- Submit a Protocol
- Receive Our Alerts
- Log in
- /
- Sign up
- My Bio Page
- Edit My Profile
- Change Password
- Log Out
- EN
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
- EN - English
- CN - 中文
- Home
- Protocols
- Articles and Issues
- For Authors
- About
- Become a Reviewer
Murine Pancreatic Islets Transplantation under the Kidney Capsule
Published: Vol 8, Iss 5, Mar 5, 2018 DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2743 Views: 11819
Reviewed by: Ruth A. FranklinSylvaine YouSara Johnson

Protocol Collections
Comprehensive collections of detailed, peer-reviewed protocols focusing on specific topics
Related protocols

A Participant-Derived Xenograft Mouse Model to Decode Autologous Mechanisms of HIV Control and Evaluate Immunotherapies
Emma Falling Iversen [...] R. Brad Jones
Apr 5, 2025 2555 Views

PBMC-Humanized Mouse Model for Multiple Sclerosis: Studying Immune Changes and CNS Involvement
Anastasia Dagkonaki [...] Lesley Probert
May 20, 2025 4045 Views

Obtaining Chondroprogenitors (Articular Cartilage-Derived Cells) via Explant Methodology
Débora Levy [...] Marco Kawamura Demange
Mar 5, 2026 69 Views
Abstract
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disease caused by the lack of insulin-producing pancreatic beta cells leading to systemic hyperglycemia. Pancreatic islet transplantation is a valid therapeutic approach to restore insulin loss and to promote adequate glycemic control. Pancreatic islet transplantation in mice is an optimal preclinical model to identify new therapeutic strategies aiming at preventing rejection and optimizing post-transplant immuno-suppressive/-tolerogenic therapies.
Islet transplantation in preclinical animal models can be performed in different sites such the kidney capsule, spleen, bone marrow and pancreas. This protocol describes murine islet transplantation under the kidney capsule. This is a widely accepted procedure for research purposes. Stress caused in the animals is minimal and it leads to reliable and reproducible results.
Background
Many alternative sites for islet implantation have been reported so far in small animal models and the ideal site must be selected according to the technical advantages of the procedure to be used and for the purpose of the experiments. Bearing in mind that the kidney capsule is an extravascular site and it is not immunoprotected, pancreatic islet transplantation under the kidney capsule remains a surgical procedure with low mortality rates leading to hyperglycemia reversion within a few days. In addition, transplantation under the kidney capsule allows histological studies and formal demonstration of islet function (Cantarelli and Piemonti, 2011; Elisa Cantarelli et al., 2013).
Materials and Reagents
- Cotton applicators, sterile (CARLO ERBA Reagents, catalog number: 9.413 161 )
- 30 G x ½ in. needle (BD, catalog number: 305106 )
- 2 ml slip tip syringe (BD, catalog number: 302204 )
- BD INTRAMEDICTM PE 50 (BD, catalog number: B427411 )
- Petri dish, Falcon® 50 x 9 mm Sterile (Corning, Falcon®, catalog number: 351006 )
- P200 pipette tip (SARSTEDT, catalog number: 70.760.002 )
- Eppendorf tubes volume 1.5 ml (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T9661-1000EA)
Manufacturer: Eppendorf, catalog number: 022363204 . - Silicone tubing adapter (2Biological Instruments, catalog number: SFM3-1550 )
- 1 ml syringe with 25 G needle (Ettore Pasquali, catalog number: 11.3500.05 )
- Suture Dermalon 5/0 19 MM (Covidien, catalog number: 1756-21 )
- Collagenase P (Roche Diagnostics, catalog number: 11213865001 )
- Betadine (MEDA PHARMA SpA, Farmacie Coli, catalog number: 023907076 )
- Avertin (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: T48402 )
- Sodium chloride ((NaCl) (CARLO ERBA Reagents, catalog number: FC72101100000 )
- Ketoprofen (PFIZER ITALIA Srl DIV.VET)
- RPMI 1640 medium (Lonza, catalog number: 12-167F )
- L-glutamine (Lonza, catalog number: 17-605E )
- HEPES buffer (Lonza, catalog number: 17-737E )
- Pen-Strep (Lonza, catalog number: 17-602E )
- Fetal bovine serum (Euroclone, catalog number: ECS0180L )
- Hank’s balanced salt solution (HBSS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific, GibcoTM, catalog number: 14175079 )
