- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Measurement of NADPH Oxidase Activity in Plants
Published: Vol 2, Iss 20, Oct 20, 2012 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.278 Views: 21807

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

A Semi-throughput Procedure for Assaying Plant NADP-malate Dehydrogenase Activity Using a Plate Reader
Kevin Baudry and Emmanuelle Issakidis-Bourguet
Aug 20, 2023 1466 Views

An in vitro Assay to Probe the Formation of Biomolecular Condensates
Yu Zhang and Shen Lisha
Sep 5, 2023 3197 Views

Immunofluorescence for Detection of TOR Kinase Activity In Situ in Photosynthetic Organisms
Ana P. Lando [...] Giselle M. A. Martínez-Noël
Dec 20, 2024 1813 Views
Abstract
NADPH oxidase is a membrane-bound enzyme that generates (O2-) by transferring electrons from NADPH to molecular oxygen O2. O2-is spontaneously dismasted to the more stable form H2O2. Both O2-and H2O2 are forms ofreactive oxygen species (ROS), which are involved in regulation of many cellular activities such as transcription, intracellular signaling, and host defense. The NADPH oxidase - dependent generation of O2- in total membrane fraction of plant tissue has been determined by the reduction of the tetrazolium salt XTT by O2-. In the presence of O2-, XTT generates a soluble yellow formazan that can be quantified spectrophotometrically.
Materials and Reagents
- Sucrose
- HEPES
- EDTA
- DTT
- L-cysteine
- MgCl2
- PVP
- Complete, Mini, EDTA-free Protease Inhibitor Cocktail Tablets (F. Hoffmann-La Roche, catalog number: 04693159001 )
- BSA
- Bio-Rad Protein Assay (Bio-Rad Laboratories, catalog number: 500-0006 )
- Tris-HCl
- Sodium 3,3'-( -[(phenylamino)carbonyl] -3,4-tetrazolium)-bis (4-methoxy-6-nitro) benzene-sulfonic acid hydrate (XTT) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: X4626 )
- NADPH (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: N1630 )
- Protein extraction working solution (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Microtiter plate reader (Infinite M200 Pro, Tecan)
- Microcentrifuge (AqquSpin Micro R) (Thermo Fisher Scientific)
- Ultracentrifuge ( Optima TLX , Beckman)
- Microtiter plate (BD Biosciences, catalog number: 353075 )
Procedure
- Protein extraction and separation of membrane fraction from plant tissues
- Harvest tissue in liquid nitrogen. If not used immediately, keep at -80 °C until processing.
- Grind tissue in liquid nitrogen and weigh out 0.5 g of the ground tissues in empty Falcon tube that has been pre-chilled in liquid nitrogen and used to tare the scale.
- Add 6 ml of ice-cold protein extraction buffer to ground tissues on ice.
- Vortexat room temperature to mix thoroughly.
- Filter homogenized tissue through four layers of cheese cloth and transfer filtrate (flow-through) to 2-ml microcentrifuge tubes, on ice.
- Centrifuge at 10,000 x g for 45 min at 4 °C and transfer supernatant to ultra- centrifuge tube.
- Separate total membrane fractions by ultra-centrifugation at 203,000 x g for 60 min at 4 °C.
- Discard supernatant and resuspend pellet in 1 ml ice-cold 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4).
- Harvest tissue in liquid nitrogen. If not used immediately, keep at -80 °C until processing.
- Protein estimation using Bradford microassay (160 μl)
- Prepare BSA standards ranging from 5 μg-25 μg/ml as follows:
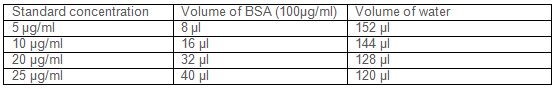
These standards will be used to generate a standard curve. - Use 96 well microtiter plate to prepare reaction mix.
- Prepare blank byadding 160 μl of water to one well in triplicates.
- Prepare test samples by adding 2 μl of supernatant (from section 1) to 158 μl of water.
- Add 40 μl of Bradford Assay reagent to BSA standards, blank and test samples.
- Mix and incubate at room temperature for 5 min and read absorbance at 595 nm (A595) on plate reader spectrophotometer.
