- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
MIFE Technique-based Screening for Mesophyll K+ Retention for Crop Breeding for Salinity Tolerance
Published: Vol 5, Iss 9, May 5, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1466 Views: 10451
Reviewed by: Tie LiuRumen Ivanov

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

A Simple Sonication Method to Isolate the Chloroplast Lumen in Arabidopsis thaliana
Jingfang Hao and Alizée Malnoë
Aug 5, 2023 2289 Views

A Plate Growth Assay to Quantify Embryonic Root Development of Zea mays
Jason T. Roberts [...] David M. Braun
Oct 20, 2023 2258 Views

Detection and Quantification of Programmed Cell Death in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: The Example of S-Nitrosoglutathione
Lou Lambert and Antoine Danon
Aug 5, 2024 1591 Views
Abstract
Potassium is known as a rate-limiting factor for crop yield and plays an important role in plants response under abiotic stresses. Recently, cytosolic K+ retention ability in leaf mesophyll has emerged as an important component of plant salt tolerance mechanism (Wu et al., 2013; Wu et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2015). In this protocol, the procedure for screening leaf mesophyll for K+ retention by the MIFE (microelectrode ion flux estimation) technique is described in detail using wheat as an example. By measuring NaCl-induced K+ efflux in leaf mesophyll, a large number of plant accessions can be screened and categorised according to their salinity stress tolerance. The method provides a rapid and reliable tool that targets the activity of specific membrane transporters directly contributing to salinity tolerance trait and, because of this, has a competitive advantage over traditional whole-plant phenotyping. While the focus of this protocol is on wheat, the suggested method may be adopted for screening K+ retention in leaf mesophyll in any other crop species.
Keywords: K+ retentionMaterials and Reagents
- Two to three week old wheat seedlings
- NaCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 746398 )
- KCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 746436 )
- CaCl2 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C5670 )
- K+ LIX (liquid ion exchanger) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 60031 )
- Tributylchlorosilane (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 282707 )
- ddH2O
- 95% ethanol (VWR International, catalog number CHESEA042-20L-P )
- Commercial bleach (contains 42 g/L NaClO)
- Agar (Oxoid, catalog number: LP0011 )
- Parafilm
- Basic salt medium (BSM) solution (mM) (see Recipes)
- Backfilling solution for K+ ion selective microelectrode (see Recipes)
- Filling solution for a reference electrode (see Recipes)
- K+ calibration solutions (μM) (see Recipes)
- Potting mix (see Recipes)
Equipment
- The MIFE (microelectrode ion flux estimation) system (designed, manufactured and distributed by the University of Tasmania)
(http://www.phys.utas.edu.au/physics/biophys/mifecom/MIFEHome/Home.html) - Glasshouse
- Vertical electrode puller (Narishige, model: PP-830 )
- Electrode filling station (contains a three-dimensional micromanipulator and a microscope)
- Laboratory fume cupboard (model: 1800)
- Inverted tissue culture microscope (Radical Instruments, model: RTC-6 )
- Microscope (Nikon, model: 100100 ) used in the electrode filling station
- Micromanipulator (Narishige, model: MMT-5 ) used in the electrode filling station
- Oven (Euromiad compact cooker, model: MC 110 T )
- Distiller (Labglass, model: 03DD )
- pH meter (Thermo Fisher Scientific, model: Orion 420 A +)
- Burner
- Magnetic stirrer (ISG® Hotplate and Magnetic stirrer, model: 153-005 ) and stirring bars
- Borosilicate glass capillaries (GC 150-10) (1.5 O.D. x 0.86 I.D. x 100 L mm) (Harvard Apparatus, catalog number: 30-0053 )
- Borosilicate glass capillaries (GC 100-10) (1.0 O.D. x 0.56 I.D. x 100 L mm) (Harvard Apparatus, catalog number: 30-0016 )
- Petri dishes (85 mm and 35 mm diameters)
- Perspex holder for immobilization of the leaf samples
- Metal electrode rack for electrode silanization
- Plastic electrode holder for storing silanized electrode blanks
- Standard surgical blades (Kiato stainless steel, model: BS 2982:1992, ISO 7740 )
- Syringe (Terumo, catalog number: SS-10L )
- Plastic needle (20 μl) (Eppendorf, catalog number: 5424 956.003 )
- Plastic-coated weights
- Silver wire (A-M Systems, catalog number: 787000 )
- 4.5 L PVC (polyvinyl chloride) pots
Procedure
- Plant material preparation
- Sow 12 to 14 seeds in a 4.5 L PVC pot (with a saucer) using the standard potting mix and grow them under glasshouse conditions (day/night temperature 23/18 °C; ~ 11 to 13 h photoperiod).
