- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
End-synapsis Assay
Published: Vol 3, Iss 18, Sep 20, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.900 Views: 9100
Reviewed by: Lin FangTie LiuFanglian He

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

SMART (Single Molecule Analysis of Resection Tracks) Technique for Assessing DNA end-Resection in Response to DNA Damage
Angela Altieri [...] Alfano Luigi
Aug 5, 2020 6061 Views
Abstract
Many environmental agents induce double-strand breaks (DSBs) in DNA. Unrepaired or improperly repaired DSBs can lead to cell death or cancer. Nonhomologous end joining is the primary DNA double-strand break repair pathway in eukaryotes. During NHEJ pathway, several proteins recognize and bind DNA ends, bring the ends in a synaptic complex and, finally, process and ligate the ends.
Briefly, NHEJ starts with Ku protein. Ku binds the broken DNA ends and recruits the catalytic subunit of DNA dependent protein kinase (DNA-PKcs) forming DNA-PK. After processing, the XRCC4/Ligase IV complex executes the final ligation stimulated by Cernunnos-XLF.
Here, we describe an end-synapsis assay. This assay can be used in order to delineate which proteins are necessary to bring the DNA ends in a stable synaptic complex during NHEJ. Briefly, NHEJ competent extracts from human cells were incubated with both a double-stranded DNA fragment bound to streptavidin-coated magnetic beads and the same soluble radio-labeled fragment. The beads were then washed in mild salt buffer and the radioactivity recovered with the beads was measured by scintillation counting. Control experiments without extracts or with DNA-free beads were run in parallel to determine unspecific background.
Materials and Reagents
- NHEJ competent human cells (e.g. AHH1 lymphoblastoid cells, Nalm6 pre-B cells, HeLa epithelial cells, MRC5SV fibroblasts, etc.)
- ~500 bp double-stranded DNA fragments amplified by PCR, biotinylated at one end or non-biotinylated
- [32P]-ATP
- T4 polynucleotide kinase
- Streptavidin paramagnetic beads (Dynabeads M280 streptavidin) (Life Technologies, Invitrogen™, catalog number: 112.06D )
- Glucose
- Hexokinase (Calbiochem, catalog number: 376811 )
- PBS
- Triethanolamine
- Magnesium acetate
- Dithiothreitol
- BSA (e.g. enzymatic restriction reaction grade)
- Potassium acetate
- EJ buffer (see Recipes)
Equipment
- PCR thermal cycler
- Scintillation counter
- Heat block (Eppendorf Thermomixer® comfort)
Procedure
- First, PCR is used to synthesize a ~500 bp dsDNA fragment (e.g. from pBluescript plasmid) with a non-biotinylated or biotinylated reverse primer and a non-biotinylated forward primer, producing a fragment biotinylated at one end (500 bio) or not. The non biotinylated fragment was then radiolabeled with T4 polynucleotide kinase in the presence of [32P]-ATP (500*).
- Next, beads associated with biotinylated DNA fragments were prepared: per point, 0.5 pmol of 500 bio dsDNA fragment were immobilized on 10 μl streptavidin paramagnetic beads as recommended by the manufacturer.
- In parallel, NHEJ competent cells extracts from human cells were used (Bombarde et al., 2010). Briefly, exponentially growing cells were lysed through three freeze/thaw cycles in lysis buffer containing protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktail, then lysates were incubated at 4 °C for 20 min, cleared by centrifugation, and dialyzed against dialysis buffer as described (Bombarde et al., 2010). Protein concentration was determined using the Bradford assay and end-joining extracts were stored at -80 °C. Here, 40 μg extracts were incubated for 10 min at 30 °C with 2 mM glucose and 0.2 U hexokinase. Glucose and hexokinase is an ATP consuming system used to prevent any ligation activity (Calsou et al., 2003).
