- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Isolation and Characterization Procedure for Indole Alkaloids from the Marquesan Plant Rauvolfia Nukuhivensis
Published: Vol 5, Iss 20, Oct 20, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1625 Views: 12442
Reviewed by: Arsalan DaudiZhaohui LiuSamik Bhattacharya

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Isolation of Intact Vacuoles from Arabidopsis Root Protoplasts and Elemental Analysis
Chuanfeng Ju [...] Zhenqian Zhang
Mar 5, 2023 2053 Views

Analysis of Modified Plant Metabolites Using Widely Targeted Metabolite Modificomics
Jianing Zhang [...] Jun Yang
Apr 5, 2025 1469 Views

High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Quantification of Glyphosate, Aminomethylphosphonic Acid, and Ascorbate in Culture Medium and Microalgal Cells
Juan Manuel Ostera [...] Gabriela Malanga
Apr 5, 2025 1181 Views
Abstract
A plethora of natural products, mostly secondary metabolites, are isolated and purified from many different organisms, like plants, fungi, algae, marine invertebrates, etc. The extraction procedure is specific to each organism, but some guidelines are usually followed for any purification procedure regarding targeted metabolites, such as alkaloids. Alkaloids are secondary metabolites that contain basic nitrogen in their structures and they are often associated with interesting biological properties especially in pharmacology field. This protocol describes the isolation procedure of indole alkaloids from Rauvolfia nukuhivensis directly from the ethanol extract of the plant material yielding different skeleton-type compounds including non-basic derivatives (ajmaline, sarpagine, macroline and β-carboline). The procedure details the guidelines and the steps to characterize new or known isolated compounds, beginning from the plant collection to the molecule level with the use of spectroscopic techniques (NMR, MS, UV). We detailed the extraction and fractionation procedures followed by the purification of compounds, as well as their physico-chemical characterizations. The procedure is illustrated by the example of the purification of a large array of indole alkaloids from the bark of Rauvolfia nukuhivensis.
Materials and Reagents
- Rauvolfia nukuhivensis (Voucher JFB 2808): In our example, the bark of Rauvolfia nukuhivensis was collected at Maauu in “Terre Déserte” area on Nuku Hiva Island, Marquesas archipelago, French Polynesia, at an altitude of 477 m and identified by Dr Jean-François Butaud. A voucher specimen (JFB 2808) has been deposited at the Herbarium of French Polynesia. The sample was dried after collection at 30 °C using an air dryer device and stored in the room until grinding and extraction.
- Ethanol (95%) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fisher chemical)
- Methanol (HPLC grade from Fisher chemical)
- Dichloromethane (HPLC grade from Fisher chemical)
- Cyclohexane (HPLC grade from Fisher chemical)
- Ethyl acetate (HPLC grade from Fisher chemical)
Equipment
- SEB Prep'line grinder (SEB)
- Semi-preparative HPLC column Luna 5 μm C18 (50 mm x 10 mm) (Phenomenex, model: RP-C18 )
- Vacuum liquid chromatography (Buchner filter from Buchi, chromatography performed with vacuum pump) (BÜCHI Labortechnik AG)
- High Pressure Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Waters 600 system equipped with a Waters 717 Plus autosampler, a Waters 998 photodiode array detector (WATERS, model: Waters 998 photodiode array detector ), and a Sedex 75 evaporative light-scattering detector (SEDERE, model: Sedex 75)
- NMR spectrometer (Bruker Corporation, model: Bruker Avance 500 MHz )
- Polarimeter (jascoinc, model: Jasco P-2000 )
- Spectropolarimeter (jascoinc, model: Jasco J-810 )
- Mass spectrometer (Bruker Corporation, model: Bruker ESQUIRE 3000 plus )
- Thermo Finnigan LTQ Orbitrap mass spectrometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Procedure
- Sample collection
The isolation procedure starts with the collection of the sample which is identified by a botanist and certified with the record of a voucher specimen. In our example, the bark of Rauvolfia nukuhivensis was collected at Maauu in “Terre Déserte” area on Nuku Hiva Island, Marquesas archipelago, French Polynesia, at an altitude of 477 m and identified by Dr Jean-François Butaud. A voucher specimen (JFB 2808) has been deposited at the Herbarium of French Polynesia. The sample was dried after collection at 30 °C using an air dryer device and stored in the room until grinding and extraction. - Extraction and isolation
Prior to extraction, batches of 50 g of bark pieces were ground into powder during at least 5 periods of 1 min repeated grinding with the rotor setting at 10,000 rpm. In order to avoid overheating of the grinder, the system was covered with plastic and cooled in ice between each grinding process.
