- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Generation of Human iNKT Cell Lines
Published: Vol 3, Iss 6, Mar 20, 2013 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.418 Views: 23664

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Identification and Sorting of Adipose Inflammatory and Metabolically Activated Macrophages in Diet-Induced Obesity
Dan Wu [...] Weidong Wang
Oct 20, 2025 2232 Views

Selective Enrichment and Identification of Cerebrospinal Fluid-Contacting Neurons In Vitro via PKD2L1 Promoter-Driven Lentiviral System
Wei Tan [...] Qing Li
Nov 20, 2025 1335 Views

Revisiting Primary Microglia Isolation Protocol: An Improved Method for Microglia Extraction
Jianwei Li [...] Guohui Lu
Dec 5, 2025 1460 Views
Abstract
Natural killer T (NKT) cells comprise an important immunoregulatory T cell subset and express cell surface proteins characteristic of both natural killer cells and T cells. Invariant NKT (iNKT) cells are activated by lipid antigen presented in the context of CD1d molecules, in contrast to classic T cell subsets which recognize peptide antigens presented by MHC molecules. Following activation, iNKT cells rapidly secrete large amounts of cytokines and can lyse tumor cells and virally infected cells; however, iNKT cells are reduced in patients with autoimmune disease and cancer. The potential to characterize and investigate the prospective use of iNKT cells for therapeutic purposes has significantly increased with the ability to stimulate and expand human iNKT cells. In this protocol, we describe a method to generate and propagate primary human iNKT cells. Specifically, primary iNKT cells were isolated from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC), and then expanded periodically with irradiated α-GalCer loaded autologous immature dendritic cells (DC) in the presence of human IL-2.
Materials and Reagents
- Blood sample to collect iNKT cells
- Ficoll-Paque Plus (GE Healthcare Biosciences, catalog number: 17-1440 )
- PE-anti-Vα24Jα18 antibody (6B11) (Biolegend, catalog number: 342904 )
- Anti-CD16/32 antibody (Biolegend, catalog number: 101320 )
- Anti-Vα24 antibody (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: IM2283 )
- Anti-CD3 antibody (Biolegend, catalog number: 300312 )
- Recombinant human GM-CSF (R&D Systems, catalog number: 215-GM )
- Recombinant human IL-4 (R&D Systems, catalog number: 204-IL )
- Recombinant human IL-2 (Proleukin) (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 354043 )
- Human dendritic cell isolation kit (human CD14- magnetic microbeads) (MiltenyiBiotec, catalog number: 130-050-201 )
- Mitomycin C (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M4287 )
- Human iNKT cell isolation kit (Vα24Jα18- magnetic microbeads) (MiltenyiBiotec, catalog number: 130-094-842 )
- α-galactosylceramide (α-GalCer, KRN7000) (Enzo Life Sciences, catalog number: BML-SL232 )
- RPMI-1640 medium (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 11875 )
- Non-essential vitamin solution (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 11140-050 )
- MEM Vitamin solution (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 11120-052 )
- Sodium Pyruvate (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 11360-070 )
- 2-mercaptoethanol (Life Technologies, Gibco®, catalog number: 21985-023 )
- Nalgene Freezing Container (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 15-350-50 )
- Antibiotics: penicillin-streptomycin
- Heat inactivated fetal bovine serum
- MACS buffer (see Recipes)
- Complete medium (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Centrifuge with swing out rotor and capable of 300-700 x g
- BD LSR II flow cytometer (BD Biosciences)
- Sterilized Pasteur pipettes
- 50 ml conical tubes
- 0.22 μM filter
- T-175 flask
- T-25 flask
- 37 °C 5% CO2 incubator
Procedure
- Collect peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). For Ficoll density gradient centrifugation separation of lymphocytes from a buffy coat or leukopheresis pack, first dilute heparinized blood with an equal volume of 1x PBS at room temperature.
- Add 15 ml of Ficoll (warmed to room temperature) to 50 ml conical tubes. Then slowly overlay 25 ml of the diluted blood mixture on top of the Ficoll. Centrifuge at 400 x g for 30 min at room temperature with the brake off.
- Carefully remove the 2-3 ml lymphocyte interface (white ring between the media and Ficoll, please see schematic diagram in Figure 1) with a sterilized Pasteur pipette and transfer to a new 50 ml conical tube.
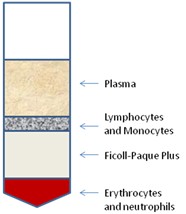
Figure 1. Schematic of Ficoll-Paque Plus separation of human peripheral blood
- Wash the cells by resuspending the cell pellets in 5 ml PBS, then combine all of the pellets into one 50 ml tube, and fill the tube with PBS to 50 ml and spin down cells at 400 x g for 10 min at room temperature with the brake on.
- Discard the supernatant and combine the tubes from a single individual donor to a single tube and wash the PBMCs again with 20 ml PBS. Then count the PBMCs and resuspend at a concentration of 5 x 107 cells/ml in ice-cold MACS buffer.
