- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to Assess Histone Marks in Auxin-treated Arabidopsis thaliana Inflorescence Tissue
Published: Vol 10, Iss 23, Dec 5, 2020 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3832 Views: 5318
Reviewed by: Wenrong HePingtao DingYingnan Hou

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Agrobacterium-Mediated Transient Gene Expression Optimized for the Bioenergy Crop Camelina sativa
Pawan Kumar [...] Jean T. Greenberg
Apr 5, 2024 2114 Views

Identification of S-locus F-box Protein Sequences in Diploid Potato, Solanum okadae, via Degenerate PCR
Amar Hundare [...] Timothy P. Robbins
Jun 5, 2025 1995 Views

Quantitative Analysis of the Arabidopsis Leaf Secretory Proteome via TMT-Based Mass Spectrometry
Sakharam Waghmare [...] Rucha Karnik
Nov 20, 2025 2020 Views
Abstract
Chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled with quantitative PCR (ChIP-qPCR) or high-throughput sequencing (ChIP-seq) has become the gold standard for the identification of binding sites of DNA binding proteins and the localization of histone modification on a locus-specific or genome-wide scale, respectively. ChIP experiments can be divided into seven critical steps: (A) sample collection, (B) crosslinking of proteins to DNA, (C) nuclear extraction, (D) chromatin isolation and fragmentation by sonication, (E) immunoprecipitation of histone marks by appropriate antibodies, (F) DNA recovery, and (G) identification of precipitated protein-associated DNA by qPCR or high-throughput sequencing. Here, we describe a time-efficient protocol that can be used for ChIP-qPCR experiments to study the localization of histone modifications in young inflorescences of the model plants Arabidopsis thaliana.
Keywords: ChIPBackground
Eukaryotic genomes are organised in chromosomes in which DNA associates with histones to form chromatin. Tight interactions between histones and DNA impedes the accessibility of DNA to other factors. Consequently, the location of histones relative to important regulatory DNA sequences and the strength of histone-DNA contacts can either hide or expose genes providing yet another layer of gene regulation. In chromatin, both histones and DNA can be chemically modified (Zhou et al., 2010; Schübeler, 2015). Depending on the physical properties of the modification, the chromatin state can either prevent or enhance the transcription of the underlying genes (Kouzarides, 2007; Yang et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2015). In plants, the epigenetic state of the chromatin has been shown to be a crucial determinant of gene expression in response to developmental or environmental stimuli (Yang et al., 2014; Wu et al., 2015; Chung et al., 2019; Kuhn et al., 2020).
The plant hormone auxin regulates almost all aspect of a plant’s life cycle. A mechanism for auxin perception has been established involving a nuclear signalling pathway. This pathway is based on the de-repression of Auxin Response Factors (ARFs) via auxin-induced degradation of Aux/IAA transcriptional repressors. Aux/IAAs inhibit ARF activity towards target genes by recruiting the co-repressor TOPLESS (TPL) to repress auxin-dependent gene expression. TPL/TPRs mediate their repressive effect by attracting histone deacetylases (HDACs) (Krogan et al., 2012; Weijers and Wagner, 2016). We have identified an alternative auxin signalling mechanism which is essential for gynoecium development in Arabidopsis thaliana. In this noncanonical pathway, auxin directly affects the activity of complexes involving an atypical ARF, called ETTIN (ETT/ARF3) towards downstream targets (Simonini et al., 2016 and 2017, Kuhn et al., 2020). Recently, we found that direct auxin binding by ETT leads to dissociation from co-repressor proteins of the TPL/TPR family followed by induction of gene expression. Moreover, we showed that this correlates with ETT-dependent auxin-responsive histone acetylation of the target genes (Kuhn et al., 2020).
Chromatin immunoprecipitation coupled with quantitative PCR (ChIP-qPCR) has become the gold standard for the identification and characterisation of histone modifications at given gene loci. Since ETT is primarily involved in floral reproductive development, we optimized existing ChIP protocols (Yang et al., 2014, Qüesta et al., 2016) to study the effect of auxin on histone modifications in inflorescence tissue. The protocol that we present here has been successfully applied to evaluate several epigenetic marks including H3K27Ac (Kuhn et al., 2020) in Arabidopsis inflorescence tissue.
