- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Chlorophyll Fluorescence Measurements in Arabidopsis Wild-type and Photosystem II Mutant Leaves
Published: Vol 5, Iss 14, Jul 20, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1532 Views: 12584
Reviewed by: Tie LiuAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols
![Assessing Long-distance Transport from Photosynthetic Source Leaves to Heterotrophic Sink Organs with [<sup>14</sup>C]CO<sub>2</sub>](https://en-cdn.bio-protocol.org/imageup/arcimg/20171211011113752.jpg?t=1768685256)
Assessing Long-distance Transport from Photosynthetic Source Leaves to Heterotrophic Sink Organs with [14C]CO2
Umesh P Yadav [...] Brian G Ayre
Dec 20, 2017 6569 Views
![Quantifying the Capacity of Phloem Loading in Leaf Disks with [<sup>14</sup>C]Sucrose](https://en-cdn.bio-protocol.org/imageup/arcimg/20171211011350163.jpg?t=1768685256)
Quantifying the Capacity of Phloem Loading in Leaf Disks with [14C]Sucrose
Umesh P Yadav [...] Brian G Ayre
Dec 20, 2017 8013 Views
13CO2-labelling and Sampling in Algae for Flux Analysis of Photosynthetic and Central Carbon Metabolism
Or Geffen [...] Haim Treves
Sep 5, 2023 1921 Views
Abstract
Chlorophyll fluorescence measurement is a widely used technique to determine photosynthetic performance. Light energy absorbed by a chlorophyll molecule can be dissipated by driving photochemical energy conversion, as heat in non-photochemical quenching processes, or it is re-emitted as fluorescence. The loss of light energy as chlorophyll fluorescence is primarily derived from photosystem II. Photosystem II is a thylakoid-embedded multiprotein complex which provides the high redox potential needed to oxidize water. Within photosystem II photons of light are captured and used to energize electrons. Energized electrons are fed into the linear electron transport chain and photosystem II replenishes lost electrons with electrons from splitting of water. Chlorophyll fluorescence yield can be quantified using a modulated fluorometer device. In such a device, a modulated measuring light beam (switched on and off at a high frequency) and the parallel detection of fluorescence exclusively excited by the measuring light allows chlorophyll fluorescence measurements in the presence of photosynthetic (actinic) light. In addition, high intensity, but short duration light flashes (saturating pulses) are used to determine maximum fluorescence yields in dark and light adapted leaves. In this protocol the procedure to receive a typical fluorescence graph of Arabidopsis wild-type leaves is given. Furthermore, this procedure can be used to identify Arabidopsis mutant plants affecting photosystem II, on the basis of the respective fluorescence graphs and values.
Keywords: ArabidopsisMaterials and Reagents
- Arabidopsis wild-type plants (Ecotype: Col-0)
- Arabidopsis mutant plant of interest (Ecotype: Col-0)
- Stender Vermehrungssubstrat A210, 70 potting soil (Stender AG)
- Planting pots (7 x 6 x 6 cm)
- Plant tray and plastic wrap
- Tweezers (not sterile)
Equipment
- Cold room or refrigerator (4 °C)
- Growth chamber (12 h light/12 h dark with 21 °C/18 °C and a PFD of ~ 100 µmol/m2/s)
- Dual-PAM-100 for measuring chlorophyll fluorescence (Heinz Walz GmbH, model: Dual-PAM-100) connected to a PC and operated by the Dual-PAM software (see Note 1)
- Dark room
Software
- Dual-PAM software
Procedure
- Growing Arabidopsis plants
- Seeds of Arabidopsis wild-type and mutants lines are transferred to planting pots (approximately 20 seeds per pot) filled with completely soaked soil. Place a plastic wrap to cover the plants to keep necessary humidity.
- Put the pots in a tray in 4 °C for 3 days to synchronize germination.
- Transfer tray into a growth chamber with the plastic wrap still covering.
- Normally seeds germinate within 4-5 days, remove the plastic wrap 2 days afterwards.
- Transfer individual plants into fresh pots (one plant per pot) filled with fresh, soaked soil after 7 further days using slightly curved tweezers.
- Cultivate Arabidopsis plants in the same condition as before for another 1 or 2 weeks. See Note 2.
- Seeds of Arabidopsis wild-type and mutants lines are transferred to planting pots (approximately 20 seeds per pot) filled with completely soaked soil. Place a plastic wrap to cover the plants to keep necessary humidity.
