- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
PCR-RFLP Genotyping of Point Mutations in Caenorhabditis elegans
Published: Vol 2, Iss 6, Mar 20, 2012 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.128 Views: 25844

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Detection of piggyBac-mediated Transposition by Splinkerette PCR in Transgenic Lines of Strongyloides ratti
Hongguang Shao and James B. Lok
Jan 5, 2014 15188 Views

Implementation of Fusion Primer-Driven Racket PCR Protocol for Genome Walking
Yinwei Gu [...] Haixing Li
Dec 5, 2025 941 Views

CAPS-Based SNP Genotyping for Nitrogen-Response Phenotypes in Maize Hybrids
Jannis Jacobs [...] Peter K. Lundquist
Dec 20, 2025 550 Views
Abstract
This protocol describes the basic principle of PCR/restriction digest genotyping of point mutations in worms, based on the principle of Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) analysis. This type of genotyping is, particularly, useful when phenotypic analysis of animals carrying point mutations is difficult (e.g., in a complex genetic background).
I will illustrate the general procedures, using an example of daf-2 gene, encoding the sole insulin/IGF-1 receptor of C. elegans. Gems et al.(1998) did a very elegant job and characterized a series of mutations of daf-2, including the following two temperature-sensitive hypomorphic alleles:
daf-2(e1370): Substitution C/T (wild type/mutant), amino acid change: Missense P to S
Flanking sequences:
5’-CTCTATGAAATGGTTACACTCGGTGCTCAGCATATATTGGTTTGAGTAATGAGGTGT
Intracellular kinase domain, Class I, strong phenotype.
daf-2(e1368): Substitution C/T (wild type/mutant), amino acid change: Missense S to L
Flanking sequences:
5’-TCCGGAATTTACGTATTGAGGCAAAGTACTGTTCAGAAATVTATATGCTATCACAGT
Extracellular ligand binding domain, Class II, weak phenotype.
Here I will show you how to design the primers for PCR-RFLP analysis.
daf-2(e1370): Designed by Seung-Jae Lee from the Kenyon lab
Forward primer: 5’-CGGGATGAGACTGTCAAGATTGGAGATTTCGG-3’
Reverse primer: 5’-CAACACCTCATCATTACTCAAACCAATCCATG-3’
On the (-) strand, the nucleotide next to the 3’ end of reverse primer is G in wild-type allele, which is mutated to T in daf-2(e1370). Thus, by introducing another mutation (double C here, highlighted) into the reverse primer, it creates an Nco I-restriction site (i.e., CCATGG) only for PCR products derived from wild-type but NOT daf-2(1370).
daf-2(e1368): Designed by Peichuan Zhang from the Kenyon lab
Forward primer: 5’-GTTCCGGAATTTACGACGTATTGAGGCAACG-3’
Reverse primer: 5’-CTATCGGATCGAGTGGTATATTTAAC-3’
Similarly, on the (+) strand, the nucleotides next to the 3’ end of forward primer are TC in wild-type allele, and TT in daf-2(e1368). Thus, by introducing another mutation (C here, highlighted) into the forward primer, a restriction site of Acl I (i.e., AACGTT) is generated in the presence of daf-2(1368) point mutation.
The key is to introduce new mutation(s) at the 3’ end of one of your primers. Since the difference of the sizes of digest products is just ~30-bp, the length of the primer, you have to pick the other primer to generate an amplicon of ~200-bp – 250-bp or so.
Here is a website that can help you design the primers with appropriate restriction site for genotyping: http://helix.wustl.edu/dcaps/dcaps.html (dCAPS Finder 2.0) (Neff et al., 2002).
Materials and Reagents
- PK lysis buffer
- Proteinase K (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P6556 )
- Common PCR reagent (e.g., Invitrogen PCR kit – Life Technologies, Invitrogen™, catalog number: 10342-020 ; or home-made Taq and buffer)
- Restriction enzymes (NEB)
- Agarose gel
- Ethidium bromide (Life Technologies, Invitrogen™, catalog number: 15585-011 )
- Plus DNA Ladder (Life Technologies, Invitrogen™, catalog number: 10787-018 )
Equipment
- MJ Research PTC-200 Thermo Cycler (MJ Research)
- Thin-wall PCR tubes (USA Scientific, catalog numbers: 1402-2700 or 1405-8100 )
Procedure
- Isolate genomic DNA with proteinase K digest.
