- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Measurement of Mitochondrial Respiration Rate in Maize (Zea mays) Leaves
Published: Vol 5, Iss 10, May 20, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1483 Views: 9003
Reviewed by: Tie LiuFernanda SalvatoFang Xu

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Using Silicon Polymer Impression Technique and Scanning Electron Microscopy to Measure Stomatal Aperture, Morphology, and Density
Hui-Chen Wu [...] Tsung-Luo Jinn
Aug 20, 2017 10223 Views
An Image Analysis Pipeline to Quantify Emerging Cracks in Materials or Adhesion Defects in Living Tissues
Stéphane Verger [...] Olivier Hamant
Oct 5, 2018 6629 Views

Closed Systems to Study Plant–Filamentous Fungi Associations: Emphasis on Microscopic Analyses
Vasiliki Skiada and Kalliope K. Papadopoulou
Feb 20, 2025 2719 Views
Abstract
Mitochondria play essential roles in plant growth and development as they host the oxidative phosphorylation pathways, tricarboxylic acid cycle and other important metabolisms. Disruption of mitochondrial functions frequently leads to embryo lethality. Moreover, mitochondria play roles in programmed cell death, pathogen and stress responses in plants. In contrast to animal mitochondria, plant mitochondria possess an additional electron transport pathway, the cyanide-resistant alternative pathway catalyzed by a single alternative oxidase (AOX). Unlike cytochrome pathway that is coupled to oxidative phosphorylation via proton translocation, electron transport from ubiquinol to AOX is non-phosphorylating. It releases the energy as heat. Chlorolab II liquid-phase oxygen electrode (Hansatech) is a high-precise Clark type oxygen electrode, which is equipped with the powerful WINDOWS software and could record the oxygen changes in real time. Its electrode disc comprises a central platinum cathode and a concentric silver anode. The electrode disc is connected to an electrode control unit which applies a small polarising voltage between the platinum and silver electrodes. In the presence of oxygen, a small current is generated proportional to oxygen content in the sample. It could respond sensitively and rapidly to small changes of oxygen content in the sample. This protocol describes how to measure the mitochondrial total respiration rate, cytochrome pathway capacity as well as alternative pathway capacity in maize leaves with chlorolab II oxygen electrode.
Keywords: Mitochondrial total respiration rateMaterials and Reagents
- Leaves of maize seedlings
- Potassium cyanide (KCN) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 207810 )
- Salicylhydroxamic acid (SHAM) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S607 )
- Sodium dithionite (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 71699 )
- Reaction medium buffer (see Recipes)
- 0.2 M KCN (see Recipes)
- 0.2 M SHAM (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Chlorolab II liquid-phase oxygen electrode (Hansatech)
- Thermostatic water bath
- Circulating water pump
- Microsyringe (50 μl)
Procedure
- The maize seedlings were cultured in potting soil under the growth conditions (at 22 ± 2 °C with a 16-h light / 8-h dark photoperiod and light density of 150 µmol/m2/s) for 2 weeks.
- Before measurement, the maize seedlings were kept in the dark for about 2 h in order to reduce the influence of photosynthesis.
- Open the thermostatic water bath and set its temperature to 25 °C; meanwhile, put the reaction medium buffer (about 200 ml) and circulating water pump into it.
- Clean the oxygen electrode: Dip a swab into the rapid electrode disc polish (provided with the equipment), and clean the anode and cathode of the electrode with it (Figure 1A); then wash the electrode with distilled water, and remove the surface water with an absorbent paper.