Note: DNA end-synapsis is an early step of NHEJ which relies on protein/DNA interactions and is reversible (e.g. by washing with high salts or detergent) while ligation is the final step and is irreversible (resistant to harsh washes). Ligation has to be prevented to focus the analysis on synapsis.
- 10 μl of mocked (control) or DNA-treated beads were washed twice in 100 μl of 0.5x PBS.
- Wet mocked or DNA-treated beads were mixed at 16 °C for 30 min in 10 μl EJ buffer containing 0.1 pmol of radioactive 500* DNA fragment and 40 μg of NHEJ competent cell extracts pre-incubated as above. The beads were gently hand-agitated by every 5 min.
- After incubation, supernatant was removed for storage and wet beads were washed twice in 50 μl 0.5x PBS.
- The washes were pooled with the supernatant.
- Radioactivity associated with supernatants and beads were measured in a scintillation counter.
- Results are expressed as the % of radioactivity pulled down after subtraction of the counts in the sample without 500 bio on the beads (Figure 1).
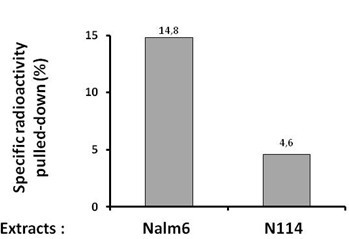
Figure 1. Quantification of the specific radioactivity pulled-down under synapsis conditions in vitro with extracts of Nalm6 or N114 cells. N114 cells have a defect in Lig4 expression which impacts on synapsis formation.
Recipes
- EJ buffer
50 mM Triethanolamine (pH 8.0)
0.5 mM magnesium acetate
1 mM dithiothreitol
0.1 mg/ml BSA
60 mM potassium acetate
Acknowledgments
The end-synapsis protocol was adapted from a reported assay (DeFazio et al., 2002) This work was partly supported by grants from La Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer (Equipe labellisée), Electricité de France (EDF, Conseil de Radioprotection) and the Institut National Contre le Cancer (XXL-screen program). J. Cottarel was supported by a PhD fellowship from La Ligue Nationale Contre le Cancer. P. Calsou is a scientist from INSERM, France.
References
- Bombarde, O., Boby, C., Gomez, D., Frit, P., Giraud-Panis, M. J., Gilson, E., Salles, B. and Calsou, P. (2010). TRF2/RAP1 and DNA-PK mediate a double protection against joining at telomeric ends. EMBO J 29(9): 1573-1584.
- Calsou, P., Delteil, C., Frit, P., Drouet, J. and Salles, B. (2003). Coordinated assembly of Ku and p460 subunits of the DNA-dependent protein kinase on DNA ends is necessary for XRCC4-ligase IV recruitment. J Mol Biol 326(1): 93-103.
- Cottarel, J., Frit, P., Bombarde, O., Salles, B., Negrel, A., Bernard, S., Jeggo, P. A., Lieber, M. R., Modesti, M. and Calsou, P. (2013). A noncatalytic function of the ligation complex during nonhomologous end joining. J Cell Biol 200(2): 173-186.
- DeFazio, L. G., Stansel, R. M., Griffith, J. D. and Chu, G. (2002). Synapsis of DNA ends by DNA-dependent protein kinase. EMBO J 21(12): 3192-3200.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Cottarel, J. and Calsou, P. (2013). End-synapsis Assay. Bio-protocol 3(18): e900. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.900.
- Cottarel, J., Frit, P., Bombarde, O., Salles, B., Negrel, A., Bernard, S., Jeggo, P. A., Lieber, M. R., Modesti, M. and Calsou, P. (2013). A noncatalytic function of the ligation complex during nonhomologous end joining. J Cell Biol 200(2): 173-186.
Category
Cancer Biology > General technique > Biochemical assays > DNA structure and alterations
Cancer Biology > Genome instability & mutation > Biochemical assays > DNA structure and alterations
Molecular Biology > DNA > DNA-protein interaction
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link











