- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Synchronization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cells in G1 Phase of the Cell Cycle
Published: Vol 4, Iss 20, Oct 20, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1273 Views: 16961
Reviewed by: Kanika GeraEmilia Krypotou Anonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Yeast Single-cell RNA-seq, Cell by Cell and Step by Step
Mariona Nadal-Ribelles [...] Lars M. Steinmetz
Sep 5, 2019 7720 Views

A Microfluidic Platform for Tracking Individual Cell Dynamics during an Unperturbed Nutrients Exhaustion
Théo Aspert [...] Gilles Charvin
Jul 20, 2022 2898 Views
Abstract
The baker’s yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a widely used model organism in molecular biology because of the high homology it shares with human cells in many basic cellular processes such as DNA replication, repair, recombination, transcription, and because of the ease its genome can be manipulated. Other advantages of working with yeast are its fast production rate which is comparable to bacteria’s, and its cheap maintenance.
To examine certain phenomena, for example whether a mutation affects the passage through a cell cycle phase, it can be necessary to work with a yeast culture, in which all the cells are in the same phase of the cell cycle. Yeasts can be arrested and kept in different phases of the cell cycle. Here we describe the method that allows synchronizing and keeping yeast cells in the G1 phase of the cell cycle with the mating pheromone, α-factor. Only MATa cells can be synchronized with α-factor which is produced by MATα cells. It is highly recommended to use a MATa bar1 deletion strain. The BAR1 gene encodes for an extracellular protease that inactivates α-factor by cleaving it (MacKay et al., 1988). To counteract the Bar1 protease activity when using BAR1 cells, 100-1000 times more α-factor is needed as compared to bar1 deletion cells (α-factor is quite expensive!), and still the synchrony will be transient. In contrast, bar1 deletion cells can be kept in G1 phase with α-factor for several hours, and the degree of synchronization is usually higher than using a BAR1 strain. Moreover, bar1 deletion cells can be synchronized even at high cell density, whereas BAR1 cells, due to the activity of the secreted Bar1 protease, only at low cell density.
Materials and Reagents
- MATa bar1 deletion strain (can be engineered in the lab, or purchased from stock repositories like EUROSCARF)
- Yeast extract
- Peptone
- D-glucose
- 95% ethanol
- Yeast extract-peptone-dextrose (YPD) media (see Recipes) (or other media needed for the strain in use)
- α-factor (α-mating factor acetate salt) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T6901-5MG ) (see Recipes)
- Pronase (protease, from streptomyces griseus) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P6911-5G ) (see Recipes)
Equipment
- 30 °C incubator-shaker (180-200 rounds per minute)
- Microscope
- Glass slide
- Coverslips
- Centrifuge
- Spectrophotometer
- Vortex
- Culture tube
- Culture flask
Procedure
- Grow up a small overnight starter culture inoculated from one single colony from a YPD plate in YPD in a culture tube (180 rpm, 30 °C). Usually 1/10th of the final working culture is enough for the starter.
- From the overnight culture inoculate into fresh media to get OD600:0.2 in a culture flask or tube (this is your working culture with its working volume).
- Grow the culture to get the required amount of cells, but do not go higher than OD600:0.8 because at very high density even bar1 deletion cells do not synchronize. Keep in mind that during synchronization the density of the culture will increase since cells that already passed G1 will complete the cycle until they reach G1 of the next cycle.
- Spin down the cells and discard the media (3 min with 3,000 rpm at room temperature).
- Wash the cell pellet with at least 10 cell pellet volumes of water.
- Spin down the cells and discard the water (3 min, 3,000 rpm RT).
- Resuspend the cells in working volume of fresh YPD containing 50 ng/ml α-factor.
- Grow the cells.
- After 60, 90, 120 min check the cells under the microscope with 40x magnification. Before checking vortex the samples thoroughly to disturb clamps. G1 arrested cells have typical pear shape. Usually between 90 and 120 min ~100% synchrony can be observed.
- To release the cells from the arrest, spin down the cells and wash them with water.
- Repeat washing.
- Resuspend the cells in the working volume of fresh YPD containing 50 µg/ml pronase. It is important to add pronase because even a remaining small amount of α-factor can inhibit release.
- After adding pronase cells will enter the cell cycle. Depending on your goal, you can let them cycle, treat them with different agents, or collect them at any desired time points. Pronase does not affect cell growth.
This experiment is easy to reproduce once you can recognize arrested cells (Figure 1). If your strain has a selectable marker, you can carry out the experiment using the appropriate media instead of YPD.
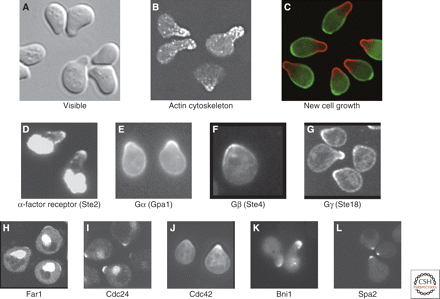
Figure 1. Yeast cells treated with α-factor. (Source: Arkowitz, 2009)
Recipes
- YPD liquid
1% yeast extract
2% peptone
2% D-glucose
- α-factor
1 mg/ml stock solution in EtOH
Stored at -20 °C
- Pronase
40 mg/ml stock solution in sterile distillated water
Stored at -20 °C
Acknowledgments
This protocol is a modified form of the one published by Amberg et al. (2005). We used this protocol in our work (Daraba et al., 2014). Funding support: Wellcome Trust, 070247/Z/03/A.
References
- Amberg, D. C., Burke, D. J. and Strathern, J. N. (2005). Methods in Yeast Genetics: A Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Course Manual, 2005 Edition. ISBN 978-087969728-0.
- Arkowitz, R. A. (2009). Chemical gradients and chemotropism in yeast. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1(2): a001958.
- Daraba, A., Gali, V. K., Halmai, M., Haracska, L. and Unk, I. (2014). Def1 promotes the degradation of Pol3 for polymerase exchange to occur during DNA-damage--induced mutagenesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PLoS Biol 12(1): e1001771.
- MacKay, V. L., Welch, S. K., Insley, M. Y., Manney, T. R., Holly, J., Saari, G. C. and Parker, M. L. (1988). The Saccharomyces cerevisiae BAR1 gene encodes an exported protein with homology to pepsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 85(1): 55-59.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Unk, I. and Daraba, A. (2014). Synchronization of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Cells in G1 Phase of the Cell Cycle. Bio-protocol 4(20): e1273. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1273.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial cell biology > Cell isolation and culture
Cell Biology > Cell isolation and culture > Cell growth
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