- After seedlings have emerged, thin plants to leave eight uniform plants per pot.
- Grow wheat plants until they are 15 to 20 days old (Figure 1).
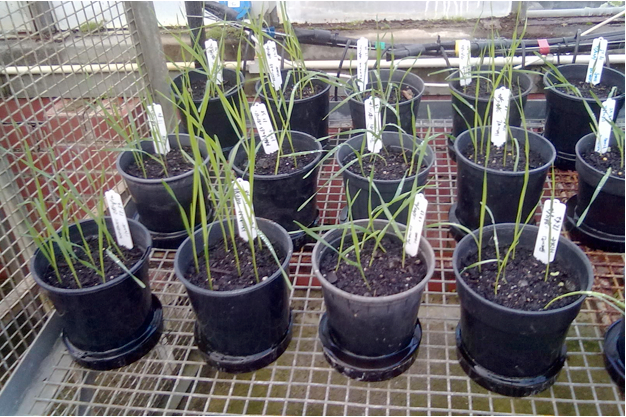

Figure 1. Two week- old wheat seedlings grown in a glasshouse
- Sow 12 to 14 seeds in a 4.5 L PVC pot (with a saucer) using the standard potting mix and grow them under glasshouse conditions (day/night temperature 23/18 °C; ~ 11 to 13 h photoperiod).
- Preparation of ion selective microelectrodes
- Electrode blank preparation
- Insert a non-filamentous borosilicate glass capillary (GC 150-10; 1.5 O.D. x 0.86 I.D. x 100 L mm) into a vertical electrode puller.
- Pull the glass capillary by heating the middle part into two blanks with external tip diameter of about 3-4 μm.
- Store the pulled blank electrodes in a stainless steel rack (Figure 2) in a vertical position with the tips positioned upwards.
- Put the steel rack with the blank electrodes into an oven located in a fume hood cabinet and heat them overnight at 225 °C.
- After 8-10 h of heating, cover the steel rack with a round shape steel lid and heat for a further 15 min.
- Inject a few drops of tributylchlorosilane under the lid (70 μl for a steel rack containing 36 blank electrodes, Figure 2) and heat for a further 10 min with the lid on. Depending on the number of blank electrodes in the steel rack, the volume of injected tributylchlorosilane should be adjusted.
