- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Determination of Hydroquinone Dioxygenase Activity
Published: Vol 5, Iss 17, Sep 5, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1580 Views: 8181
Reviewed by: Fanglian HeKanika GeraAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

H2 Production from Methyl Viologen–Dependent Hydrogenase Activity Monitored by Gas Chromatography
Nuttavut Kosem
Dec 5, 2023 1769 Views

Monitoring Protein Stability In Vivo Using an Intein-Based Biosensor
John S. Smetana [...] Christopher W. Lennon
Apr 20, 2025 1584 Views

Endo-1,4-β-D-xylanase Assay Using Azo-Xylan and Variants Thereof
Luca Bombardi [...] Salvatore Fusco
Apr 20, 2025 1927 Views
Abstract
We recently demonstrated the presence of a quinone detoxification pathway present in Firmicutes. It is based on two enzyme activities, namely a hydroquinone dioxygenase, YaiA, described here, and a hydroquinone reductase, YaiB, described in a separate protocol. In Lactococcus lactis (L. lactis), these enzymes are encoded by the yahCD-yaiAB operon. The operon is induced by copper to prevent the synergistic toxicity of quinones and copper. The hydroquinone dioxygenase, YaiA, converts hydroquinones to 4-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde, using molecular oxygen as oxidant according to the reaction: hydroquinone + O2 → 4-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde + H+ We here describe two methods for measurements for hydroquinone dioxygenase activity, based on oxygen consumption measured with an oxygen electrode and the spectrophotometric detection of 4-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde. Both assays are conducted with crude cell extracts.
Materials and Reagents
- Hydroquinone dioxygenase from an Escherichia coli (E. coli) strain heterologously overexpressing such an enzyme from a plasmid (Mancini et al., 2015)
- Hydroquinone (100 mM in ethanol) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H9003 )
- 50 mM Tris-Cl [pH 7.5, 10% (v/v) glycerol]
- 20 mM Tris-Cl (pH 7.5)
- 10 mg/ml DNaseI (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 11284932001 )
- 10 mM isopropyl-b-D-thiogalactoside (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: I6758 )
- 100 mM 4-hydroxybenzoate (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H5501 )
- 100 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P7626 )
- 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (Roche Diagnostics)
- Nitrocellulose filters (0.45 μm pore size)
- 100 mM hydroquinone (see Recipes)
- 50 mM Tris-Cl (see Recipes)
- 20 mM Tris-Cl (see Recipes)
- 10 mg/ml DNaseI (see Recipes)
- 10 mM isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside (see Recipes)
- 100 mM 4-hydroxybenzoate (see Recipes)
- 100 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Thermostated spectrophotometer (Shimadzu, model: UV2600 or similar)
- Clark electrode (Warner Instruments, model: 1302 or any other commercial oxygraph)
- French Press
Procedure
- Preparation of crude E. coli extracts containing YaiA
E. coli BL21(DE) containing plasmid pCA31 (Mancini et al., 2015) was grown aerobically in 300 ml of LB broth containing 100 μg/ml of ampicillin at 37 °C to an OD at 600 nm of 0.4. Then, 0.1 mM isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside was added, and growth was continued for 8 h at room temperature. Cells were harvested by centrifugation, and pellets suspended in 20 mM Tris-Cl (pH 7.5), containing 1 mM 4-hydroxybenzoate to stabilize protein as described elsewhere (Moonen et al., 2008), 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, and 100 μg/ml of DNaseI. Cells were then broken by three passages through a French Press at 40 MPa, and cell debris was removed by centrifugation at 4 °C for 20 min at 90,000 x g. The supernatant was filtered through a 0.45 μm nitrocellulose filter and stored frozen at -20 °C until used. - YaiA Activity assay by spectrophotometry
- Mix 50 mM Tris-Cl, pH 7.5, 10% (v/v) glycerol with 1 mg of crude extract in a total volume of 990 µl and warm to 30 °C in the spectrophotometer. This temperature was chosen since the origin of YaiA is L. lactis, which grows best at 30 °C.
- Zero the spectrophotometer and record the baseline spectrum from 300 to 400 nm. Start the reaction by adding 10 µl of 100 mM hydroquinone (final concentration 1 mM) and record spectra every 5 to 15 min, depending on the rate of the reaction. Calculate the specific activity from the increase in absorption at 320 nm, using an extinction coefficient for 4-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde of 11,000 M-1 cm-1 (Moonen et al., 2008; Spain and Gibson, 1991). Running spectra rather than measuring absorption at 320 nm is important to assured that the desired reaction is measured in the crude extracts. This should be further validated by calculating difference spectra (see Figure 1 and Note 1).