The procedure can be divided into three steps, the extraction process, one or more fractionation steps, according to the chemical complexity of the crude extract, and finally the isolation process. For our samples, two successive fractionations were performed, with a range of solvents described in Tables 1 and 2.
Figure 1. Bark of Rauvolfia nukuhivensis after and before the grinding process
Table 1. Solvent composition of the first fractionationFraction Solvent Proportion FA Water - FB Water/Methanol 1:1 FC Methanol - FD Methanol/Dichloromethane 1:1 FE Dichloromethane - - For our example of the plant Rauvolfia nukuhivensis, its dried bark (250 g) was ground by industrial equipment.
- The dried ground bark was macerated in 750 ml of ethanol during 16 h at room temperature and then the solvent was filtered (0.45 µm) and concentrated by evaporation to yield a crude oil.
- The resulting extract (21 g) was dissolved by sonication for 10 min in a mixture of 200 ml methanol/dichloromethane (1:1) and then filtered.
- The fractionation was carried out by vacuum liquid chromatography on RP-C18 column and eluted with solvents of decreasing polarity as shown in Table 1.
- Fraction FC provided 8.43 g of an oily residue and showed the presence of indole alkaloids by HPLC-DAD.
- Consequently, a portion of fraction FC (600 mg) was further fractionated by normal phase (diol) flash column chromatography using solvents of increasing polarity as shown in Table 2.
Table 2. Solvent composition of the second fractionation
Sub-fraction Solvent Proportion f1 Cyclohexane - f2 Cyclohexane/Ethyl acetate 3:1 f3 Cyclohexane/Ethyl acetate 1:1 f4 Cyclohexane/Ethyl acetate 1:3 f5 Ethyl acetate - f6 Ethyl acetate/Methanol 3:1 f7 Ethyl acetate/Methanol 1:1 f8 Ethyl acetate/Methanol 1:3 f9 Methanol - f10 Methanol/Dichloromethane 1:1 - Each obtained fraction contains a lower compound diversity than the extract and thus facilitates the isolation and purification procedure.
- Fraction FCf7 was selected for final purification on HPLC mainly because of its weight but also the high chemical diversity.
- Purification of FCf7 (50.2 mg) major compounds was performed by RP-C18 semi-preparative HPLC (Phenomenex, Luna 5 μm C18, 250 mm x 10 mm) with a gradient of water/methanol/trifluoro acetic acid (from 70:30:0.1 to 30:70:0.1, flow 3 ml/min) to afford, after a drying step under nitrogen gas flow, pure compound 1 (4.7 mg), 2 (2.8 mg) 3 (1.83 mg), 4 (2.17 mg), 5 (3.25 mg), 6 (3.24 mg), 7 (1.23 mg), 8 (6.43 mg), 9 (1.82 mg), 10 (1.71 mg), 11 (1.39 mg), 12 (2.00 mg) and 13 (2.20 mg).
- For our example of the plant Rauvolfia nukuhivensis, its dried bark (250 g) was ground by industrial equipment.
- Characterization
The last step of the procedure involves different spectral and chromatographic techniques for a full description of the purified compound. To date, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is the most common technique to elucidate the structure of a compound. However, other techniques are needed to along with NMR for a better characterization, including high-resolution mass spectroscopy, UV spectra, optical rotation, infrared spectra, and circular dichroism if needed. NMR spectroscopy is frequently used in two major ways, 1D and 2D. For a better understanding of NMR spectroscopy see for example Keeler (2011); Lewitt (2001) and Fan (1996).
In our case, we chose to study and describe several physicochemical characteristics of each compound, listed here: UV-Vis spectra were recorded by HPLC-DAD. NMR spectra were measured on a Bruker Avance 500 MHz spectrometer with pulsed field gradient and signals were referenced to the residual solvent signals (CD3OD, at δH 3.31 and δC 49.0 ppm). For this step, each was diluted in 700 µl of CD3OD. Electrospray Ionization Mass spectrometry (ESIMS) and High Resolution ESIMS (HRESIMS) data were measured with a Bruker ESQUIRE 3000 plus mass spectrometer and a Thermo Finnigan LTQ Orbitrap mass spectrometer, respectively. HPLC purification was carried out on a Waters 600 system equipped with a Waters 717 Plus autosampler, a Waters 998 photodiode array detector, and a Sedex 75 evaporative light-scattering detector (Sedere, France). Optical rotation and circular dichroism were measured on a Jasco P-2000 polarimeter and a Jasco J-810 spectropolarimeter, respectively.