- Calcium chloride dihydrate (CaCl2·2H2O) (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: C5080 )
- Histopaque®-1077 (Sigma-Aldrich, catalog number: H8889 )
- RPMI/glutamine/HEPES/Pen-Strep/FBS (see Recipes)
- HBSS/Ca/HEPES (see Recipes)
Equipment
- Forceps (Graefe forceps, 100 mm, curved (ProSciTech, catalog number: T131C ), Tweezers, style 3 (ProSciTech, catalog number: T03-212 )
- Scissor (ProSciTech, catalog number: TS103-200SB )
- Surgical Shaver (2Biological Instruments, catalog number: 2BTOSRC )
- Cautery (Global medical solutions, catalog number: BAA00 )
- Thermostatic bath (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: TSGP02 )
- Inverted microscope (Compact, Modular Stereo, Leica, model: Leica M60 )
- Incubator at 37 °C with 5% CO2, relative humidity ambient to 80% [e.g., Series II 3110 Water-Jacketed CO2 incubators (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: FormaTM II 3110 Series )]
- Pipetman P20/P200/P1000 (Gilson)
- Microsyringe 25 μl Hamilton syringe (Hamilton, catalog number: 80401 )
- Heating pad 25 x 40 cm, Two Temperature Range (2Biological Instruments, LCPH)
- Herasafe KS, Class II biological safety cabinet with UV surface disinfection irradiator (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Thermo ScientificTM, model: HerasafeTM KS II , catalog number: 51022481)
Software
- Prism software (GraphPad, USA)
Procedure
- Preparation of islets for transplantation
- Isolation of pancreatic islet using the appropriate protocol (Graham et al., 2016)
- Briefly, sacrifice animal by cervical dislocation, open the mouse abdominal cavity and cut through the peritoneum.
- Place 3 ml of collagenase P into a 2 ml slip tip syringe with a 30 G needle. Perform the bile duct injection procedure and dissect the inflated pancreas, being careful not to cut the stomach, the intestines or other abdominal organs.
- Pour the inflated pancreases in a collection tube on ice. When all pancreata have been resected, incubate for 15 min at 37 °C in water-bath. Add ice-cold HBSS/Ca/HEPES as quick as possible to stop the digestion process. Disrupt the pancreases by vigorously hand shaking the tubes.
- Upon obtaining the digested tissue, the islets are separated by density gradient, recovered from the gradient interface, washed with RPMI 10% FBS and collected in a 50 ml Falcon tube containing 30 ml of RPMI 10% FBS.
Note: RPMI with serum is demonstrated to maintain (or even augment) glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in murine islets (Andersson, 1978).
- Briefly, sacrifice animal by cervical dislocation, open the mouse abdominal cavity and cut through the peritoneum.
- Afterwards, 5 ml of islets is transferred into a Petri dish that is gently swirled to collect the islets at the center.
- Under an inverted microscope, healthy islets are picked with a P200 sterile pipette tip. Healthy islets have smooth borders in the absence of dark centers (Figure 1). Visual examination of the islets can provide basic information regarding health. Hand-picked healthy islets are then transferred into a new Petri dish containing 3 ml of fresh RPMI 10% FBS.
Anticipate using one Petri dish for the totality of islets to be injected to one mouse.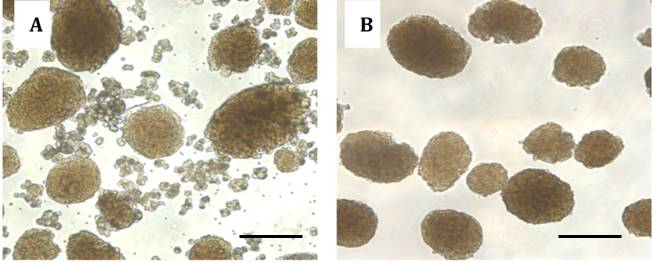
Figure 1. Images of pancreatic islets. Islets isolated before hand-picking (A). Purified islets after hand-picking (B). Scale bars represent 150 µm. - Isolated islets are highly stressed due to physical and chemical processing. To improve overall islet viability, islets cultured in Petri dishes are rested overnight in an incubator at 37 °C with 5% CO2. This allows a better discrimination between dead and alive islets as well as an optimum islets recovery. In case transplantation needs to be performed the same day of islet collection, due to experimental requirements, healthy islets are placed directly into a 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube with 1 ml of sterile RPMI 10% FBS and kept on ice until transplantation. The following day islets are checked under the microscope to confirm viability. If needed, healthy islets are re-collected, leaving behind dead cells. Healthy islets are then transferred from each Petri dish into a sterile 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube containing 1 ml of fresh sterile RPMI 10% FBS (Figure 2).
