- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Nab Escaping AAV Mutants Isolated from Mouse Muscles
Published: Vol 8, Iss 9, May 5, 2018 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2841 Views: 7593
Reviewed by: Longping Victor TseGeorge William CarnellVikas Duhan

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

Analysis of the Effect of Sphingomyelinase on Rubella Virus Infectivity in Two Cell Lines
Noriyuki Otsuki [...] Makoto Takeda
Sep 5, 2018 6086 Views

Primer ID Next-Generation Sequencing for the Analysis of a Broad Spectrum Antiviral Induced Transition Mutations and Errors Rates in a Coronavirus Genome
Shuntai Zhou [...] Ronald Swanstrom
Mar 5, 2021 7460 Views

An Improved Focus-Forming Assay for Determination of the Dengue Virus Titer
Maharah Binte Abdul Mahid [...] Kitti Wing Ki Chan
Oct 20, 2024 2396 Views
Abstract
Neutralizing antibodies (Nabs) are a major challenge in clinical trials of adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector gene therapy, because Nabs are able to inhibit AAV transduction in patients. We have successfully isolated several novel Nab-escaped AAV chimeric capsids in mice by administrating a mixture of AAV shuffled library and patient serum. These AAV chimeric capsid mutants enhanced Nab evasion from patient serum with a high muscle transduction efficacy. In this protocol, we describe the procedures for selection of the Nab-escaped AAV chimeric capsid, including isolation and characterization of Nab-escaping AAV mutants in mice muscle.
Keywords: AAVBackground
Adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors have been used in many preclinical studies and clinical trials. Many diseases have received eventual treatment using AAV gene therapy. However, the presence of neutralizing antibodies in circulation poses a major challenge for AAV vector application in future clinical trials. Many approaches have been explored to evade activities of Nab. Herein, we described the approach with directed evolution for selection of Nab-escaping mutants from an AAV shuffling library.
DNA shuffling is a powerful strategy for generating diverse mutants. Through successive rounds of phenotypic selection, DNA shuffling libraries were characterized by higher quality and more targeted diversification. High-throughput selection of capsid mutants from AAV shuffling libraries has been used as a promising strategy to explore AAV mutants with the abilities to target specific tissues and evade Nabs. However, most of these selecting methods were only tested in vitro; some studies even used rabbit anti-AAV2 sera or human intravenous immunoglobulin. The approach of in vivo selection of capsid mutants could provide a platform to generate more effective AAV mutants that not only escape Nab from patient serum but also enhance transduction in specific tissues.
Materials and Reagents