The structures for some compounds have been reported in Martin et al. (2012) and Martin et al. (2015). Some examples are provided here (Figure 2). We have also provided NMR spectroscopic data summarized in Tables 3 and 4.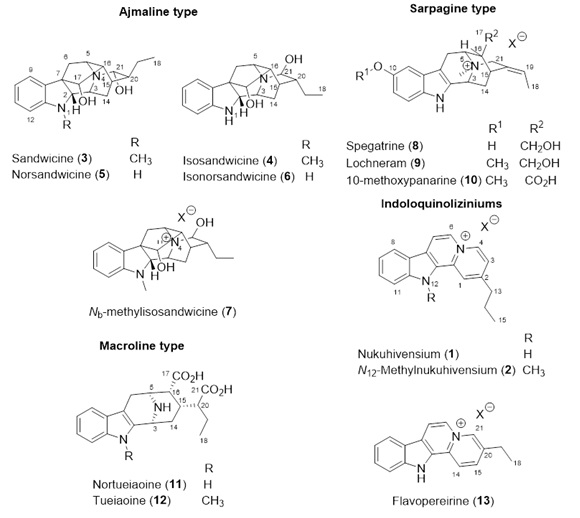
Figure 2. Structure of compounds 1-13 isolated from the bark extract of Rauvolfia nukuhivensis. Nukuhivensium (1). Yellow-coloured amorphous powder; UV measured by HPLC/DAD (MeOH/H2O/TFA) λmax 223,6 ; 241,3 ; 289,9 ; 340,0 ; 381,7 nm; 1H and 13C NMR see Table 3; HRESIMS m/z 261.13953 [M]+ (calcd for C18H17N2+, 261.13917). N12-methylnukuhivensium (2). Yellow-coloured amorphous powder; UV measured by HPLC/DAD (MeOH/H2O/TFA) λmax 224,8 ; 236,6 ; 248,4 ; 286,7 ; 335,2 ; 392,6 nm; 1H and 13C NMR see Table 3; HRESIMS m/z 275.15417 [M]+ (calcd for C19H19N2+, 275.15482). Nortueiaoine (11): Light yellow amorphous powder; [α]20D - 1.1 (MeOH); 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectroscopic data, see Table 4; ESIMS m/z 343.1 [M+H]+ ; HRESIMS m/z 343.16611 [M+H]+ (calcd for C19H23N2O4+, 343.16578). Tueiaoine (12) Light yellow amorphous powder ; [α]20D + 1.2 (MeOH); 1H NMR and 13C NMR spectroscopic data, see Table 4; ESIMS m/z 357.2 [M+H]+ ; HRESIMS m/z 357.18289 [M+H]+ (calcd for C20H25N2O4+, 357.18143).
Table 3. 1H (500 MHz) and 13C (125 MHz) NMR data for indoloquinolizinium derivatives 1 and 2 in CD3ODNukuhivensium (1) N12-methylnukuhivensium (2) Position δC in ppm δH in ppm, mult. (J in Hz) δC in ppm δH in ppm, mult. (J in Hz) 1 120.5 8.65, s 121.5 8.96, s 2 154.4 - 154.1 - 3 124.4 7.83, d (7.0) 123.9 7.86, d (7.0) 4 137.6 9.19, d (7.0) 138.4 9.24, d (7.0) 6 128.1 8.84, d (7.0) 128.1 8.90, d (7.0) 7 117.2 8.61, d (7.0) 116.8 8.66, d (7.0) 7a 125.0 - 125.6 - 7b 122.5 128.9 8 123.3 8.36, d (8.0) 122.8 8.41, d (8.0) 9 122.9 7.50, dd (8.0; 7.0) 123.5 7.54, dd (8.0, 7.0) 10 131.0 7.74, dd (8.0; 7.0) 131.2 7.83, dd (8.0,7.0) 11 113.6 7.84, d (8.0) 112.1 7.95, d (8.0) 11a 143.3 144.9 12 34.6 4.58, s 12a 131.7, C 131.4 12b 134.3, C 135.2 13 38.6, CH2 3.06, t (7.7) 38.7 3.09, t (7.7) 14 23.9, CH2 1.94, tq (7.7; 7.5) 24.4 1.93, tq (7.7, 7.5) 15 14.0, CH3 1.12, t (7.5) 14.0 1.12, t (7.5)
Table 4. 1H (500 MHz) and 13C (125 MHz) NMR data for macroline derivatives 11 and 12 in CD3ODNortueiaoine (11) Tueiaoine (12) Position δC in ppm δH in ppm, mult. (J in Hz) δC in ppm δH in ppm, mult. (J in Hz) 2 128.9 - n.d. - 3 49.1 4.89, br s 47.8 5.08, br s 5 50.9 4.31, d (8.0) 51.2 4.26, d (7.5) 6α 25.5 3.52, dd (17.5, 7.5) 25.0 3.50, dd (17.5, 7.5) 6β 2.99, d (17.5) 7 107.7 - 108.2 - 8 127.0 - 127.2 - 9 119.2 7.51, d (8.0) 119.8 7.51, d (8.0) 10 120.8 7.09, ddd (8.0, 7.0, 1.0) 121.3 7.09, br dd (8.0, 7.0) 11 123.7 7.18, ddd (8.0, 7.0, 1.0) 124.2 7.25, br dd (8.0, 7.0) 12 112.5 7.38, br d (8.0) 110.9 7.43, d (8.0) 13 138.1 - 139.8 - 14α 28.4 2.16, td (12.5, 3.0) 28.3 2.20, td (12.5, 3.0) 14β 2.02, br d (12.5) 15 30.2 2.17, m 30.6 2.11, br t (11.5 Hz) 16 48.0 3.08, br s 49.3 2.93, m 17 177.1 - n.d. - 18 10.3 0.66, t (7.5) 10.7 0.71, t (7.5) 19 23.1 1.64, m 22.9 1.58, m 1.38, m 1.31, m 20 49.0 2.42, br t (7.5) 50.2 2.41, m 21 177.9 - n.d. - CH3-N1 29.3 3.73, s
