- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Polysome Preparation, RNA Isolation and Analysis
Published: Vol 2, Iss 21, Nov 5, 2012 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.286 Views: 28360

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Purification of Bacterial RNA from Infected Macrophages
Lior Lobel [...] Anat A. Herskovits
Nov 20, 2015 11188 Views

Protocol for Ribosome Profiling in Bacteria
Fuad Mohammad and Allen R. Buskirk
Dec 20, 2019 10275 Views

mRNA Delivery Platform Based on Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles for Tumor Vaccine
Xiaoyu Gao [...] Xiao Zhao
Jul 5, 2023 3077 Views
Abstract
During mRNA translation, 40S and 60S ribosomal subunits bind to target mRNA forming into an 80S complex (monosome). This ribosome moves along the mRNA during translational elongation to facilitate tRNA reading codon, where translation is activated and many monosomes can bind the same mRNA simutaneously, which forms polysomes. Polysomes can be size-fractionated by sucrose density gradient centrifugation. The more specific mRNA in polysomes implies more active translational status of the mRNA.
Materials and Reagents
- Cells (Neuroblastoma cell line SKN-SH)
- Protease inhibitors (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: P8340-5ML )
- DTT (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: 43815 )
- Cycloheximide (CHX) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C7698 )
- Heparin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H3149 )
- Sucrose (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: S1888 )
- Phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol (Life Technologies, Invitrogen™, catalog number: 15593-031 )
- Sodium acetate (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: S209-500 )
- 1x PBS
- 1x Trypsin-EDTA, 0.05% Trypsin/0.53 mM EDTA (Cellgro, catalog number: 25-052-CV )
- RPMI-1640 (Hyclone, catalog number: SH30096.01 )
- Tris-Base (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP-152-1 )
- KCl (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: BP-366-500 )
- MgCl2 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: M-2393 )
- Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T8787-250ML )
- DNAase/RNAase free Ethanol (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: E7023-500ML )
- DNAase/RNAase free water (BioExpress, catalog number: UPW-1000 )
- Ultracentrifuge tubes (14 x 89 mm) (Beckman Coulter, catalog number: 344059 )
- Polysome extraction buffer (PEB) (see Recipes)
- Sucrose solutions (see Recipes)
Equipment
- BR-188 Density gradient fractionation system (Brandel)
- Beckman optima L-70 ultracentrifuge (Beckman)
- 7500 Real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems)
- Boekel scientific orbitron rotator I, 115 V (Boekel Scientific)
Procedure
- Prepare neuroblastoma cell line SKN-SH cells 2.5-5 x 107/group, normally 2 to 3 150 cm2 flasks with 50 ml of RPMI-1640 medium.
- Before harvest, cells are incubated in complete RPMI-1640 medium (RPMI-1640 medium with FBS, Pen/Strep and Glutamine) containing a final concentration of 100 μg/ml CHX for 10 min at 37 °C.
- Discard medium andrinse cells twice with cold 10 ml 1x PBS containing 100 μg/ml CHX.
- Harvest cells, briefly add 7 ml of trypsin into each flask, incubate at 37 °C for 3 min, then collect cells with 10 ml PBS containing 100 μg/ml CHX (this step is not needed for suspension cells).
- After centrifugation, resuspend cells in 1 ml of 1x PBS, then transfer them into 1.7 ml micro centrifuge tube.