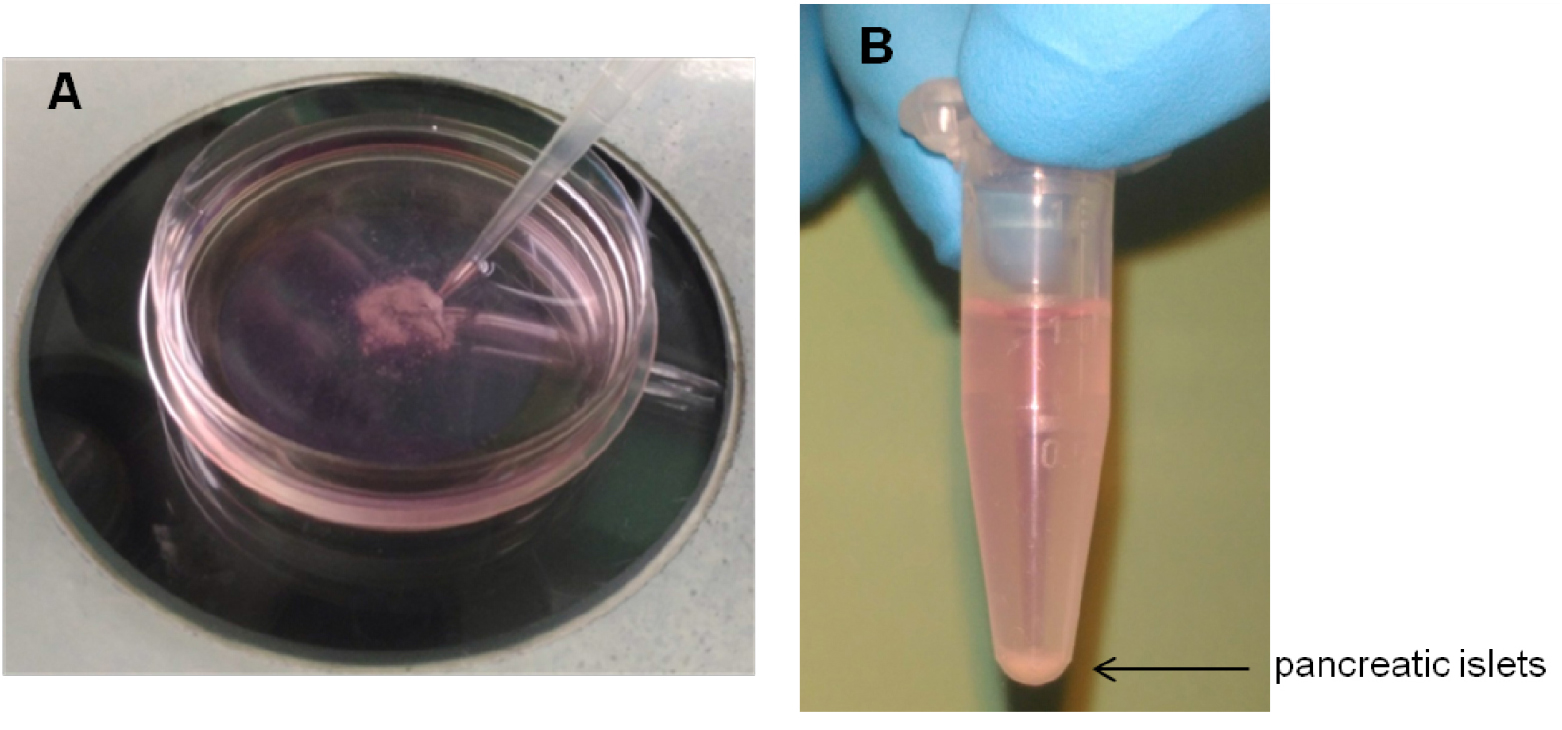
Figure 2. Collection and preparation of pancreatic islets. Healthy pancreatic islets transferred into a Petri dish are collected with a P200 (A) and transferred into a sterile 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube (B). - The number of hand-picked islets to be transplanted under the kidney capsule varies from 300 to 600 depending on the experimental conditions required or the mouse strain used (e.g., chemically-induced or spontaneous diabetes, C57BL/6 or NOD, transgenic or knockout) (Battaglia et al., 2006; Gagliani et al., 2011 and 2015; Fousteri et al., 2015a and 2015b) (see Table 1).
