- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Visualization of RNA at the Single Cell Level by Fluorescent in situ Hybridization Coupled to Flow Cytometry
Published: Vol 8, Iss 12, Jun 20, 2018 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2892 Views: 7280
Reviewed by: Ivan ZanoniShanie Saghafian-HedengrenAnonymous reviewer(s)

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

An In Vitro Model of Murine Osteoclast-Mediated Bone Resorption
Xiaoyue Sun [...] Lingxin Zhu
Nov 5, 2024 2239 Views

Culture and Characterization of Differentiated Airway Organoids from Fetal Mouse Lung Proximal Progenitors
Zhonghui Zhang [...] Qiuling Li
Dec 5, 2024 1829 Views

Simple and Rapid Model to Generate Differentiated Endometrial Floating Organoids
Adriana Bajetto [...] Tullio Florio
Feb 5, 2026 232 Views
Abstract
The protocol described here has been developed to detect RNA at the single cell level. Fluorescent probes hybridize to target RNAs and are detected by flow cytometry after multiple amplification steps. Different types of RNA can be detected such as mRNA, long noncoding RNA, viral RNA or telomere RNA and up to 4 different target probes can be used simultaneously. We used this protocol to specifically measure the expression of two transcription factor mRNAs, MAFB and IRF4, in human monocytes.
Keywords: RNABackground
RT-qPCR is one major technique used to easily assess RNA expression. Cells are lysed and analyzed in bulk. Hence, cell heterogeneity is lost. In particular, it is impossible using RT-qPCR to address whether subpopulations may be identified based on the expression of RNA. RNA Fluorescent In Situ Hybridization (FISH) is a way to detect RNA in single cells. This technique requires hybridization of fluorescent probes on RNA targets that are then detected using an imaging system such as a confocal microscope. However, this method is time-consuming and allows the analysis of a limited number of individual cells.
We demonstrated by RT-qPCR that human monocytes cultured in RPMI with M-CSF, IL-4, and TNFa express after three hours the transcription factors MAFB and IRF4 (Goudot et al., 2017). MAFB and IRF4 are involved in the differentiation of monocytes into monocyte-derived macrophages (mo-mac) and monocyte-derived DC (mo-DC) respectively. To decipher whether monocytes express both transcription factors or if this expression is mutually exclusive, we performed in situ hybridization coupled to flow cytometry using PrimeFlow RNA assay.
Materials and Reagents
- P1000, P200, P20 pipettes tips (any supplier)
- 15 and 50 ml conical tubes (any supplier)
- PrimeFlow RNA tubes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 19197 )
- PrimeFlow® RNA 96-well plate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 44-17005 )
- PrimeFlow® RNA Wash Buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 00-19180 )
- Fixable Viability Dye eFluorTM 506 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, eBioscienceTM, catalog number: 65-0866-14 )
- PrimeFlow® RNA Fixation Buffer 1A (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 00-18100 )
- PrimeFlow® RNA Fixation Buffer 1B (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 00-18200 )
- PrimeFlow® RNA Fixation Buffer 2 (8x) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 00-18400 )
- PrimeFlow® RNA Permeabilization Buffer (10x) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 00-18300 )
- PrimeFlow® RNase Inhibitors (100x) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 00-16002 )
- PrimeFlow® RNA Target Probe Diluent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 00-19185 )
- PrimeFlow® RNA Label Probe Diluent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 00-19183 )
- PrimeFlow® Compensation kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 88-17001 )
- PrimeFlow® RNA Storage Buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 00-19178 )
- AlexaFluor 647 IRF4 (Thermo Fisher Scientific, PF-204, assay ID: VA1-13919-PF) and AlexaFluor 488 MAFB (Thermo Fisher Scientific, PF-204, assay ID: VA4-16783-PF) probe sets
- PBS (Eurobio, catalog reference: CS1PBS01-01 )
- EDTA (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 15575020 )
- Human serum (BioWest, catalog number: S4190-190 )
- RPMI-Glutamax medium (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 61870010 )
- Penicillin and streptomycin (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 15140122 )
- Fetal calf serum (Biosera, catalog number: FB-1001 )
- M-CSF (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-096-492 )
- IL-4 (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-093-922 )
- TNFa (Miltenyi Biotec, catalog number: 130-094-014 )
- FICZ (Enzo Life Sciences, catalog number: BML-GR206-0100 )
- Flow cytometry buffer (see Recipes)
- Culture medium for monocyte differentiation (see Recipes)
Equipment
- P1000, P200, P20 pipettes
- Incubator
- Fridge
- Freezer
- Metal heat block (if 1.5 ml tubes are used)
- Refrigerated centrifuge for Eppendorf tubes (Eppendorf, model: 5424R ) or plates (Eppendorf, model: 5810R )
- Flow cytometer with 3 lasers (488 nm, 561 nm, 633 nm)
Software
- FlowJo V10 (Tree Star)
Procedure
Notes:
- This protocol was adapted from the protocol of PrimeFlow RNA Assay kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific).
