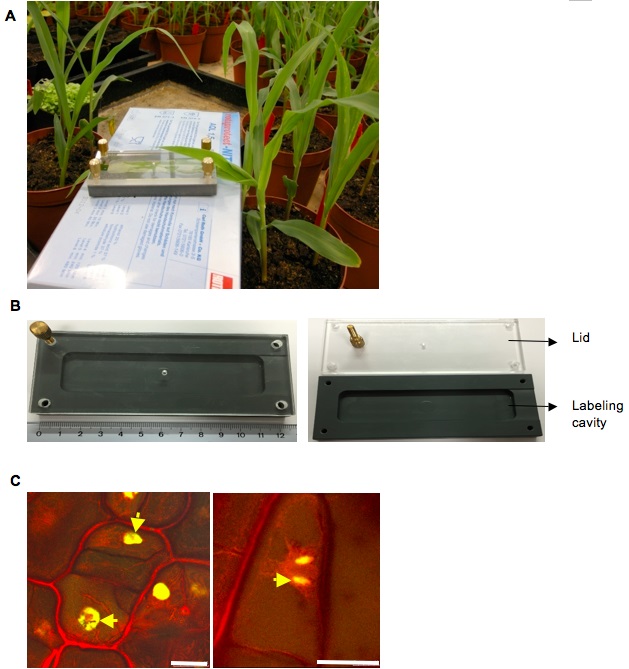

Figure 1. EdU labelling to detect DNA synthesis in U. maydis infected maize seedlings. A. Labeling of EdU in a maize seedling to detect S phase cells in infected leaves. B. An image of the EdU labeling chamber with the lid (Left), The lid of the chamber removed for insertion of the seedling sample (Right). C. Cell division events observed in a maize seedling infected by U. maydis wild-type strain SG200 at 4 dpi. (Left) EdU incorporation into a cell will result in equally labeled contiguous daughter cells after cell division as indicated by yellow arrows. (Right) The mitotic events are nicely preserved by this EdU method of labeling (scale bars = 25 µm). - After 5 h of labeling, the 2 cm area below the syringe mark on the leaves is detached and fixed in 100% (v/v) ethanol. The material is collected in 15 ml Falcon tubes. This area of the maize leaf shows maximum colonization with U. maydis as it shows chlorosis to small tumorous symptoms at 4dpi.
For tassel samples- U. maydis tassel infections are performed by a syringe inoculation method by delivering 1 ml of sporidial inoculum as previously described (Walbot and Skibbe, 2010).
- For the tassel tissues, the EdU labeling assay is done at 3 dpi, to capture the mitotically active anthers before they switch to meiosis.
- At 3 dpi the immature infected tassel (anther size approx. 1-1.5 mm; Figure 2) is bathed with 1 ml of 20 µM EdU after delivery.
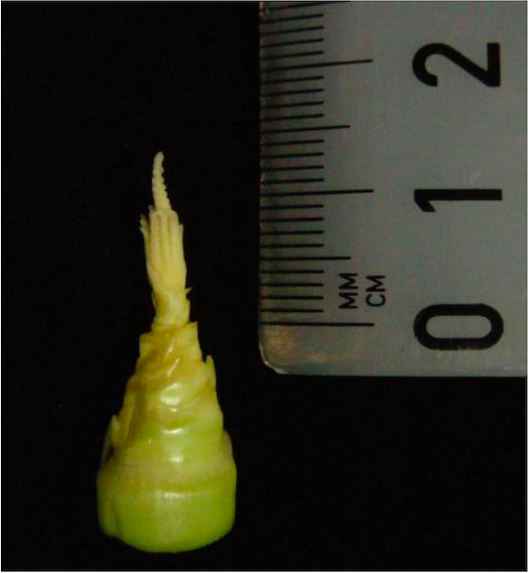
Figure 2. Immature maize tassel at time point of EdU treatment - The injected EdU enters through the small air spaces between the external organs of the spikelets and reaches anthers over the labeling time of 5 h.
- After the labeling procedure, the tassel is dissected out and around 150 anthers from different parts of the tassel were collected to ensure random sampling with equal probability of labeled anthers and fixed in 100% (v/v) ethanol 5 h after labeling.
- The U. maydis seedling or tassel infections are carried out by the syringe inoculation method by injecting the inoculum into the desired maize organ (Redkar and Doehlemann, 2016).
- Permeabilization and staining of labeled EdU
- The EdU staining procedure is done as described by implementation of a modified protocol (Kelliher and Walbot, 2011). For seedling samples, approx. 1 cm pieces of the collected tissues which are fixed in ethanol are used. For tassel samples, around 100 individual anthers from different parts of the tassel are used. The labeling procedure is done in 2 ml microcentrifuge tubes for seedling and anther samples.