Table 1. Number of pancreatic islets required to reach normoglycemia in different mouse models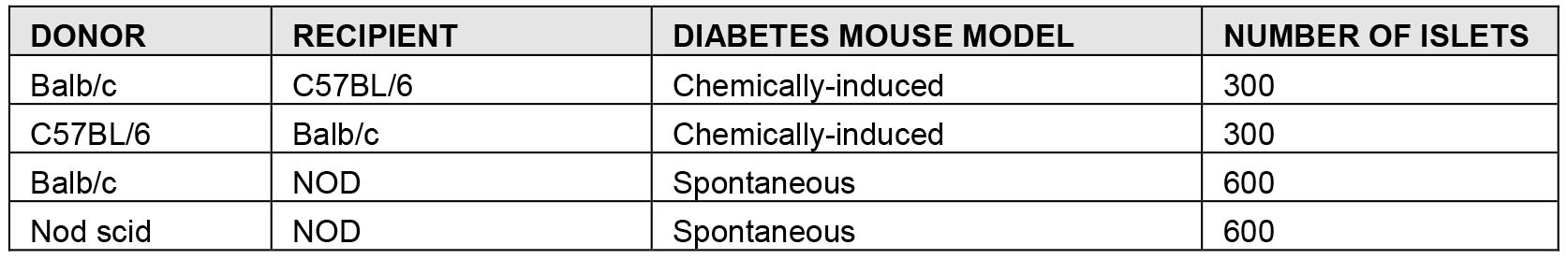
- Transplantation under the kidney capsule
- All instruments and reagents used must be sterile. Ideal transplant recipients should be between 6 to 10 weeks old.
- The recipient mouse is anesthetized by an intraperitoneal injection of a weight-adjusted dose of avertin (240 mg/kg).
Note: Avertin is a quick-acting, non-pharmaceutical grade anesthetic that is used for short duration surgical procedures in mice. It provides rapid and deep anesthesia, followed by fast and full postoperative recovery. This agent is listed on an approved Animal Protocol of the Italian Ministry of Health and procedures are performed by appropriately trained personnel. All guidelines for preparation and storage of avertin are followed. - The level of anesthesia can be tested by pinching the animal’s toes. The mouse’s eyes are kept continuously humid with a physiologic saline solution, 0.9 % NaCl until the mouse awakens to prevent corneal drying.
- When anesthesia takes effect, islets are prepared for transplantation. All the islets sedimented (by gravity effect) in the 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube are transferred into a 25 μl Hamilton syringe connected to a P200 tip using the screw mechanism that allows for a slow less strenuous aspiration. Place a silicone tube adapter over the syringe tip. Insert PE50 tubing into the silicone adapter. Turn the Hamilton syringe the opposite site to let the islets into the PE 50 tube. Be careful to not lose the islets from the edge of the tip (Video 1 and Figure 3).