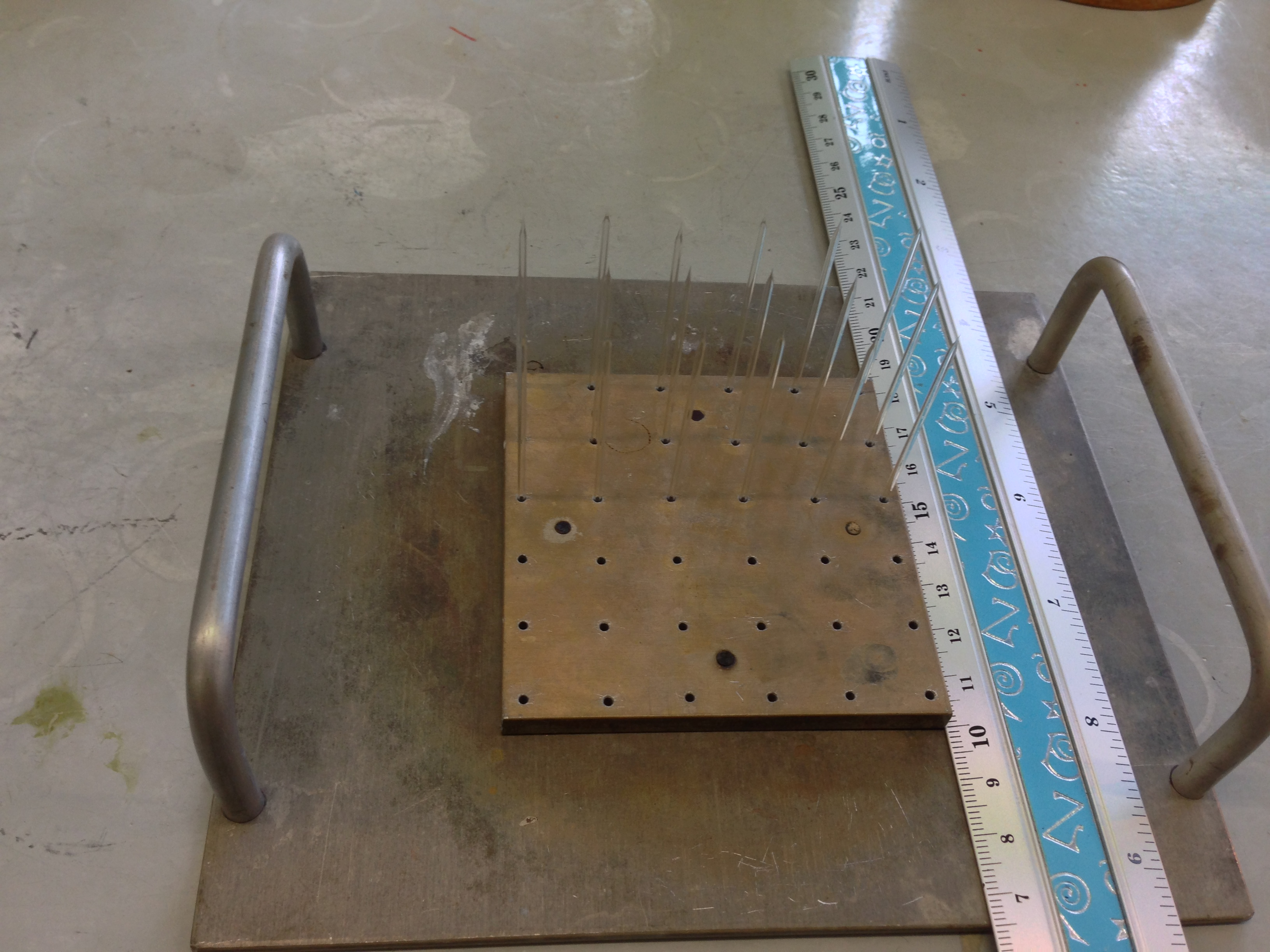
Figure 2. Pulled blank electrodes stored in the metal electrode rack - Remove the lid from the steel rack and continue heating the blank electrodes in the oven for a further 30 min.
- Switch off the oven and let the electrode blanks cool down inside the oven.
- Transfer the silanized blank electrodes to electrodes holder (Figure 3) and cover with a lid. Prepared electrode blanks can be stored up to a month.
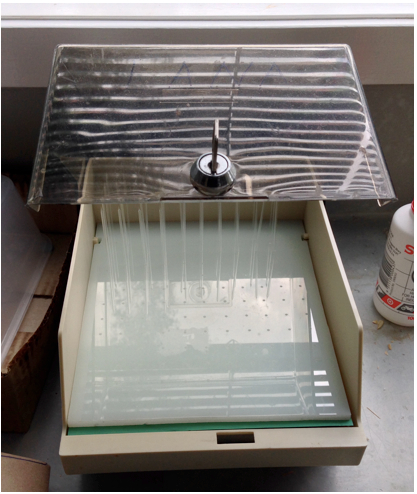
Figure 3. Perspex-made electrode holder
- Insert a non-filamentous borosilicate glass capillary (GC 150-10; 1.5 O.D. x 0.86 I.D. x 100 L mm) into a vertical electrode puller.