- GeneMate individual 0.2 ml PCR tubes (BioExpress, catalog number: T-3035-1 )
- BD Veo insulin syringes with BD Ultra-Fine 6 mm x 31G needle (BD, catalog number: 324910 )
- CorningTM 96-Well Clear Bottom Black Polystyrene Microplates (Corning, catalog number: 3904 )
- VWR® Tissue Culture 48-well Plate (VWR, catalog number: 10861-560 )
- BALB/c mice, typically of 6 weeks old female mice
- ElectroMAXTM DH10BTM Cells (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: 18290015 )
- Adherent HEK 293 cells and Huh7 cells
- MAX EfficiencyTM DH10BTM Cells (Thermo Fisher Scientific, InvitrogenTM, catalog number: 18297010 )
- JBS DNA-Shuffling Kit (Jena Bioscience, catalog number: PP-103 )
- DNase I, RNase-free (1 U/µl) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, catalog number: EN0521 )
- EDTA
- QIAquick PCR Purification Kit (250) (QIAGEN, catalog number: 28106 )
- Purified single-stranded AAV (any serotype) (Xiao et al., 1998)
- PfuUltra High-Fidelity DNA polymerase (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA)
- Wild type AAV2 plasmid psub201, plasmid pXR2 (RepCap plasmid) and pXX6-80 (a helper plasmid contains the genes E4, E2a and VA from adenovirus)
- 1x PBS (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 14190144 )
- Patient serum from clinical study for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (Bowles et al., 2012)
- Adenovirus dl309
- DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit (QIAGEN, catalog number: 69504 )
- SwaI (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R0604S )
- XbaI (New England Biolabs, catalog number: R0145S )
- Passive lysis buffer (Promega, catalog number: E1941 )
- Luciferase Assay Substrate (Promega, catalog number: E151A )
- XenoLight D-Luciferin - Bioluminescent Substrate (PerkinElmer, catalog number: 122799 )
- 25 mg/ml D-luciferin substrate (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Pipettes
- Bio-Rad Thermal Cyclers (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 1709703 )
- Tabletop centrifuge (Eppendorf, model: 5424 , catalog number: 022620401)
- VICTOR Multilabel Plate Reader (PerkinElmer)
- Small animal anesthesia system (Xenogen, XGI-8 Gas Anesthesia System)
- IVIS Lumina In Vivo imaging system (PerkinElmer)
Software
- Living Image software (PerkinElmer)
Procedure
- The generation of a new AAV shuffling library
Note: There are multiple methods that can be used to generate DNA shuffling library, and a handful of kits available from manufacturers. DNA shuffling library can be generated using JBS DNA shuffling kit. The process of generation of AAV shuffling library is shown in Figure 1.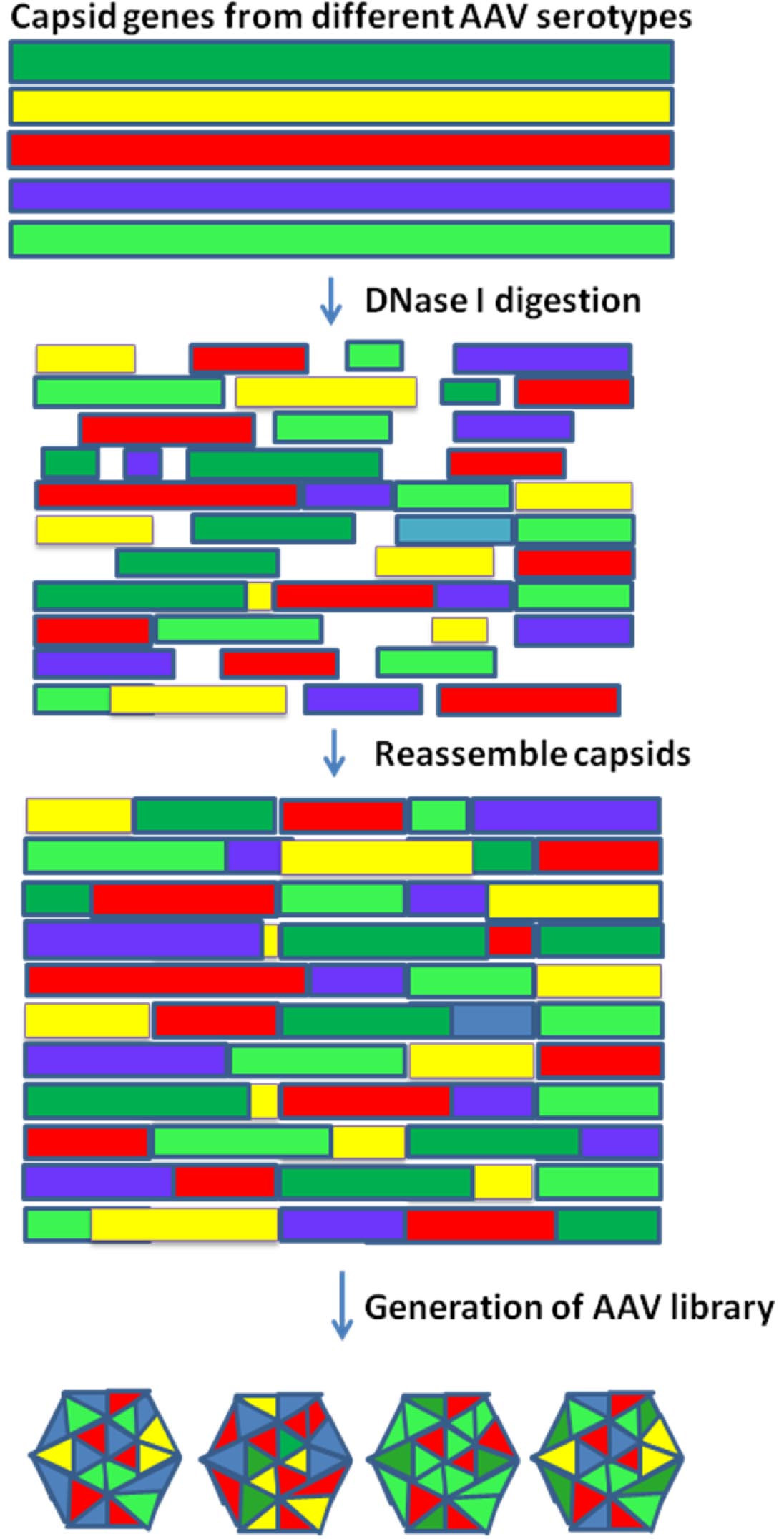
Figure 1. Flow chart for generation of AAV shuffling library- Amplify the capsid genes by PCR assay using AAV serotypes 1, 2, 3, 6, 8 and 9 mixed in equal ratios as templates. The primers sequences were shown in Table 2 of Li et al. (2008).