Tip 1. Typically, a large amount of PK lysis buffer is prepared (for the recipe, please refer to Caenorhabditis elegans/DNA/Single worm PCR) with supplement of proteinase K, and then small aliquots are stored (e.g., 1 ml) at -20 °C. This robust enzyme works well at a range from 20 μg/ml to 100 μg/ml, and the key is to activate it at 60 °C for ~1 h and then kill it at 95 °C for ~15 min or so. You do not want to see proteinase K torture your Taq enzyme during the subsequent PCR reaction.
Tip 2. I prefer to pick reasonable numbers (e.g, 10) of gravid adult animals and stick them into a PCR tube with PK lysis buffer (e.g, 20 μl). It does not hurt to use more than 1 worm per PCR reaction (genomic DNA from ~1/2 worm works just fine for most robust PCR genotyping). For PCR-RFLP, it’d be better to use more than 1 worm per reaction (e.g., 5 to 10). However, too much DNA template, in some cases, may inhibit your PCR reactions. - Perform a standard PCR, 20 μl per reaction.
- Set up the PCR, by adding the following component into a thin-wall PCR tube on ice in this order:
DNAase-free ddH2O 11.0 μl dNTP mix (10 mM each) 0.4 μl (final, 200 μM each) Forward primer (10 μM) 0.4 μl (final, 0.2 μM each) Reverse primer (10 μM) 0.4 μl (final, 0.2 μM each) PCR buffer (10x) 2.0 μl (final, 1x) MgCl2 (50 mM) 0.8 μl (final, 2.0 mM) Worm lysates (20 μl) 2.0 μl Taq (5 U/μl) 0.1 μl (final, 0.5 U per reaction) - Run PCR (put the tube on the block when it is hot):
1 cycle 94 °C, 3 min 30 cycles 94 °C, 10 sec; 58 °C, 30 sec; 72 °C, 30 sec 1 cycle 72 °C, 10 min
- Set up the PCR, by adding the following component into a thin-wall PCR tube on ice in this order:
- Digest with respective enzymes, 37 °C, O/N. Prepare multiplex (N+2) for N reactions:
Aliquot 5.0 μl into each PCR tube.ddH2O 2.5 μl 10x buffer 2.5 μl Enzyme (5 U/μl to 20 U/μl) 0.2 μl - Resolve O/N digest of PCR products on 2.0%-2.5% agarose gel.
For daf-2(1370):
Bands expected from Nco I-digest (NEB buffer 3): Wild-type, 202-bp; mutation, 234-bp.
For daf-2(1368):
Bands expected from Acl I-digest (NEB buffer 4 + BSA): Wild-type, 215-bp; mutation, 186-bp.
Tip 3. Due to the small difference between the sizes of products, it is recommended to run the gel for a long time. Always add wild-type and mutants with known genotypes as controls. Ethidium bromide migrates toward cathode (-), just the opposite to the direction of DNA migration. To help subsequent visualization of DNA under UV light, it would be advised to add a few microliter of ethidium bromide (10 mg/ml) into the electrophoresis buffer near the anode (+).