Materials and Reagents
Spray bottle TurnNSpray 500 ml (R&L Slaughter, catalog number: 215-2962 )
Corning 50 ml centrifuge tubes (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: CLS430829-500E )
Elastic rubber bands
Paper towel
Aluminium Foil
Funnel (6 cm diameter)
2 ml DNA low binding (LoBind) tubes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 0030108078 )
1.5 ml DNA low binding (LoBind) tubes (Eppendorf, catalog number: 022431021 )
Arabidopsis thaliana
Indole-3-acetic acid (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: I5148 )
Silwet L-77 (De Sangosse Ltd., catalog number: 0640 )
Miracloth (MERK, catalog number: 475855 )
Liquid nitrogen
10x Phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 11666789001 )
Formaldehyde (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F8775 )
Glycine (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: G/0800/60 )
Sterile water
Succrose (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S/8600/60 )
Ficoll 400 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: F8636 )
Dextran from Leuconostoc spp. (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 31389 )
HEPES (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H4034 )
Magnesium chloride (MgCl2) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M8266 )
Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T9284 )
DL-Dithiothreitol (DTT; Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D0632 )
cOmplete EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche Molecular Systems, catalog number: 4693132001 )
Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane (TRIS; Sigmal-Aldrich, catalog number: B2005 )
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA; Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E6758 )
20% Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) solution (Severn Biotech; catalog number: 20-4002-05 )
Sodium Chloride (NaCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S7653 )
Dynabeads Protein A (Invitrogen, catalog number: 10001D )
Anti-H3 Antibody (Rabbit polyclonal Antibody; Abcam, catalog number: ab1791 )
Anti-H3K27ac Antibody (Rabbit polyclonal Antibody; Abcam, catalog number: ab4729 )
Sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S5761 )
Proteinase K (Roche Molecular Systems, catalog number: 40693800 )
Phenol:Chloroform:Isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 77617 )
Sodium acetate (NaAc) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S7670 )
Ethanol absolute (VWR Chemicals, catalog number: 20821.330 )
LightCycler 480 Multiwell Plate 96, white (Roche Molecular Systems, catalog number: 04729692001 )
LightCycler® 480 Sealing Foil (Roche Molecular Systems, catalog number: 04729757001 )
Oligo-nucleotide primers (Integrated DNA Technologies)
SYBR Green JumpStart Taq Ready Mix (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S4438 )
RNase A (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: EN0531 )
Agarose (Melford Biolaboratories Ltd., catalog number: A20080-1000.0 )
100 bp DNA ladder (New England Biolabs Ltd., catalog number: N3221S )
Stock Solutions (see Recipes)
2 M Glycine
0.5 M HEPES KOH pH 7.4
1 M MgCl2
1 M Tris-HCl pH 8
0.5 M EDTA
5 M NaCl
3 M NaAc
1 M DTT
20% (v/v) Triton X-100
10% (v/v) SDS
ChIP Buffers (see Recipes)
Honda Buffer
Nuclei Lysis Buffer
ChIP Dilution Buffer
Low Salt Wash Buffer
High Salt Wash Buffer
TE Buffer
Elution Buffer
Equipment
Tweezers (DUMONT BIOLOGICAL TYPE 5 SS-1, TAAB Laboratories Equipment, catalog number: T083 )
Glass beaker 100 ml
Mortar and pistil
Bel-Art Space Saver Vacuum Desiccator (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 11852732 )
Vacuum rump (Edwards, model: IEC34-1 )
Tube rotor (Stuart Scientific, model: SB1 )
Centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5810R )
Swing-bucket rotor with 50 ml tube adaptors (Eppendorf, model: A-4-81 )
Fixed-angle rotor for 48 x 1.5/2.0 ml tubes (Eppendorf, model: FA-45-48-11 )
Sonicator (Diagenode, Model Bioruptor Plus )
Magnetic separator rack (GE Healthcare, MagRack6, catalog number 28-9489-64 )
Thermomixer (Eppendorf, Model Eppendorf ThermoMixer C )
CFX96 touch real-time PCR detection system (Bio-Rad)
Vacuum concentrator (Eppendorf, model: Concentator Plus )
Gel electrophoresis system (Thermo Electric Corporation, model: CSSU1214 )
Power pack (Kikusui Electronics Corporation, model: PAB 350-0.2 )
Procedure
Sample treatment and collection
This section describes the plant cultivation and treatment procedures for Arabidopsis thaliana and Capsella rubella inflorescence tissue subjected to auxin treatments. Cultivation and treatment procedures may differ for other species, tissues and treatments.