- Filling up electrodes
- Prepare a K+ LIX containing tube by dipping a pulled borosilicate glass capillary (GC 100-10; 1.0 O.D. x 0.56 I.D. x 100 L mm) with a broken tip (~ 50 μm diameter) into a bottle containing K+ LIX.
- Immobilize the silanized electrode blank in a microelectrode filling station and break the electrode tip against a flat glass surface under a microscope (step 1 showed in Figure B4a) to achieve the electrode tip diameter of 2-3 μm.
- Immobilize prepared K+ LIX tube horizontally in the filling station against the prepared microelectrode blank (step 2 showed in Figure 4a). Align tips of the microelectrode and the LIX-containing tube under the microscope (Figure 4b).
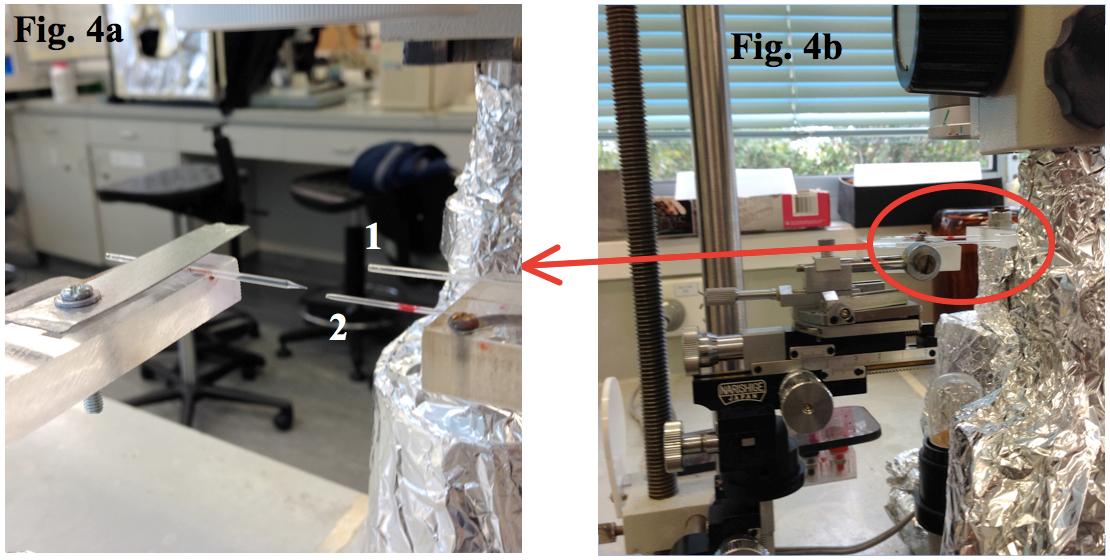
Figure 4. The blank electrode and a glass capillary containing K+ LIX are aligned at the filling station - Back-fill the microelectrode with a K+ backfilling solution using a syringe with a plastic needle. Ensure the absence of any air bubble adhered to the glass capillary in the electrode tip. Add more back filling solution if the latter occurred.
- Front-fill the electrode by briefly putting the electrode tip in a contact with the open tip of the LIX-containing tube to achieve a column length of about 100-150 μm.
- Store prepared microelectrode in containing a basic salt medium (BSM) solution (Figure 5).