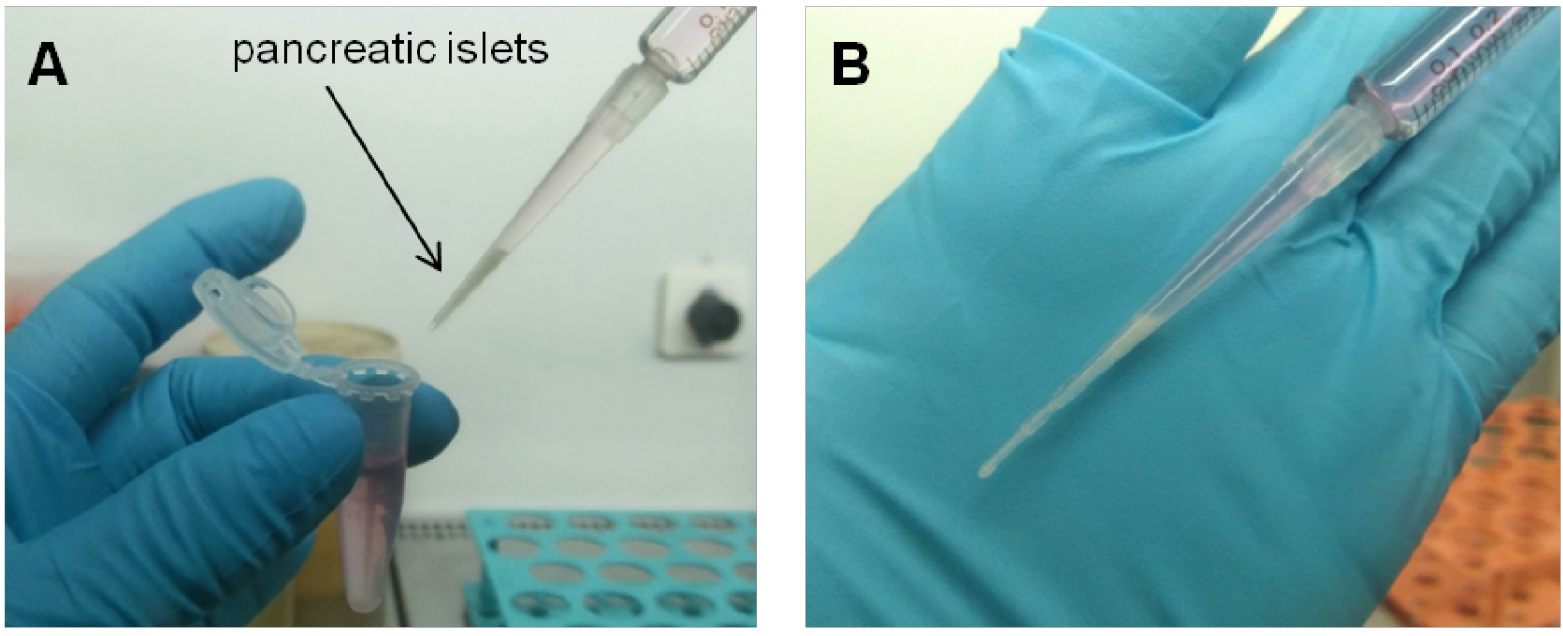
Figure 3. Collection of pancreatic islets with Hamilton syringe. Pancreatic islets are collected with the Hamilton syringe into a P200 tip (A) and then moved into the PE 50 tube (B).Video 1. Preparation of islets for transplantation. Pancreatic islets are collected into a P200 tip and transferred into the PE50 tubing by slowly turned the Hamilton syringe. - While the mouse is under anesthesia, the transplant area is shaved with the electric shears and disinfected with betadine (Video 2). Video 2. Mouse preparation for islet transplantation. The transplant area is disinfected and the mouse’s eyes are kept humid.
- Localize the kidney using your fingers and make a 1-1.5 cm incision in the skin on the left back side to visualize the peritoneum. Make the 0.5-1 cm incision in the peritoneum to expose the kidney. Slight pressure is applied to both sides of the incision, to allow the kidney to slide out of the abdominal cavity. Keep the surface of the exposed kidney wet with sterile saline using soaked cotton-tipped applicator. Repeat wetting as many times as necessary to prevent the kidney capsule from drying out (Video 3). Video 3. Incision and kidney exposure. A small incision is made in the skin and in the peritoneum exposing the kidney.
- Make a small scratch on the right flank of the kidney capsule using a syringe 25 gauge needle, to allow the PE50 filled with islets and attached to a Hamilton syringe to be inserted. Reach the posterior end of the capsule and carefully create some space by moving the PE50 tube and slowly inject the islets. Once all islets are injected, carefully remove the PE50 tube, dry the area and cauterize.