Grow Arabidopsis plants on soil at 22 °C in long day conditions (16 h day/8 h dark) until inflorescences emerge (3-4 weeks).
Treat inflorescences by spraying the full tray of plants with a solution containing 100 µM Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA, auxin) and 0.015% Silwet L-77 or MOCK (only 0.015% Silwet L-77) in water (Note 1).
Return treated plants to the growth room for two hours.
Using tweezers collect 3 g of young inflorescence tissue in a 50 ml Falcon Tube (Note 2).
Collect a total of three biological replicates (3 times 3 g) for one experiment (Note 3).
Crosslinking
Transfer the collected samples onto Miracloth squares (~5 x 5 cm), fold into small bags and close them securely with an elastic band (Note 4).
Place samples in a glass beaker (100 ml) and add 50 ml 1% Formaldehyde solution (Note 5).
Note: Formaldehyde is toxic, work in fume cabinet.
Place the glass beakers in the vacuum desiccator and turn it on.
Crosslink samples in 1% formaldehyde solution for 3 times 5 min, releasing the vacuum after 5 min and reapply when fully released (Note 6).
Quench the reaction by adding 2 M glycine solution to a final concentration of 125 mM and apply vacuum for 5 min.
Release vacuum and discard quenched 1% Formaldehyde solution.
Wash samples twice with 1x PBS and twice with water.
Blot them dry on paper towel and then fold the tissue into aluminium foil.
Flash freeze packets in liquid nitrogen.
*Stopping point (store at -80 °C).
Note: Unless stated otherwise all subsequent steps should be carried out on ice using pre-cooled buffers.
Nuclear extraction
Using pre-cooled mortar and pistil, grind the plant material in liquid nitrogen into fine powder.
Suspend ground up plant material in 25 ml Honda Buffer and homogenise for 10 min at 4 °C on a rotor.
Filter through one layer of Miracloth (~7 x 7 cm) using a funnel into new 50 ml Falcon tube. Squeeze the Miracloth to maximise the yield.
Centrifuge at 850 x g for 20 min (4 °C).
Gently resuspend the pellet in 1 ml Honda Buffer (Note 7).
Centrifuge at 850 x g for 5 min (4 °C).
Repeat step 5 and 6 twice to clear the extract.
*Stopping point (pellet can be stored overnight at -20 °C).
Chromatin fragmentation by sonication
Centrifuge 4,000 x g for 1 min (4 °C).
Remove residual Honda Buffer and resuspend pellet in 300 μl of Nuclei Lysis Buffer.
Split the sample in two 2 ml Lobind tubes (~250 μl per tube).
Take a 25 μl of this new suspension for your non-sonicated control and store at -20 °C.
Sonicate 3 times for 5 min on medium strength using a Bioruptor water bath sonicator (Diagenode) using a 30 s ON/OFF cycle, to fragment the chromatin. Mix samples between each 5 min period (Note 8).
Centrifuge the samples for 10 min, 4,000 x g, 4 °C.
Transfer the supernatant to fresh 2 ml Lobind tubes.
Take a 25 μl to check sonication efficiency and store at -20 °C (Note 9).
*Stopping point (samples can be stored overnight at -20 °C).
Immunoprecipitation (IP)
Dilute the samples ten-fold with ChIP Dilution Buffer (~2 ml).
