- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Detection of Transposable Element Insertion Site Polymorphisms by Sequence-Specific Amplification Polymorphism (SSAP)
Published: Vol 4, Iss 5, Mar 5, 2014 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1054 Views: 11655
Reviewed by: Tie Liu

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Experimental Pipeline for SNP and SSR Discovery and Genotyping Analysis of Mango (Mangifera indica L.)
Michal Sharabi-Schwager [...] Ron Ophir
Aug 20, 2016 11559 Views

Investigation of Transposon DNA Methylation and Copy Number Variation in Plants Using Southern Hybridisation
Vivek Hari Sundar G. and P. V. Shivaprasad
Jun 5, 2022 3411 Views

CAPS-Based SNP Genotyping for Nitrogen-Response Phenotypes in Maize Hybrids
Jannis Jacobs [...] Peter K. Lundquist
Dec 20, 2025 550 Views
Abstract
Transposable elements represent a major part of any eukaryotic genomes. Notably in plants they can account for more than 80% of the whole genomic sequence (such as in maize). Due to their mobility across the genome, they can act as mutagens but can also be considered as an important source of genetic diversity. It has been shown that they may be activated following various stresses, and it has been assumed that they may contribute to genome evolution and adaptation. Molecular methods have thus been proposed to allow identification of new transposition events, or more generally to tag transposable element insertion site polymorphisms. Sequence-Specific Amplification Polymorphism (SSAP) is a high throughput method derived from AFLP, which has been first tested on the barley genome (Waugh et al., 1997). Its efficiency in tagging TEs in comparison to AFLP is based on the use of specific primers anchored in the TE sequences of interest, requiring the TEs under survey to be previously characterized. SSAP can thus be used to identify any genomic reorganization in the vicinity of TE insertion sites, and still represents an efficient approach to analyse evolutionary dynamics of TEs.
Keywords: AllopolyploidyMaterials and Reagents
- Restriction of genomic DNA using endonucleases
- Genomic DNAs from the samples to be analysed at concentrations of 100 ng/µl.
- Endonuclease enzyme insensitive to DNA methylation, generating cohesive ends
Note: TE sequence ends have to be devoid of any corresponding restriction sites.
- Genomic DNAs from the samples to be analysed at concentrations of 100 ng/µl.
- Adapter ligation
- Two oligonucleotides which form a double-stranded adapter, with an overhang complementary to the overhang left by the restriction enzyme used. In the case of EcoRI (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fermentas) the 5’ overhang is AATT and the oligonucleotide sequences are 5’-CTCGTAGACTGCGTACC-3’ and 5’-AATTGGTACGCAGTCTAC-3’. Annealing of the two oligonucleotides will constitute the adapter (purple rectangles in Figure 1).
- T4 DNA ligase (1-3 U/μl) with the corresponding ligase buffer (Promega Corporation, catalog number: M1801 )
- Sterile ultrapure water
- Two oligonucleotides which form a double-stranded adapter, with an overhang complementary to the overhang left by the restriction enzyme used. In the case of EcoRI (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Fermentas) the 5’ overhang is AATT and the oligonucleotide sequences are 5’-CTCGTAGACTGCGTACC-3’ and 5’-AATTGGTACGCAGTCTAC-3’. Annealing of the two oligonucleotides will constitute the adapter (purple rectangles in Figure 1).
- Pre-amplification
- PCR reagents
- Homemade Taq DNA polymerase is of sufficient quality for the PCR reactions but Taq Promega has also been used (Promega corporation, catalog number: M8301 ) with the corresponding Taq polymerase buffer.
- 25 mM MgCl2
- dNTPs (10 µM each)
- Homemade Taq DNA polymerase is of sufficient quality for the PCR reactions but Taq Promega has also been used (Promega corporation, catalog number: M8301 ) with the corresponding Taq polymerase buffer.