- Treat a total of 4 μg of the DNA templates by 0.4 U of DNase I at 37 °C for 5 min. Stop DNase activation by adding 1 μl 25 mM EDTA, and then heat inactivation at 75 °C for 10 min.
- Purify DNA fragments in size of 100-300 bp using DNA purification Kit following standard procedures.
- Denature, re-anneal and repair the purified DNA fragments by Pfu Ultra High-Fidelity DNA polymerase to reassemble random capsid genes in 0.2 ml PCR tube. Run the PCR assay using the program in Table 1 (Li et al., 2008; Yang et al., 2009).
Table 1. PCR cycling parameter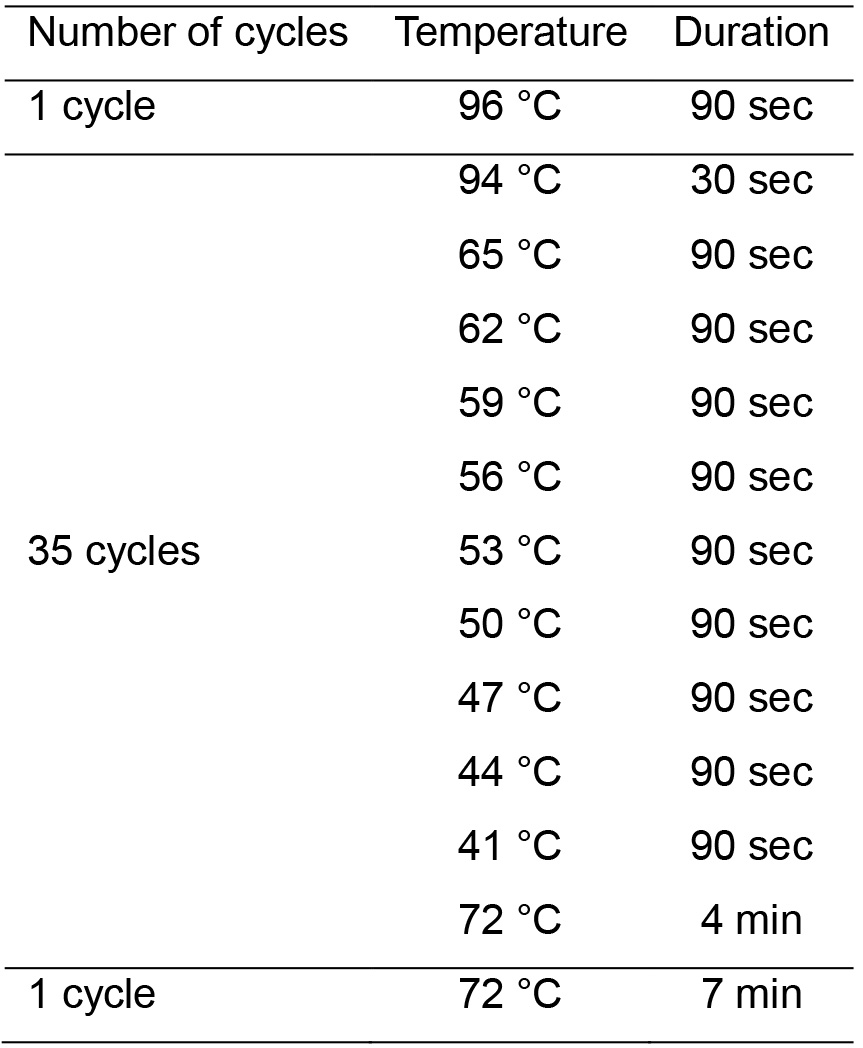
- Clone the capsids from DNA shuffling library into wild-type AAV2 plasmid psub201 to generate AAV capsid DNA library (Li et al., 2008; Li et al., 2016).
- Produce AAV shuffling library in HEK293 cells by co-transfection of two plasmids: pXX6-80 and AAV capsid DNA library.
- Purify single-stranded AAV with CsCl gradient ultracentrifugation and measure virus titer of shuffled AAV by quantitative PCR (Xiao et al., 1998).