Note: Take 20 μl sonicated homogenate as Input control.
Prepare the antibody coated magnetic beads.
Take 15 μl of Protein A magnetic beads for each IP and wash three times with 1 ml ChIP dilution buffer.
Resuspend magnetic beads in 50 μl ChIP Dilution Buffer per IP.
Bind 1 μg of antibody per IP to the beads.
To IP H3 we use the anti-H3 antibody and to IP H3K27Ac we use the anti-H3K27ac Antibody.
Incubate on a rotor for an hour at 4 °C.
Add 50 μl anti-H3 antibody-coated beads to one half of the samples and 50 μl antibody-coated beads to the other half of the samples.
Incubate on a rotor at 4 °C for at least 4 h.
*Stopping point (this step can also be done overnight).
Wash the beads sequentially (each time 5 min at 4 °C incubation on the rotor) with 1 ml with:
Twice Low Salt Washing Buffer.
Twice High Salt Washing Buffer.
Twice TE Buffer.
Note: For each of these washes, leave on the magnetic stand for one minute at a time.
After the last TE wash transfer the sample to a fresh 1.5 ml Lobind tube then separate on the magnetic stand and remove TE.
DNA recovery
Elute from beads twice with 200 μl pre-heated Elution Buffer. Incubate for 15 min at 65 °C with 800 rpm agitation. Collect the two elutions (400 μl total volume) in one fresh 1.5 ml Lobind tube and discard the magnetic antibody coated beads.
Bring the Input samples to 400 μl using Elution Buffer.
To reverse crosslink, add 16 μl 5M NaCl to the eluate and incubate at 65 °C and 600 rpm agitation overnight.
After reverse crosslinking, add 3 μl Proteinase K (20 mg/ml) and incubate for 1 h at 45 °C.
To extract DNA, add 400 μl Phenol:Chloroform:Isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1), vortex for 30 s and centrifuge at 4,000 x g for 10 min at room temperature.
Transfer the aqueous layer (~400 μl) in a fresh 1.5 ml Lobind tube.
To precipitate DNA, add 0.1 volume (40 μl) 3 M NaAc and 2 volumes (800 μl) 100% ethanol (mix well) and incubate at -20 °C for 1.5 h.
Centrifuge at 4,000 x g for 30 min (4 °C).
Wash pellet with 500 μl ice cold 70% ethanol, centrifuge for 10 min at 4,000 x g (4 °C).
Remove all traces of ethanol and dry the pellet in vacuum concentrator for 10 min (65 °C).
Resuspend the pellet in the required volume of nuclease free water (Note 10).
Identification of precipitated protein-associated DNA by qPCR
Setup qPCR reactions in triplicate per antibody, treatment and primer pair as follows (Note 11):
Per reaction (10 μl final volume): 3 μl DNA, 5 μl SYBR Green JumpStart Taq ReadyMix (Sigma), 0.125 μl Forward Primer (10 μM), 0.125 μl Reverse Primer (10 μM), 1.75 μl water.
Run the reaction on qPCR machine using the following conditions: 95 °C for 2 min followed by 60 cycles at 95 °C for 10 s, 60 °C for 10 s and 72 °C for 30 s.
Analyse the data as described under “Data analysis”.
Data analysis
Note: We have analysed the data published in Kuhn et al. (2020) using described protocol.
Once the Ct (Cycle threshold) values have been obtained calculate the mean between the three technical replicates.
Calculate the ratio between each IP with the corresponding Input for all target regions:
MEAN = 2-(MEAN(IP)-MEAN(Input)) to transform to linear scale.
Calculate the enrichment of the Histone H3 modification of interest (e.g., H3K27Ac) as the ratio between the H3K27Ac and H3 for each biological replicate at each target region.
Calculate mean and standard deviation between all biological replicates at each target region.
Analyse the statistical differences between hormone treated and MOCK samples at each target region using two-way ANOVA with post hoc Bonferroni multiple comparison test.