- Recording chlorophyll fluorescence
- Make sure that the Dual-PAM-100 device is properly connected to the PC and placed in a dark room.
- Place 3-4 week old Arabidopsis wild-type plants in a dark room for at least 30 min (this incubation is called dark adaptation). Perform subsequent steps in darkness. (Optional) Turn on green light for handling plants.
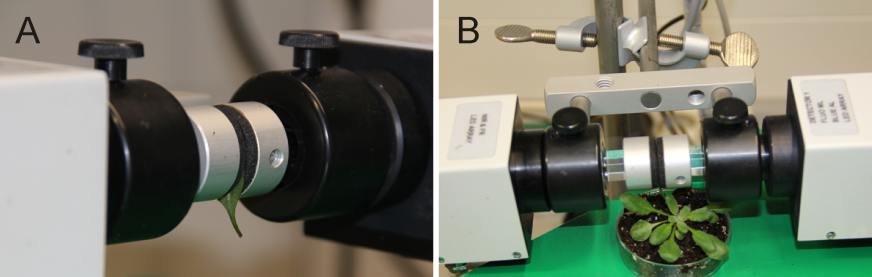
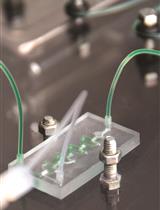
Figure 1. Set up sample leaves between the measuring head of the Dual-Pam-100 device. For the protocol given here (e.g. duration time 6 min) a detached leaf is fixed between the measuring head (A). For modified protocols it might be useful to keep the plant intact by using an attached leaf between the measuring head (B).
- Take a middle aged (e.g. the seventh leaf from the apex by counting down) wild-type rosette leaf and fix it between Dual-PAM-100 measuring heads (Figure 1A). (Optional) Try to fix the leaf, still attached to the remaining plant, between the measuring heads (Figure 1B).
- Switch on the Dual-PAM software and define the settings. To measure chlorophyll fluorescence choose the <Fluo> and <SP-analysis> mode. A typical set up includes measuring light at 12 µmol/m2/s, the saturated pulse (SP) at 10,000 µmol/m2/s for 800 ms and the actinic light at 70 µmol/m2/s. Save user settings, thus allowing quick start.
- Open the <Slow Kinetics> window and apply measuring light for approximately 10 sec, fluorescence level is minimal (F0).
- Application of a saturated pulse will induce a maximal fluorescence level (Fm).
- After another minute switch on actinic light. Adjust the light intensity of the actinic light to growth light (see above). Perform actinic light treatment for 5 min, the level of fluorescence at that point is called Ft (= F0’ in <Report> window).
- A second saturated pulse is applied, which allows the measurement of the maximum fluorescence in the light (Fm’).
- Switch off actinic light, stop recording, export <Slow Kin. File> into a table calculation program (e.g. Excel) and recreate the graph (Figure 2A). Optional: Values can be averaged to recreate the graph. Repeat the measurement 3 times with different wild-type plants, but use leaves of corresponding age (e.g. the seventh leaf from the apex by counting down).
- Repeat the measurement with a leaf of the dark-adapted mutant plant (Figure 2B).
- Make sure that the Dual-PAM-100 device is properly connected to the PC and placed in a dark room.