- Pre-amplification primers (10 μM each)
- One primer is anchored in the adapter: 5’-GACTGCGTACCAATTC-3’ (primer P1 in Figure 1).
- The other primer is anchored in the TE of interest, close to its end to limit the size of amplicon (primer P2 in Figure 1).
- One primer is anchored in the adapter: 5’-GACTGCGTACCAATTC-3’ (primer P1 in Figure 1).
- PCR reagents
- Selective amplification
- PCR reagents (see pre-amplification step)
- Selective amplification primers (10 μM each)
- One primer is anchored in the adapter, with the addition of 3 nucleotides at the 3’ end (primer P3 in Figure 1) to limit the number of bands to be visualized and analyzed by gel electrophoresis. Several combinations of A, T, G and C should be used to target different genomic localizations of TE insertion sites.
- The other primer is defined to perform a nested PCR in comparison with the pre-amplification step (primer P4 in Figure 1); this primer is labelled with a 5’-IRDye. DNA labelled with IRDye (infrared dye) has to be stored in the dark at -20 °C. To minimize exposure to light, wrap the tube in aluminium foil.
- One primer is anchored in the adapter, with the addition of 3 nucleotides at the 3’ end (primer P3 in Figure 1) to limit the number of bands to be visualized and analyzed by gel electrophoresis. Several combinations of A, T, G and C should be used to target different genomic localizations of TE insertion sites.
- PCR reagents (see pre-amplification step)
- Acrylamide gel for SSAP profile analysis
- Kimwipes
- Urea (Merck KGaA, catalog number: 1.08488.1000 )
- Long Ranger Acrylamide (50%) (Lonza, catalog number: 50611 )
- APS (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 161-0700 )
- Temed (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 161-0801 )
- Absolute ethanol
- Formamide (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F9037 )
- 10x TBE buffer (Tris/Borate/EDTA) (see Recipes)
- 5.5% acrylamide gel (see Recipes)
- Loading buffer (see Recipes)
- Kimwipes
Equipment
- 1.5 ml Eppendorf tubes
- Centrifuge
- Parafilm
- Incubator or oven
- Water bath
- 96-well PCR plates
- 0.45 μm filters
- LI-COR DNA analyzer (LI-COR) and corresponding equipment (plates, combs, spacers...)
- Thermal cycler
- Horizontal shaker
Procedure
Note: Adapted from Waugh et al. (1997) and Pouilly et al. (2008); as used in Sarilar et al. (2013).
- Targeting TE insertion sites
- Restriction of genomic DNAs
- Make a restriction reaction mixture that will be distributed equally into individual Eppendorf tubes. The reaction mixture combines (in order) sterile ultrapure water (with a final volume of 36 µl per reaction), the 1x enzyme buffer and the selected endonuclease (6 U per reaction), taking into account that 5 µl of genomic DNA will be added into the mix.
- Distribute 31 µl of the reaction mixture into each Eppendorf tube.
- Add 5 µl of each DNA solution to be analysed (which correspond to 500 ng of genomic DNA) to the corresponding tube.
- Mix gently the solution in each tube by pipeting, and centrifuge shortly.
- Incubate at least 3 h at 37 °C.
- Stop the enzyme activity by incubating the tubes 20 min at 65 °C.
- Put the tubes on ice, centrifuge briefly and replace them on ice. Proceed immediately to the ligation step.
- Make a restriction reaction mixture that will be distributed equally into individual Eppendorf tubes. The reaction mixture combines (in order) sterile ultrapure water (with a final volume of 36 µl per reaction), the 1x enzyme buffer and the selected endonuclease (6 U per reaction), taking into account that 5 µl of genomic DNA will be added into the mix.
- Prepare the adapters and ligate them to the restricted DNAs
- In a 0.5 ml Eppendorf tube, mix the two oligonucleotides (100 µM each) in equal proportions to make the adapter solution (final concentration of 50 µM).
- Incubate the mix at 95 °C for 5 min (in a thermocycler) and let cool it down on the bench at room temperature.