- Up to 4 different target probes may be used simultaneously.
Thermo Fisher Scientific provides 4 probe types:
Type 1: Alexa Fluor 647
Type 4: Alexa Fluor 488
Type 6: Alexa Fluor 750
Type 7: Alexa Fluor 568
In our protocol, we used Type 1 IRF4 and Type 4 MAFB. - We recommend using the 96-well v-bottom plates supplied by Thermo Fisher Scientific for an easier and faster procedure. Discard supernatant by inverting the plate. However, other plates or tubes can also be used. (see ‘Notes’ for details)
- For this protocol, we used human CD14+ monocytes purified from fresh blood that were kept on ice (baseline) or cultured in RPMI with 100 ng/ml of M-CSF or 100ng/ml M-CSF, 5 ng/ml of IL-4, 5ng/ml of TNFa and 62 nM of FICZ for 3 or 12 h (Goudot et al., 2017).
- Day 1: from cell harvest to cell fixation
- Pre-warm PrimeFlow RNA Wash Buffer to room temperature.
- Pre-warm the incubator to 40 °C. You need to turn on the incubator 24 h prior to using it to ensure temperature stability.
- Distribute 1.5 x 106 cells per well.
- Stain cells with 50 μl of eFluorTM 506 fixable viability dye (1/250 dilution in flow cytometry buffer) for 20 min.
- Centrifuge at 450 x g for 5 min and discard the supernatant.
- Add 200 μl of flow cytometry buffer to each sample and resuspend cells by pipetting.
- Centrifuge at 450 x g for 5 min and discard the supernatant.
- Prepare Fixation Buffer 1 by mixing equal parts of PrimeFlow RNA Buffer 1A and PrimeFlow RNA Buffer 1B.
- Distribute 200 μl of Fixation Buffer 1 to each sample and mix by pipetting. Incubate for 30 min at 2-8 °C.
- Centrifuge at 1,000 x g for 4 min at 4 °C and discard supernatant.
- Prepare 1x PrimeFlow RNA Permeabilization Buffer. Dilute 10x PrimeFlow RNA Buffer to 1x with RNase-free water and add RNase inhibitors at 1/100 dilution.
- Distribute 200 μl of Permeabilization Buffer 1 to each sample and mix by pipetting. No incubation is required. Centrifuge at 1,000 x g for 4 min at 4 °C. Discard supernatant.
- Repeat Step A11.
- Prepare 1x Fixation Buffer 2. Dilute 8x PrimeFlow RNA Fixation Buffer 2 in PrimeFlow RNA Wash Buffer. Mix by inverting.
- Distribute 200 μl of Fixation Buffer 2 to each sample and mix by pipetting. Incubate for 60 min in the dark at room temperature.
- Centrifuge at 1,000 x g for 4 min at room temperature and discard supernatant.
- Add 200 μl of PrimeFlow RNA Wash buffer to each sample and resuspend cells by pipetting. Centrifuge at 1,000 x g for 4 min at 4 °C and discard supernatant.
- Repeat Step A16.
- Store cells in 100 μl of PrimeFlow RNA Wash Buffer with RNase inhibitors diluted 1/100 overnight in the dark at 4 °C.
- Pre-warm PrimeFlow RNA Wash Buffer to room temperature.
- Day 2: Target probe hybridization
Note: For the following steps, to ensure reproducibility across wells, it is important that the residual volume after each wash remains lower than 10 μl. The volume for the hybridization step (Procedure B) must be 200 μl.- Thaw 20x target Probe sets at room temperature.
- Pre-warm Prime Flow RNA Target probe diluent to 40 °C and PrimeFlow RNA Wash Buffer at room temperature. You will need 100 μl of Prime Flow RNA Target probe diluent maximum per sample.
