- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Endocytosis Detection in Magnaporthe oryzae
Published: Vol 9, Iss 15, Aug 5, 2019 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3322 Views: 4833
Reviewed by: LAXMI NARAYAN MISHRAAshish RanjanAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Genetic Tagging and Imaging of Proteins with iFAST in Candida albicans
Jonas Devos [...] Wouter Van Genechten
Oct 5, 2024 1485 Views

Silencing Arbuscular Mycorrhizal Fungal Gene Using Chitosan Nanoparticle-Mediated dsRNA Delivery System
Chumei Yan [...] Xianan Xie
Jun 5, 2025 2635 Views

A Reliable In Planta Inoculation and Antifungal Screening Protocol for Rhizoctonia solani-Induced Sheath Blight in Rice
Alinaj Yasin [...] Palash Deb Nath
Nov 5, 2025 1568 Views
Abstract
Endocytosis is an intracellular trafficking pathway that occurs in nutrient uptake, signal transduction and reconstruction of cell polarity and is conserved in eukaryotic cells. In fungi, endocytosis plays crucial roles in the physiology of hyphal growth and pathogenicity. vidence for endocytosis in filamentous fungi is detected by the membrane-selective dyes FM4-64. Cells of a range of filamentous fungal species readily take up these dyes. However, the method for endocytosis detection has not been well established in Magnaporthe oryzae. Here, we provide a protocol for tracking endocytosis in Magnaporthe oryzae.
Keywords: EndocytosisBackground
Endocytosis is an important cellular process that internalizes extracellular materials and retrieves membrane and proteins from the plasma membrane. Endocytosis starts from the plasma membrane and transports proteins, lipids and molecules from the external environment to degradative organelles, or recycled back to the plasma membrane by vesicles and endosomes (Kaksonen et al., 2003). Several studies have demonstrated the existence of endocytosis with the fluorescent dye FM4-64, a specific tracer of endocytosis, suggesting this organelle may be involved in endocytic membrane recycling in filamentous fungi (Fischer-Parton et al., 2000; Wedlich-Soldner et al., 2000; Penalva, 2005; Li et al., 2017). FM4-64 is also used for detecting membrane traffic from endosomes toward the vacuole and autophagy in yeast (Hayden et al., 2013; Journo et al., 2008). Many protocols for detecting endocytosis have been established in Aspergillus oryzae and yeast (Higuchi et al., 2011; Higuchi et al., 2009; Kamble et al., 2011). However, there is no specific protocol established for Magnaporthe oryzae, which is the causal agent of rice blast, the most serious fungal disease in the world. Here, we describe a reliable and simple protocol for detecting the endocytic pathway of M. oryzae.
Materials and Reagents
- Microscope slide (Sail brand, catalog number: 7105)
- Microscope cover glass (Fisher brand, catalog number: 12-540-A)
- Hyphae of Magnaporthe oryzae
- M. oryzae Guy11, used as the parental wild type strain. (MoARK1 gene knock-out mutant ∆Moark1 was obtained in our previous work. All the strains were cultured on complete medium [CM] agar plates. Liquid CM medium was used to prepare the mycelia for endocytosis assay. The strain Guy11 was stored in our laboratory.)
- N-(3-triethylammoniumpropyl)-4-(pdiethyl-aminophenyl-hexatrienyl) pyridinium dibromide FM4-64 (Invitrogen, catalog number: T13320)
- Latrunculin B (Cayman, catalog number: 10010631)
- Double-distilled H2O (ddH2O)
- DMSO (Sigma, catalog number: D2650)
- D-glucose (Sigma, catalog number: 47829)
- Peptone (Sangon biotech, catalog number: A505247)
- Yeast extract (Oxoid, catalog number: LP0021)
- Casamino acid (Sangon biotech, catalog number: A603060)
- Biotin (Sigma, catalog number: B4501)
- Pyridoxin (Sigma, catalog number: P9755)
- Thiamine (Sangon biotech, catalog number: A600939)
- Riboflavin (Sangon biotech, catalog number: A600470)
- p-aminobenzoic acid (Amresco, catalog number: 0779)
- Nicotinic Acid (Sigma, catalog number: 72309)
- Liquid complete medium (Liquid CM medium) (see Recipes)
- Vitamin solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Eppendorf micropipette (1,000 μl, 100 μl, 10 μl)
- Confocal fluorescence microscope (Zeiss LSM710, 63x oil)
Procedure
- Culture the wild type strain Guy11 and ∆Moark1 on solid CM medium for 4 days at 28 °C. Cut the agar culture into 1 mm x 1 mm squares and culture the squares in liquid CM for 2 more days.
- Prepare a stock solution of FM4-64 (1.3 mg/ml in DMSO) and dilute in distilled H2O at a final concentration of 5 μg/ml, keep this staining solution on ice.