- The fixed samples in ethanol are washed once with fresh 100% (v/v) ethanol followed by two washes in PBS (pH 7.4) + 2% (w/v) BSA. More washes with the PBS buffer are helpful for complete removal of chlorophyll from the seedling samples.
- The samples are then transferred to permeabilization solution [PBS +1% (v/v) Triton X-100] at room temperature for 20 min with rocking for 50-60 rotations per minute (rpm)/min. This step can also be done on a regular shaker with the same rpm. Triton treatment results in active nuclear staining and is compatible with EdU co-staining. It is known to prevent cell shrinkage and quick penetration of the fixative to allow better preservation of mitotic stages (Kotogany et al., 2010). The image representation of a cell stained with EdU and showing the well preserved mitotic event is shown in Figure 1B.
- The samples are washed twice in PBS + 2% (w/v) BSA then directly incubated for 30 min at room temperature with EdU Click-IT cocktail for detection. E.g., for approx. 2.5 ml EdU cocktail the following components were added (Click iT EdU reaction buffer - 2.2 ml; CuSO4 -100 µl; Alexa Fluor azide - 6 µl; Reaction buffer additive - 250 µl). For the seedling samples, 500 µl of this cocktail solution was used in each transparent microcentrifuge tube where as for anthers this corresponded to 100 µl.
- The EdU reaction cocktail is also supplemented with 20 μg/ml Propidium iodide (PI). This is mainly to co-stain the fungal hyphae and the non-dividing host cell nuclei.
- This EdU reaction cocktail is then incubated at room temperature for 50 min and then vacuum infiltrated at 250 millibar 3 times for 5 min each along with a regular interval of 5 min with atmospheric pressure.
- After the infiltration, the samples are washed twice in PBS (pH 7.4) + 2% (w/v) BSA, transferred to new PBS (pH 7.4), and can be kept at 4 °C in the dark (up to several days) before imaging.
- The EdU staining procedure is done as described by implementation of a modified protocol (Kelliher and Walbot, 2011). For seedling samples, approx. 1 cm pieces of the collected tissues which are fixed in ethanol are used. For tassel samples, around 100 individual anthers from different parts of the tassel are used. The labeling procedure is done in 2 ml microcentrifuge tubes for seedling and anther samples.
- Microscopy of the EdU labeled leaves and anthers
All confocal analysis may be performed on a TCS SP5 confocal laser scanning microscope, or a comparable device. The laser channels used for confocal fluorescence analysis of excitation and detection wavelengths are summarized in Table 1.
Tabel 1. Lasers used and the excitation and detection wavelengthDetection Excitation wavelength Detection wavelength Pinhole used EdU coupled to WGA AF488 488 nm 490-540 nm ~ 90 µm Propidium iodide 561 nm 570-640 nm ~ 90 µm
All the images taken by the Leica TCS SP5 Confocal microscope were processed and analyzed by the Leica Imaging Software.
Recipes
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (2%) in PBS (pH 7.4)
Add 20 g of BSA to 1 L of PBS buffer (pH 7.4) - Propidium iodide stock solution
10 mg/ml in PBS (storage in the dark at -20 °C). This stock solution is directly added to the EdU reaction cocktail to include the co-stain in working concentration.
Acknowledgments
Our work was funded by the Max Planck Society, the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), the Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst (DAAD) and the Cluster of Excellence on Plant Science (CEPLAS). The protocol is adapted from Kelliher and Walbot (2011) and Redkar et al. (2015).
References
- Kelliher, T. and Walbot, V. (2011). Emergence and patterning of the five cell types of the Zea mays anther locule. Dev Biol 350(1): 32-49.
- Kotogany, E., Dudits, D., Horvath, G. V. and Ayaydin, F. (2010). A rapid and robust assay for detection of S-phase cell cycle progression in plant cells and tissues by using ethynyl deoxyuridine. Plant Methods 6(1): 5.
- Redkar, A. and Doehlemann, G. (2016). Ustilago maydis virulence assays in maize. Bio-protocol 6(6): e1760.
- Redkar, A., Hoser, R., Schilling, L., Zechmann, B., Krzymowska, M., Walbot, V. and Doehlemann, G. (2015). A secreted effector protein of Ustilago maydis guides maize leaf cells to form tumors. Plant Cell 27(4): 1332-1351.
- Walbot, V. and Skibbe, D. S. (2010). Maize host requirements for Ustilago maydis tumor induction. Sex Plant Reprod 23(1): 1-13.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Redkar, A. and Doehlemann, G. (2016). EdU Based DNA Synthesis and Cell Proliferation Assay in Maize Infected by the Smut Fungus Ustilago maydis. Bio-protocol 6(6): e1761. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1761.
Category
Plant Science > Plant immunity > Disease bioassay
Microbiology > Microbe-host interactions > In vivo model > Plant
Molecular Biology > DNA > DNA synthesis
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