- Dilute target probes 1/20 in PrimeFlow Target Probe diluent. Mix by inverting.
- Distribute 100 μl of diluted target probes to each sample (100 μl of cells) and mix by pipetting. Incubate plate with the lid on for 2.5 h at 40 °C in the dark.
- Centrifuge at 1,000 x g for 4 min at room temperature. Discard supernatant.
- Add 200 μl of PrimeFlow RNA Wash buffer to each sample and resuspend cells by pipetting. Centrifuge at 1,000 x g for 4 min at 4 °C and discard supernatant.
- Repeat Step B6.
- Add 100 μl of PrimeFlow RNA Wash Buffer to each sample and resuspend cells by pipetting.
- Thaw 20x target Probe sets at room temperature.
- Day 2: Signal amplification
Note: For the following steps, to ensure reproducibility across wells, it is important that the residual volume after each wash remains lower than 10 μl. The volume for all the hybridization steps must be 200 μl.- Pre-warm PrimeFlow RNA pre-Amp mix, PrimeFlow RNA Amp Mix and PrimeFlow Label probe RNA Diluent to 40 °C.
- Distribute 100 μl of PrimeFlow RNA pre-amp mix to each sample and mix by pipetting. Incubate for 1.5 h at 40 °C in the dark.
- Centrifuge at 1,000 x g for 4 min at room temperature. Discard supernatant.
- Add 200 μl of PrimeFlow RNA Wash buffer to each sample and resuspend cells by pipetting. Centrifuge at 1,000 x g for 4 min at 4 °C and discard supernatant.
- Repeat Step C4.
- Distribute 100 μl of PrimeFlow RNA Wash Buffer to each sample. Then distribute 100 μl of PrimeFlow RNA Amp Mix to each sample and mix by pipetting. Incubate for 1.5 h at 40 °C in the dark.
- Thaw PrimeFlow RNA Label Probes (100x) in the dark.
- Centrifuge the plate at 1,000 x g for 4 min at room temperature. Discard supernatant.
- Add 200 μl of PrimeFlow RNA Wash buffer to each sample and resuspend cells by pipetting. Centrifuge at 1,000 x g for 4 min at 4 °C and discard supernatant.
- Repeat Step C9.
- Dilute 100x PrimeFlow RNA Label Probes in PrimeFlow RNA Label Probe diluent.
- Distribute 100 μl of PrimeFlow RNA Wash Buffer to each sample. Distribute then 100 μl of diluted PrimeFlow RNA Label probes to each sample. Mix by pipetting. Incubate for 1 h at 40 °C in the dark. The final concentration of PrimeFlow RNA Label probes is 0.5x.
- Centrifuge at 1,000 x g for 4 min at room temperature. Discard supernatant.
- Add 200 μl of PrimeFlow RNA Wash buffer to each sample and resuspend cells by pipetting. Centrifuge at 1,000 x g for 4 min at 4 °C and discard supernatant.
- Repeat Step C14.
- Distribute 200 μl of Flow cytometry Buffer to each sample. Centrifuge at 1,000 x g for 4 min at room temperature. Discard supernatant and resuspend cells in 100 μl of flow cytometry Buffer.
- Pre-warm PrimeFlow RNA pre-Amp mix, PrimeFlow RNA Amp Mix and PrimeFlow Label probe RNA Diluent to 40 °C.
- Day 2: Data acquisition
- Prepare single-color compensation tubes for AF488 and AF647 using the PrimeFlow® Compensation kit. You should also have single color controls for your fixable dye and for each fluorescent antibody you used.
- Label two tubes ‘AF488’ and ‘AF647’.
- Mix UltraComp eBeads microspheres by vortexing.
- Add one drop of UltraComp eBeads to each tube.
- Add 5 μl of AF488 compensation control and AF647 compensation control to the appropriate tube. Mix by flicking.
- Incubate for 30 min at 4 °C in the dark.
- Add 1 ml of Flow cytometry staining buffer to each tube.
- Centrifuge at 500 x g for 4 min at room temperature.
- Discard the supernatant, 100 μl of residual volume should remain.
- Resuspend in residual volume by vortexing.
- Label two tubes ‘AF488’ and ‘AF647’.
- Set PMT voltages on the cytometer using single color compensation tubes. Each single color tube will have both a negative and a positive bead population.
