- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
High-resolution Immunoelectron Microscopy Techniques for Revealing Distinct Subcellular Type 1 Cannabinoid Receptor Domains in Brain
(*contributed equally to this work) Published: Vol 9, Iss 2, Jan 20, 2019 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3145 Views: 9722
Reviewed by: Edgar Soria-GomezEstibaliz GonzalezAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Immunofluorescent Staining Assay of 3D Cell Culture of Colonoids Isolated from Mice Colon
Trisha Mehrotra [...] Didier Merlin
Mar 5, 2024 2484 Views

A Step-By-Step Protocol for Correlative Light and Electron Microscopy Imaging of Proteinaceous Deposits in Cultured Cells and Human Brain Tissues
Peizhou Jiang and Dennis W. Dickson
Aug 5, 2025 2337 Views

Intraepidermal Nerve Fiber Quantification of the Mouse Hind Paw Footpads: A Detailed and Simplified Protocol
Anastasia Yerushkin [...] Amir Dori
Dec 5, 2025 1224 Views
Abstract
Activation of type 1 cannabinoid (CB1) receptors by endogenous, exogenous (cannabis derivatives) or synthetic cannabinoids (i.e., CP 55.940, Win-2) has a wide variety of behavioral effects due to the presence of CB1 receptors in the brain. In situ hybridization and immunohistochemical techniques have been crucial for defining the CB1 receptor expression and localization at the cellular level. Nevertheless, more advanced methods are needed to reveal the precise topography of CB1 receptors in the brain, especially in unsuspected sites such as other cell types and organelles with low receptor expression (e.g., glutamatergic neurons, astrocytes, mitochondria). High-resolution immunoelectron microscopy provides a more precise detection method for the subcellular localization of CB1 receptors in the brain. Herein, we describe a single pre-embedding immunogold method for electron microscopy based on the use of specific CB1 receptor antibodies and silver-intensified 1.4 nm gold-labeled Fab' fragments, and a combined pre-embedding immunogold and immunoperoxidase method that employs biotinylated secondary antibodies and avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex for the simultaneous localization of CB1 receptors and protein markers of specific brain cells or synapses (e.g., GFAP, GLAST, IBA-1, PSD-95, gephyrin). In addition, a post-embedding immunogold method is also described and compared to the pre-embedding labeling procedure. These methods provide a relatively easy and useful approach for revealing the subcellular localization of low amounts of CB1 receptors in glutamatergic synapses, astrocytes, neuronal and astrocytic mitochondria in the brain.
Keywords: Endocannabinoid systemBackground
The endocannabinoid system (eCBs) is widely distributed in the nervous system, and, through the activation of CB1 receptors, plays an important role in normal brain function (Herkenham et al., 1990; Tsou et al., 1998; Kano et al., 2009; Castillo, 2012; Katona and Freund, 2012; Lutz et al., 2015; Pertwee, 2015; Lu and Mackie, 2016; Busquets-Garcia et al., 2018).
Pre- and post-embedding immunocytochemical techniques for electron microscopy are valuable methods that can provide precise CB1 receptor localization in brain and peripheral tissues. The pre-embedding immunogold labeling method has been successfully employed in our laboratory for the localization of various receptors, ion channels and enzymes in the mammalian brain, and has served to reveal a unique and interesting presence of CB1 receptors in mitochondria (Bénard et al., 2012; Hebert-Chatelain et al., 2014 and 2016; Mendizabal-Zubiaga et al., 2016; Gutiérrez-Rodríguez et al., 2018). The advantages are reflected by its ease of applicability and relatively inexpensive tissue preparation equipment and relatively good ultrastructural preservation. In addition, it offers the ability to perform correlative light microscopy on stained sections in order to reveal general patterns of CB1 receptor labeling prior to examination with the electron microscope. Success of the pre-embedding detection method has been improved by the development of ultra-small gold secondary conjugates (Nanogold®) in combination with gold particle enlarging chemistry, making it possible for probes to detect deeper into tissues, thus reducing the inherent limitation of antibody penetration and molecule detection while enhancing the resolution of receptor localization. In combination with immunoperoxidase and 3,3’-diaminobenzidine (DAB) reaction product immunochemistry, pre-embedding procedures can reveal protein co-localizations with cell specificity and at high resolution.
With post-embedding immunogold labeling methods, the epitopes are theoretically exposed at the section surface, diffusion of immunoreagents is avoided, is quantitative, allows simultaneous labeling by using different gold particle sizes (Hermida et al., 2010, Hunt et al., 2013) and the labeling is reliable on serial ultrathin sections (Hermida et al., 2006). However, the sensitivity is only moderate, not all antibodies work successfully in the resin-embedded tissue conditions required for the technique, and membrane and structural protein visibility is typically compromised since post-fixation with osmium tetroxide is avoided due to its destructive effects on antigens. Last, but not least, the equipment required for post-embedding labeling procedures can be unaffordable.