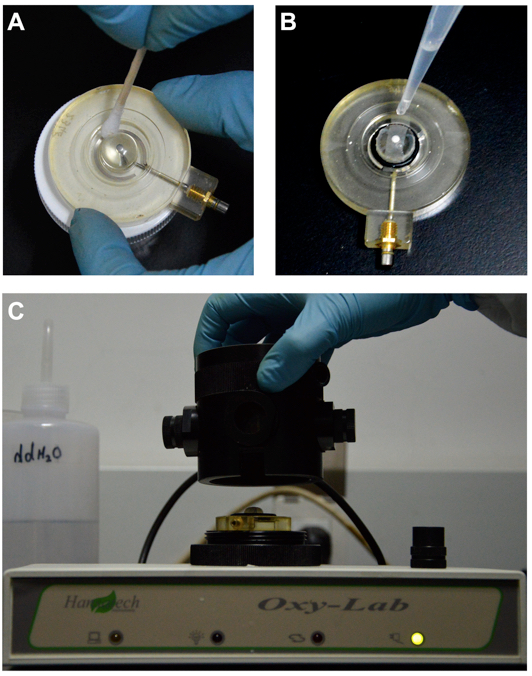
Figure 1. Preparation of electrode disc. A. Clean the electrode disc. B. Install the electrode membrane. C. Install the electrode disc. - Install the electrode membrane on the basis of instructions (Figure 1B):
- Place a small drop of electrolyte (the half saturation KCl) on top of the dome of the electrode disc (cathode);
- Place a piece of 1.5 cm wide and 3.5 cm long salt-bridge paper over the electrolyte, and ensure that at least one corner is in the electrode well to act as a wick;
- Cover this with a piece of electrode membrane (P. T. F. E membrane), which is selectively permeable to oxygen molecules;
- Place the small O-ring over the dome of the electrode disc with applicator tool;
- Add several drops of electrolyte into the electrode groove (anode).
Notes: The electrode membrane surface should be smooth and free of air bubbles.
- Place a small drop of electrolyte (the half saturation KCl) on top of the dome of the electrode disc (cathode);
- Install the electrode disc (Figure 1C): Holding the electrode chamber vertically, place the electrode into it so that the membrane-covered dome forms the floor of the electrode chamber.
- The balance of oxygen electrode: Add 50 ml of distilled water into the beaker, and fully stir it for a few minutes in order to sufficiently dissolve O2; put 2 ml of the air-saturated distilled water and the magnetic follower in the reaction chamber and start the oxygen electrode; connect circulating water pump with it to keep the temperature constant in the reaction chamber. The oxygen electrode should be balanced for about 30 min before calibration (Figure 2A).
- The calibration of the oxygen electrode:
- Establish “air line” in the reaction chamber.
Press successively “Calibrate” - “Oxygen” - “New” on the toolbar; then input the actual temperature and the atmospheric pressure in the calibration window and press “OK”; the oxygen concentration of distilled water in the chamber will be recorded in real time; when trace is stable, press “stop”. - Establish “zero oxygen line” in the reaction chamber.
When the screen displays “Establish zero oxygen in the chamber”, add the high concentration of sodium dithionite solution (prepared when using) into the reaction chamber with microsyringe, then press “OK”; at this time, the oxygen in distilled water will be consumed by sodium dithionite; When the oxygen concentration decreases nearly to zero and the trace is stable, the screen will display again “Establish air line in the chamber”; discard the solution in the reaction chamber and wash the reaction chamber, the cover and the magnetic follower with distilled water repeatedly; then add 2 ml of the air-saturated distilled water into the chamber, and press “OK”; when trace is stable, press “stop”. The calibration is completed.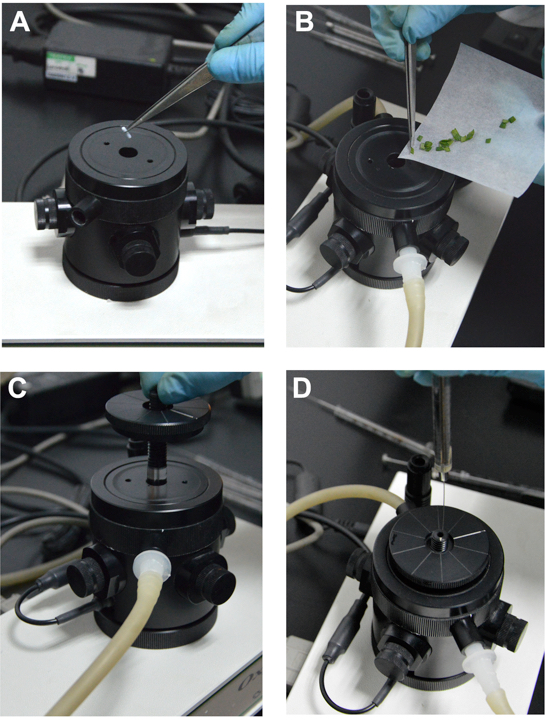
Figure 2. Respiration rate determination. A. Balance of oxygen electrode. B. Place the leaves into the reactive chamber and balance for 5 min. C. Put the electrode chamber cover and start recording respiration rate. D. Add the inhibitor with microsyringe in the process of determination.