Note: Is highly recommended to use new PE50 tubes for each set of islets to be transplanted to avoid blood clotting. (Video 4 and Figure 4).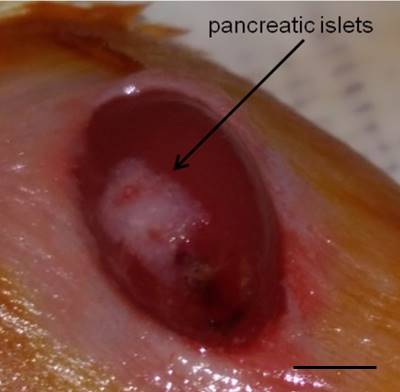
Figure 4. Islets under the kidney capsule. Islets (white) are localized under the kidney capsule. Scale bar represent 3 mm.Video 4. Islet transplantation. Pancreatic islets are transplanted under the kidney capsule. - The kidney is then placed back into the cavity and residual blood is cleaned with physiological solution. Both incisions (peritoneum and skin) are sutured with 3 or 4 stitches based on the size of the incision (Video 5 and Figure 5).
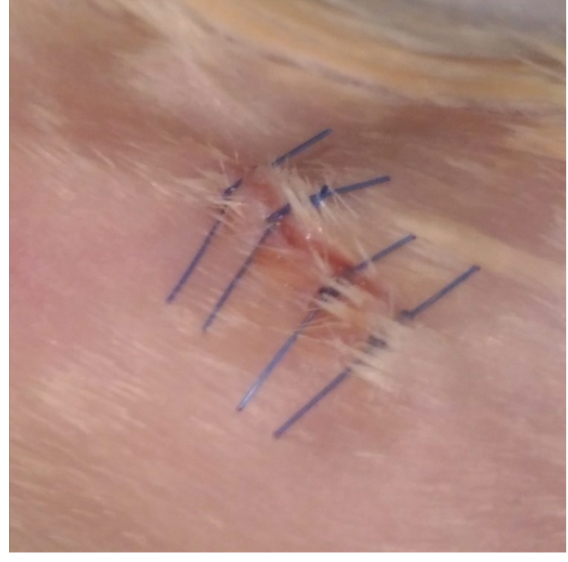
Figure 5. Surgical seamsVideo 5. Closing and mouse revival. The peritoneum and the skin are sutured. Subcutaneous injection of ketoprofen is made and the mice are placed on a heating pad until are active. - The mice are treated with ketoprofen (5 mg/kg) subcutaneously and placed on a heating pad. Animals should be kept warm until they recover from anesthesia and must be monitored until maintaining upright posture and walking normally. Blood glucose levels usually normalize 24 h after the procedure.
- All instruments and reagents used must be sterile. Ideal transplant recipients should be between 6 to 10 weeks old.
Data analysis
- In islet transplantation, blood glucose levels are used to define the outcome of islet engraftment, survival, rejection and tolerance according to the transplant model. Islet engraftment is usually defined as the achievement of normoglycemia, while graft rejection is defined by the subsequent development of hyperglycemia. Both in the syngeneic and allogeneic model, islet transplantation failure should be defined either as the inability to reach non-fasting blood glucose levels < 250 mg/dl or death within the first 7 d after islet transplantation (i.e., surgical death). (Cantarelli et al., 2013)
- Several drug-based treatments (Gagliani et al., 2011), as well as regulatory cell-based therapies have proved their efficacy in the establishment of long-term tolerance allogeneic murine islet transplantation. To test the development of an active state of tolerance and discard the possibility that treated mice are immune suppressed, mice that do not reject the graft 100 days after transplantation (graft rejection is considered after two consecutive glucose measurements with value > 250 mg/dl) are commonly boosted in vivo with donor-origin splenocytes. A total of 30 x 106 splenocytes isolated from the original islet donor are injected intraperitoneally (i.p.), and blood glucose levels are monitored daily thereafter. Mice still normoglycemic 30-50 days from boosting have developed a long-term tolerance to the allogenic islets (Gagliani et al., 2011).
- Statistical analysis
Islet allograft survival is commonly determined by Kaplan-Meier survival curves and compared using the logrank test. Prism software (GraphPad, USA) is used for all analyses (Fousteri et al., 2015b). When multiple comparisons are made, post hoc comparisons use ANOVA with Bonferroni correction. For two-group comparisons, unpaired two-tailed t-tests with unequal variance are used. In all cases, a two-tailed P value of < 0.05 is considered significant (Battaglia et al., 2006).