Plot the mean and standard deviation of the ratio (H3K27Ac/H3) along the length of the examined target region.
Notes
Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) is insoluble in water and needs to be freshly prepared in ethanol to a stock concentration of 100 mM. Mock treatment has to contain the same amount of ethanol as the auxin treatment. When treating the plants, make sure that you spray equally with treatment and mock solution. Treatment of ~100 Arabidopsis plants requires ~100 ml solution.
We only harvested inflorescence tissue that contained closed flower buds. Flowers that were opened or young siliques were removed.
To obtain 3 g sample inflorescences of ~100 plants need to be harvested. We recommend to collect one pair of biological replicates (one replicate per genotype, mock and IAA-treatment) at the same time and to repeat collection three times to obtain three replicates for an experiment. We recommend having two people collecting to reduce the time.
If including more than one genotype or treatment, it is advised to use one glass beaker per treatment and genotype to prevent mixing of samples.
Crosslinking time may need optimisation depending on protein and tissue. The optimal crosslink time crosslinks your protein of interest to the DNA but does not block the epitope. This can be tested by Western blotting.
Do not start timing the 5 min before the first bubbles emerge.
This can be done with a 100 μl pipette. We recommend cutting the pipette tip to prevent damaging the nuclei.
Sonication conditions can differ between sonicators and depend on samples. Generally four parameters are essential for the efficiency of the DNA fragmentation: 1) the temperature of the sample (we recommend to maintain a temperature of 4 °C throughout the sonication), 2) the concentration of formaldehyde used for crosslinking (the higher the concentration leads increases the sonication time), 3) the volume in which sonication is performed (we recommend not to sonicate more than 250 μl of lysate in a 1.5 ml tube), 4) the concentration of SDS in the lysis buffer (more SDS leads to easier lysis during sonication).
Sonication test:
Once your sonication conditions are well established, you can skip this step. Bring sonication and non-sonication aliquots to 100 μl volume with elution buffer.
Add 1 μl of 10 mg/ml RNase A, mix well and incubate for 1 h at 37 °C.
Add 100 μl of Phenol:Chloroform:Isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1), vortex for 30 s and centrifuge 4,000 x g for 10 min at room temperature.
Transfer the aqueous phase to a fresh 1.5 ml Lobind tube and add 0.1 volumes (10 μl) of 3 M NaAc (pH 5.5) and 2 volumes (200 μl) of 100% EtOH. Vortex and incubate for 1.5h at -20 °C.
Centrifuge for 4,000 x g for 20 min at 4 °C.
Remove the supernatant and dry the pellet for 10 min in vacuum concentrator (65 °C).
Resuspend the pellet in 10 μl water.
Run samples on a 1.5% Agarose gel.
Visualise the gel. The DNA should be visible as a smear between 100 bp and 500 bp (Figure 1). The smaller the DNA is fragmented the higher the resolution of the experiment.
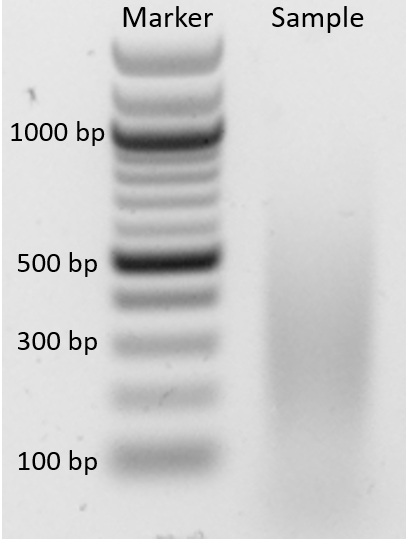
Figure 1. Sonication test. Marker (NEB 100 bp ladder); Sample showing the bulk of DNA fragments range from 100-500 bp.The volume of water depends on the number of qPCR reactions that will be run (3 μl DNA per reaction).