Note: A leukopak is typically used for these studies and the initial volume of blood is 400-450 ml, but the product has been enriched for leukocytes and the final volume used for Ficoll separation in step 1 is around 40 ml. After the completion of step 5, it is best to continue with the rest of the protocol. If not, the cells should be cultured with complete medium at 107 cells/ml in T-175 flask overnight in 37 °C 5% CO2 incubator, and must be processed into the next step in 24 h. - DAY 1- Isolate human CD14+ cells: Use human CD14- magnetic microbeads according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- For CD14+ PBMCs, culture 107 cells with 8 ml complete medium and 20 ng/ml rhGM-CSF and 20 ng/ml rhIL-4 for 4-5 days in T-25 flask to generate immature dendritic cells (DCs). Freeze the extra cells for future use at 107/vial.
- Keep the CD14neg fraction for iNKT cell isolation. In order to maintain the cells, culture in complete medium and 10 U/ml rhIL-2 at 107/ml in a T-175 flask. It is not necessary to replace medium when expanding DC cells.
- For CD14+ PBMCs, culture 107 cells with 8 ml complete medium and 20 ng/ml rhGM-CSF and 20 ng/ml rhIL-4 for 4-5 days in T-25 flask to generate immature dendritic cells (DCs). Freeze the extra cells for future use at 107/vial.
- DAY 5-To expand the primary iNKT cells: Collect CD14neg PBMCs and wash with 10 ml complete medium. Use the human iNKT cell isolation kit according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- To isolate Vα24+ hNKT cells:
- Collect CD14- PBMC and wash with wash medium once.
- Resuspend the pellets with 30 ml ice cold MACS buffer and pass through a 70 μm sterile cell strainer, then spin at 400 x g for 5 min.
- Resuspend pellets with 1 ml MACS buffer, add anti-Vα24 antibody, 5 μg/106 positive cells (NKT cells comprise 0.01%-0.5% of the lymphocyte population in PBMC). Incubate on ice for 30 min.
- Wash cells twice in 30 ml ice cold MACS buffer.
- Resuspend pellets with 1 ml MACS buffer, add anti-mouse IgG microbeads 20 μl/106 positive cells. Incubate on ice for 20 min.
- Wash cells once in 30 ml ice cold MACS buffer, while centrifuging prepare an MS column by adding 500 μl MACS buffer.
- Resuspend the cells in 500 μl ml MACS buffer. Then pipette the cells into the MS separating column. Make sure to avoid generating bubbles by pipetting slowly. Rinse the column by adding 500 μl ml MACS buffer. Repeat twice. Add 1 ml fresh MACS buffer and remove column from magnet. Place column into a 15 ml conical tube. Insert plunger and push out contents to obtain purified iNKT cells. Count NKT cell enriched fraction. You should have 0.02-0.5 million cells.
- Collect CD14- PBMC and wash with wash medium once.
- To isolate Vα24+ hNKT cells:
- In order to expand primary human iNKT cells:
- First, pretreat the immature DCs with mitomycin C. Resuspend immature DCs at 5 x 106 cells/ml in RPMI containing 0.05 mg/ml mitomycin C, incubate at 37 °C in the dark for 30 min, then wash three times with 10 ml complete media.
- Pulse immature DCs by incubating the cells in complete medium (12 well plates/1 ml per well) containing 200 ng/ml α-GalCer and 20 U/ml rhIL-2 at 2-3 X 106 cells/ml at 37 °C for 1 h.
- First, pretreat the immature DCs with mitomycin C. Resuspend immature DCs at 5 x 106 cells/ml in RPMI containing 0.05 mg/ml mitomycin C, incubate at 37 °C in the dark for 30 min, then wash three times with 10 ml complete media.
- To the 12 well plates- Add 1 ml in complete medium containing 20 U/ml rhIL-2 Vα24+ human iNKT cells to wells containing α-GalCer-loaded DCs (DC:iNKT should be 5:1, for example 2 x 106 DC cells + 0.4 x 106 iNKT cells), mix gently.
- After 2 days, collect cells with a sterilized serological pipet and transfer into 15 ml tubes. Bring volume to 10 ml with RPMI medium containing 5% FBS. Centrifuge at 300 x g for 10 min with braking, discard supernatant, and resuspend cells with complete medium plus 20 U/ml rhIL-2 at 0.4 x 106 cells/ml, and then culture cells in 12 well plate at 3 ml/well.
- Culture cells for 7-10 days, and replace medium every 2 days as step 9.
- Flow cytometric analysis of expanding iNKT cells.
Gate on lymphocytes and check purity by flow cytometric analysis, using PE-anti-Vα24Jα18 antibody (6B11) - see Figure 2.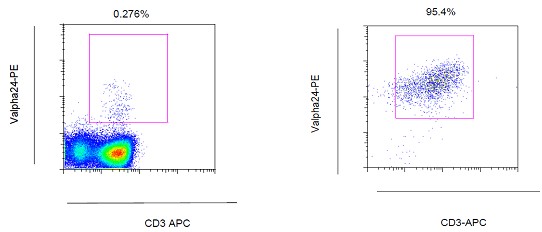
Figure 2. A. iNKT cells among human PBMCs; B. iNKT cell line isolated and expanded from human PBMCs
Flow cytometry procedure:- Collect 0.1 x 106 cells, and transfer into 1.5 ml tube, and filled with 1 ml FACS buffer (0.2% FBS in PBS).