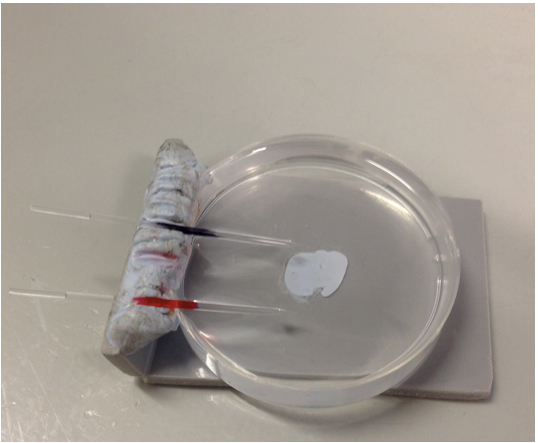
Figure 5. Electrodes stored in BSM solution
- Prepare a K+ LIX containing tube by dipping a pulled borosilicate glass capillary (GC 100-10; 1.0 O.D. x 0.56 I.D. x 100 L mm) with a broken tip (~ 50 μm diameter) into a bottle containing K+ LIX.
- Electrode blank preparation
- Preparation of a reference electrode
- Place pulled blank microelectrodes with broken tips (~ 50 μm tip diameter) into a wide neck glass container tips down.
- Prepare ~50 ml 2% (w/v) agar solution in 1 M KCl and melt it in a water bath.
- Pour the melted agar solution over prepared electrode blanks to immerse them completely in the agar solution. Ensure that internal parts of the glass capillaries are filled with the agar solution.
- Seal the top of the glass container once it has cooled down and store in a fridge for further use.
- For a reference electrode preparation, cut ~5 cm of a silver wire.
- Chlorinate the silver wire by immersing it into bottle containing commercial bleach for ~1-2 min leaving one end of the wire (~5 mm) exposed to air. Ensure that immersed part of the wire turned black.
- Insert the chlorinated silver wire into the prepared reference electrode blank (glass capillary filled with the 1 M KCl agar solution). Leave un-chlorinated part of the silver wire (5 mm) outside the glass capillary.
- Secure silver wire in the glass capillary with a strip of parafilm. Ensure that un-chlorinated part of the wire stays un-covered. Immerse the prepared reference electrode in a container with BSM and store them in a fridge until use.
- Place pulled blank microelectrodes with broken tips (~ 50 μm tip diameter) into a wide neck glass container tips down.
- Microelectrode calibration
Three calibration solutions with concentrations covering expected K+ concentration in the measured solution are used to calibrate K+ microelectrode. For example, for BSM containing 500 μM KCl, following KCl calibration solutions used are (μM): 250, 500, and 1,000.- Place prepared K+ microelectrode in the MIFE electrode holder and ensure that the channel used is connected to an amplifier. Insert the electrode in BSM.
- Connect the reference electrode to a channel designated for the reference electrode and insert it in the same BSM.
- Run the MIFE software CHART from the appropriate directory (see http://www.phys.utas.edu.au/physics/biophys/mifecom/MIFEHome/Home.html for details).
- Press “Alt + S” to <s>tart creating a calibration file.
- Press F7 to specify channel used for K+ microelectrode. Press “Enter”.
- Insert K+ microelectrode into the first K+ calibration solution (250 μM). Press F7 to specify K+ concentration used. Record calibration outputs for 20-30 sec. Once the recorded line is strait, press F7 to accept it. In case the line is not acceptable, press “No” in F7 menu and repeat the calibration.
- Insert the K+ microelectrode into other calibration solutions (500 μM and 1,000 μM, one at a time) and repeat step D6.
- Press “Alt + H” to end the data acquisition. Then press “Y” for <Y>es to confirm your choice.
- On completion of K+ microelectrode calibration, its quality must be checked. Press “Alt + E” to enter the <E>lectrometer menu, then choose “A” to <A>average data, then press “C” for the <C>alibration average. Average calibration file <.AVC> will be created by the CHART software automatically, and also the information about a set of parameters, e.g. slop, intercept, and correlation coefficients, of K+ microelectrode will be displayed in the screen.