- Calculation of photochemical quenching parameters
- Open the <Report> window. Values for F0 and Fm are given. Calculate the maximum quantum yield according to the following formular (Maxwell and Johnson, 2000): Fv/Fm = (Fm – F0)/Fm
- Values for Ft (= F0 in <Report> window) and Fm’ are given in <Report>. Calculate the effective quantum yield of PSII photochemistry (Maxwell and Johnson, 2000):
ΦII = (Fm’ - Ft)/ Fm’
- Open the <Report> window. Values for F0 and Fm are given. Calculate the maximum quantum yield according to the following formular (Maxwell and Johnson, 2000): Fv/Fm = (Fm – F0)/Fm
Representative data
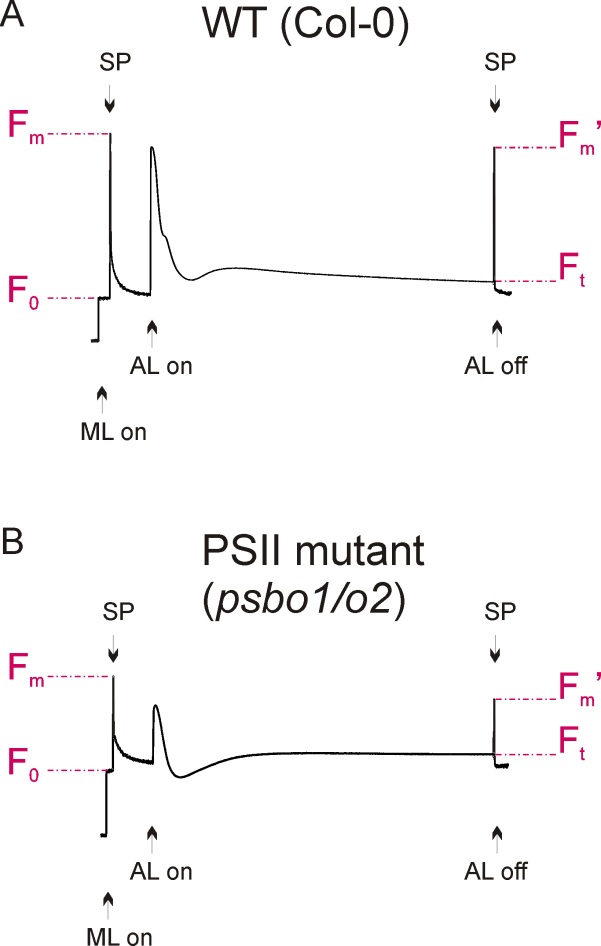
Figure 2. Fluorescence graphs of a wild-type (A) and a reference PSII mutant plant (B), see Note 3. Application of measuring light (ML) and saturated light pulses (SP) are indicated. Exposure to actinic light is shown and fluorescence parameters F0, Fm, Ft and Fm’ are denoted.
Notes
- For first time users it is recommended to start with the Junior PAM device, because of its easy set up and use (Heinz Walz GmbH, http://www.walz.com/products/chl_p700/junior-pam/introduction.html).
- It is important to grow healthy Arabidopsis plants, because any stress condition will eventually affect photosynthetic performance. Do not injure the root system upon transfer. Water plants approximately twice a week.
- A typical wild-type fluorescence graph is shown in Figure 2A. The fluorescence graph of a reference photosystem II mutant (psbo1/o2) is shown in Figure 2B. This mutant was generated by crossing psbo1-3 and psbo2-2, which carry a T-DNA insertion in exon 1 of PsbO1 and in the 5’ UTR of PsbO2, respectively (Figure 3A). Disruption of PsbO1 and PsbO2 entails a reduced PsbO protein level (Figure 3B). Particular mentionable is the drop of fluorescence below the F0 value after switching on actinic light. This phenomenon concomitant with a reduced Fv/Fm value is typically observed in PSII mutants (Peng et al., 2006; Armbruster et al., 2010; Schneider et al., 2014). Almost any PSII mutant with these characteristics is reduced in growth (Figure 3C).
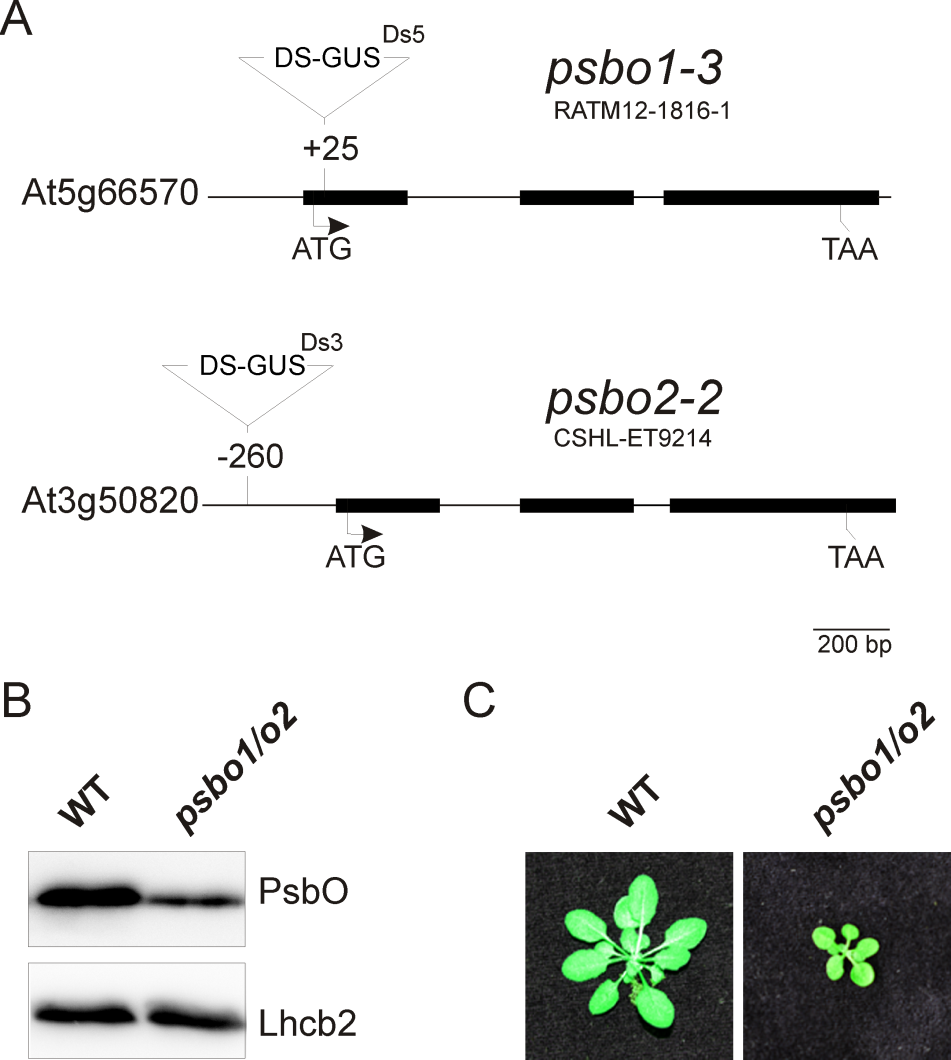