- Centrifuge cell 600 x g for 5 min, and then discard supernatant.
- Resuspend cells in 50 μl FACS buffer, and add 0.5 μl anti-CD16/32 antibody for 15 min to block non-specific binding, and then wash as step a.
- Resuspend cells in 50 μl FACS buffer, and add 5 μl PE anti-Vα24 antibody and 5 μl APC anti-CD3 antibody for 30 min on ice in dark, and then wash as step a.
- Resuspend cells in 200 μl PBS, and run samples on an LSRII FACS machine.
- Collect 0.1 x 106 cells, and transfer into 1.5 ml tube, and filled with 1 ml FACS buffer (0.2% FBS in PBS).
- To maintain iNKT cells culture: Culture iNKT cells in complete medium plus 20 U/ml rhIL-2, and every 2-3 days replaced with fresh medium. When the density of viable cells is greater than 2 x 106 cells/ml, the cells should be diluted to 0.4 x 106 cells/ml with complete medium plus 20 U/ml rhIL-2. To prepare stocks of iNKT cells, iNKT cells with ice-cold RPMI medium plus 10% DMSO and 20% FBS at 5 x 106 cells/ml medium/frozen vial, using Nalgene Freezing Container.
Recipes
- Complete medium
RPMI medium
100 mM sodium pyruvate
10 mM non-essential vitamin solution
100 mM MEM Vitamin solution
5 x 105 M 2-mercaptoethanol
50 U/ml penicillin-streptomycin
10% heat inactivated fetal bovine serum - MACS buffer
1 L PBS free of Ca2+ and Mg2+
5 g BSA
2 mmol EDTA
sterilized by passing through 0.22 μM filter
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH), National Cancer Institute Grants K01 CA131487, R21 CA162273, and R21 CA162277 to T.J. Webb, NIH AI 70258 to M. Tsuji, the NIH AI 44129, CA 108835, and P01 AI072677 to J.P. Schneck. The method was published in Webb et al. (2012) and it is an adaptation of the methods used by Exley et al. (1997), Harada et al. (2005) and Shiratsuchi et al. (2009).
References
- Dellabona, P., Padovan, E., Casorati, G., Brockhaus, M. and Lanzavecchia, A. (1994). An invariant V alpha 24-J alpha Q/V beta 11 T cell receptor is expressed in all individuals by clonally expanded CD4-8- T cells. J Exp Med 180(3): 1171-1176.
- Exley, M., Garcia, J., Balk, S. P. and Porcelli, S. (1997). Requirements for CD1d recognition by human invariant Valpha24+ CD4-CD8- T cells. J Exp Med 186(1): 109-120.
- Fowlkes, B. J., Kruisbeek, A. M., Ton-That, H., Weston, M. A., Coligan, J. E., Schwartz, R. H. and Pardoll, D. M. (1987). A novel population of T-cell receptor alpha beta-bearing thymocytes which predominantly expresses a single V beta gene family. Nature 329(6136): 251-254.
- Harada, Y., Imataki, O., Heike, Y., Kawai, H., Shimosaka, A., Mori, S., Kami, M., Tanosaki, R., Ikarashi, Y., Iizuka, A., Yoshida, M., Wakasugi, H., Saito, S., Takaue, Y., Takei, M. and Kakizoe, T. (2005). Expansion of alpha-galactosylceramide-stimulated Valpha24+ NKT cells cultured in the absence of animal materials. J Immunother 28(4): 314-321.
- Prigozy, T. I., Naidenko, O., Qasba, P., Elewaut, D., Brossay, L., Khurana, A., Natori, T., Koezuka, Y., Kulkarni, A. and Kronenberg, M. (2001). Glycolipid antigen processing for presentation by CD1d molecules. Science 291(5504): 664-667.
- Shiratsuchi, T., Schneck, J., Kawamura, A. and Tsuji, M. (2009). Human CD1 dimeric proteins as indispensable tools for research on CD1-binding lipids and CD1-restricted T cells. J Immunol Methods 345(1-2): 49-59.
- Webb, T. J., Bieler, J. G., Schneck, J. P. and Oelke, M. (2009). Ex vivo induction and expansion of natural killer T cells by CD1d1-Ig coated artificial antigen presenting cells. J Immunol Methods 346(1-2): 38-44.
- Webb, T. J., Li, X., Giuntoli, R. L., 2nd, Lopez, P. H., Heuser, C., Schnaar, R. L., Tsuji, M., Kurts, C., Oelke, M. and Schneck, J. P. Molecular identification of GD3 as a suppressor of the innate immune response in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 72(15): 3744-3752.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2013 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Li, X., Tsuji, M., Schneck, J. and Webb, T. J. (2013). Generation of Human iNKT Cell Lines. Bio-protocol 3(6): e418. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.418.
Category
Immunology > Immune cell isolation > Maintenance and differentiation
Cell Biology > Cell isolation and culture > Cell isolation
Immunology > Immune cell isolation > Lymphocyte
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link