- Examine displayed parameters: only K+ microelectrode with a slope above 50 mV per decade and a correlation coefficient above 0.999 are accepted and can be used for further experiments. If the calibration result doesn’t meet the requirement, new electrode has to be prepared and the calibration process repeated.
- Place prepared K+ microelectrode in the MIFE electrode holder and ensure that the channel used is connected to an amplifier. Insert the electrode in BSM.
- Preparing specimens
- Excise second youngest expanded leaf and place it in a beaker containing tap water.
- Using a sharp blade, cut the leaf segments angularly into small cross-sectional segments to expose mesophyll (5 to 8 mm each).
- Place leaf segments in an 85 mm diameter Petri dish containing BSM solution peeled side down and leave them floating on the surface in the darkness overnight to minimize possible confounding effects of tissue damage on ion fluxes (Shabala and Newman, 1999).
- After 10 to 12 h, mount the leaf segment in a Perspex holder and place it in a measuring chamber containing BSM solution.
- Press the holder to the bottom of the Petri dish with a plastic-coated weight.
- Leave the prepared sample to adapt for about 30 min.
- The leaf sample is ready for measurements now.
- Excise second youngest expanded leaf and place it in a beaker containing tap water.
- Measuring NaCl-induced K+ efflux from the leaf mesophyll by the MIFE technique
- Place the measuring chamber on a microscope stage and insert the reference electrode into it.
- Position the calibrated K+ microelectrode 40 μm away from the exposed mesophyll (Wu et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2015) under high magnification (200x) of the inverted microscope using three dimensional micromanipulators of the MIFE technique.
- Start the MIFE program CHART as described above for calibration.
- Set up a travel range of 70 μm between two positions and moving cycle of 6 sec/ 6 sec to enable electrode movement in a 12 sec square-wave cycle by a computer-controlled hydraulic manipulator.
- Record K+ fluxes from leaf samples under control (BSM solution) conditions for 5 min.
- Add concentrated NaCl stock solution to achieve 100 mM NaCl in the BSM solution and mix well with a pipette.
- Record NaCl-induced K+ fluxes for 10 min.
- Press “Alt + H” to end the data acquisition followed by “Y” for <Y>es to confirm your choice.
- Create an average file by pressing “Alt + E” to enter the <E>lectrometer menu, then choose “A” for <A>average option and “M” for the <M>anipulator cycle average. A box with “Experimental parameter values” will open. Press <Z> and type radius of the root (in μm); press <U> and type distance between the root and the microelectrode (typically 40 μm), then press <OK>. A new box will appear in the screen with indication of a valid time. Accept all by pressing <Enter>. An <.AVM> file will be created.
- Quit the CHART program by pressing “Alt + Q”.
- Place the measuring chamber on a microscope stage and insert the reference electrode into it.
- Flux calculation
- Run MIFEFLUX software by typing “mflux” in the MIFE directory [see Shabala et al. (2012) for details].
- Type the name of the recorded AVC file (calibration of the electrodes). Follow the prompt, and then type the name of the AVM file for which flux calculation is required.
- Choose <C> for cylindrical diffusion geometry (Newman, 2001; Shabala et al., 2006) and press <Enter>. A flux file with an extension <.flx> will be generated. The same calibration file can be used for calculating more flux files.
- Copy flux files to your working directory and use Excel for data analyses.
- Run MIFEFLUX software by typing “mflux” in the MIFE directory [see Shabala et al. (2012) for details].
- Flux data analyses
- Open Excel and find a flux file of interest in , open it.
- Plot K+ flux values against time and assess flux changes. Negative values of the flux are associated with K+ efflux, the larger the value the higher K+ efflux through the plasma membrane. The lower is the value, the better is K+ retention ability (and, hence, salt tolerance).
- Pay specific attention to a peak and steady state values under different conditions (in the presence and the absence of NaCl in the BSM).
- Open Excel and find a flux file of interest in , open it.