- Make a ligation reaction mixture, by combining (in order) sterile ultrapure water (with a final volume of 50 µl per reaction), 1x ligase buffer, adapter solution (50 pmol) and T4 DNA ligase (1 U per reaction).
- Distribute 14 µl of the reaction mixture into the Eppendorf tubes containing each 36 µl of restricted DNAs.
- Mix gently using a pipette and then centrifuge shortly.
- Incubate at 20-25 °C overnight (on the bench) to allow ligation.
- Dilute the ligation products to 1/10 in 96-well PCR plates: 90 µl of sterile ultrapure water + 10 µl of the restriction-ligation products.
Note: Store non-diluted restriction-ligation products at -20 °C, but keep 1/10 diluted restriction-ligation products at 4 °C to avoid DNA degradation because of freezing - thawing cycles.
- In a 0.5 ml Eppendorf tube, mix the two oligonucleotides (100 µM each) in equal proportions to make the adapter solution (final concentration of 50 µM).
- Pre-amplification
- Use the first primer pair P1/P2 (Figure 1b) for the pre-amplification.
- Make a pre-amplification PCR reaction mixture by combining (in order) sterile ultrapure water (with a final volume of 20 µl per reaction), 1x Taq polymerase buffer, MgCl2 (2.5 mM), dNTP solution (200 µM), primer P1 anchored in the adapter (8 pmol), primer P2 anchored in the TE under study (8 pmol) and Taq DNA polymerase (3-4 U).
- Distribute 17 µl of the pre-amplification reaction mixture into the wells of a 96-well PCR plate.
- Add 3 µl of the 1/10 diluted restriction-ligation products. Mix gently for each reaction by pipeting 2-3 times.
- Centrifuge.
- PCR program
- 1 cycle at 72 °C for 2 min
- 1 cycle at 94 °C for 3 min
- 25 cycles of (94 °C for 30 sec, 56 °C for 30 sec and 72 °C for 1 min)
- 1 cycle at 72 °C for 5 min
- Keep at 10 °C
- 1 cycle at 72 °C for 2 min
- Verification of the pre-amplification products can be performed by agarose gel electrophoresis: Load 4 µl of the reaction product (with loading buffer) and run the electrophoresis for ~20 min at 100 V.
Note: A smear should be obtained (an example of the gel is shown in Figure 1b). - Dilute the pre-amplification product in 96-well PCR plates according to the plate layout to carry out the separation of fragments using the LI-COR DNA analyzer.
Note: The factor of dilution is usually 1/10 (36 µl of sterile ultrapure water + 4 µl of pre-amplification product) but it has to be adapted (1/2, 1/5, 1/10, or no dilution) according to the intensity of the smear observed after electrophoresis, in order to get homogeneous selective amplification products.
- Use the first primer pair P1/P2 (Figure 1b) for the pre-amplification.
- Selective amplification
- Use the second primer pair P3/P4 (Figure 1c) for the selective amplification to perform a nested PCR (to increase the specificity of the PCR reaction).
- Make a selective PCR reaction mixture by combining (in order) sterile ultrapure water (with a final volume of 20 µl per reaction), 1x Taq polymerase buffer, MgCl2 (2.5 mM), dNTP solution (200 µM), selective primer P3 anchored in the adapter with 3 additional selective nucleotides (4 pmol), selective primer P4 anchored in the TE under study and labelled with IRDye (4 pmol) and Taq DNA polymerase (1.5-2 U).
Note: The primer labelled with the IRDye is sensitive to the light; the PCR plate has to be covered with aluminium foil to avoid degradation. - Distribute 15 µl of the selective PCR reaction mixture into the wells of a 96-well PCR plate.
- Add 5 µl of the diluted pre-amplification products. Mix gently for each reaction by pipeting 2-3 times.
- Centrifuge.