Representative data
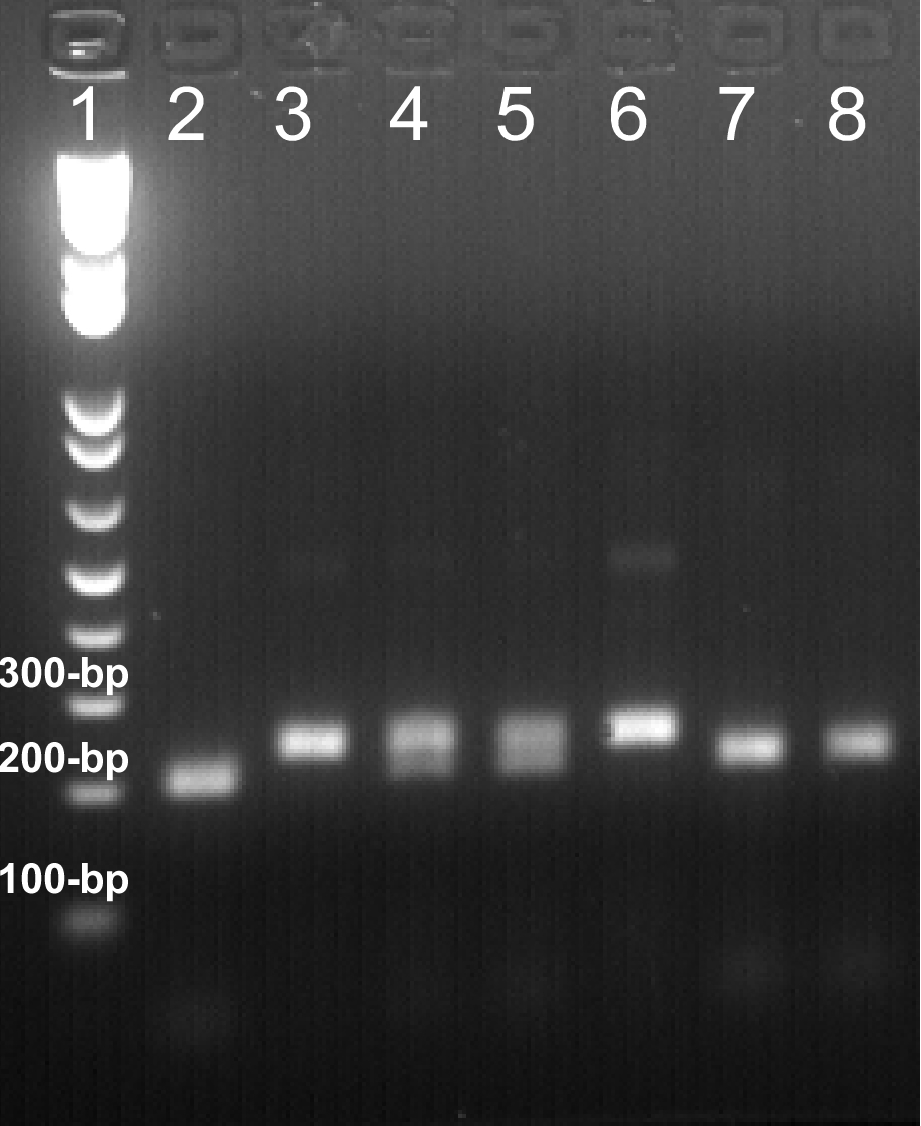
Figure 1. Representative data of PCR genotyping are shown here. 20 μl of daf-2(e1370) allele-genotyping PCR products were digested with Nco I at 37 ºC overnight. The digested DNA fragments were resolved on a 2.0% agarose gel. Expected sizes of DNA bands: wild-type, 202-bp; daf-2(e1370) mutation, 234-bp. Lane 1: 1 Kb Plus DNA Ladder. Lane 2, 7, 8: daf-2(e1370)+/+; Lane 4, 5: daf-2(e1370)+/-; Lane 3, 6: daf-2(e1370)-/-. The results are highly reproducible, and necessary controls should always be included to assure the results.
Recipes
- PK lysis buffer
10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0)
50 mM KCl
2.5 mM MgCl2
0.45% Tween-20
0.05% gelatin
20 g/ml proteinase K
Prepare and store small aliquots at -20 °C
Acknowledgments
This protocol was adapted from work performed by members of the Kenyon lab, including PZ. PZ was supported by a postdoctoral fellowship from the Larry Hillblom Foundation.
References
- Gems, D., Sutton, A. J., Sundermeyer, M. L., Albert, P. S., King, K. V., Edgley, M. L., Larsen, P. L. and Riddle, D. L. (1998). Two pleiotropic classes of daf-2 mutation affect larval arrest, adult behavior, reproduction and longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 150(1): 129-155.
- Neff, M. M., Turk, E. and Kalishman, M. (2002). Web-based primer design for single nucleotide polymorphism analysis. Trends Genet 18(12): 613-615.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2012 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Zhang, P. (2012). PCR-RFLP Genotyping of Point Mutations in Caenorhabditis elegans. Bio-protocol 2(6): e128. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.128.
Category
Molecular Biology > DNA > Genotyping
Molecular Biology > DNA > PCR
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