Figure 3. Generation of a reference PSII mutant plant (psbo1/o2) by crossing the homozygous T-DNA insertion line RATM12-1816-1 and homozygous T-DNA insertion line CSHL-ET9214 (A). The PsbO protein content is reduced in the psbo1/o2 mutant line as deduced from immunoblotting using a PsbO- and anLhcb2-specific antibody (B). Wild-type and psbo1/o2 mutant plants were grown for 4 weeks in a growth chamber (C).
Acknowledgments
This protocol was adapted or modified from previous work by Meurer et al. (1995). We thank Thilo Rühle for discussion and comments on the protocol. This work was carried out in the laboratory of Prof. Dario Leister (Biozentrum der LMU München, Department Biologie I, Munich, Germany) and supported by funds from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (LE 1265/20-1) to D.L.
References
- Armbruster, U., Zuhlke, J., Rengstl, B., Kreller, R., Makarenko, E., Ruhle, T., Schunemann, D., Jahns, P., Weisshaar, B., Nickelsen, J. and Leister, D. (2010). The Arabidopsis thylakoid protein PAM68 is required for efficient D1 biogenesis and photosystem II assembly. Plant Cell 22(10): 3439-3460.
- Maxwell, K. and Johnson, G. N. (2000). Chlorophyll fluorescence--a practical guide. J Exp Bot 51(345): 659-668.
- Meurer, J., Meierhoff, K. and Westhoff, P. (1995). Isolation of high-chlorophyll-fluorescence mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana and their characterization by spectroscopy, immunoblotting and Northern hybridization. Planta 198, 385-396.
- Peng, L., Ma, J., Chi, W., Guo, J., Zhu, S., Lu, Q., Lu, C. and Zhang, L. (2006). LOW PSII ACCUMULATION1 is involved in efficient assembly of photosystem II in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 18(4): 955-969.
- Schneider, A., Steinberger, I., Strissel, H., Kunz, H. H., Manavski, N., Meurer, J., Burkhard, G., Jarzombski, S., Schunemann, D., Geimer, S., Flugge, U. I. and Leister, D. (2014). The Arabidopsis Tellurite resistance C protein together with ALB3 is involved in photosystem II protein synthesis. Plant J 78(2): 344-356.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Steinberger, I., Egidi, F. and Schneider, A. (2015). Chlorophyll Fluorescence Measurements in Arabidopsis Wild-type and Photosystem II Mutant Leaves. Bio-protocol 5(14): e1532. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1532.
Category
Plant Science > Plant physiology > Photosynthesis
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