Materials and Reagents
- Glass vials (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: C4010-LV1)
- Glass slides (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S8902)
- Aluminum foil (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 326852)
- Syringes (Proquinorte)
- Nickel mesh grids: grids for pre-embedding electron microscopy (Electron Microscopy Sciences, catalog number: G-150 Ni), storage temperature: RT
- Nickel single slot formvar coated grids (aperture grids: grids for post-embedding electron microscopy) (Electron Microscopy Sciences, catalog number: FFGA1000-Ni-50), storage temperature: RT
- Antibodies
Antibody Manufacturer; species; catalog number; RRID Anti-cannabinoid receptor type-1 (CB1) Frontier Institute Co., ltd; goat polyclonal; CB1-Go-Af450; AB_2571592 Anti-cannabinoid receptor type-1 (CB1) Frontier Institute Co., ltd; guinea pig polyclonal; CB1-GP-Af530; AB_2571593 Anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) Sigma-Aldrich; mouse monoclonal; G3893; AB_257130 Anti-gephyrin Synaptic Systems; mouse monoclonal; 147021; AB_2232546 Anti-A522 (EAAT1 [GLAST]) Prof. Niels Christian Danbolt University of Oslo; rabbit polyclonal; Ab#314; AB_2314561 Anti-metabotropic glutamate receptor 2/3 (mGluR2/3) Chemicon (Millipore); rabbit polyclonal; AB1553, AB_11212089 Biotinylated anti-mouse secondary antibody Vector Labs; BA-2000; AB_2313581 Biotinylated anti-rabbit secondary antibody Vector Labs; BA-1000; AB_2313606 1.4 nm gold-conjugated anti-guinea pig IgG (Fab’ fragment) secondary antibody Nanoprobes; goat; #2055 1.4 nm gold-conjugated anti-goat IgG (Fab’ fragment) antibody Nanoprobes; rabbit; #2004 Colloidal gold-18 nm anti-goat IgG antibody Jackson Immunoresearch; donkey; 705-215-147 F(ab’)2 anti-rabbit IgG fragments conjugated to 10 nm colloidal gold particles British Biocell International; goat; GFAR10 - Lowicryl HM20 kit (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 15924), storage temperature: RT
- VECTASTAIN Elite ABC HRP Kit (Peroxidase, Standard) (Vector Laboratories, catalog number: PK-6100), storage temperature:
4 °C - HQ Silver: silver enhancement kit for EM (Nanoprobes, catalog number: 2012), storage temperature: -20 °C
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: A7906), storage temperature: 4 °C
- 3,3′-diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride hydrate (DAB): C12H14N4•4HCl•xH2O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: D5637), storage temperature: -20 °C
- Ethanol absolute: CH3CH2OH (PanReac AppliChem, catalog number: A1613), storage temperature: RT
- Glycerol: HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G9012), storage temperature: RT
- Glycine: NH2CH2COOH (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: G8898), storage temperature: RT
- Ketamine hydrochloride/xylazine hydrochloride solution for anesthesia (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: K4138), storage temperature: 4 °C
- Methanol: CH3OH (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 322415), storage temperature: RT
- Propane: CH3CH2CH3 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 536172), storage temperature: RT
- (R)-(+)-propylene oxide: C3H6O (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 540048), storage temperature: RT
- Saponin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 84510), storage temperature: RT
- Sodium azide (NaN3) (PanReac AppliChem, catalog number: 122712.1609), storage temperature: RT
- Sodium borohydride: NaBH4 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 71320), storage temperature: RT
- Osmium tetroxide aqueous solution (4%) (Electron Microscopy Sciences, catalog number: 19150), storage temperature: RT
- Di-Sodium hydrogen phosphate (Na2HPO4) (Merck, catalog number: 1.06586.1000), storage temperature: room temperature (RT) (used in Recipes 1-3)
- Epoxy embedding medium, hardener DDSA: C16H26O3 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 45346), storage temperature: RT (used in Recipe 6)
- Epoxy embedding medium, hardener MNA: C10H10O3 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 45347), storage temperature: RT (used in Recipe 6)
- Epoxy embedding medium: EponTM 812 substitute (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 45345), storage temperature: RT (used in Recipe 6)
- Glutaraldehyde (25%) in aqueous solution for synthesis: C5H8O2 (Merck, catalog number: 8.20603.1000), storage temperature: 4 °C (used in Recipe 1)
- Hydrochloric acid (HCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H1758), storage temperature: RT (used in Recipe 2)
- Lead(II) nitrate: (PbNO3)2 (PanReac AppliChem, catalog number: 131473), storage temperature: RT (used in Recipe 8)
- N-benzyldimethylamine: C9H13N (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 185582), storage temperature: RT (used in Recipe 6)
- Paraformaldehyde: (CH2O)n (Merck, catalog number: 1.04005.1000), storage temperature: RT (used in Recipe 1)
- Picric acid solution (1.3%) dissolved in H2O (saturated): (O2N)3C6H2OH (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P6744), storage temperature: RT (used in Recipe 1)
- Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG): C2nH4nH2On+1 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 202444), storage temperature: RT
- Potassium chloride (KCl) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P9541), storage temperature: RT (used in Recipe 2)
- Potassium phosphate monobasic (KH2PO4) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 229806), storage temperature: RT (used in Recipe 2)
- Sodium chloride (NaCl) (PanReac AppliChem, catalog number: 131659.1211), storage temperature: RT (used in Recipes 2-4)
- Sodium hydroxide pellets (PanReac AppliChem, catalog number: 131687.1211), storage temperature: RT (used in Recipe 8)
- Sodium phosphate monobasic monohydrate (NaH2PO4•H2O) (PanReac AppliChem, catalog number: 131965.1211), storage temperature: RT (used in Recipes 1-3)
- Tri-sodium citrate 2-hydrate: Na3C6H5O7•2H2O (Merck, catalog number: 6448), storage temperature: 4 °C (used in Recipe 8)
- Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: X100), storage temperature: RT (used in Recipe 5)
- Trizma® base: NH2C(CH2OH)3 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T1503), storage temperature: RT (used in Recipes 4 and 5)
- Trizma® hydrochloride: NH2C(CH2OH)3•HCl (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T3253), storage temperature: RT (used in Recipe 4)
- Uranyl acetate: UO2(CH3COO)2 (Electron Microscopy Sciences, catalog number: 22400), storage temperature: RT (used in Recipe 7)
- Fixative solution (see Recipes)
- Phosphate buffered saline (PBS 1x) (see Recipes)
- 0.1 M phosphate buffer (0.1 M PB) (see Recipes)
- Tris-hydrogen chloride buffered saline (TBS 1x) (see Recipes)
- Tris-buffered saline with Triton X-100 (TBST) (see Recipes)
- Epon resin (see Recipes)
- Uranyl acetate (2%, aqueous) staining solution (see Recipes)
- Reynold’s lead citrate staining solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Erlenmeyer flasks (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: Z567868)
- Shaker (Heidolph, Duomax 1030)
- Oven (Grupo Selecta, Dryterm)
- Vibratome (Leica Biosystems, model: Leica VT1000 S)
- Super platinum knife (Gillette)
- Ultramicrotome (RMC Products, model: PowerTome XL)
- Histo 6 mm diamond knife 45° (Diatome)
- Ultra 2.4 mm diamond knife 45° (Diatome)
- Transmission electron microscope (Philips, model: EM208S)
- Digital Morada camera (Olympus SIS Morada camera)
- Cryofixation unit (Reichert-Jung, model: KF 80)
- Freeze substitution system (Reichert AFS)
Software
- Adobe Photoshop (CS3, Adobe Systems, San Jose, CA, USA)
- ImageJ (NIH, USA; RRID:SCR_003070)
- GraphPad Prism 5 (GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, USA; RRID:SCR_002798)
Procedure
- PRE-EMBEDDING (Figure 1)
Preservation of brain tissue- Anesthetize animals (at least n = 3) by intraperitoneal injection of ketamine/xylazine (80/10 mg/kg body weight).