- Wash the hyphae with distilled water and stain with FM4-64 on glass slide, about 20 μl working solution dropped on the hyphae and stain for 2 min at room temperature.
- Before observation, wash the hyphae with ddH2O.
- Take photographs under a confocal fluorescence microscope (63x oil, 570/620 nm excitation, 590 nm dichroic, 630/660 nm emission is used to observe the fluorescence of FM4-64) after exposure to FM4-64. A representative picture of the plasma membrane and the inner cellular membrane components after staining 2 min with FM4-64 is shown in Figure 1.
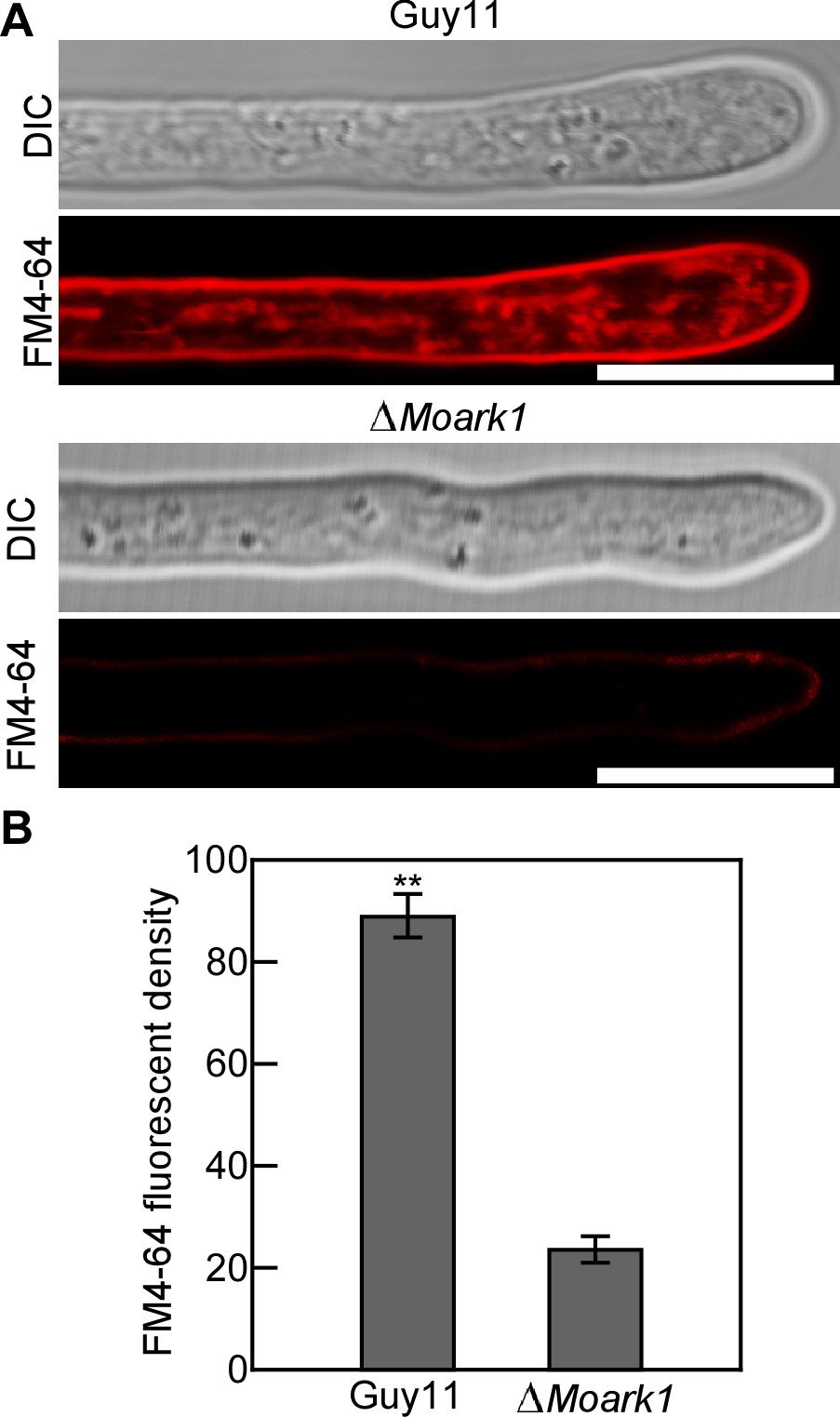
Figure. 1 Endocytosis assay in M. oryzae. A. The wild type strain Guy11 and the ∆Moark1 were grown in liquid CM for 48 h before the addition of FM4-64 and photographs were taken under a confocal fluorescence microscope (Zeiss LSM710, 63x oil) after 2 min of exposure to FM4-64. Bars = 10 μm. B. The calculation of relative fluorescent density. Error bars represent SD and double asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (**, P < 0.01). - Prepare a stock solution of Latrunculin B (Lat B) in DMSO at a concentration of 25 mg/ml and dilute in distilled H2O at a final concentration of 0.1 μg/ml. Lat B is used as an actin polymerization inhibitor to disrupt endocytosis (Kaksonen et al., 2003).