Notes
- Temperature-controlled room (~ 23 °C) is required.
- The K+ microelectrode must be changed daily.
- A capillary with the K+ LIX must be changed weekly.
- After silanizing, the flat side of the microelectrode must be flamed to avoid scratching the chlorinated silver wire.
- In general, the reference electrode must be changed weekly. Once the reference electrode is changed, the electrodes must be re-calibrated and the AVC file generated used for flux calculation of an AVM file generated using the same reference electrode.
- As tributylchlorosilane is toxic, electrode salinization should be conducted in a fume hood.
- An overview image of the whole measurement setup is available in our previously published papers (Wu et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2015).
Recipes
- Basic salt medium (BSM) solution (pH ~5.7)
0.1 mM CaCl2
0.5 mM KCl - Backfilling solution for K+ ion selective microelectrode
200 mM KCl - Filling solution for a reference electrode
1 M KCl
2% Agar - K+ calibration solutions (μM)
250, 500, and 1000 μM KCl - Potting mix
80% composted pine bark
10% sand and 10% coir peat, plus complete N:P:K (8:4:10), 1 kg/m3
Dolomite, 8 kg/m3
Gypsum, 1 kg/m3
Iron sulphate, 1 kg/m3
Isobutylenediurea, 1 kg/m3
Trace element mix, 0.75 kg/m3
Wetting agent, 0.75 Kg/m3
Zeolite, 0.75 Kg/m3
pH 6.0
Acknowledgments
This protocol was adapted from our previous publications (Wu et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2015; and Shabala et al., 2012). This work was supported by the Grain Research and Development Corporation grants to SS and MZ and by the Australian Research Council Discovery grant to SS.
References
- Newman, I. A. (2001). Ion transport in roots: measurement of fluxes using ion-selective microelectrodes to characterize transporter function. Plant Cell Environ 24(1): 1-14.
- Shabala, S., Cuin, T. A., Shabala, L. and Newman, I. (2012). Quantifying kinetics of net ion fluxes from plant tissues by non-invasive microelectrode measuring MIFE technique. Methods Mol Biol 913: 119-134.
- Shabala, S., Demidchik, V., Shabala, L., Cuin, T. A., Smith, S. J., Miller, A. J., Davies, J. M. and Newman, I. A. (2006). Extracellular Ca2+ ameliorates NaCl-induced K+ loss from Arabidopsis root and leaf cells by controlling plasma membrane K+ -permeable channels. Plant Physiol 141(4): 1653-1665.
- Shabala, S. and Newman, I. I. (1999). Light-induced changes in hydrogen, calcium, potassium, and chloride ion fluxes and concentrations from the mesophyll and epidermal tissues of bean leaves. Understanding the ionic basis of light-induced bioelectrogenesis. Plant Physiol 119(3): 1115-1124.
- Wu, H., Shabala, L., Barry, K., Zhou, M. and Shabala, S. (2013). Ability of leaf mesophyll to retain potassium correlates with salinity tolerance in wheat and barley. Physiol Plant 149: 515–527.
- Wu, H., Shabala, L., Zhou, M. and Shabala, S. (2014). Durum and bread wheat differ in their ability to retain potassium in leaf mesophyll: implications for salinity stress tolerance. Plant Cell Physiol 55(10): 1749-1762.
- Wu, H., Zhu, M., Shabala, L., Zhou, M. and Shabala, S. (2015). K+ retention in leaf mesophyll, an overlooked component of salinity tolerance mechanism: A case study for barley. J Integr Plant Biol 57(2): 171-185.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Wu, H., Shabala, L., Zhou, M. and Shabala, S. (2015). MIFE Technique-based Screening for Mesophyll K+ Retention for Crop Breeding for Salinity Tolerance. Bio-protocol 5(9): e1466. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1466.
Category
Plant Science > Plant physiology > Abiotic stress
Plant Science > Plant physiology > Ion analysis
Biochemistry > Other compound > Ion > Potassium
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link