- Acquire each single color compensation tube. A minimum of 2,000 total events is recommended to enable proper calculation of compensations.
- Acquire each sample tube. A minimum of 100,000 total events is recommended.
- Prepare single-color compensation tubes for AF488 and AF647 using the PrimeFlow® Compensation kit. You should also have single color controls for your fixable dye and for each fluorescent antibody you used.
Data analysis
Data analysis was performed with FlowJo V10. Single color tubes were used to calculate the compensation matrix. Monocytes were cultured with M-CSF only (that drives mo-mac differentiation) or with a cocktail of M-CSF, IL-4, TNF-a and FICZ (that induces monocytes to differentiate preferentially into mo-DC). We found that a part of monocytes express MAFB mRNA and others IRF4 mRNA (Figure 1). No monocyte expressed the two mRNA simultaneously (Figure 1). PrimeFlow RNA assay showed that monocytes cultured for 3 h with M-CSF, IL-4, TNFa and FICZ express MAFB or IRF4 and that their expression levels are mutually exclusive (Goudot et al., 2017).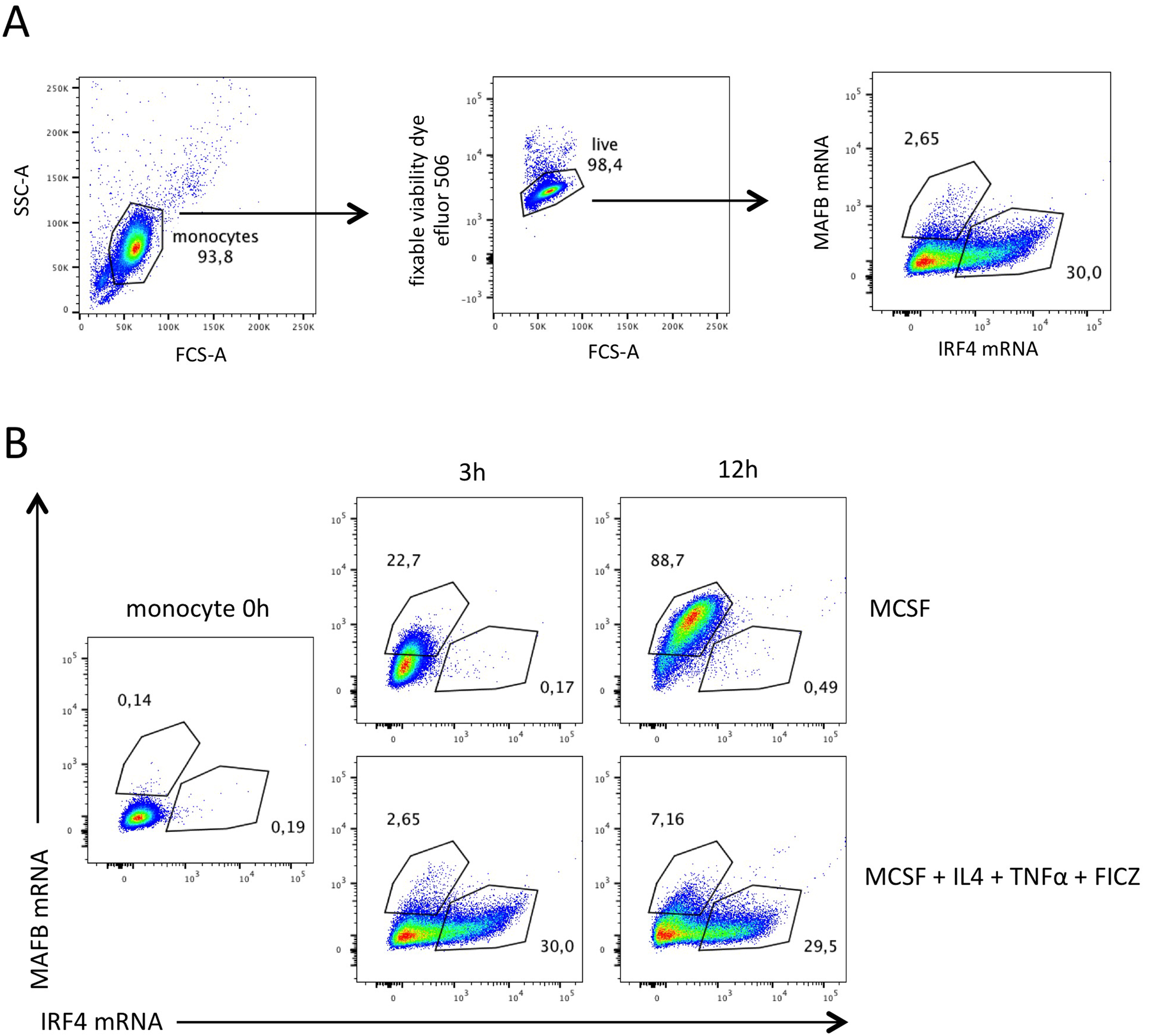
Figure 1. Proportions of MAFB+ and IRF4+ monocytes at 3 h and 12 h. Monocytes were subjected to PrimeFlow RNA assay directly after isolation or after 3 h or 12 h of culture with M-CSF or with M-CSF, IL-4, TNFa and FICZ. AlexaFluor488-MAFB and AlexaFluor647-IRF4 probes were used. A. Gating strategy. Debris and dead cells were gated out. B. MAFB mRNA and IRF4 mRNA expression.