- PCR program: a typical touchdown program is performed (Vos et al., 1995) to increase the specificity of the PCR amplification.
- 1 cycle at 94 °C for 4 min
- 13 cycles of [94 °C for 30 sec, 65 °C (then -0.7 °C per cycle) for 30 sec and 72 °C for 1 min]
- 25 cycles of (94 °C for 30 sec, 56 °C for 30 sec and 72 °C for 1 min)
- 1 cycle at 72 °C for 5 min
- Keep at 10 °C
Note: Maintain the 96-well PCR plates out of the light by covering them with aluminium foil and once the program is finished keep them at -20 °C.
- 1 cycle at 94 °C for 4 min
- Use the second primer pair P3/P4 (Figure 1c) for the selective amplification to perform a nested PCR (to increase the specificity of the PCR reaction).
- Restriction of genomic DNAs
- Electrophoresis run on LI-COR DNA analyzer to separate amplified products
- Prepare the DNA analyzer according to manufacturer’s instructions.
- Use 0.25 mm spacers between glass plates and prepare 40 ml of 5.5% acrylamide gel.
- Do pre-run with autofocus and following parameters: 45 °C; 2,000 W; 25 mA.
- Load the gel
- Mix the PCR products of selective amplification (2 µl) with equal amount of loading buffer.
- Heat the samples at 95 °C for 5 min for DNA denaturation and snap cool on ice before loading. Keep also on ice while loading the samples on the acrylamide gel.
- Load 0.5 µl of each sample in each well. Between each deposit, rinse the multi-syringe in water. Load on the same acrylamide gel the samples which have to be compared, and load the controls on each gel if necessary.
- Mix the PCR products of selective amplification (2 µl) with equal amount of loading buffer.
- Analyze the SSAP multiband fingerprints by scoring polymorphic bands which may correspond to TE insertion site polymorphisms (Figure 1d).
Note: Wear gloves when working with acrylamide because of its carcinogenic and toxic properties.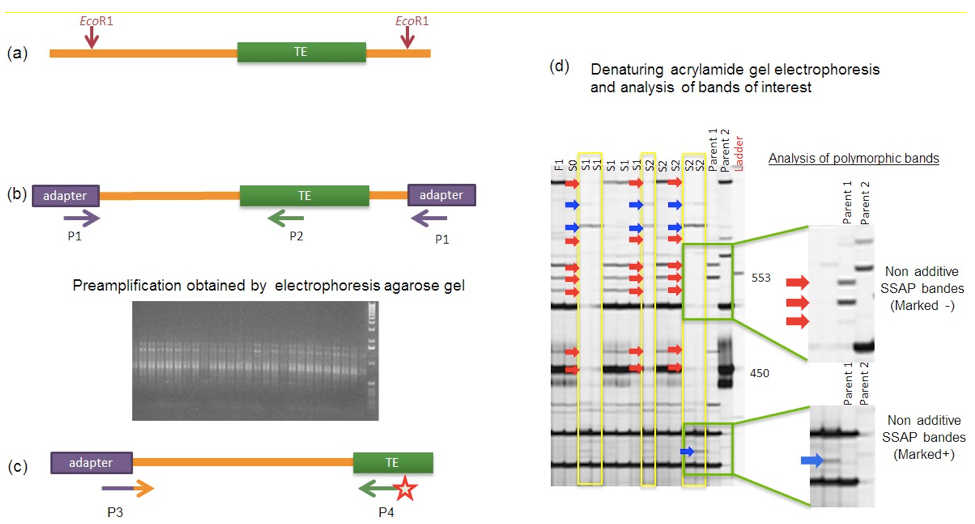
Figure 1. Schematic description of the different steps of the SSAP procedure to detect TE insertion site polymorphisms. (a). The genomic DNAs to be analysed are restricted using an endonuclease (here EcoRI, as used in Sarilar et al., 2013) and then ligated to corresponding adapters. (b). A pre-amplification is performed on the restriction-ligation products using a specific PCR primer pair (to be designed) with one primer (P1) complementary to the adapter and the other primer (P2) anchored in the TE of interest. As illustrated by the picture, the pre-amplification should lead to a PCR product visualized as a smear after agarose gel electrophoresis. (c). The resulting PCR products are then subjected to a selective PCR amplification using another specific PCR primer pair (to be designed) with one primer (P3) complementary to the adapter with 3 additional selective nucleotides and the other primer (P4) anchored in the TE and labeled with an IRDye (at the 5’ end). (d). The resulting amplicons are finally resolved in a denaturing acrylamide gel; polymorphic bands can be visualized and scored as non-additive SSAP bands (being additional + or missing -) when comparing the progeny profiling with the parental ones (as illustrated here for the analysis of resynthesized allotetraploid lines in comparison with their diploid progenitors, Sarilar et al., 2013). Identification of the nature of the polymorphism responsible for non-additivity (e.g. transposition, genomic rearrangement, polymorphism at the endonuclease cutting site) requires further cloning and sequencing of the corresponding SSAP amplicon.