- Amplify the capsid genes by PCR assay using AAV serotypes 1, 2, 3, 6, 8 and 9 mixed in equal ratios as templates. The primers sequences were shown in Table 2 of Li et al. (2008).
- Isolation of Nab escaping AAV mutants from mouse muscles
- Mix 1 x 1010 particles of the AAV shuffling library virus in 50 μl PBS with 50 μl undiluted patient serum at 4 °C for 2 h.
- Inject the AAV/serum mixture using insulin syringes via intramuscular (i.m.) route into the hind leg muscle of 6-week-old female BALB/c mice (injection volume 100 μl).
- Three days post-treatment, inject 107 virus particles (vg) of adenovirus (Adv) dl309 via i.m. into the same muscle to amplify AAV genomes in vivo.
Note: Any replicable Adv can be used in this step. - Collect muscles from injected mice at 2 days post Adv administration, and extract total DNA using DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit.
Note: There are several methods that can be used to isolate DNA from tissues, and a handful of kits available from many manufacturers to do it. Here, we performed a genomic DNA isolation from mouse muscle using DNeasy Blood and Tissue Kit. In this protocol, the isolation of genomic DNA from muscle relies upon the columns and spin steps. Please follow the protocol of the manufacturer. - Amplify AAV mutant capsids by PCR assay using the genomic DNA from the muscle as templates. The sequences of the primers are F1 5’-CAACTCCATCACTAGGGGTTC and R1 5’-CATGGGAAAGGTGCCAGA, which are localized at the AAV2 rep and AAV2 ITR, respectively. Run PCR assay using PfuUltra High-Fidelity DNA polymerase, following the program in Table 2.
Table 2. PCR cycling parameters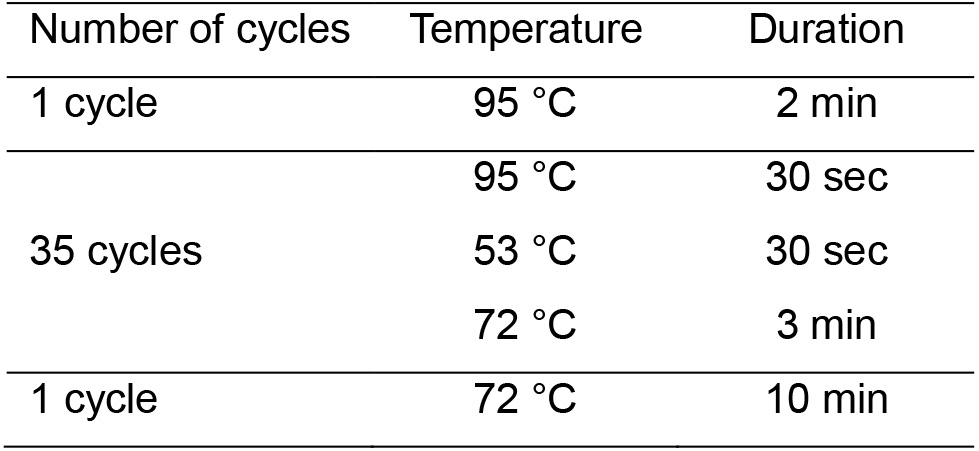
- Purify PCR products by the QIAquick PCR Purification Kit.
- Digest with SwaI and XbaI and ligate into pXR2 digested with the same endonucleases. Transform the constructed plasmids into a culture of DH10b competent cells.
Note: The plasmid pXR2 can be any expression plasmid with Rep gene of AAV for further AAV package. - Sequence clones and generate AAV/luc mutant vectors (Xiao et al., 1998).
- Mix 1 x 1010 particles of the AAV shuffling library virus in 50 μl PBS with 50 μl undiluted patient serum at 4 °C for 2 h.
- Nab escaping ability of AAV mutants in vitro
Note: Cell lines that can be transduced by AAV can be used for neutralizing assay. Add the serum/AAV mixture when the cells are suspended.- Seed Huh7 cells into a 48-well plate at a density of 105 cells for each well.
- Incubate two-fold dilutions of the serum (from 1:4 to 1:1,024) with AAV-Luc (1 x 108 vg) for 1 h at 37 °C.
- Add the mixture (diluted serum and AAV) into Huh7 cells and incubate for 48 h at 37 °C.
- Discard the culture media.
- Lyse cells with 100 μl 1x of passive lysis buffer for 30 min.
- Transfer the 20 μl lysed medium into 96-well black plate.
- Add luciferase substrate (100 μl) into 96-well black plate and briefly mix with lysed medium.
