- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Detection of Hydroxyproline O-galactoside by LC/MS
Published: Vol 6, Iss 2, Jan 20, 2016 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1710 Views: 6913
Reviewed by: Renate WeizbauerHarrie van ErpAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Enzymatic Starch Quantification in Developing Flower Primordia of Sweet Cherry
Nestor Santolaria [...] Afif Hedhly
Apr 5, 2025 1897 Views

New Approach to Detect and Isolate Rhamnogalacturonan-II in Arabidopsis thaliana Seed Mucilage
Dayan Sanhueza and Susana Saez-Aguayo
Sep 5, 2025 1248 Views

Detailed Method for the Purification of Rhamnogalacturonan-I (RG-I) in Arabidopsis thaliana
Liang Zhang [...] Breeanna R. Urbanowicz
Feb 5, 2026 144 Views
Abstract
Hydroxyproline (Hyp) O-galactosylation is a plant-specific post-translational modification found in extracellular glycoproteins such as arabinogalactan proteins (AGPs). Hyp O-galactosylation is mediated by Hyp O-galactosyltransferase (HPGT) that catalyzes the transfer of a D-galactopyranosyl residue to the hydroxyl group of Hyp residues of peptides from the sugar donor UDP-α-D-Gal. Here we describe an LC/MS-based method for the detection of Hyp O-galactoside.
Materials and Reagents
- Cotton
- 1 ml Micropipette tip
- Hyp O-galactosylated peptides or proteins
- 0.22 M Ba(OH)2
- 0.32 M sulfuric acid
- 1 M NaOH
- 1 M HCl
- 10% aqueous ammonia
- 80% acetonitrile containing 0.1% formic acid
- 99.9% acetonitrile (HPLC grade) containing 0.1% formic acid
- Water (HPLC grade) containing 0.1% formic acid
Equipment
- Heat block
- Centrifugal evaporator
- BT AG 50W-X8 Resin (100-200 mg resin, H+ form) (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 143-5441 )
- Micro centrifuge
- Micro HPLC system (JASCO International Co., model: micro21 LC-01 )
- LCQ Deca XP-plus ESI ion-trap mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific)
- TSK-gel Amide-80 (3 μm) column (2.0 x 150 mm) (Tosoh Bioscience LLC, catalog number: 21865 )
Procedure
- Ba(OH)2 hydrolysis
- Dissolve galactosylated peptide in 500 μl 0.22 M Ba(OH)2 in a glass vial with cap.
- Incubate at 105 °C, 6 h.
- Incubate on ice for 5 min.
- Add 500 μl of 0.32 M sulfuric acid on ice.
- Centrifuge at 20,000 x g for 5 min.
- Dissolve galactosylated peptide in 500 μl 0.22 M Ba(OH)2 in a glass vial with cap.
- Partial purification of Ba(OH)2 hydrolysate (Figure 1)
- Plug a 1 ml micropipette tip with a small amount of cotton.
- Pack 200 mg AG 50W-X8 resin into the tip column.
- Wash the column with 1 ml of 1 M NaOH by gravity flow.
- Wash the column with 1 ml of 1 M HCl by gravity flow.
- Wash the column with 1 ml of water by gravity flow.
- Apply supernatant of the Ba(OH)2 hydrolysate of the galactosylated peptide to the tip column.
- Wash the column with 1 ml of water by gravity flow.
- Elute with 1 ml of 10% aqueous ammonia by gravity flow.
- Evaporate the sample to dryness.
- Dissolve in 100 μl 80% acetonitrile containing 0.1% formic acid.

Figure 1. Partial purification of Ba(OH)2 hydrolysate. Supernatant of the Ba(OH)2 hydrolysate of the galactosylated peptide was applied to the tip column.
- Plug a 1 ml micropipette tip with a small amount of cotton.
- LC/MS analysis
10 μl aliquots of the assay solution will be analyzed by LC-MS using a micro HPLC (high pressure liquid chromatography) system connected to an LCQ Deca XP-plus ESI ion-trap mass spectrometer. Chromatographic separation is performed by normal-phase HPLC on a TSK-gel Amide-80 (3 μm) column (2 x 150 mm).
- The mobile phase is composed of HPLC grade water containing 0.1% formic acid (eluent A) and HPLC grade acetonitrile containing 0.1% formic acid (eluent B). The column temperature is maintained at 25 °C.
- The HPLC flow rate is 100 μl/min, and the elution gradient was 60 to 40% B over 10 min.
- Subject the HPLC eluate to coupled electrospray ionization (ESI) in the positive ionization mode.
- MS source parameters are as follows:
- Capillary temperature: 200 V
- Capillary voltage: 42 V
- Source voltage: 5 kV
- Source current: 8.5 μA
- Sheath gas flow: 50
- Aux gas flow: 0
- Sweep gas flow: 0
- The mass range: m/z 500-2000
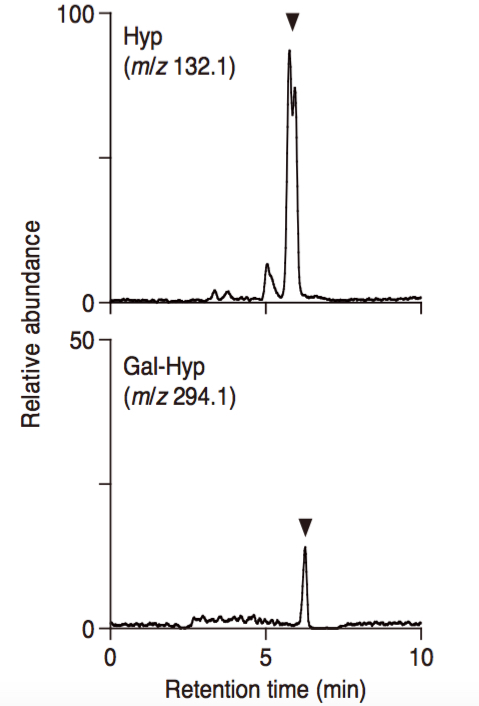
Figure 2. Detection of Hyp O-galactoside in Ba(OH)2 hydrolysates of in vitro galactosylated AGP14 by LC-MS. The sample was analyzed by selected ion monitoring of Hyp (m/z 132.1) and Gal-Hyp (m/z 294.1). Ba(OH)2 hydrolysis yields a diastereomeric pair of amino acids.
- Capillary temperature: 200 V
- The mass spectra are obtained by selected ion monitoring in zoom scan mode (Hyp: m/z 132.1, Gal-Hyp: m/z 294.1).
- The mobile phase is composed of HPLC grade water containing 0.1% formic acid (eluent A) and HPLC grade acetonitrile containing 0.1% formic acid (eluent B). The column temperature is maintained at 25 °C.
Acknowledgments
This is the detailed protocol for the detection of HPGT activity described by Ogawa-Ohnishi and Matsubayashi (2015). This research was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (S) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology (No. 25221105).
References
- Ogawa-Ohnishi, M. and Matsubayashi, Y. (2015). Identification of three potent hydroxyproline O-galactosyltransferases in Arabidopsis. Plant J 81(5): 736-746.
- Ogawa-Ohnishi, M., Matsushita, W. and Matsubayashi, Y. (2013). Identification of three hydroxyproline O-arabinosyltransferases in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Chem Biol 9(11): 726-730.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2016 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Ogawa-Ohnishi, M. and Matsubayashi, Y. (2016). Detection of Hydroxyproline O-galactoside by LC/MS. Bio-protocol 6(2): e1710. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1710.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Carbohydrate
Biochemistry > Carbohydrate > Polysaccharide
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