Conclusion
Our protocol shows a significant improvement for the isolation of indole alkaloids. Indeed, with the classical extraction, the non-basic compounds would not have been extracted such as ionic compounds like nukuhivensiums. In a continuous work for improvements of structural, physical and chemical characteristics, additional NMR spectroscopy can be performed, in order to describe the relative configuration of some compounds, like NOESY experiments.
This protocol allowed the characterization of different structure of indole alkaloids different skeletons as well as stereoisomers (normal and iso compounds such as sandwicine and isosandwicine) and analogous series (normal and Nor- compounds such as sandwicine and Norsandwicine). Therefore, the method described here is more efficient and requires less time solvent consuming.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Fanglian He for inviting us to write this manuscript. The authors are grateful to Diren (Direction de l’Environnement de la Polynésie française) department for financial aid. This protocol have been written with the great help of Pr. Olivier P. Thomas, and the authors thank him for his work and advice.
References
- Fan, T. (1996). Metabolite profiling by one-and two-dimensional NMR analysis of complex mixtures. Prog Nucl Mag Res Sp 28(2): 161-219.
- Keeler, J. (2011). Understanding NMR spectroscopy. John Wiley & Sons.
- Lewitt, M. H. (2001). Spin dynamics: basics of nuclear magnetic resonance. John Wiley & Sons.
- Martin, N. J., Ferreiro, S. F., Barbault, F., Nicolas, M., Lecellier, G., Paetz, C., Gaysinski, M., Alonso, E., Thomas, O. P., Botana, L. M. and Raharivelomanana, P. (2015). Indole alkaloids from the Marquesan plant Rauvolfia nukuhivensis and their effects on ion channels. Phytochemistry 109: 84-95.
- Martin, N. J., Prado, S., Lecellier, G., Thomas, O. P. and Raharivelomanana, P. (2012). Nukuhivensiums, indolo[2,3-a]quinoliziniums from the Marquesan plant Rauvolfia nukuhivensis. Molecules 17(10): 12015-12022.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Martin, N. J., Nicolas, M., Lecellier, G. and Raharivelomanana, P. (2015). Isolation and Characterization Procedure for Indole Alkaloids from the Marquesan Plant Rauvolfia Nukuhivensis. Bio-protocol 5(20): e1625. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1625.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Other compound
Plant Science > Plant metabolism > Metabolite profiling
Biochemistry > Other compound > Alkaloid
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