- Establish “air line” in the reaction chamber.
- During measurement, about 0.15 g of maize seedling leaves were cut into the same size fragments (about 2 mm2), and O2 consumption rate was measured in the reaction medium buffer at 25 °C in the dark (Figure 2B).
- Measurement procedure: add 2 ml of the reaction medium buffer and leaves into the reaction chamber; balance for 5 min and then start recording O2 consumption for 2-3 min; stop recording and add 20 µl 0.2 M KCN with microsyringe into the reaction chamber, 1 min later, restart recording for 2-3 min; stop recording and add 20 µl 0.2 M SHAM, 2 min later, restart recording for 2-3 min. To avoid oxygen-limiting conditions inside the reaction chamber, all measurements were terminated before O2 reached about 50 to 60% of air saturation levels (Figure 2C and D).
- Respiration rate calculation: In the experiment, KCN and SHAM were used to inhibit the activity of cytochrome c oxidase and alternative oxidase, respectively. Mitochondrial total respiration (TP) was defined as O2 consumption rate in the absence of any additions. Residual respiration (RP) was defined as O2 consumption rate in the presence of 2 mM KCN and 2 mM SHAM. Cytochrome pathway capacity (CP) was defined as TP minus the values of O2 consumption rate in the presence of 2 mM KCN. Alternative pathway capacity was defined as TP minus both CP and RP (Figure 3).
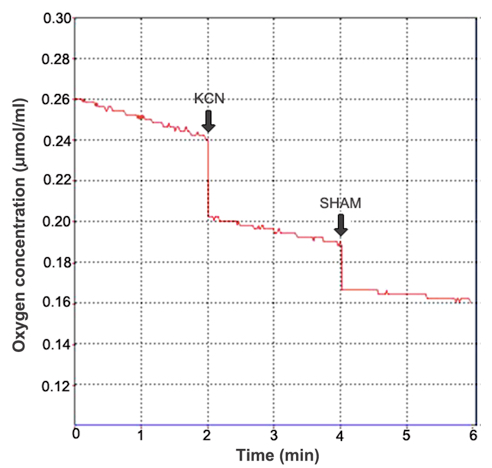
Figure 3. Calculation of the respiration rate. After the oxygen electrode was calibrated, the computer could display the actual O2 concentration in the reaction chamber in real time (Y-axis). Thus, the respiration rate could be calculated on the basis of the volume of reaction buffer in the reaction chamber, the changes of oxygen concentration, the reaction time and the fresh weight (FW) of leaves. The respiration rate can be expressed as µmol O2/min/g FW.
Recipes
- Reaction medium buffer
10 mM HEPES
10 mM MES
2 mM CaCl2
Adjust pH to 6.8 with KOH - 0.2 M KCN
Dissolved in distilled water - 0.2 M SHAM
Dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO)
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Research Grants Council of the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region to B.-C.T. (Project no. 473512 and 473611), and a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China to B.-C.T. (Project No. 31170298).
References
- Li, X. J., Zhang, Y. F., Hou, M., Sun, F., Shen, Y., Xiu, Z. H., Wang, X., Chen, Z. L., Sun, S. S., Small, I. and Tan, B. C. (2014). Small kernel 1 encodes a pentatricopeptide repeat protein required for mitochondrial nad7 transcript editing and seed development in maize (Zea mays) and rice (Oryza sativa). Plant J 79(5): 797-809.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Wang, X., Chang, N., Bi, Y. and Tan, B. (2015). Measurement of Mitochondrial Respiration Rate in Maize (Zea mays) Leaves. Bio-protocol 5(10): e1483. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1483.
Category
Plant Science > Plant metabolism > Respiration
Plant Science > Plant cell biology > Tissue analysis
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