Recipes
- RPMI/glutamine/HEPES/Pen-Strep/FBS
500 ml RPMI 1640 (RPMI)
5 ml L-glutamine
5 ml HEPES buffer
5 ml Pen-Strep
50 ml fetal bovine serum
Combine all reagents in a sterile biosafety cabinet
Store at 4 °C - HBSS/Ca/HEPES
1 L of Hank’s balanced salt solution (HBSS)
2 mM CaCl2
20 mM HEPES
Combine all reagents in a sterile biosafety cabinet
Store at 4 °C
Acknowledgments
This protocol has been used by members of our laboratory since it was first published (Battaglia et al., 2006) and it was adapted by Gregori and colleagues (Gregori et al., 2015).
The experiments using the mice were performed with approval of and strictly following the guidelines of the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Ospedale San Raffaele and communicated to the Ministry of Health. We would like to thank the members of the group for the support. This protocol is commonly used in our studies of optimizing post-transplant therapeutic strategies in wild-type or transgenic mouse models of type 1 diabetes (Battaglia et al., 2006; Gagliani et al., 2011 and 2015; Fousteri et al., 2015a and 2015b). No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
References
- Andersson, A. (1978). Isolated mouse pancreatic islets in culture: effects of serum and different culture media on the insulin production of the islets. Diabetologia 14(6): 397-404.
- Battaglia, M., Stabilini, A., Draghici, E., Gregori, S., Mocchetti, C., Bonifacio, E. and Roncarolo, M. G. (2006). Rapamycin and interleukin-10 treatment induces T regulatory type 1 cells that mediate antigen-specific transplantation tolerance. Diabetes 55(1): 40-49.
- Cantarelli, E., Citro, A., Marzorati, S., Melzi, R., Scavini, M. and Piemonti, L. (2013). Murine animal models for preclinical islet transplantation: No model fits all (research purposes). Islets 5(2): 79-86.
- Cantarelli, E. and Piemonti, L. (2011). Alternative transplantation sites for pancreatic islet grafts. Curr Diab Rep 11(5): 364-374.
- Fousteri, G., Jofra, T., Di Fonte, R. and Battaglia, M. (2015a). Combination of an antigen-specific therapy and an immunomodulatory treatment to simultaneous block recurrent autoimmunity and alloreactivity in non-obese diabetic mice. PLoS One 10(6): e0127631.
- Fousteri, G., Jofra, T., Di Fonte, R., Gagliani, N., Morsiani, C., Stabilini, A. and Battaglia, M. (2015b). Lack of the protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN22 strengthens transplant tolerance to pancreatic islets in mice. Diabetologia 58(6): 1319-1328.
- Gagliani, N., Gregori, S., Jofra, T., Valle, A., Stabilini, A., Rothstein, D. M., Atkinson, M., Roncarolo, M.G., and Battaglia, M. (2011). Rapamycin combined with anti-CD45RB mAb and IL-10 or with G-CSF induces tolerance in a stringent mouse model of islet transplantation. PLoS One 6(12): e28434.
- Gagliani, N., Jofra, T., Posgai, A. L., Atkinson, M. A. and Battaglia, M. (2015). Immune depletion in combination with allogeneic islets permanently restores tolerance to self-antigens in diabetic NOD mice. PLoS One 10(11): e0142318.
- Graham, K. L., Fynch, S., Papas, E. G., Tan, C., Kay, T. W. and Thomas, H. E. (2016). Isolation and culture of the islets of langerhans from mouse pancreas. Bio-protocol 6(12): e1840.
- Gregori S, Mangia P, Bacchetta R, Tresoldi E, Kolbinger F, Traversari C, Carballido JM, de Vries JE, Korthäuer U, Roncarolo MG. (2005). An anti-CD45RO/RB monoclonal antibody modulates T cell responses via induction of apoptosis and generation of regulatory T cells. J Exp Med 201(8): 1293-305.
Article Information
Copyright
© 2018 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
How to cite
Jofra, T., Galvani, G., Georgia, F., Silvia, G., Gagliani, N. and Battaglia, M. (2018). Murine Pancreatic Islets Transplantation under the Kidney Capsule. Bio-protocol 8(5): e2743. DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2743.
Category
Immunology > Animal model > Mouse
Cell Biology > Cell Transplantation > Allogenic Transplantation
Do you have any questions about this protocol?
Post your question to gather feedback from the community. We will also invite the authors of this article to respond.
Share
Bluesky
X
Copy link