- Measure luciferase activity using luminometer reader (VICTOR Multilabel Plate Reader).
- Define Nab titers as the highest dilution for which luciferase activity is 50% lower than serum-free controls.
- Seed Huh7 cells into a 48-well plate at a density of 105 cells for each well.
- Nab escaping ability of AAV mutants in mice
- Incubate 1 x 1010 vg of AAV/luc mutants isolated from muscles with the 5-fold diluted patient serum or PBS for 2 h at 4 °C.
- Inject the AAV/serum mixture (total volume 100 μl) in the legs of six-week-old female BALB/c mice via i.m.
- Image luciferase expression in mice at 3 weeks post-injection. Anesthetize mice using an isoflurane vaporizer and inject with 120 mg/kg of D-Luciferin substrate intraperitoneally 5 min before imaging. Place the mice inside the camera box of the IVIS system. Start imaging with an exposure capturing in mice.
- Incubate 1 x 1010 vg of AAV/luc mutants isolated from muscles with the 5-fold diluted patient serum or PBS for 2 h at 4 °C.
Data analysis
- After the mixture of AAV shuffling library and patient serum was injected into the muscles of the mice, imaging was carried out by the IVIS Lumina In Vivo imaging system, and the photon signal was measured by Living Image software. The results were shown in Figure 1b of the original paper (Li et al., 2016).
- The AAV mutant capsids were recovered and sequenced. The results were shown in Figure 1a of the original paper (Li et al., 2016).
- The recovered AAV mutant capsids were used to package the AAV mutants. The mixtures of the AAV mutants and patient serum were administrated into muscles of mice. The imaging was carried out by the IVIS Lumina In Vivo imaging system and the photon signal was measured by Living Image software. The results were shown in Figure 2 of the original paper (Li et al., 2016).
Recipes
- 25 mg/ml D-luciferin substrate
Prepare 25 mg/ml D-luciferin solution in DPBS
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH grants R01DK084033 (to C.L. and R.J.S.), P01HL112761, R01AI072176, R01AR064369 and U54AR056953 (to R.J.S). R.J.S. is the founder and a shareholder at Asklepios Biopharmaceutical. He holds patents that have been licensed by UNC to Asklepios Biopharmaceutical, for which he receives royalties. This protocol is adapted from Li et al. (2016).
References
- Bowles, D. E., McPhee, S. W., Li, C., Gray, S. J., Samulski, J. J., Camp, A. S., Li, J., Wang, B., Monahan, P. E., Rabinowitz, J. E., Grieger. J. C., Govindasamy, L., Agbandje-Mckenna, M., Xiao, X., and Samulski, R. J. (2012) Phase 1 gene therapy for Duchenne muscular dystrophy using a translational optimized AAV vector. Mol Ther 20(2), 443-455.
- Li, W., Asokan, A., Wu, Z., Van Dyke, T., DiPrimio, N., Johnson, J. S., Govindaswamy, L., Agbandje-McKenna, M., Leichtle, S., Eugene Redmond, D., Jr., McCown, T. J., Petermann, K. B., Sharpless, N. E. and Samulski, R. J. (2008). Engineering and selection of shuffled AAV genomes: A new strategy for producing targeted biological nanoparticles. Mol Ther 16(7): 1252-1260.
- Li, C, Wu S, Albright B, Hirsch M, Li W, Tseng YS, Agbandje-Mackenna M, McPhee S, Asokan A, Samulski, R.J., (2016). Development of patient-specific AAV vectors after neutralizing antibody selection for enhanced muscle gene transfer. Mol Ther 24(1): 53-65.
- Xiao, X., Li, J. and Samulski, R. J. (1998). Production of high-titer recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors in the absence of helper adenovirus. J Virol 72(3): 2224-2232.
- Yang, L., Jiang, J., Drouin, L. M., Agbandje-McKenna, M., Chen, C., Qiao, C., Pu, D., Hu, X., Wang, D. Z., Li, J. and Xiao, X. (2009). A myocardium tropic adeno-associated virus (AAV) evolved by DNA shuffling and in vivo selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(10): 3946-3951.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Chai, Z., Samulski, R. J. and Li, C. (2018). Nab Escaping AAV Mutants Isolated from Mouse Muscles. Bio-protocol 8(9): e2841. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2841.
Category
Immunology > Antibody analysis > Antibody function
Microbiology > Antimicrobial assay > Antiviral assay
Molecular Biology > Protein > Anti-microbial analysis
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link