- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
In vivo Heterotopic Bone Formation Assay Using Isolated Mouse and Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Published: Vol 5, Iss 3, Feb 5, 2015 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1389 Views: 17963
Reviewed by: Salma HasanAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Spheroid Sheets: A Scalable Platform for Producing Tissue Membrane Constructs
Quang Bach Le [...] Deepak Choudhury
Nov 20, 2025 1540 Views

A Protocol to Induce Brown and Beige Adipocyte Differentiation From Murine and Human Adipose-Derived SVF
Rohit Raj Yadav [...] Narendra Verma
Dec 5, 2025 1657 Views

Optimization of Adipogenic Differentiation Protocol for Murine and Human Cell Culture Models
Junwan Fan [...] Wenyan He
Jan 20, 2026 230 Views
Abstract
Exogenous (human or mouse) mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) seed in HA scaffold and transplant subcutaneously in immunodeficient mice, the cells can finally form bone tissues in the in vivo environment. This protocol describes how to get heterotopic bone formation in mice by mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in hydroxyapatite (HA) scaffolds. This is a simple and robust approach to detect the bone formation by tissue engineering approaches in vivo, and it also fits for examining the roles of different factors in bone formation.
Keywords: Bone formationMaterials and Reagents
- Human or mouse mesenchymal stem cells (cultured, treated or transfected)
Note: If using the primary bone marrow stem cells (attached cells from bone marrow culturing), it’s better to use cells in low passages (not over passage 3); if using MSC cell lines, it’s also better to use low passages than high passages.
- Mice [NOD.CB17-Prkdc
/J mice (NOD/SCID), around 8 weeks old]
- Hydroxyapatite/tricalcium phosphate (HA/TCP) (Zimmer, catalog number: 60-130)
- 4% paraformaldehyde
- Hematoxylin/Eosin (H&E) staining solution
- Formic acid solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 1 ml syringes
- Cotton sticks (Pro-Ophtha)
- Scalpels
- Racks (for fixing the syringes in vertical position in cell incubator)
- Tools for mouse surgery (scalpel, forceps, needle holder, scissors, sutures, sterile swabs, sterile drapes)
- Scan microscopy (Leica Microsystems or any scan microscopy)
- Computer (with image analysis software, such as ImageJ® or Photoshop CS®)
Software
- ImageJ® or Photoshop CS®
Procedure
- Prepare the implants (stromal stem cells with HA/TCP scaffolds)
- Take the 1 ml syringes, cut off the tips with a scalpel and let the syringe tip side open, but keep the piston inside as it is.
- Weight 40 mg hydroxyapatite (HA/TCP) and transfer into each syringe.
- Put a cut cotton stick to close the open side of the syringe.
- Autoclave the syringes with hydroxyapatite (HA/TCP).
- Take the sterilized syringes and HA/TCP back to cell culture room. Place syringes in a rack (syringes must be kept vertical).
- Open the syringes, add 100 μl 10% FBS MEM medium to each HA/TCP scaffold. Mix by 1 ml tip up and down pipetting to wet the HA/TCP thoroughly.
- MSC cells (treated or transfected) are trypsinized and counted.
- 5 x 105 cells in 200 μl medium are transferred into HA/TCP in the syringe.
- Mix thoroughly but gently by 1 ml tip up and down pipetting.
- Place racks with syringes in the incubator, 37 °C, 5% CO2, overnight (see in Figure 1).
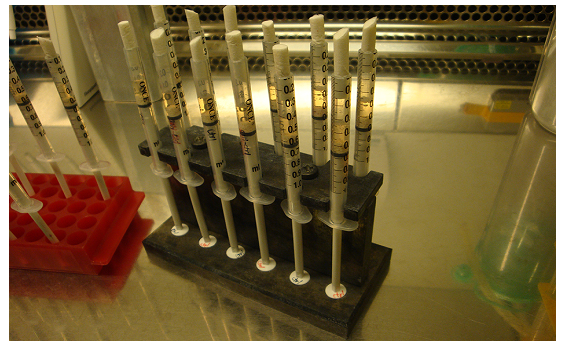
Figure 1. Racks with syringes
- Next day, bring the transplant cells in the HA/TCP into the animal room. Ready for transplant cells subcutaneously in mice.
- Take the 1 ml syringes, cut off the tips with a scalpel and let the syringe tip side open, but keep the piston inside as it is.
- Implantation in mice
- NOD/SCID mice, feed in sterilized animal room, around 8 weeks old. Each mouse can hold four implants in four positions (right-front, left-front, right-back, left-back).
Note: In order to avoid variation induced by individual mice or implantation position, suggest that in each mouse, with the control and experiment group; in each position, randomly implant the different treated samples.
- Anaesthesia the mice using the general protocol. Let the mice lay relax with the back upside (see in Figure 2A).
- Shaving the fur of mice at middle of back, at one side of spine. Ethanol sterilizes the skin at the shaved area. Let it dry for a while (see in Figure 2B).
- Cut a 1-1.5 cm gap in the skin (see in Figure 2C).
- Push the piston of the syringe with cells inside, to get rid of the extra medium upper the implant.
- Insert the 1 ml syringe with cells in HA/TCP into the cut gap in the skin. Go 1.5 cm forward under the skin to the front position from the cut gap to reach the front implantation position (see in Figure 2D-E).
- Push the piston of syringe and let the implant (HA/TCP with cells) out, settle implant at the position under the skin (see in Figure 2E).
- Slowly drag the syringe out, discard it (see in Figure 2F).
- Repeat the same step using another implant, this time let the syringe insert 1.5 cm back under the skin to the back position from the cut gap to reach the back implantation position.
- After both front and back implants done, suture the cut over the skin (see in Figure 2G).