- Perfuse animals through the left ventricle with PBS (0.1 M, pH 7.4, 20-25 °C) for ~20 s at RT, followed by ice-cold fixative solution made up of 4% formaldehyde (freshly depolymerized from paraformaldehyde), 0.2% picric acid, and 0.1% glutaraldehyde in PB (0.1 M, pH 7.4). Fixative solution/mouse: 250 ml. Perfusion time 15 min. Fixative solution/rat: 500 ml. Perfusion time: 30 min.
- Remove the brain from the skull and post-fix in the fixative solution for ~1 week at 4 °C. Store samples in 0.1 M PB diluted fixative (1:10) containing 0.025% sodium azide at 4 °C until use.
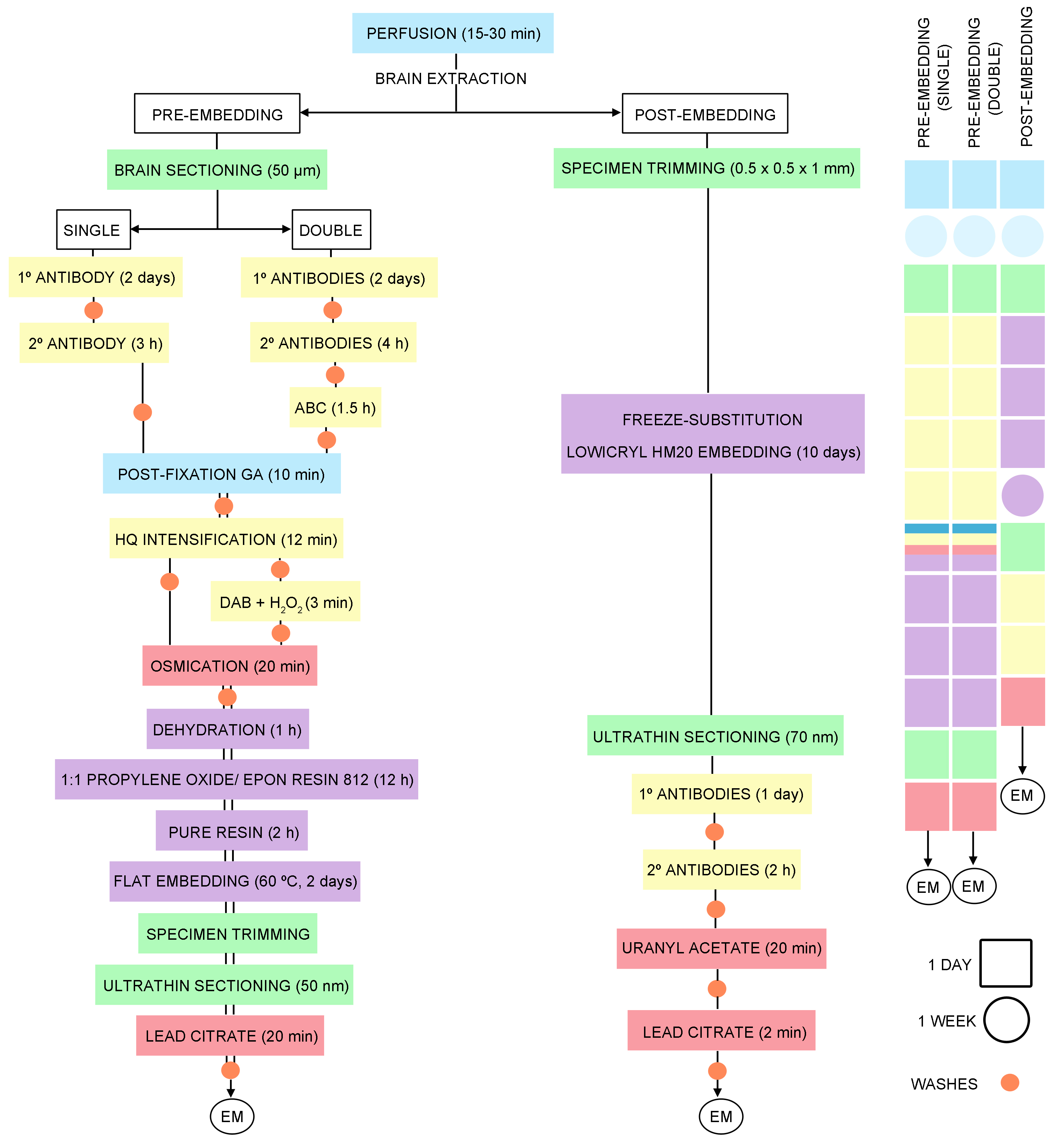
Figure 1. Timeline of the general steps for pre- and post-embedding immunoelectron microscopy techniques
Pre-embedding immunogold method for electron microscopy (Figures 1, 2A and 3A)- Cut 50 µm-thick sections on a vibratome and place into 12-well cell culture plates in 0.1 M PB (pH 7.4) at RT. Sections from each brain are in separate plates for storage at 4 °C in 0.1 M PB (pH 7.4) with 0.025% sodium azide. Two or three sections per brain containing the area of interest are selected and placed in a new plate. Total volume per well: 1 ml.
- Pre-incubate in blocking solution (1 ml/well) containing 10% BSA, 0.02% saponin and 0.1% sodium azide in TBS 1x (pH 7.4) on a shaker (300 rpm) for 30 min at RT.