- For Lat B staining, pretreat the hyphae with Lat B when cultured in Step 1 for 30 min prior to the addition of FM4-64.
- Repeated Steps 2-5.
Data analysis
For endocytosis defect analysis, culture the strains Guy11 and the gene knock-out mutants in the background of Guy11 for 2 days on microscope slides overlaid with complete medium (CM) before staining with FM4-64 dye and take photographs at various times after FM4-64 exposure, and the signal appeared on the plasma membrane and endomembrane compartments in Guy11, but did not occur or delayed until 20-30 min after staining in the mutant cells (Li et al., 2017). Each result is presented at least three replicated measurements. The significance of differences between treatments is statistically evaluated using SDs and one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) in SPSS 2.0 (https://spss.en.softonic.com/, Chicago, IL, USA). Data for two specific different treatments are compared statistically using ANOVA, followed by an F-test if the ANOVA result is significant at P < 0.05 or P < 0.01.
Recipes
- Liquid CM medium
10 g D-glucose
2 g peptone
1 g yeast extract
1 g casamino acid
1 ml Vitamin Solution
Hygrothermal high pressure sterilization at 121 °C for 20 min. - Vitamin Solution
0.01 g Biotin
0.01 g Pyridoxin
0.01 g Thiamine
0.01 g Riboflavin
0.01 g p-aminobenzoic acid
0.01 g Nicotinic Acid
Add ddH2O to 100 ml and store in a dark glass bottle at 4 °C
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (grant number KYT201805) and Innovation Team Program for Jiangsu Universities (2017).
Competing interests
No conflicts of interest or competing interests.
References
- Fischer-Parton, S., Parton, R.M., Hickey, P.C., Dijksterhuis, J., Atkinson, H.A. and Read, N.D. (2000). Confocal microscopy of FM4-64 as a tool for analysing endocytosis and vesicle trafficking in living fungal hyphae. J Microsc 198(3): 246-259.
- Hayden, J., Williams, M., Granich, A., Ahn, H., Tenay, B., Lukehart, J., Highfill, C., Dobard, S. and Kim, K. (2013). Vps1 in the late endosome-to-vacuole traffic. J Biosci 38(1): 73-83.
- Higuchi, Y., Arioka, M. and Kitamoto, K. (2011). Functional analysis of the putative AAA ATPase AipA localizing at the endocytic sites in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus oryzae. FEMS Microbiol Lett 320(1): 63-71.
- Higuchi, Y., Shoji, J.Y., Arioka, M. and Kitamoto, K. (2009). Endocytosis is crucial for cell polarity and apical membrane recycling in the filamentous fungus Aspergillus oryzae. Eukaryot Cell 8(1): 37-46.
- Journo, D., Winter, G. and Abeliovich, H. (2008). Monitoring Autophagy in Yeast Using Fm 4-64 Fluorescence. Methods Enzymol 451: 79-88.
- Kaksonen, M., Sun, Y. and Drubin, D. G. (2003). A pathway for association of receptors, adaptors, and actin during endocytic internalization. Cell 115(4): 475-487.
- Kamble, C., Jain, S., Murphy, E. and Kim, K. (2011). Requirements of Slm proteins for proper eisosome organization, endocytic trafficking and recycling in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biosci 36(1): 79-96.
- Li, L., Chen, X., Zhang, S., Yang, J., Chen, D., Liu, M., Zhang, H., Zheng, X., Wang, P., Peng, Y. and Zhang, Z. (2017). MoCAP proteins regulated by Moark1-mediated phosphorylation coordinate endocytosis and actin dynamics to govern development and virulence of Magnaporthe oryzae. PLoS Genet 13(5): e1006814.
- Peñalva, M.A. (2005). Tracing the endocytic pathway of Aspergillus nidulans with FM4-64. Fungal Genet Biol 42: 963-975.
- Wedlich-Soldner, R., Bolker, M., Kahmann, R. and Steinberg, G. (2000). A putative endosomal t-SNARE links exo- and endocytosis in the phytopathogenic fungus Ustilago maydis. EMBO J 19(9): 1974-1986.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2019 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Liu, M. and Zhang, Z. (2019). Endocytosis Detection in Magnaporthe oryzae. Bio-protocol 9(15): e3322. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3322.
Category
Microbiology > Microbial cell biology > Cell staining
Microbiology > Microbe-host interactions > Fungus
Cell Biology > Cell staining > Other compound
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