- Do the same on the other side of spine on the back of the mouse (see in Figure 2H).
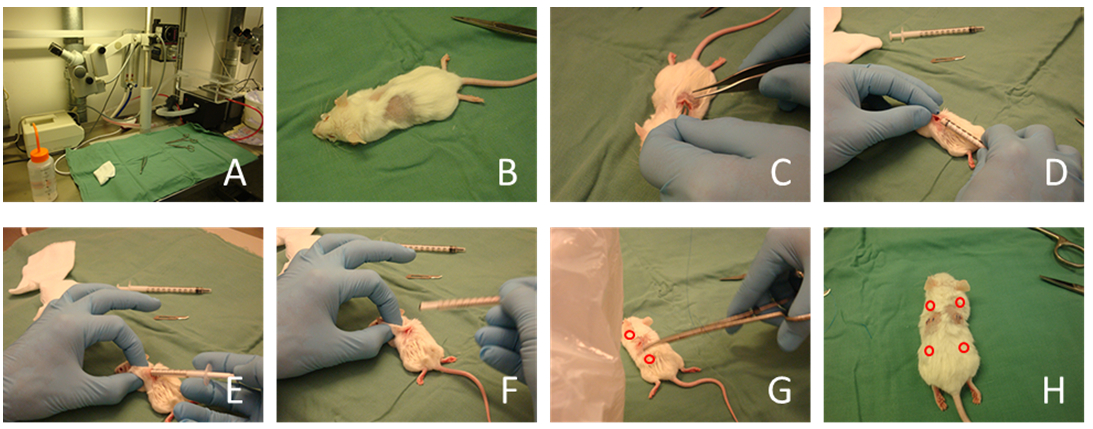
Figure 2. Implantation in mice
- Continue till all the implants put into mice.
- Keep the mice warm and under-watch in watch room overnight.
- Then transfer mice into the regular feeding room (sterilized animal room).
- Wait for 8 weeks till the bone formation in the implants.
- NOD/SCID mice, feed in sterilized animal room, around 8 weeks old. Each mouse can hold four implants in four positions (right-front, left-front, right-back, left-back).
- Fixing, embedding and H&E staining of implants
- Sacrifice the mice, take out each implant from each position, directly fix in 4% paraformaldehyde overnight.
- Discard the paraformaldehyde, decalcified implant in formic acid for 3 days at 4 °C, then keep in PBS at 4 °C.
- Embed the implants in paraffin using the general protocol.
- Cut each implant into sections (4-μm), at least three sections at different three positions of the implant.
- Stain all the sections with H&E Y using the general protocol.
- Sacrifice the mice, take out each implant from each position, directly fix in 4% paraformaldehyde overnight.
- Scan the sections under microscopy
- Take the section staining slides to the microscopy room.
- Scan each section (the whole section) under microscopy.
- Save the scanned pictures in disk.
- Take the section staining slides to the microscopy room.
- Analyze the bone formation volume by image analysis software
- Open each section scan picture in Photoshop or other image analysis software. The bone formation area stains as red (pink), the HA/TCP scaffolds stain as dark brown, non-differentiated MSCs show as blue spots.
- Pick all the red areas (bone tissue) in the section by proper tool (such as ‘magic pen’ in the Adobe Photoshop), read out the size (pixels) of the whole red (pink) area. Then pick the whole section area, read out the size (pixels) of the whole implant section area. Calculate bone formation ratio in each section as:
Bone volume (Bv) = Red area size/Whole section size
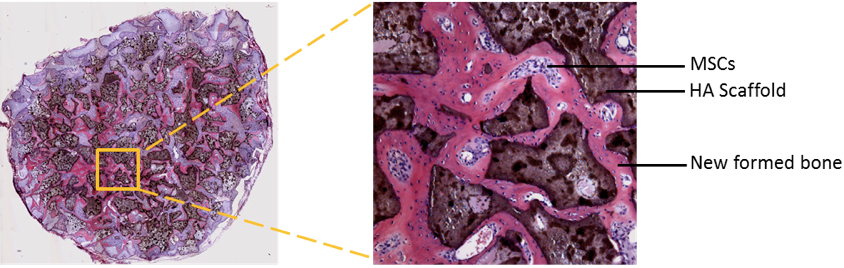
Figure 3. Scanned section
- Do the same analysis for all the staining sections for each implant.
- Put all the data together in the excel sheet, calculate the mean, standard variation, and perform proper statistic analysis to compare the difference between different groups.
- Open each section scan picture in Photoshop or other image analysis software. The bone formation area stains as red (pink), the HA/TCP scaffolds stain as dark brown, non-differentiated MSCs show as blue spots.
Notes
- Mouse MSC can always reach the bone formation ratio 15-30%; while human MSC always has 5-12% bone formation ratio.
Recipes
- Formic acid solution
0.4 M formic acid
0.5 M sodium formate
References
- Abdallah, B. M., Ditzel, N. and Kassem, M. (2008). Assessment of bone formation capacity using in vivo transplantation assays: procedure and tissue analysis. Osteoporosis, Springer: 89-100.
- Chen, L., Holmstrom, K., Qiu, W., Ditzel, N., Shi, K., Hokland, L. and Kassem, M. (2014). MicroRNA-34a inhibits osteoblast differentiation and in vivo bone formation of human stromal stem cells. Stem Cells 32(4): 902-912.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2015 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Chen, L. and Ditzel, N. (2015). In vivo Heterotopic Bone Formation Assay Using Isolated Mouse and Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Bio-protocol 5(3): e1389. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1389.
Category
Stem Cell > Adult stem cell > Mesenchymal stem cell
Cell Biology > Cell isolation and culture > Cell growth
Cell Biology > Cell isolation and culture > Cell differentiation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