Primers should be designed to amplify fragments (the ideal fragment length is ~100 bp) with regular spacing across the whole gene locus of interest. The resolution of the experiments increases with increasing amplicon density. Before use, all qPCR primers should be tested for their efficiency and specificity. The amplification efficiency of primers can be tested using a genomic DNA dilution series (1/4 to 1/4096) (Figure 2A). The specificity of primers was confirmed by analysing the melting curves (65 °C to 95 °C) (Figure 2B). qPCR reactions should be prepared and performed as described in the experimental procedures (G1-3).
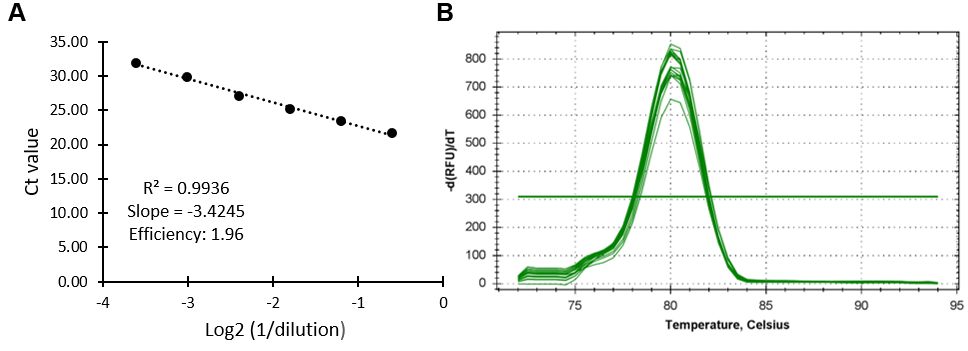
Figure 2. Example a suitable qPCR primer. A. Amplification efficiency of a suitable primer should show a correlation between amplification and dilution (R2) of 0.95-1 and a primer efficiency (10-1/slope) of 2 ± 0.1. B. Melt peak indicating high specificity of the primer pair.
Recipes
Stock Solutions
2 M Glycine
Autoclave0.5 M HEPES KOH pH 7.4
Autoclave
1 M MgCl2
Autoclave
1 M Tris-HCl pH 8
Autoclave0.5 M EDTA
Autoclave5 M NaCl
Autoclave3 M NaAc
Autoclave1 M DTT
Weigh 1.54 g of DTT and dissolve in 10 ml water
Filter sterilize after all DTT is dissolved and make 1 ml aliquots
Store at -20 °C
20% (v/v) Triton X-100
Dilute Triton X-100 five times with water to obtain 20% Triton X-100
10% (v/v) SDS
Dilute 20% (v/v) SDS with 1 volume water to obtain 10% (v/v) SDS solution
ChIP Buffers
Honda Buffer
0.44 M sucrose
1.25% (w/v) Ficoll
2.5% (w/v) Dextran T40
20 mM HEPES KOH pH 7.4
0.5% (v/v) Triton X-100
10 mM MgCl2
0.5 mM DTT
1 tablet per 50 ml cOmplete EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche)
Nuclei Lysis Buffer
50 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0
10 mM EDTA
1% (v/v) SDS
1 tablet per 50 ml cOmplete EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche)
ChIP Dilution Buffer
16.7 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0
1.2 mM EDTA
1.1% (v/v) Triton X-100
167 mM NaCl
1 tablet per 50 ml cOmplete EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche)
Low Salt Wash Buffer
20 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0
2 mM EDTA
150 mM NaCl
0.1% (v/v) SDS
1% (v/v) Triton X-100
1 tablet per 50 ml cOmplete EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche)
High Salt Wash Buffer
20 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0
2 mM EDTA
500 mM NaCl
0.1% (v/v) SDS
1% (v/v) Triton X-100
1 tablet per 50 ml cOmplete EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche)
TE Buffer
10 mM Tris-HCl pH 8.0
1 mM EDTA
1 tablet per 50 ml cOmplete EDTA-free protease inhibitor cocktail (Roche)
Elution Buffer
0.1 M NaHCO3
1% (v/v) SDS
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Yang Dong and Emilie Knight for critical comments on the protocol. We also express our gratitude to Caroline Dean, Hongchun Yang and Julia Qüesta for their helpful advice throughout the development of this protocol. This protocol was adapted from Kuhn et al., 2020 . This work was supported by grant BB/S002901/1 to L.Ø., the Norwich Research Park Biosciences Doctoral Training Partnership [grant number BB/M011216/1 to A.K.] and by the Institute Strategic Programme grant (BB/P013511/1) to the John Innes Centre all from the UKRI Biotechnological and Biological Sciences Research Council.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
References
- Chung, Y., Zhu, Y., Wu, M. F., Simonini, S., Kuhn, A., Armenta-Medina, A., Jin, R., Ostergaard, L., Gillmor, C. S. and Wagner, D. (2019). Auxin Response Factors promote organogenesis by chromatin-mediated repression of the pluripotency gene SHOOTMERISTEMLESS. Nat Commun 10(1): 886.