- Incubate with goat polyclonal anti-CB1 receptor antibody (diluted 1:100, 1 ml/well) diluted in 10% BSA/TBS 1x containing 0.004% saponin and 0.1% sodium azide on a shaker. Place dish on an orbital shaker for two days at 4 °C.
- Wash five times in 1% BSA/TBS (3 x 1 min and 2 x 10 min).
- Incubate with 1.4 nm gold-conjugated rabbit anti-goat IgG (Fab' fragment, 1:100, Nanoprobes Inc., Yaphank, NY, USA; 1 ml/well) in 1% BSA/TBS with 0.004% saponin on a shaker for 3 h at RT.
- Wash three times in 1% BSA/TBS (10 min each). Keep the tissue in 1% BSA/TBS on a shaker overnight at 4 °C.
- Post-fix with 1% glutaraldehyde prepared in TBS (1 ml/well) for 10 min at RT.
- Wash three times in double distilled water (10 min each).
- Transfer sections to glass test tubes.
- Intensify gold particles with the HQ Silver kit (Nanoprobes Inc., Yaphank, NY, USA; 1 ml/tube) in the dark for 12 min.
- Wash three times in double distilled water (1 min each).
- Wash three times in 0.1 M PB (pH 7.4) (10 min each).
- Transfer sections to glass vials (15 ml, 3 x 5 cm).
- Osmicate (1% osmium tetroxide in 0.1 M PB, pH 7.4; 1 ml/vial) in the dark for 20 min.
- Wash three times in 0.1 M PB (pH 7.4) (10 min each).
- Dehydrate in graded ethanols (50%, 70%, 96%; 5 min/each) followed by three times in 100% ethanol (5 min each) (1 ml/vial).
- Replace with propylene oxide (3 x 5 min, 1 ml/vial).
- Infiltrate sections with a 1:1 mixture of propylene oxide and Epon resin 812 (1 ml/vial) on a shaker overnight at RT.
- Mix with pure Epon resin 812 (1 ml/vial) for > 2 h at RT.
- Place sections between two glass slides and wrap slides with aluminum foil.
- Polymerize resin-embedded sections at 60 °C for 2 days.
- Cut 1 μm semi-thin sections on ultramicrotome.
- Trim block and cut 60 nm ultra-thin sections with a diamond knife and collect on nickel mesh grids.
- Stain sections with 2.5% lead citrate (1 drop/grid) for 20 min at RT.
- Wash three times in double distilled water (1 drop/grid) (10 min each).
- Examine under a Philips EM208S transmission electron microscope.
- Photograph sections using a digital Morada camera (Olympus).
Double pre-embedding immunogold and immunoperoxidase method (Figures 1, 2B and 3B-3D)- Cut 50 µm-thick sections on vibratome and collect in 12-well cell culture plates in 0.1 M PB (pH 7.4) at RT. Sections from each brain are in separate plates for storage at 4 °C in 0.1 M PB (pH 7.4) with 0.025% sodium azide. Two or three sections per brain containing the area of interest are selected and placed in a new plate. Total volume per well: 1 ml.
- Pre-incubate in blocking solution (1 ml/well) containing 10% BSA, 0.02% saponin and 0.1% sodium azide in TBS 1x, pH 7.4 on a shaker (300 rpm) for 30 min at RT.
- Incubate sections with goat polyclonal anti-CB1 receptor antibody or guinea pig polyclonal anti-CB1 receptor antibody (diluted 1:100, 1 ml/well) in combination with either a mouse monoclonal anti-GFAP antibody (1:1,000), rabbit polyclonal anti-GLAST antibody (0.3 µg/ml), or mouse monoclonal anti-gephyrin antibody (1:250) prepared in 10% BSA/TBS 1x containing 0.004% saponin and 0.1% sodium azide. Place dish on an orbital shaker for 2 days at 4 °C.
Note: The guinea pig polyclonal anti-CB1 antibody is used for double immunolabeling with the rabbit polyclonal anti-GLAST antibody. - Wash five times in 1% BSA/TBS (3 x 1 min and 2 x 10 min).
- Incubate with corresponding biotinylated secondary antibody (1:200) and 1.4 nm gold-conjugated secondary rabbit anti-goat IgG (Fab’ fragment, 1:100, Nanoprobes Inc., Yaphank, NY, USA) or 1.4 nm gold-conjugated secondary goat anti-guinea pig IgG (Fab’ fragment, 1:100, Nanoprobes Inc., Yaphank, NY, USA) diluted in 1% BSA/TBS with 0.004% saponin on a shaker for 4 h at RT.
- Wash three times in 1% BSA/TBS (10 min each) on a shaker at RT.
- Incubate in avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) (1:50) prepared in washing solution (1 ml/well) for 1.5 h at RT.
- Wash three times in 1% BSA/TBS (10 min each). Keep tissue in 1% BSA/TBS on a shaker overnight at 4 °C.
- Post-fix with 1% glutaraldehyde in TBS (1 ml/well) for 10 min at RT.
- Wash three times in double distilled water (10 min each).
- Sections are transferred to test tubes.
- Intensify gold particles with the HQ Silver kit (Nanoprobes Inc., Yaphank, NY, USA; 1 ml/tube) in the dark for 12 min.
- Wash three times in double distilled water (1 min each).
- Wash three times in 0.1 M PB (pH 7.4) (10 min each).
- Sections are transferred to glass vials (15 ml, 3 x 5 cm).
- Incubate in 0.05% DAB and 0.01% hydrogen peroxide prepared in 0.1 M PB (1 ml/vial) for 3 min at RT.
- Wash three times in 0.1 M PB (pH 7.4) (10 min each).
- Osmicate samples (1% osmium tetroxide in 0.1 M PB, pH 7.4; 1 ml/vial) in the dark for 20 min.
- Wash three times in 0.1 M PB (pH 7.4) (10 min each).
- Dehydrate in graded ethanols (50%, 70%, 96%; 5 min/each) followed by three times in 100% ethanol (5 min each) (1 ml/vial).
- Replace with propylene oxide (3 x 5 min, 1 ml/vial).
- Infiltrate sections with a 1:1 mixture of propylene oxide and Epon resin 812 (1 ml/vial) on a shaker overnight at RT.