Notes
- Temperature during hybridization is a critical point. Pre-warm the incubator to 40 °C at least 24 h before using it and make sure that the temperature remains stable.
- You may stain cells with surface markers (between Steps A6 and A7) or intracellular markers (between Steps A12 and A13). Stain cells in the dark at the optimal conditions (time and antibody dilutions). Dilute antibodies in 1x PrimeFlow RNA Permeabilization Buffer for the intracellular staining.
- The protocol lasts 2 days and cells can be stored overnight in PrimeFlow RNA Wash Buffer at 4 °C. However, you may skip Step A19 and continue through the protocol. You may also stop after Step B8. In that case, add RNase inhibitors at the dilution of 1/100 to PrimeFlow RNA Wash Buffer in Step B8 and store cells overnight in the dark at 4 °C.
- Step A14 can be performed overnight in the dark at 4 °C. In that case, perform Steps A15 to B8 on Day 2 and skip Step A18.
- You can buy the probe sets you need from Thermo Fisher Scientific. If there are no commercial probes you need, custom-made probes can also be designed by Thermo Fisher Scientific.
- The protocol is designed for 96-well plates. However, you may also use graduated 1.5 ml tubes provided by Thermo Fisher Scientific. For all hybridization steps at 40 °C, place tubes in a metal rack. To discard supernatant from 1.5 ml tubes, aspirate it and do not disrupt the pellet. Residual volume should be 100 μl. If tubes are used, use 1 ml instead of 200 μl of Buffer in Steps A8, A11, and A14. Use also 1 ml of PrimeFlow RNA Wash Buffer instead of 200 μl in all wash steps. Classical polystyrene 96-well v-bottom plates may also be used.
Recipes
- Flow cytometry buffer
PBS (Eurobio)
2 mM EDTA (Invitrogen)
0.5% of human serum (You can replace human serum with 1% fetal calf serum or BSA) - Culture medium for monocyte differentiation
RPMI-Glutamax medium (Gibco)
Penicillin and streptomycin
10% fetal calf serum
100 ng/μl M-CSF
5 ng/μl IL-4
5 ng/μl TNFa
62 nM FICZ
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Agence Nationale de la Recherche (program “Investissements d’Avenir” ANR-10-LABX-0043, ANR-10-IDEX-0001-02 PSL, and ANR-17-CE15-0011-01), INSERM and Fondation Bristol-Myers Squibb pour la Recherche en Immuno-Oncologie.
Competing interests
Authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Goudot, C., Coillard, A., Villani, A. C., Gueguen, P., Cros, A., Sarkizova, S., Tang-Huau, T. L., Bohec, M., Baulande, S., Hacohen, N., Amigorena, S. and Segura, E. (2017). Aryl hydrocarbon receptor controls monocyte differentiation into dendritic cells versus macrophages. Immunity 47(3): 582-596. e6.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Coillard, A. and Segura, E. (2018). Visualization of RNA at the Single Cell Level by Fluorescent in situ Hybridization Coupled to Flow Cytometry. Bio-protocol 8(12): e2892. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2892.
Category
Immunology > Immune cell staining > Flow cytometry
Developmental Biology > Cell growth and fate > Differentiation
Cell Biology > Cell staining > Nucleic acid
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link