Enzyme kinetics- To determine the Km for hydroquinone, run enzyme reactions with 1, 3, 10, 30, 100, 300 and 1,000 µM hydroquinone.
- Determine the initial reaction rate, v0, for each reaction. If the reaction is linear, v0 is the slope of the linear regression of the data (e.g. calculated with the corresponding function built into Excel). If the reaction curve is sigmoidal, only the initial (highest) slope should be considered. Plot v0 versus the substrate concentrations, S.
- Fit the curve to obtain the affinity for the substrate, Km, and the maximal velocity, vmax. Alternatively, plot v0 versus 1/S to obtain a Lineweaver-Burk plot. The regression line intercepts the ordinate at 1/vmax and the abscissa at -1/Km.
- To determine the Km for hydroquinone, run enzyme reactions with 1, 3, 10, 30, 100, 300 and 1,000 µM hydroquinone.
- Mix 50 mM Tris-Cl, pH 7.5, 10% (v/v) glycerol with 1 mg of crude extract in a total volume of 990 µl and warm to 30 °C in the spectrophotometer. This temperature was chosen since the origin of YaiA is L. lactis, which grows best at 30 °C.
- YaiA activity assay by measuring oxygen consumption
- In a 1 ml chamber fitted with a Clark oxygen electrode or in any commercial oxygraph chamber, thermostated to 30 °C, mix 50 mM Tris-Cl (pH 7.5), 10% (v/v) glycerol, with 1 mg of crude extract.
- When a constant rate of oxygen consumption is attained (basal oxygen consumption due to other enzyme activities), inject 10 µl of 100 mM hydroquinone into the chamber and continue to record the oxygen consumption.
- Subtract the basal oxygen consumption from the rate observed with hydroquinone. Calculate the specific activity by calculating the oxygen consumption, based on the chamber volume and the oxygen content of the buffer, which can be taken from Estabrook (1967) or, if high precision is required calculated as described by Rasmussen and Rasmussen (2003). Under our conditions, buffer at 30 °C contains 222 µM O2.
Enzyme kinetics- To determine the Km for hydroquinone, run enzyme reactions with 1, 3, 10, 30, 100, 300 and 1,000 µM quinone.
- Determine the initial reaction rate, v0, for each reaction and plot v0 versus the substrate concentrations, S.
- Fit the curve to obtain the affinity for the substrate, Km, and the maximal velocity, vmax. Alternatively, plot 1/v0 versus 1/S to obtain a Lineweaver-Burk plot, from which Km and vmax can be determined.
- To determine the Km for hydroquinone, run enzyme reactions with 1, 3, 10, 30, 100, 300 and 1,000 µM quinone.
- In a 1 ml chamber fitted with a Clark oxygen electrode or in any commercial oxygraph chamber, thermostated to 30 °C, mix 50 mM Tris-Cl (pH 7.5), 10% (v/v) glycerol, with 1 mg of crude extract.
Representative data
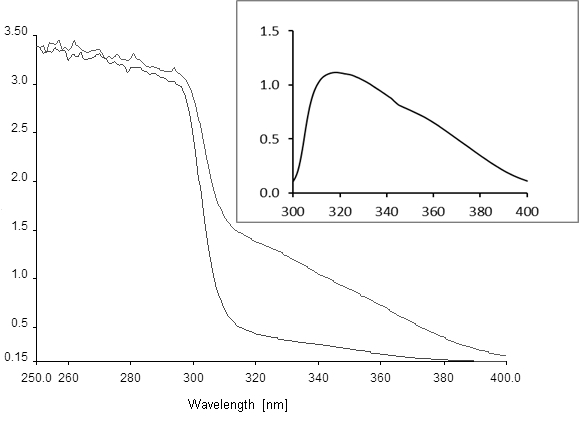
Figure 1. Absorption spectra of hydroquinone conversion to 4-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde. The lower curve was recorded at time 0 and the upper curve after 60 min of reaction. Inset, difference spectrum recorded between YaiA-containing extract incubated with and without 1 mM hydroquinone for 1 h, showing the absorption maximum of the reaction product at 320 nm. Axis labels are the same as in the main figure. Note that the spectra will look differently if substituted hydroquinones are used as the substrate for YaiA, but are not expected to change for different YaiA-like enzymes.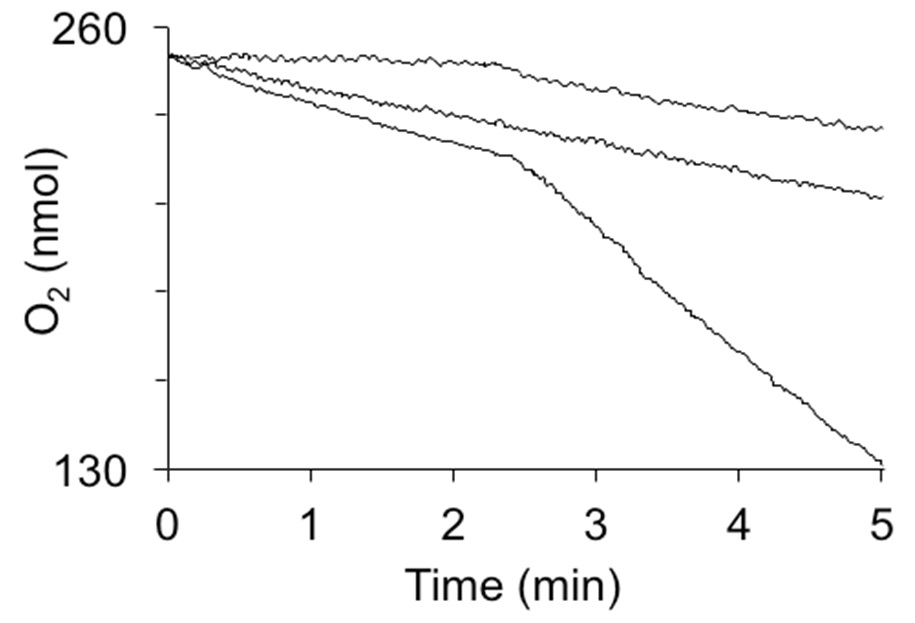