- Mix with pure Epon resin 812 (1 ml/vial) for > 2 h at RT.
- Place sections between two glass slides and wrap slides in aluminum foil.
- Polymerize resin-embedded sections in an oven at 60 °C for 2 days.
- Cut 1 μm semi-thin sections on ultramicrotome.
- Trim block and cut 60 nm ultra-thin sections with a diamond knife and collect on nickel mesh grids.
- Stain sections with 2.5% lead citrate (1 drop/grid) for 20 min at RT.
- Wash three times in double distilled water (1 drop/grid) (10 min each).
- Examine under a Philips EM208S transmission electron microscope.
- Photograph sections using a digital Morada camera (Olympus).
- POST-EMBEDDING (Figure 1)
Single/double labeling with post-embedding immunogold method (Figures 1, 2C and 3E-3F)- Preservation of brain tissue. For optimal ultrastructure, anesthetize and perfuse the animals as above.
- Remove the brain from the skull and post-fix in the fixative solution for ~1 week at 4 °C. Then, store the brains in 0.1 M PB diluted fixative (1:10) plus 0.025% sodium azide at 4 °C and rinse in PB until next step.
- Specimen trimming (cut small rectangular pieces of 0.5 x 0.5 x 1 mm from the region of interest).
- Cryoprotect in glycerol (10%, 20%, and 30% in PB) and rapidly freeze in liquid propane using a cryofixation unit (KF80; Reichert, Vienna, Austria).
- Freeze-substitute with methanol and 0.5% uranyl acetate.
- Embed in Lowicryl HM20 (Lowi, Waldkraiburg, Germany).
Immunogold labeling procedure- Cut 1 μm semi-thin sections on ultramicrotome.
- Collect 70 nm ultra-thin sections on nickel single slot formvar coated grids.
- Wash specimens with TBST containing 0.1% NaBH4 and 50 mM glycine (10 μl drop/grid) for 10 min.
- Rinse 3 times in TBST (10 μl drop/grid) (1 min each).
- Pre-incubate in blocking solution (10 μl drop/grid) containing 10% BSA in TBST for 10 min.
- Incubate (10 μl drop/grid) with anti-CB1 receptor (1:50) or anti-mGluR2/3 (1:50) antibodies or with a mixture of them prepared in 2% BSA/TBST, overnight at 4 °C.
- Wash three times in TBST (10 μl drop/grid) (10 min each).
- Pre-incubate in blocking solution (10 μl drop/grid) containing 10% BSA and 0.5% PEG in TBST for 10 min.
- Incubate (10 μl drop/grid) with secondary antibodies coupled to different gold particle size: donkey 18 nm colloidal gold conjugated affinity purified anti-goat IgG (for CB1) and goat F(ab’)2 anti-rabbit IgG coupled to 10 nm colloidal gold particles (for mGluR2/3), diluted 1:20 in 2% BSA/TBST for 2 h at RT.
- Wash three times in double-distilled water (10 μl drop/grid) (10 min each).
- Counterstain with 2% uranyl acetate (20 min) and 2.5% lead citrate (2 min) (10 μl drop/grid).
- Wash three times in double distilled water (10 μl drop/grid) (10 min each).
- Examine under a Philips EM208S transmission electron microscope.
- Photograph specimens using a digital Morada camera (Olympus).

Figure 2. Schematics illustrating the three immunolabeling methods for high-resolution electron microscopy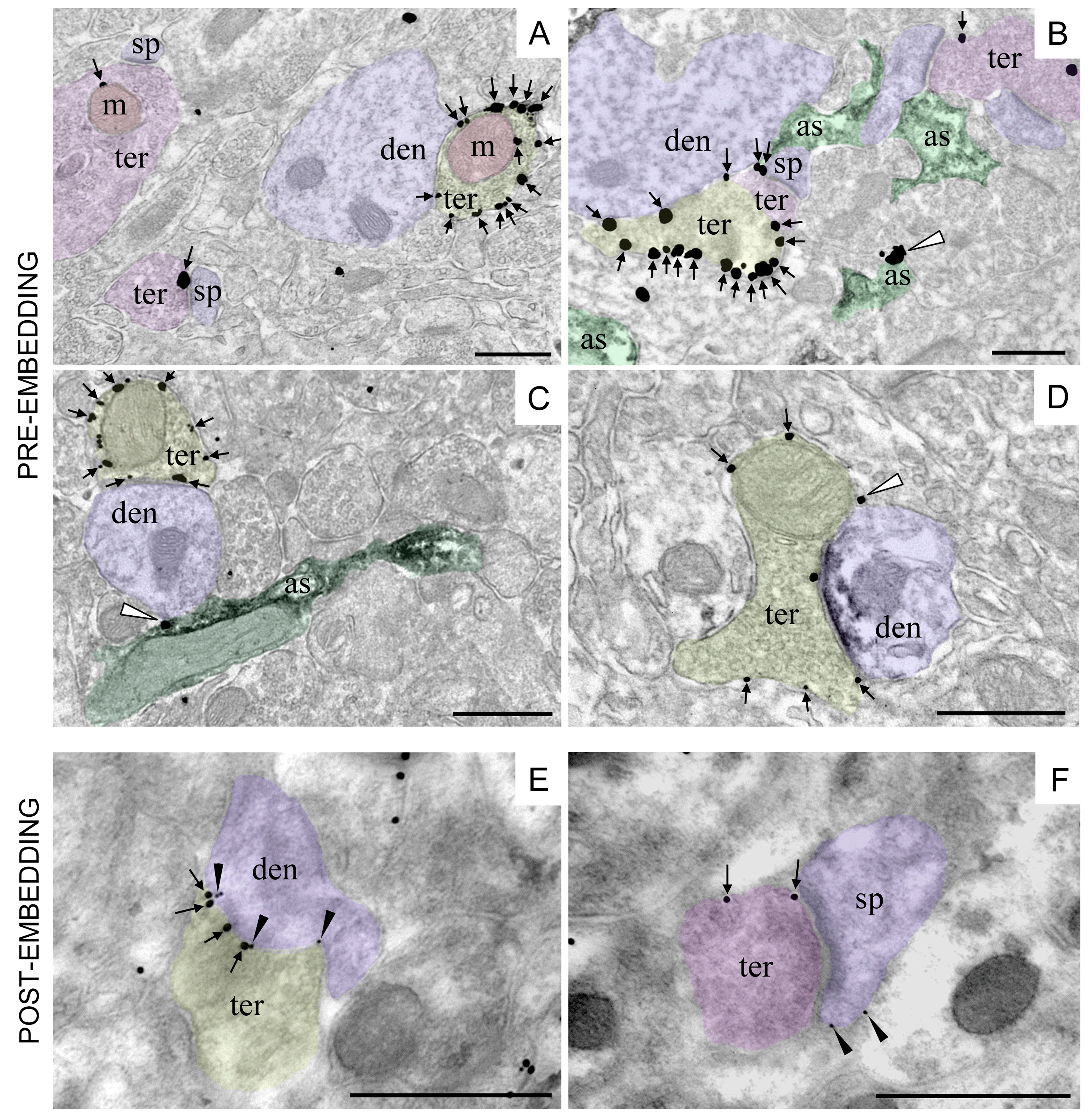
Figure 3. CB1 receptor immunolocalization in different subcellular compartments of the rodent brain. Single pre-embedding immunogold (A) and double pre-embedding immunogold and immunoperoxidase methods (B-D). A. CB1 receptor labeling (arrows) at a presynaptic GABAergic terminal (ter, yellow) adjacent to a dendrite (den, purple). CB1 receptor particle is localized to a presynaptic glutamatergic terminal (ter, pink) associated with a spine (sp, purple). Mitochondria (m, red) exhibit CB1 receptor immunolabeling in both glutamatergic (ter, pink) and GABAergic (ter, yellow) presynaptic terminals (CA1 stratum radiatum, adult mouse hippocampus). B. CB1 receptor labeling (arrows) at a presynaptic GABAergic terminal (ter, yellow), glutamatergic terminals (ter, purple) and in one astrocyte branch (white arrowhead; as, green) in the mouse piriform cortex. Astrocytes are labeled with anti-GLAST/immunoperoxidase/DAB method (black precipitate in as). C. CB1 receptor labeling (arrows) at a presynaptic GABAergic terminal (ter, yellow) adjacent to a dendrite (den, purple) and in one astrocyte process (white