- Lyse cells with 1 ml PEB Buffer containing 1% Triton-X100, vortex 15 sec and keep on ice for 30 min.
- Centrifuge at 14,000 rpm for 30 min at 4 °C and collect supernatants that are ready to be loaded on sucrose gradients of 10%-50% consistency.
- Make sucrose solutions according to the recipe step.
- Make 10 ml gradient by adding 2.0 ml of each solution (50% on bottom, 10% on top) and load into ultracentrifuge tube.
- Add 1 ml of cell extract to the top of each gradient. Cover each tube with parafilm, put it in a SW41 rotor andspin samples at 38,000 rpm for 120 min at 4 °C.
- Collect 13 fractions from the top to the bottom of the tube using BR-188 density gradient fractionation system.
- Machine setting options: fraction collection time: 1 min and 15 sec/fraction; pump speed, 0.75 ml/min; chart speed, 60 cm/h).
- Keep all fractions at -80 °C, it’s good for extraction of RNA in 1 month.
- For RNA extraction, thaw all samples on ice.
- Pick 0.5 ml of each sample into a new 2 ml-microcentrifuge tube, keep on ice.
- Mix the water saturation Phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol (25:24:1) completely.
- Add 500 μl of the mixed Phenol/chloroform/isoamyl alcohol into each tube, when pipetting keep shaking with hand to avoid water separating out.
- Vortex for 30 sec and then keep rotating at 4 °C for 5 min.
- Centrifuge at 14,000 rpm for 10 min at 4 °C, at the same time prepare new 2 ml-microcentrifuge tube for each sample, add 3 M Sodium Acetate (pH 5.2) 50 μl/tube.
- Very carefully pipet out all the aqueous phase and put it into the prepared fresh 2 ml-microcentrifuge tube.
- Then add 1.5 ml (3 volumes) of 100% ethanol, vortex 30 sec.
- Keep the samples at -80 °C for 3 h.
- Centrifuge at 14,000 rpm for 30 min at 4 °C.
- Wash pellet with cold 70% RNase free ethanol by rotating for 5 min.
- Centrifuge pellet at 14,000 rpm for 5 min at 4 °C.
- Discard supernatants and remain the pellet in the tubes.
- Put tubes on ice to let all the liquid evaporated.
- Add 30-50 μl of DNase/RNase free H2O and subjected to quantitated RT-PCR.
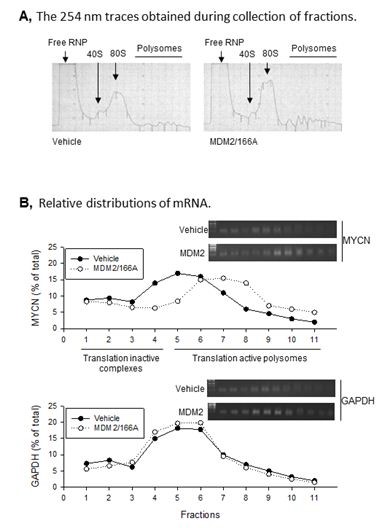
Figure 1. MDM2 regulates MYCN translation. A. Representative polysomal profiles from control vector- and MDM2/166A-transfected SK-N-SH cells. The 254-nm traces obtained during collection of fractions are shown. B. Relative distributions of MYCN and GAPDH mRNA in SK-N-SH cells transfected either with vehicle or MDM2/166A.
Recipes
- Polysome extraction buffer (PEB)
(Triton-X100 Free)
20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5)
50 mM KCl
10 mM MgCl2
1 mM DTT
100 μg/ml CHX
200μg/ml Heparin - Preparation of 50%, 40%, 30%, 20%, 10% sucrose solutions as following
Make 50% Sucrose solution (25 g sucrose + PEB without Triton-X100 to 50 ml)
Dilute 50% sucrose solution into the solutions of 40%, 30%, 20% and 10% in PEB buffer
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health (R01 CA123490 and R01CA143107 to MZ) and CURE (MZ and LG).
References
- Gu, L., Zhang, H., He, J., Li, J., Huang, M. and Zhou, M. (2012). MDM2 regulates MYCN mRNA stabilization and translation in human neuroblastoma cells. Oncogene 31(11): 1342-1353.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2012 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Zhang, H. and Zhou, M. (2012). Polysome Preparation, RNA Isolation and Analysis. Bio-protocol 2(21): e286. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.286.
Category
Molecular Biology > RNA > mRNA translation
Molecular Biology > RNA > RNA extraction
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