- Kouzarides, T. (2007). Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 128(4): 693-705.
- Krogan, N. T., Hogan, K. and Long, J. A. (2012). APETALA2 negatively regulates multiple floral organ identity genes in Arabidopsis by recruiting the co-repressor TOPLESS and the histone deacetylase HDA19. Development 139(22): 4180-4190.
- Kuhn, A., Ramans Harborough, S., McLaughlin, H. M., Natarajan, B., Verstraeten, I., Friml, J., Kepinski, S. and Ostergaard, L. (2020). Direct ETTIN-auxin interaction controls chromatin states in gynoecium development. Elife 9: e51787.
- Qüesta, J. I., Song, J., Geraldo, N., An, H. and Dean, C. (2016). Arabidopsis transcriptional repressor VAL1 triggers Polycomb silencing at FLC during vernalization. Science 353(6298): 485-488.
- Schübeler, D. (2015). Function and information content of DNA methylation. Nature 517(7534): 321-326.
- Simonini, S., Deb, J., Moubayidin, L., Stephenson, P., Valluru, M., Freire-Rios, A., Sorefan, K., Weijers, D., Friml, J. and Ostergaard, L. (2016). A noncanonical auxin-sensing mechanism is required for organ morphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 30(20): 2286-2296.
- Simonini, S., Bencivenga, S., Trick, M. and Ostergaard, L. (2017). Auxin-Induced Modulation of ETTIN Activity Orchestrates Gene Expression in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 29(8): 1864-1882.
- Weijers, D. and Wagner, D. (2016). Transcriptional Responses to the Auxin Hormone. Annu Rev Plant Biol 67: 539-574.
- Wu, M. F., Yamaguchi, N., Xiao, J., Bargmann, B., Estelle, M., Sang, Y. and Wagner, D. (2015). Auxin-regulated chromatin switch directs acquisition of flower primordium founder fate. Elife 4: e09269.
- Yang, H., Howard, M. and Dean, C. (2014). Antagonistic roles for H3K36me3 and H3K27me3 in the cold-induced epigenetic switch at Arabidopsis FLC. Curr Biol 24(15): 1793-1797.
- Zhou, V. W., Goren, A. and Bernstein, B. E. (2011). Charting histone modifications and the functional organization of mammalian genomes. Nat Rev Genet 12(1): 7-18.
Article Information
Copyright
Kuhn and Østergaard. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY 4.0).
How to cite
Readers should cite both the Bio-protocol article and the original research article where this protocol was used:
- Kuhn, A. and Østergaard, L. (2020). Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) to Assess Histone Marks in Auxin-treated Arabidopsis thaliana Inflorescence Tissue. Bio-protocol 10(23): e3832. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3832.
- Kuhn, A., Ramans Harborough, S., McLaughlin, H. M., Natarajan, B., Verstraeten, I., Friml, J., Kepinski, S. and Ostergaard, L. (2020). Direct ETTIN-auxin interaction controls chromatin states in gynoecium development. Elife 9: e51787.
Category
Plant Science > Plant molecular biology > Protein
Developmental Biology > Morphogenesis > Organogenesis
Molecular Biology > DNA > DNA-protein interaction
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link