arrowhead; as, green) in the molecular layer of the mouse dentate gyrus. Astrocytes are labeled with anti-GFAP/immunoperoxidase/DAB method (black precipitate in as). D. CB1 receptor labeling (arrows) at a presynaptic terminal (ter, yellow) combined with anti-gephyrin/immunoperoxidase/DAB method (black precipitate in den, purple) to positively identify the inhibitory postsynaptic membrane of a GABAergic synapse. White arrowhead: CB1 receptor labeling at a thin astrocytic process filling the intercellular space (rat prelimbic cortex). E-F. Double post-embedding immunogold method revealing the localization of presynaptic CB1 receptors (ter; 18 nm-diameter gold particles) and postsynaptic mGluR2/3 (den, sp; 10 nm-diameter gold particles) at inhibitory (ter, yellow) and excitatory (ter, pink) synapses in the mouse dentate molecular layer. Scale bars= 500 nm.
Data analysis
- Semi-quantification of CB1 receptor immunolabeling in pre-embedding method
With the aim of maximizing the standard conditions, the pre-embedding immunogold method is applied simultaneously to all the sections obtained from the animals under study (at least n = 3). Three replicated experiments are done for each animal.
Immunogold-labeled resin-embedded vibratome sections are first visualized under the light microscope in order to select portions of the region of interest (i.e., CA1 hippocampus, dentate molecular layer, prelimbic cortex or piriform cortex) with reproducible CB1 receptor immunolabeling. Then, semi-thin sections from resin-embedded tissue are cut and the first five ultra-thin sections are collected onto two grids. To further standardize the conditions between the different animals, only the first 1.5 µm from each specimen surface is collected and randomly photographed. Sampling is always performed carefully and in the same way for all the animals studied. To avoid bias, investigators remained blind when taking and analyzing the electron micrographs.
The excitatory and inhibitory synapses are identified by their ultrastructural features; excitatory synapses are asymmetrical with postsynaptic densities and presynaptic axon terminals containing abundant, clear and spherical synaptic vesicles. Inhibitory synapses are symmetrical with slender postsynaptic membranes and axon terminals containing pleomorphic synaptic vesicles. Because of the lack of postsynaptic membrane density, the inhibitory nature of the synapse might be misleading unless serial sections were done. An alternative to circumvent this is to use an antibody against gephyrin, a postsynaptic anchor protein marker of inhibitory synapses which can be used to unequivocally identify inhibitory synapses. CB1 receptors in astrocytes are assessed in astrocytic processes containing GFAP or GLAST DAB immunodeposits.
The proportion of the CB1 receptor labeling on different compartments identified as described above is then tabulated. Positive labeling is considered when at least one CB1 receptor immunoparticle is within ~30 nm of the membrane of the specific compartment under study, and ≥ 80 nm from other membranes in the case of mitochondrial labeling. Metal particles are then counted and CB1 receptor density (particles/µm membrane) in the positive compartments is determined with ImageJ software by measuring their membrane length. We also estimate the proportion of CB1 receptor immunoparticles in different profiles versus the total CB1 receptor expression. This gives information about the CB1 receptor distribution throughout different compartments of a particular brain region (excitatory and inhibitory synapses, astrocytes, mitochondria, other cellular compartments). As for astrocytes, the distance from astrocytic CB1 receptor immunoparticles to the nearest synapse is also calculated to determine how the receptors are distributed in the context of the tripartite synapse. To do this, the nearby synapses surrounding the CB1 receptor positive astrocytic elements are identified, distances measured (ImageJ software), the nearest synapse to the astrocytic immunoparticle selected, and data from all the nearest synapses tabulated and analyzed.