- Prepare the DNA analyzer according to manufacturer’s instructions.
Recipes
- 10x TBE buffer (1 L)
Tris Base 108 g
Boric acid 55 g
40 ml of EDTA (0.5 M, pH 8)
ddH2O qsp 1 L
Filter sterilize (0.45 µM) - 5.5% acrylamide gel (40 ml)
Add 15.6 g urea to 20 ml ddH2O; agitate while heating until obtain a translucent solution
Add 4.8 ml of 10x TBE buffer
Filter 0.45 µm to remove any urea crystals
Add 4.4 ml Long ranger (50%)
Complete with ddH2O up to 40 ml
When ready to inject gel solution, add for polymerization- 264 µl of 10% APS
- 26.4 µl Temed
- 264 µl of 10% APS
- Loading buffer
Mix 40 mg of bromophenol blue with 2 ml of EDTA (0.5 M, pH 8) and 0.5 ml of ddH2O
Complete with 47.5 ml of formamide
Note: Loading buffer is carcinogenic because of formamide, it has to be handled with gloves and under the flow hood.
Acknowledgments
This protocol is adapted from Waugh et al. (1997) and Sarilar et al. (2013).
References
- Pouilly, N., Delourme, R., Alix, K. and Jenczewski, E. (2008). Repetitive sequence-derived markers tag centromeres and telomeres and provide insights into chromosome evolution in Brassica napus. Chromosome Res 16(5): 683-700.
- Sarilar, V., Palacios, P. M., Rousselet, A., Ridel, C., Falque, M., Eber, F., Chevre, A. M., Joets, J., Brabant, P. and Alix, K. (2013). Allopolyploidy has a moderate impact on restructuring at three contrasting transposable element insertion sites in resynthesized Brassica napus allotetraploids. New Phytol 198(2): 593-604.
- Vos, P., Hogers, R., Bleeker, M., Reijans, M., van de Lee, T., Hornes, M., Frijters, A., Pot, J., Peleman, J., Kuiper, M. and et al. (1995). AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23(21): 4407-4414.
- Waugh, R., McLean, K., Flavell, A. J., Pearce, S. R., Kumar, A., Thomas, B. B. and Powell, W. (1997). Genetic distribution of Bare-1-like retrotransposable elements in the barley genome revealed by sequence-specific amplification polymorphisms (S-SAP). Mol Gen Genet 253(6): 687-694.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2014 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Sarilar, V., Palacios, P. M. and Alix, K. (2014). Detection of Transposable Element Insertion Site Polymorphisms by Sequence-Specific Amplification Polymorphism (SSAP). Bio-protocol 4(5): e1054. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.1054.
Category
Plant Science > Plant molecular biology > DNA > Genotyping
Systems Biology > Genomics > Transposons
Molecular Biology > DNA > Genotyping
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