Figure 2. Oxygen consumption by hydroquinone dioxygenase activity in crude extracts. The reactions were induced by the addition of 1 mM hydroquinone at 2.5 min. Curves from top to bottom are: 1 mg of cytoplasmic extract from E. coli not expressing hydroquinone dioxygenase, extract heated to 95 °C for 5 min, and 1 mg of cytoplasmic extract from E. coli strain expressing YaiA of Lactococcus lactis from a plasmid.
Notes
- If difference spectra between unreacted and reacted extracts show the expected absorption spectrum for 4-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde, activity may be measured by continuous recording at 320 nm.
- Hydroquinone dioxygenase from L. lactis could not be purified in an active state and in crude cell lysates of L. lactis, the activity was too low to be detected.
- 4-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde is very labile and difficult to isolate and characterize. However, no change in absorbance was observed over at least one hour once the reaction had come to completion.
- Hydroquinone must be prepared fresh on the day of use due to the spontaneous auto-oxidation to benzoquinone in the presence of oxygen. No significant autoxidation of the stock solution was observed within 8 h.
Recipes
- 100 mM hydroquinone
Dissolved in 100% ethanol
Stored at room temperature in the dark - 50 mM Tris-Cl (pH 7.5)
10% (v/v) glycerol
Stored at 4 °C or autoclave to prevent bacterial growth - 20 mM Tris-Cl (pH 7.5)
Stable at room temperature - 10 mg/ml DNaseI
Stable at -20 °C - 10 mM isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside
Stable at -20 °C - 100 mM 4-hydroxybenzoate
Stable at room temperature - 100 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
Dissolve in 100% dimethylsulfoxide and store at -20 °C
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Russian Federation Government Grant 14.Z50.31.0011 to leading scientists. The procedure has previously been described in Mancini et al. (2015).
References
- Estabrook, R. W. (1967). Mitochondrial respiratory control and the polarographic measurement of ADP:O ratios. Methods Enzymol 10, 41-47.
- Mancini, S., Abicht, H. K., Gonskikh, Y. and Solioz, M. (2015). A copper-induced quinone degradation pathway provides protection against combined copper/quinone stress in Lactococcus lactis IL1403. Mol Microbiol 95(4): 645-659.
- Moonen, M. J., Kamerbeek, N. M., Westphal, A. H., Boeren, S. A., Janssen, D. B., Fraaije, M. W. and van Berkel, W. J. (2008). Elucidation of the 4-hydroxyacetophenone catabolic pathway in Pseudomonas fluorescens ACB. J Bacteriol 190(15): 5190-5198.
- Rasmussen, H. N. and Rasmussen, U. F. (2003). Oxygen solubilities of media used in electrochemical respiration measurements. Anal Biochem 319(1): 105-113.
- Spain, J. C. and Gibson, D. T. (1991). Pathway for Biodegradation of p-Nitrophenol in a Moraxella sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 57(3): 812-819.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Mancini, S. and Solioz, M. (2015). Determination of Hydroquinone Dioxygenase Activity. Bio-protocol 5(17): e1580. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1580.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