All values are given as mean ± S.E.M. using a statistical software package (GraphPad Prism 5, GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, USA). The normality test (Kolmogorov-Smirnov normality test) is always applied before running statistical tests. Data are analyzed using parametric or non-parametric two-tailed Student’s t-test or one-way ANOVA with subsequent post-hoc analysis (Bonferroni post-test). - Quantification of CB1 receptor immunolabeling in post-embedding method
Electron micrographs of identified excitatory and inhibitory synaptic terminals are randomly obtained from a particular brain region (e.g., molecular layer of the dentate gyrus). For analysis, 50 synapses containing the criteria of intact plasma membranes, synaptic vesicles and prominent synaptic clefts are selected from each animal studied. To avoid bias, investigators remained blind when taking and analyzing the electron micrographs. The percentage of CB1 receptor positive excitatory and/or inhibitory terminals and the percentage of mGluR2/3 labeled postsynaptic dendrites receiving CB1 positive presynaptic terminals are analyzed using a statistical software package (GraphPad Prism 5, GraphPad Software Inc., San Diego, CA, USA). Labeling is considered positive as described in the pre-embedding techniques (e.g., membrane proximity). Data are shown as mean ± S.E.M. CB1 receptor density (particles/µm membrane) in positive terminals is calculated as explained before. In addition, with the aim of determining the precise sub-synaptic distribution of mGluR2/3 (or any other receptor) in postsynaptic elements relative to the presynaptic release sites, the distribution of gold particles frequency is measured. Also, the sub-synaptic CB1 receptor distribution in presynaptic boutons can be determined. In this situation, the synaptic or peri/extrasynaptic localization of the gold particle is defined with respect to its allocation in 60 nm-wide segments obtained from the edge of both the postsynaptic density and the presynaptic active zone (localization at the edge = 0). Statistical analysis is performed as described in the pre-embedding method section.
Recipes
- Fixative solution
Heat 600 ml of distilled water in a microwave to 60 °C
Add 11.5 g of Na2HPO4 (anhydrous) (MW: 141.96)
Add 40 g of paraformaldehyde (MW: 30.03) and shake at 60 °C. It could take 30 min to dissolve
Add 2.62 g NaH2PO4•H2O (MW: 137.99)
Filter the solution into an Erlenmeyer flask and add 2 ml of saturated picric acid (MW: 229.11)
Make up to 1 L with distilled water
Cool and store at 4 °C until used
Just before perfusion, add 4 ml of glutaraldehyde (25%) - Phosphate buffered saline (PBS 1x) (0.1 M, pH 7.4)
For 1 L of PBS 1x, prepare as follows:
Start with 800 ml of distilled water:
Add 8 g of NaCl (MW: 58.44)
Add 0.2 g of KCl (MW: 74.55)
Add 1.44 g of Na2HPO4 (MW: 141.96)
Add 0.24 g of KH2PO4 (MW: 136.09)
Adjust the pH to 7.4 with HCl (MW: 36.46)
Add distilled water to a total volume of 1 L - 0.1 M phosphate buffer (0.1 M PB) pH = 7.4
Stock solution: 0.2 M PB, pH = 7.4
For 1 L of 0.2 M PB, prepare as follows:
Add 5.24 g of NaH2PO4•H2O (MW: 138)
Add 23.0 g of Na2HPO4 (MW: 141.96)
Distilled water, make up the solution to 1 L
To prepare 0.1 M PB, dilute 1:1 the stock solution 0.2 M PB in distilled water - Tris-hydrogen chloride buffered saline: 3 M NaCl + 1 M Tris-HCl, pH = 7.4; (TBS 1x)
Stock solution: 0.3 M NaCl + 0.1 M Tris-HCl, pH = 7.4 (10x TBS)
For 1 L of 10x TBS, prepare as follows:
Add 175 g of NaCl (MW: 58.44)
Add 19.4 g of Trizma base (MW: 121.14)
Add 132.2 g of Trizma-HCl (MW: 157.60)
Make up solution to 1 L with distilled water
To prepare 1 L of TBS 1x, dilute 1:9 the TBS 10x stock solution in distilled water - Tris-buffered saline with Triton X-100 (TBST)
Take 450 ml of distilled water
Add 3.03 g of Trizma base (MW: 121.14)
Add 4.5 g of NaCl (MW: 58.44)
Adjust the pH to 7.4 and make the solution up to 500 ml with distilled water
Add 0.5 ml of Triton X-100 (MW: 646.86) - Epon resin
Add 81.3 g of EPON 812 (MW: 178.18)
Add 53.0 g of EPON HÄRTER DDSA (MW: 266.38)
Add 35.7 g of MNA (MW: 178.18)
Add 2.24 ml of N-Benzyldimethylamine Fluka 13370 (MW: 135.21)
Mix for at least 2 h before storing at -20 °C in syringes - Uranyl acetate (2%, aqueous) staining solution
Prepare 0.04 g uranyl acetate [UO2(CH3COO)2 (MW: 388.11)] in 2 ml of distilled water, Centrifuge at 11,600 x g for 5 min and use supernatant - Reynold’s lead citrate staining solution
Add 2.66 g of lead nitrate [Pb(NO3)2, MW 331.2)] and 3.52 g of Tri-sodium citrate dihydrate (Na3C6H5O7•2H2O, MW: 294.10) in 84 ml of double distilled water (it is normal for the solution to become cloudy when sodium citrate is added)
Prepare 0.8 g of 1 N NaOH (MW: 39.99) in 20 ml double distilled water
Add 16 ml of NaOH solution to the lead citrate solution (solution becomes clear when NaOH is added)
Filter the solution to remove any undissolved material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by The Basque Government (BCG IT764-13); MINECO/FEDER, UE (SAF2015-65034-R); Red de Trastornos Adictivos, Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISC-III) and European Regional Development Funds-European Union (ERDF-EU) (RD16/0017/0012). We would like to thank Prof. Niels Christian Danbolt for providing us with the rabbit polyclonal anti-A522 EAAT1 [GLAST] antibody and Prof. Mahmood Amiry-Moghaddam and Bjørg Riber for the Lowicryl HM20 embedding (Division of Anatomy, Department of Molecular Medicine, Institute of Basic Medical Sciences, University of Oslo, Norway).
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflicts of interest or competing interests.