Note: If spectrophotometer does not include a software to generate standard curve to automatically estimate protein content, generate a BSA standard curve by plotting known protein concentration (X-axis) vs. Absorbance (in Y-axis). Protein concentration for a given unknown sample is estimated by plotting the A595 absorbance of the unknown (in the y-axis) and determining the intersection point with the BSA standard curve and then find the concentration associated with that particular point (in the x-axis). If using excel, after plotting concentration vs A595, obtain the trendline and use the equation for the line and the A595 of the unknown to resolve the unknown concentration.
- Prepare BSA standards ranging from 5 μg-25 μg/ml as follows:
- NADPH oxidase activity assay
- Prepare fresh solution of 1 mM XTT and 1 mM NADPH.
- Prepare two different assay solutions A and B:
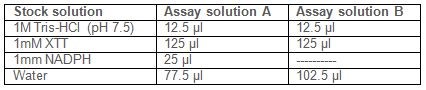
Note: Because membrane fraction can spontaneously reduce XTT, even in the absence of substrate (NADPH), it is necessary to prepare two blanks, one without NADPH, to correct for this background levels of activity. - Prepare blanks:
Blank 1: Add 10 μl of water to 240 μl of Assay solution A.
Blank 2: Add 10 μl of membrane fraction to 240 μl Assay solution B. - Prepare samples by adding 10 μl of membrane fraction (from section 1) to 240 μl of Assay solution A. Read the absorbance at 492 nm (A492) at 0 min and then 20 min intervals for one hour or until saturation point reached.
- To get final A492 Blank reading, subtracts A492 Blank1 and A492 Blank 2.
- Calculate rate of O2– generation by using an extinction coefficient 2.16 x 104 cm-(Jiang and Zhang 2002).
(ΔA492nm/min test-ΔA492nm/min blank) / (2.16X104M-1CM-1) (0.04)
ΔA492nm/min Test= A492 (sample X) at saturation point - A492 (sample X) at 0 min
ΔA492nm/min blank = A492nm (blank) at saturation point - A492nm (blank) at 0 min
0.04 = dilution factor (10 μl/250 μl)
To calculate specific activity, divide the value obtained in equation by the amount of protein present in the sample (converted to mg/ml).
- Prepare fresh solution of 1 mM XTT and 1 mM NADPH.
Recipes
- Protein extraction working solution
0.25 M sucrose
50 mM HEPES
3 mM EDTA
1 mM DTT
3.6 mM L-cysteine
0.1 mM MgCl2
0.6% PVP
10 Tablets of Complete, Mini, EDTA-free Protease Inhibitor Cocktail Tablets.
Prepare the following stock solutions:
1 M sucrose
1 M HEPES (pH 7.2)
0.25 M EDTA
1 M DTT
100 mM MgCl2
In 80 ml of water add the following reagents: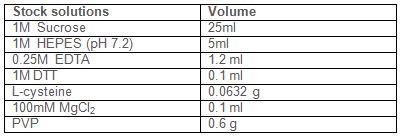
Add 10 Tablets of Complete, Mini, EDTA-free Protease Inhibitor Cocktail Tablets.
Mix well and adjust volume to 100 ml
Acknowledgments
This protocol has been adapted and modified to use in Arabidopsis from Jiang and Zhang (2002). This work was supported by the Samuel Roberts Noble Foundation.
References
- Able, A. J., Guest, D. I. and Sutherland, M. W. (1998). Use of a new tetrazolium-based assay to study the production of superoxide radicals by tobacco cell cultures challenged with avirulent zoospores of phytophthora parasitica var Nicotianae. Plant Physiol 117(2): 491-499.
- Jiang, M. and Zhang, J. (2002). Involvement of plasma-membrane NADPH oxidase in abscisic acid- and water stress-induced antioxidant defense in leaves of maize seedlings. Planta 215(6): 1022-1030.
- Rojas, C. M., Senthil-Kumar, M., Wang, K., Ryu, C. M., Kaundal, A. and Mysore, K. S. (2012). Glycolate oxidase modulates reactive oxygen species-mediated signal transduction during nonhost resistance in Nicotiana benthamiana and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 24(1): 336-352.
- Sagi, M. and Fluhr, R. (2001). Superoxide production by plant homologues of the gp91(phox) NADPH oxidase. Modulation of activity by calcium and by Tobacco mosaic virus infection. Plant Physiol 126(3): 1281-1290.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2012 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Kaundal, A., Rojas, C. M. and Mysore, K. S. (2012). Measurement of NADPH Oxidase Activity in Plants. Bio-protocol 2(20): e278. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.278.
Category
Plant Science > Plant biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Biochemistry > Protein > Activity
Biochemistry > Other compound > Reactive oxygen species
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link