Ethics
The protocols for animal care and use were approved by the Committee of Ethics for Animal Welfare of the University of the Basque Country (CEEA/M20/2016/073; CEIAB/2016/074) and were in accordance to the European Communities Council Directive of 22nd September 2010 (2010/63/EU) and Spanish regulations (Real Decreto 53/2013, BOE 08-02-2013).
References
- Bénard, G., Massa, F., Puente, N., Lourenço, J., Bellocchio, L., Soria-Gómez, E., Matias, I., Delamarre, A., Metna-Laurent, M., Cannich, A., Hebert-Chatelain, E., Mulle, C., Ortega-Gutiérrez, S., Martín-Fontecha, M., Klugmann, M., Guggenhuber, S., Lutz, B., Gertsch, J., Chaouloff, F., López-Rodríguez, M. L., Grandes, P., Rossignol, R. and Marsicano, G. (2012). Mitochondrial CB1 receptors regulate neuronal energy metabolism. Nat Neurosci 15: 558-564.
- Busquets-Garcia, A., Bains, J. and Marsicano, G. (2018). CB1 receptor signaling in the brain: extracting specificity from ubiquity. Neuropsychopharmacology 43(1): 4-20.
- Castillo, P. E. (2012). Presynaptic LTP and LTD of excitatory and inhibitory synapses. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 4(2): a005728-a005728.
- Gutiérrez-Rodríguez, A., Bonilla-Del Rio, I., Puente, N., Gomez-Urquijo, S. M., Fontaine, C. J., Egana-Huguet, J., Elezgarai, I., Ruehle, S., Lutz, B., Robin, L. M., Soria-Gomez, E., Bellocchio, L., Padwal, J. D., van der Stelt, M., Mendizabal-Zubiaga, J., Reguero, L., Ramos, A., Gerrikagoitia, I., Marsicano, G. and Grandes, P. (2018). Localization of the cannabinoid type-1 receptor in subcellular astrocyte compartments of mutant mouse hippocampus. Glia 66(7): 1417-1431.
- Hebert-Chatelain, E., Desprez, T., Serrat, R., Bellocchio, L., Soria-Gomez, E., Busquets-Garcia, A., Pagano Zottola, A. C., Delamarre, A., Cannich, A., Vincent, P., Varilh, M., Robin, L. M., Terral, G., Garcia-Fernandez, M. D., Colavita, M., Mazier, W., Drago, F., Puente, N., Reguero, L., Elezgarai, I., Dupuy, J. W., Cota, D., Lopez-Rodriguez, M. L., Barreda-Gomez, G., Massa, F., Grandes, P., Benard, G. and Marsicano, G. (2016). A cannabinoid link between mitochondria and memory. Nature 539(7630): 555-559.
- Hebert-Chatelain, E., Reguero, L., Puente, N., Lutz, B., Chaouloff, F., Rossignol, R., Piazza, P. V., Benard, G., Grandes, P. and Marsicano, G. (2014). Cannabinoid control of brain bioenergetics: Exploring the subcellular localization of the CB1 receptor. Mol Metab 3(4): 495-504.
- Herkenham, M., Lynn, A. B., Little, M. D., Johnson, M. R., Melvin, L. S., de Costa, B. R. and Rice, K. C. (1990). Cannabinoid receptor localization in brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87(5): 1932-1936.
- Hermida, D., Elezgarai, I., Puente, N., Alonso, V., Anabitarte, N., Bilbao, A., Donate-Oliver, F. and Grandes, P. (2006). Developmental increase in postsynaptic alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4 isoxazolepropionic acid receptor compartmentalization at the calyx of Held synapse. J Comp Neurol 495(5): 624-634.
- Hermida, D., Mateos, J. M., Elezgarai, I., Puente, N., Bilbao, A., Bueno-Lopez, J. L., Streit, P. and Grandes, P. (2010). Spatial compartmentalization of AMPA glutamate receptor subunits at the calyx of Held synapse. J Comp Neurol 518(2): 163-174.
- Hunt, D. L., Puente, N., Grandes, P. and Castillo, P. E. (2013). Bidirectional NMDA receptor plasticity controls CA3 output and heterosynaptic metaplasticity. Nat Neurosci 16(8): 1049-1059.
- Kano, M., Ohno-Shosaku, T., Hashimotodani, Y., Uchigashima, M. and Watanabe, M. (2009). Endocannabinoid-mediated control of synaptic transmission. Physiol Rev 89(1): 309-380.
- Katona, I. and Freund, T. F. (2012). Multiple functions of endocannabinoid signaling in the brain. Annu Rev Neurosci 35: 529-558.
- Lu, H. C. and Mackie, K. (2016). An introduction to the endogenous cannabinoid system. Biol Psychiatry 79(7): 516-525.
- Lutz, B., Marsicano, G., Maldonado, R. and Hillard, C. J. (2015). The endocannabinoid system in guarding against fear, anxiety and stress. Nat Rev Neurosci 16(12): 705-718.
- Mendizabal-Zubiaga, J., Melser, S., Benard, G., Ramos, A., Reguero, L., Arrabal, S., Elezgarai, I., Gerrikagoitia, I., Suarez, J., Rodriguez De Fonseca, F., Puente, N., Marsicano, G. and Grandes, P. (2016). Cannabinoid CB1 receptors are localized in striated muscle mitochondria and regulate mitochondrial respiration. Front Physiol 7: 476.
- Pertwee, R. G. (2015). Endocannabinoids and their pharmacological actions. In: Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology. pp 1-37.
- Tsou, K., Brown, S., Sanudo-Pena, M. C., Mackie, K. and Walker, J. M. (1998). Immunohistochemical distribution of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 83(2): 393-411.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2019 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Puente, N., Bonilla-Del Río, I., Achicallende, S., Nahirney, P. C. and Grandes, P. (2019). High-resolution Immunoelectron Microscopy Techniques for Revealing Distinct Subcellular Type 1 Cannabinoid Receptor Domains in Brain. Bio-protocol 9(2): e3145. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.3145.
Category
Neuroscience > Neuroanatomy and circuitry > Brain nerve
Developmental Biology > Cell signaling > G-protein coupled receptors
Cell Biology > Cell staining > Protein
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









